1. 论文和代码
论文:Point Fractal Network for 3D Point Cloud Completionhttps://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2020/papers/Huang_PF-Net_Point_Fractal_Network_for_3D_Point_Cloud_Completion_CVPR_2020_paper.pdfhttps://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2020/papers/Huang_PF-Net_Point_Fractal_Network_for_3D_Point_Cloud_Completion_CVPR_2020_paper.pdf
作者来自上海交通大学和上汤科技的大佬,发表在2020CVPR。
代码:
2. 论文阅读笔记
2.1 目的和框架
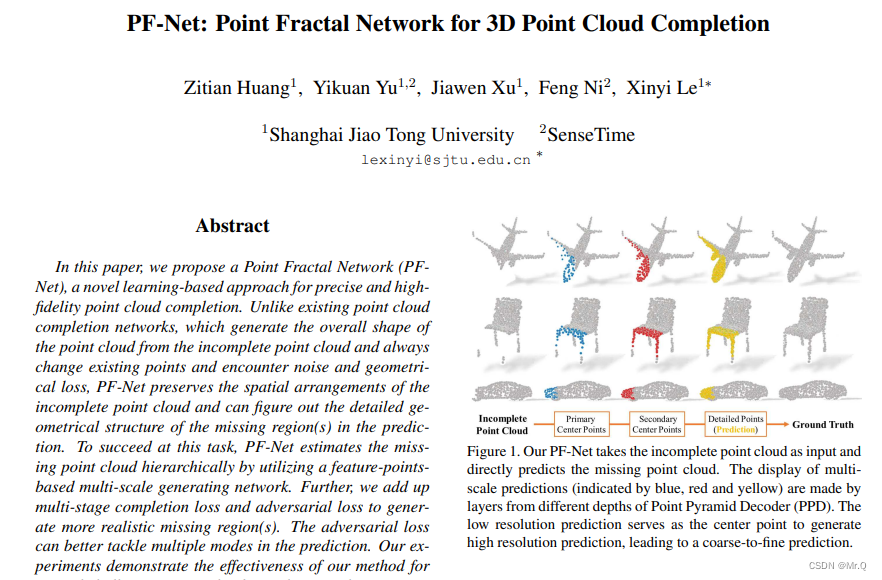
该PF-Net要做的是点云补全,即将有残缺的点云数据(比如上图飞机少了机头,或者凳子少了腿),通过一些技术补全为完整的点云数据。
简单来讲,PF-Net输入残缺后点云(飞机的机身),输出残缺的部分点云(飞机的机尾),端对端训练,作为生成器网络,生成残缺点云,再接一个判别器网络。
该网络的特点:不改变原始的数据,只生成残缺部分的点云数据。即机身的点云数据不变,直接生成机头部分的点云。
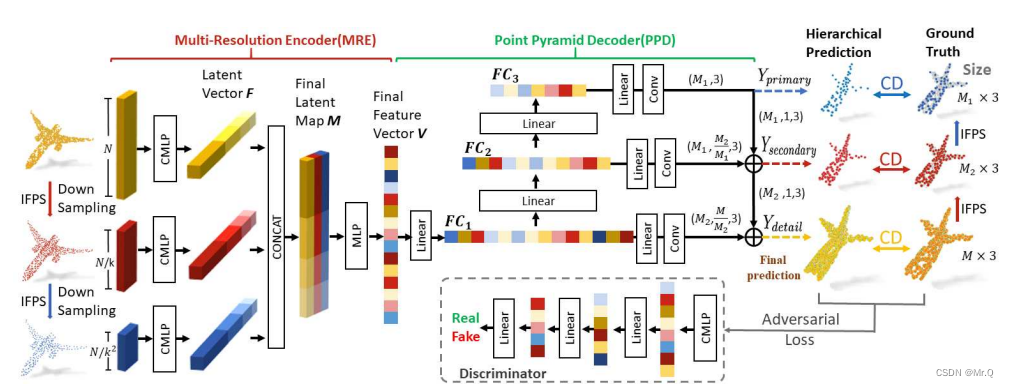
算法步骤:
(1)原始的黄色点云输入数据,经过了两次IFPS下采样,获得三种尺度的点云输入数据,其中N是原始的点云中点的个数,k是下采样倍数;
(2)再经过CMLP全链接网络,获得Latent vector F;
(3)再将各个latent vector拼接起来获得Final Laten Map M;
(4)接一个MLP和Linear全链接网络,再使用FPN特征金字塔作为解码网络,获取三种尺度下的残缺点云数据;
(5)对原始尺度下的残缺点云预测加一个判别器网络,使其生成的残缺数据更真实。
下面对各个部件,从输入到输出一个一个梳理。
2.2 IFPS 下采样
Iterative farthest point sampling (IFPS),迭代最远点采样(技术来自Pointnet++),采集点云数据中骨架点点集合,通俗的将不破坏点云整体结构的情况下,就是只保留一些点。用该技术进行才采样比CNNs更快。

上图,原始台灯有 2048个点,即使下采样到128个点(保留了6.25%),依然很好的保留了台灯的基本骨架。
实现参考iterative farthest point sample (IFPS or FPS)_Mr.Q的博客-CSDN博客迭代最远距离采样,在点云论文PointNet++和PF-Net中用于对点云数据下采样。https://blog.csdn.net/jizhidexiaoming/article/details/128198099?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
3. 源码解读
3.1 载入数据
shapenet_part_loader.py
# from __future__ import print_function
import torch.utils.data as data
import os
import os.path
import torch
import json
import numpy as np
import sys
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
dataset_path = os.path.abspath(
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, '../dataset/shapenet_part/shapenetcore_partanno_segmentation_benchmark_v0/'))
class PartDataset(data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, root=dataset_path, npoints=2500, classification=False, class_choice=None, split='train',
normalize=True):
"""
Parameters
----------
root: str. 数据集完整路径
npoints: 2048. the point number of a sample. 输入到网络中点云的点个数。
classification: bool. True. "Airplane" or "Mug" or something else.
class_choice: list. None. 训练指定的类别。
split: str. train/test
