微软的GraphRAG算得上是最早一批成熟的GraphRAG系统,它把索引阶段(抽取实体、关系、构建层级社区并生成摘要)和查询阶段的高级能力整合到了一起。这套方案的优势在于,可以借助预先计算好的实体、关系、社区摘要来回答那些宏观的、主题性的问题,这恰恰是传统RAG系统基于文档检索难以做到的。
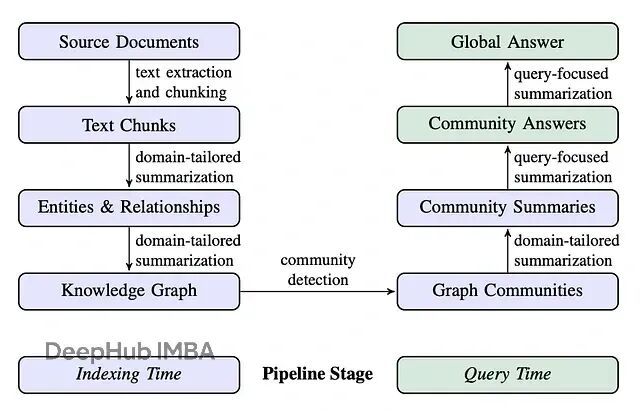
本文的重点是DRIFT搜索:Dynamic Reasoning and Inference with Flexible Traversal,翻译过来就是"动态推理与灵活遍历"。这是一种相对较新的检索策略,兼具全局搜索和局部搜索的特点。
DRIFT的工作流程是这样的:先通过向量搜索建立一个宽泛的查询起点,再利用群信息把原始问题拆解成更细粒度的后续查询。然后动态地在知识图谱上游走,抓取实体、关系等局部细节。这种设计在计算效率和答案质量之间找到了一个不错的平衡点。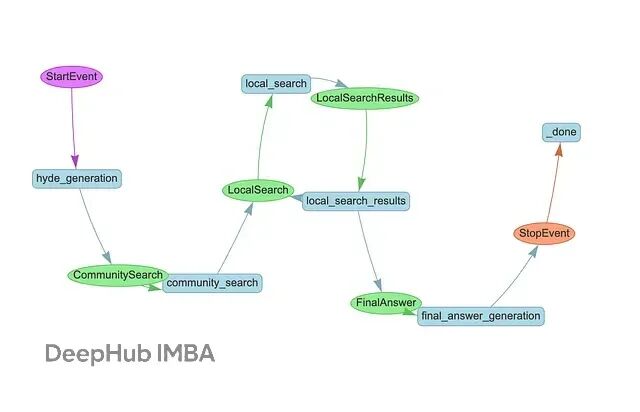
上图为使用 LlamaIndex 工作流和 Neo4j 实现的 DRIFT 搜索,核心流程分一下几步:
首先是HyDE生成,基于一份样例社区报告构造假设性答案,用来改善查询的向量表示。
接着社区搜索登场,通过向量相似度找出最相关的社区报告,给查询提供宏观上下文。系统会分析这些结果,输出一个初步的中间答案,同时生成一批后续查询用于深挖。
这些后续查询会在局部搜索阶段并行执行,从知识图谱里捞出文本块、实体、关系、以及更多社区报告。这个过程可以迭代多轮,每轮都可能产生新的后续查询。
最后是答案生成,把过程中积累的所有中间答案汇总起来,融合社区级别的宏观洞察和局部细节,生成最终响应。整体思路就是先铺开、再聚焦,层层递进。
本文用的是《爱丽丝梦游仙境》,刘易斯·卡罗尔的经典作品,这部小说角色众多、场景丰富、事件环环相扣,拿来演示GraphRAG的能力再合适不过。
数据导入
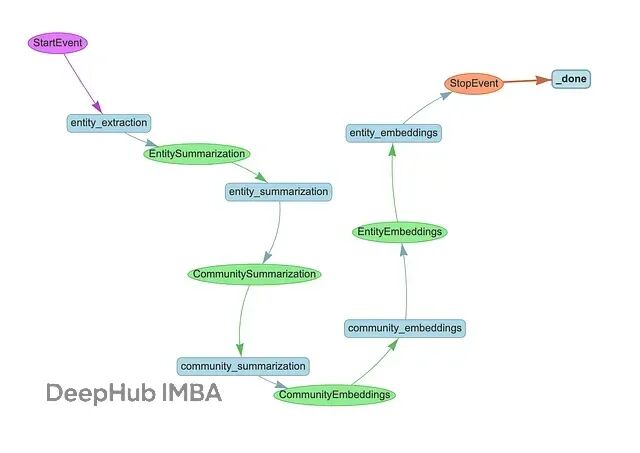
整个pipeline遵循标准的GraphRAG流程,分三个阶段:
class MSGraphRAGIngestion(Workflow):
@step
async def entity_extraction(self, ev: StartEvent) -> EntitySummarization:
chunks = splitter.split_text(ev.text)
await ms_graph.extract_nodes_and_rels(chunks, ev.allowed_entities)
return EntitySummarization()
@step
async def entity_summarization(
self, ev: EntitySummarization
) -> CommunitySummarization:
await ms_graph.summarize_nodes_and_rels()
return CommunitySummarization()
@step
async def community_summarization(
self, ev: CommunitySummarization
) -> CommunityEmbeddings:
await ms_graph.summarize_communities()
return CommunityEmbeddings()
先从文本块里抽取实体和关系,再给节点和关系生成摘要,最后构建层级社区并生成社区摘要。
摘要做完之后,要给社区和实体都生成向量嵌入,这样才能支持相似性检索。社区嵌入的代码长这样:
@step
async def community_embeddings(self, ev: CommunityEmbeddings) -> EntityEmbeddings:
# Fetch all communities from the graph database
communities = ms_graph.query(
"""
MATCH (c:__Community__)
WHERE c.summary IS NOT NULL AND c.rating > $min_community_rating
RETURN coalesce(c.title, "") + " " + c.summary AS community_description, c.id AS community_id
""",
params={"min_community_rating": MIN_COMMUNITY_RATING},
)
if communities:
# Generate vector embeddings from community descriptions
response = await client.embeddings.create(
input=[c["community_description"] for c in communities],
model=TEXT_EMBEDDING_MODEL,
)
# Store embeddings in the graph and create vector index
embeds = [
{
"community_id": community["community_id"],
"embedding": embedding.embedding,
}
for community, embedding in zip(communities, response.data)
]
ms_graph.query(
"""UNWIND $data as row
MATCH (c:__Community__ {id: row.community_id})
CALL db.create.setNodeVectorProperty(c, 'embedding', row.embedding)""",
params={"data": embeds},
)
ms_graph.query(
"CREATE VECTOR INDEX community IF NOT EXISTS FOR (c:__Community__) ON c.embedding"
)
return EntityEmbeddings()
实体嵌入同理,这样DRIFT搜索需要的向量索引就都建好了。
DRIFT搜索
DRIFT的检索思路其实很符合简单:先看大图,再挖细节。它不会一上来就在文档或实体层面做精确匹配,而是先去查群的摘要,因为这些摘要是对知识图谱主要主题的高层次概括。
拿到相关的高层信息后,DRIFT会智能地派生出后续查询,去精确检索特定实体、关系、源文档。这种两阶段的做法其实很像人类查资料的习惯:先大致了解情况再针对性地追问细节。既有全局搜索的覆盖面,又有局部搜索的精准度,而且不用把所有社区报告或文档都过一遍,计算开销控制得不错。
下面拆解一下各个阶段的实现。
群搜索
DRIFT用了HyDE技术来提升向量检索的准确率。不是直接拿用户query做embedding,而是先让模型生成一个假设性的答案,再用这个答案去做相似性搜索。道理很简单:假设答案在语义上跟真实的摘要更接近。
@step
async def hyde_generation(self, ev: StartEvent) -> CommunitySearch:
# Fetch a random community report to use as a template for HyDE generation
random_community_report = driver.execute_query(
"""
MATCH (c:__Community__)
WHERE c.summary IS NOT NULL
RETURN coalesce(c.title, "") + " " + c.summary AS community_description""",
result_transformer_=lambda r: r.data(),
)
# Generate a hypothetical answer to improve query representation
hyde = HYDE_PROMPT.format(
query=ev.query, template=random_community_report[0]["community_description"]
)
hyde_response = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-mini",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": hyde}],
reasoning={"effort": "low"},
)
return CommunitySearch(query=ev.query, hyde_query=hyde_response.output_text)
拿到HyDE query之后,做embedding,然后通过向量相似度捞出top 5的报告。接着让LLM基于这些报告生成一个初步答案,同时识别出需要深挖的后续查询。将初步答案存起来然后进行后续查询全部并行分发到局部搜索阶段。
@step
async def community_search(self, ctx: Context, ev: CommunitySearch) -> LocalSearch:
# Create embedding from the HyDE-enhanced query
embedding_response = await client.embeddings.create(
input=ev.hyde_query, model=TEXT_EMBEDDING_MODEL
)
embedding = embedding_response.data[0].embedding
# Find top 5 most relevant community reports via vector similarity
community_reports = driver.execute_query(
"""
CALL db.index.vector.queryNodes('community', 5, $embedding) YIELD node, score
RETURN 'community-' + node.id AS source_id, node.summary AS community_summary
""",
result_transformer_=lambda r: r.data(),
embedding=embedding,
)
# Generate initial answer and identify what additional info is needed
initial_prompt = DRIFT_PRIMER_PROMPT.format(
query=ev.query, community_reports=community_reports
)
initial_response = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-mini",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": initial_prompt}],
reasoning={"effort": "low"},
)
response_json = json_repair.loads(initial_response.output_text)
print(f"Initial intermediate response: {response_json['intermediate_answer']}")
# Store the initial answer and prepare for parallel local searches
async with ctx.store.edit_state() as ctx_state:
ctx_state["intermediate_answers"] = [