normalize: bool. 是否归一化
"""
self.npoints = npoints
self.root = root
self.catfile = os.path.join(self.root, 'synsetoffset2category.txt') # 映射表格
self.cat = {} # 存放映射字典, {airplane: 11231414, ...}
self.classification = classification
self.normalize = normalize
with open(self.catfile, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
ls = line.strip().split()
self.cat[ls[0]] = ls[1]
# print(self.cat)
if not class_choice is None:
self.cat = {k: v for k, v in self.cat.items() if k in class_choice}
print(self.cat)
self.meta = {}
with open(os.path.join(self.root, 'train_test_split', 'shuffled_train_file_list.json'), 'r') as f:
train_ids = set([str(d.split('/')[2]) for d in json.load(f)]) # 点云文件名称
with open(os.path.join(self.root, 'train_test_split', 'shuffled_val_file_list.json'), 'r') as f:
val_ids = set([str(d.split('/')[2]) for d in json.load(f)])
with open(os.path.join(self.root, 'train_test_split', 'shuffled_test_file_list.json'), 'r') as f:
test_ids = set([str(d.split('/')[2]) for d in json.load(f)])
# 获取datapath list [("Airplane", 点云文件路径,分割文件路径,点云文件夹id,点云文件名称), ...]
for item in self.cat:
# print('category', item)
self.meta[item] = [] # {"Airplane": [(点云文件路径,分割文件路径,点云类别id,点云文件名称), ...],
# "": [], ...}
dir_point = os.path.join(self.root, self.cat[item], 'points') # 当前类别的点云文件夹路径
dir_seg = os.path.join(self.root, self.cat[item], 'points_label') # 当前类别的分割文件夹路径
# print(dir_point, dir_seg)
fns = sorted(os.listdir(dir_point)) # 当前类别的所有点云文件名
if split == 'trainval':
fns = [fn for fn in fns if ((fn[0:-4] in train_ids) or (fn[0:-4] in val_ids))]
elif split == 'train':
fns = [fn for fn in fns if fn[0:-4] in train_ids] # 获取所有属于训练集的点云文件名称
elif split == 'val':
fns = [fn for fn in fns if fn[0:-4] in val_ids]
elif split == 'test':
fns = [fn for fn in fns if fn[0:-4] in test_ids]
else:
print('Unknown split: %s. Exiting..' % (split))
sys.exit(-1)
for fn in fns: #
token = (os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(fn))[0]) # 获取点云文件名称
self.meta[item].append((os.path.join(dir_point, token + '.pts'), os.path.join(dir_seg, token + '.seg'),
self.cat[item], token)) # {"Airplane": [(点云文件路径,分割文件路径,点云文件夹id,点云文件名称), ...]}
self.datapath = [] # [("Airplane", 点云文件路径,分割文件路径,点云文件夹id,点云文件名称), ...]
for item in self.cat:
for fn in self.meta[item]:
self.datapath.append((item, fn[0], fn[1], fn[2], fn[3]))
# ["cls_name": cls_id, ...]
self.classes = dict(zip(sorted(self.cat), range(len(self.cat)))) # {"Airplane": 0, "", 1, ...} 按首字母排序。
print(self.classes)
self.num_seg_classes = 0
if not self.classification:
for i in range(len(self.datapath) // 50):
l = len(np.unique(np.loadtxt(self.datapath[i][2]).astype(np.uint8)))
if l > self.num_seg_classes:
self.num_seg_classes = l
# print(self.num_seg_classes)
self.cache = {} # from index to (point_set, cls, seg) tuple
self.cache_size = 18000 # 加载一次后,不会重复加载
def __getitem__(self, index):
if index in self.cache: # 加载一次后,不会重复加载,所以如果在缓存中,直接取出来即可。
# point_set, seg, cls= self.cache[index]
point_set, seg, cls, foldername, filename = self.cache[index]
else:
fn = self.datapath[index]
# 1. cls. "Mug"类别id是11
cls = self.classes[self.datapath[index][0]]
# 2. point_set
point_set = np.loadtxt(fn[1]).astype(np.float32) # (2817, 3). 载入点云,并转成float32类型
if self.normalize:
point_set = self.pc_normalize(point_set)
# 3. seg
seg = np.loadtxt(fn[2]).astype(np.int64) - 1 # 分割类别id
# 4. foldername 点云文件夹
foldername = fn[3]
# 5. filename 点云文件名称
filename = fn[4]
if len(self.cache) < self.cache_size: # 载入缓存,以便下次迭代时使用
self.cache[index] = (point_set, seg, cls, foldername, filename)
# 随机选择npoints个点参与训练
choice_idx = np.random.choice(len(seg), self.npoints, replace=True) # 其实可以不用seg文件来随机
# resample
point_set = point_set[choice_idx, :]
seg = seg[choice_idx]
# To Pytorch
point_set = torch.from_numpy(point_set) # (2048,3)
seg = torch.from_numpy(seg) # (2048,)
cls = torch.from_numpy(np.array([cls]).astype(np.int64)) # (1,)
if self.classification:
return point_set, cls
else:
return point_set, seg, cls
def __len__(self):
return len(self.datapath)
def pc_normalize(self, pc):
""" pc: NxC, return NxC """
# l = pc.shape[0]
centroid = np.mean(pc, axis=0) # [-0.00400733 0.14655513 0.0053034 ]
pc = pc - centroid # 所有的值减去均值
m = np.max(np.sqrt(np.sum(pc ** 2, axis=1))) # sqrt(x1^2+y1^2+z1^2) + sqrt(x2^2+y2^2+z2^2)+... 0.55
pc = pc / m
return pc
if __name__ == '__main__':
dset = PartDataset(root='./dataset/shapenetcore_partanno_segmentation_benchmark_v0/', classification=True,
class_choice=None, npoints=4096, split='train')
# d = PartDataset( root='./dataset/shapenetcore_partanno_segmentation_benchmark_v0/',classification=False, class_choice=None, npoints=4096, split='test')
print(len(dset))
ps, cls = dset[10000]
print(cls)
# print(ps.size(), ps.type(), cls.size(), cls.type())
# print(ps)
# ps = ps.numpy()
# np.savetxt('ps'+'.txt', ps, fmt = "%f %f %f")
3.1.1 归一化操作
(1)坐标值减去各自坐标值的均值;
(2)sqrt(x1^2+y1^2+z1^2) + sqrt(x2^2+y2^2+z2^2)+... == 0.55
(3)坐标值 / 0.55
3.2 数据前处理
Trian_PFNet.py
dset = shapenet_part_loader.PartDataset(
root='/home/zxq/code/python/PF-Net-Point-Fractal-Network/dataset/shapenetcore_partanno_segmentation_benchmark_v0/',
classification=True,
class_choice=None,
npoints=opt.pnum,
split='train')
assert dset
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dset, batch_size=opt.batchSize, shuffle=True, num_workers=int(opt.workers))
real_label = 1
fake_label = 0
for i, data in enumerate(dataloader, 0):
real_point, target = data # 点云坐标(b,2048,3). 点云类别(b,1) (Airplane or Mug).