{
"intermediate_answer": response_json["intermediate_answer"],
"score": response_json["score"],
}
]
ctx_state["local_search_num"] = len(response_json["follow_up_queries"])
# Dispatch follow-up queries to run in parallel
for local_query in response_json["follow_up_queries"]:
ctx.send_event(LocalSearch(query=ev.query, local_query=local_query))
return None
这就是DRIFT的核心思路,先用HyDE增强的社区搜索铺开,再用后续查询往下钻。
局部搜索
局部搜索阶段把后续查询并行跑起来,深入到具体细节。每个查询通过实体向量检索拿到目标上下文,生成中间答案,可能还会产出更多后续查询。
@step(num_workers=5)
async def local_search(self, ev: LocalSearch) -> LocalSearchResults:
print(f"Running local query: {ev.local_query}")
# Create embedding for the local query
response = await client.embeddings.create(
input=ev.local_query, model=TEXT_EMBEDDING_MODEL
)
embedding = response.data[0].embedding
# Retrieve relevant entities and gather their associated context:
# - Text chunks where entities are mentioned
# - Community reports the entities belong to
# - Relationships between the retrieved entities
# - Entity descriptions
local_reports = driver.execute_query(
"""
CALL db.index.vector.queryNodes('entity', 5, $embedding) YIELD node, score
WITH collect(node) AS nodes
WITH
collect {
UNWIND nodes as n
MATCH (n)<-[:MENTIONS]->(c:__Chunk__)
WITH c, count(distinct n) as freq
RETURN {chunkText: c.text, source_id: 'chunk-' + c.id}
ORDER BY freq DESC
LIMIT 3
} AS text_mapping,
collect {
UNWIND nodes as n
MATCH (n)-[:IN_COMMUNITY*]->(c:__Community__)
WHERE c.summary IS NOT NULL
WITH c, c.rating as rank
RETURN {summary: c.summary, source_id: 'community-' + c.id}
ORDER BY rank DESC
LIMIT 3
} AS report_mapping,
collect {
UNWIND nodes as n
MATCH (n)-[r:SUMMARIZED_RELATIONSHIP]-(m)
WHERE m IN nodes
RETURN {descriptionText: r.summary, source_id: 'relationship-' + n.name + '-' + m.name}
LIMIT 3
} as insideRels,
collect {
UNWIND nodes as n
RETURN {descriptionText: n.summary, source_id: 'node-' + n.name}
} as entities
RETURN {Chunks: text_mapping, Reports: report_mapping,
Relationships: insideRels,
Entities: entities} AS output
""",
result_transformer_=lambda r: r.data(),
embedding=embedding,
)
# Generate answer based on the retrieved context
local_prompt = DRIFT_LOCAL_SYSTEM_PROMPT.format(
response_type=DEFAULT_RESPONSE_TYPE,
context_data=local_reports,
global_query=ev.query,
)
local_response = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-mini",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": local_prompt}],
reasoning={"effort": "low"},
)
response_json = json_repair.loads(local_response.output_text)
# Limit follow-up queries to prevent exponential growth
response_json["follow_up_queries"] = response_json["follow_up_queries"][:LOCAL_TOP_K]