batch_size = real_point.size()[0]
real_center = torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, 1, opt.crop_point_num, 3) # (b,1,512,3). # 保存裁剪点的坐标
input_cropped1 = torch.FloatTensor(batch_size, opt.pnum, 3) # (b,2048,3). 原始点云数据的坐标,后面将裁剪掉crop_point_num个点
input_cropped1 = input_cropped1.data.copy_(real_point) # input_cropped1的地址指向没变,只是重新赋值。
real_point = torch.unsqueeze(real_point, 1) # (b,2048,3) -> (b,1,2048,3)
input_cropped1 = torch.unsqueeze(input_cropped1, 1) # (b,2048,3) -> (b,1,2048,3)
p_origin = [0, 0, 0]
# 计算点云和各自视点之间的距离,并从小到大排序;裁剪点云
# input_cropped1被裁剪后的点云,real_center是被裁剪下来的点云
# Set viewpoints
vp_choice_list = [torch.Tensor([1, 0, 0]), torch.Tensor([0, 0, 1]), torch.Tensor([1, 0, 1]),
torch.Tensor([-1, 0, 0]), torch.Tensor([-1, 1, 0])]
for m in range(batch_size): # 计算batch中所有点云距离vp
cur_vp_index = random.sample(vp_choice_list, 1) # Random choose one of the viewpoint
p_center = cur_vp_index[0] # eg. [1,0,0]
distance_list = [] # 点和各自vp之间的距离
for n in range(opt.pnum): # 点云中第n个点
distance_list.append(distance_squre(real_point[m, 0, n], p_center)) # 当前点和vp之间的距离
distance_order = sorted(enumerate(distance_list), key=lambda x: x[1]) # enumerate使其变成2维,x[1]第二维度
# 裁剪掉距离视点最近的前crop_point_num个点
for sp in range(opt.crop_point_num): # distance_order[sp] == (point_idx, dist_val)
input_cropped1.data[m, 0, distance_order[sp][0]] = torch.FloatTensor([0, 0, 0]) # 坐标置为0
real_center.data[m, 0, sp] = real_point[m, 0, distance_order[sp][0]] # 保存裁剪点的坐标
label.resize_([batch_size, 1]).fill_(real_label) # (b,) -> (b,1). 填充1
# to cuda
real_point = real_point.to(device) # (b,1,2048,3) 原始完整点云坐标数据
real_center = real_center.to(device) # (b,1,512,3) 被裁剪下来的点云
input_cropped1 = input_cropped1.to(device) # (b,1,2048,3) 被裁剪后的点云
label = label.to(device) # (2,1) 1是真实,0是生成
############################
# (1) data prepare
###########################
# 被裁剪下来的点云
# scale 0
real_center = Variable(real_center, requires_grad=True)
real_center = torch.squeeze(real_center, 1) # (b,1,512,3) -> (b,512,3)
# scale 1
real_center_key1_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(real_center, 64, RAN=False) # 提取64个点作为骨架点
real_center_key1 = utils.index_points(real_center, real_center_key1_idx)
real_center_key1 = Variable(real_center_key1, requires_grad=True)
# scale 2
real_center_key2_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(real_center, 128, RAN=True) # 提取128个点作为骨架点