return LocalSearchResults(results=response_json, query=ev.query)
下一步负责编排迭代深化的过程。用
collect_events
等所有并行搜索跑完,然后判断要不要继续往下挖。如果当前深度还没到上限(这里设的max depth=2),就把所有结果里的后续查询提取出来,存好中间答案分发下一轮并行搜索。
@step
async def local_search_results(
self, ctx: Context, ev: LocalSearchResults
) -> LocalSearch | FinalAnswer:
local_search_num = await ctx.store.get("local_search_num")
# Wait for all parallel searches to complete
results = ctx.collect_events(ev, [LocalSearchResults] * local_search_num)
if results is None:
return None
intermediate_results = [
{
"intermediate_answer": event.results["response"],
"score": event.results["score"],
}
for event in results
]
current_depth = await ctx.store.get("local_search_depth", default=1)
query = [ev.query for ev in results][0]
# Continue drilling down if we haven't reached max depth
if current_depth < MAX_LOCAL_SEARCH_DEPTH:
await ctx.store.set("local_search_depth", current_depth + 1)
follow_up_queries = [
query
for event in results
for query in event.results["follow_up_queries"]
]
# Store intermediate answers and dispatch next round of searches
async with ctx.store.edit_state() as ctx_state:
ctx_state["intermediate_answers"].extend(intermediate_results)
ctx_state["local_search_num"] = len(follow_up_queries)
for local_query in follow_up_queries:
ctx.send_event(LocalSearch(query=query, local_query=local_query))
return None
else:
return FinalAnswer(query=query)
这样就形成了一个迭代细化的循环,每一层都在前一层的基础上继续深挖。达到最大深度后,触发最终答案生成。
最终答案
最后一步把整个DRIFT搜索过程中积攒的所有中间答案汇总成一个完整的响应:这里包括社区搜索的初步答案,以及局部搜索各轮迭代产出的答案。
@step
async def final_answer_generation(self, ctx: Context, ev: FinalAnswer) -> StopEvent:
# Retrieve all intermediate answers collected throughout the search process
intermediate_answers = await ctx.store.get("intermediate_answers")
# Synthesize all findings into a comprehensive final response
answer_prompt = DRIFT_REDUCE_PROMPT.format(
response_type=DEFAULT_RESPONSE_TYPE,
context_data=intermediate_answers,
global_query=ev.query,
)
answer_response = await client.responses.create(
model="gpt-5-mini",
input=[
{"role": "developer", "content": answer_prompt},
{"role": "user", "content": ev.query},
],
reasoning={"effort": "low"},
)
return StopEvent(result=answer_response.output_text)
总结
DRIFT搜索提供了一个挺有意思的思路,在全局搜索的广度和局部搜索的精度之间找到了平衡。从社区级上下文切入,通过迭代的后续查询逐层下探,既避免了遍历所有社区报告的计算负担,又保证了覆盖面。
这里还有改进空间,比如目前的实现对所有中间答案一视同仁,如果能根据置信度分数做个筛选,最终答案的质量应该会更好,噪声也能降下来。后续查询也可以先按相关性或信息增益排个序,优先追踪最有价值的线索。
另一个值得尝试的方向是加一个查询精炼步骤,用LLM分析所有生成的后续查询,把相似的归并起来避免重复搜索,过滤掉那些大概率没什么收获的查询。这样能大幅减少局部搜索的次数,同时不影响答案质量。
完整代码
https://github.com/neo4j-contrib/ms-graphrag-neo4j/blob/main/examples/drift_search.ipynb
有兴趣的可以自己跑跑看,或者在这个基础上做些改进。
作者:Tomaz Bratanic