real_center_key2 = utils.index_points(real_center, real_center_key2_idx) # 被裁剪下来的点云
real_center_key2 = Variable(real_center_key2, requires_grad=True)
# 被裁剪后的点云
# scale 0
input_cropped1 = torch.squeeze(input_cropped1, 1) # (b,1,2048,3) -> (b,512,3)
# scale 1
input_cropped2_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(input_cropped1, opt.point_scales_list[1], RAN=True) # 1024
input_cropped2 = utils.index_points(input_cropped1, input_cropped2_idx)
# scale 2
input_cropped3_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(input_cropped1, opt.point_scales_list[2], RAN=False) # 512
input_cropped3 = utils.index_points(input_cropped1, input_cropped3_idx)
input_cropped1 = Variable(input_cropped1, requires_grad=True)
input_cropped2 = Variable(input_cropped2, requires_grad=True)
input_cropped3 = Variable(input_cropped3, requires_grad=True)
# to cuda
input_cropped2 = input_cropped2.to(device)
input_cropped3 = input_cropped3.to(device)
input_cropped = [input_cropped1, input_cropped2, input_cropped3] # 被裁剪后的点云 from diff scales
得到数据:
real_center: (b,512,3). 被裁剪下来的点云
input_cropped: list of tensor. (b,2048,3), (b,1024,3), (b,512,3) . 裁剪后的点云
label_center: (b,1). 0/1是否是真是点云
real_center_key1: (b,128,3). 被裁剪下来的点云(下次样)
real_center_key2: (b,64,3). 被裁剪下来的点云(下次样)
3.3 网络输入输出
3.3.1 判别器训练
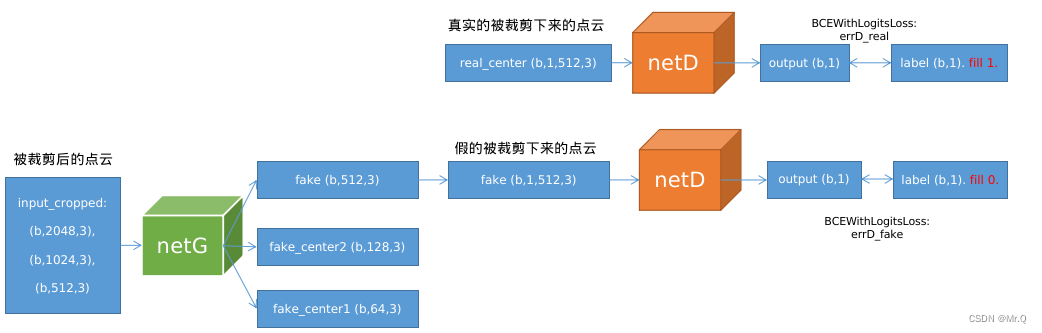
(1)输入真实的被裁剪下来的点云,判别器进行判断,计算errD_real_loss;
(2)利用被裁剪后的点云,生成假的被裁剪下来的点云,再经过判别器,计算errD_fake_loss;
判别器的目标是:
- 真的判定为真的,即图中real_center的预测值越接近1,损失越小;
- 假的判定为假的,即图中fake的预测值越接近0,损失越小。
对应的代码
point_netG = point_netG.train()
point_netD = point_netD.train()
############################
# (2) Update D network
###########################
point_netD.zero_grad()
real_center = torch.unsqueeze(real_center, 1) # (b,512,3) -> (b,1,512,3)
output = point_netD(real_center) # (b,1,512,3). output: (b,1)
# label: (b,1) fill with 1. 对于判别器来说,output值越大越好,损失值越小
errD_real = criterion(output, label)
errD_real.backward()
# input_cropped: (2,2048,3)/(2,1024,3)/(2,512,3). fake_1: (b,64,3), fake_2: (b,128,3), fake: (b,512,3).
fake_center1, fake_center2, fake = point_netG(input_cropped)
fake = torch.unsqueeze(fake, 1) # (b,512,3) -> (b,1,512,3)
label.data.fill_(fake_label) # (b,1). label赋值为0
output = point_netD(fake.detach()) # output: (b,1)
# label: (b,1) fill with 0. 对于判别器来说,output值越小越好,损失值越小
errD_fake = criterion(output, label) #
errD_fake.backward()
errD = errD_real + errD_fake # errD 没有参与训练,只是用于打印,没啥其他用处。
optimizerD.step()
3.3.2 生成器训练
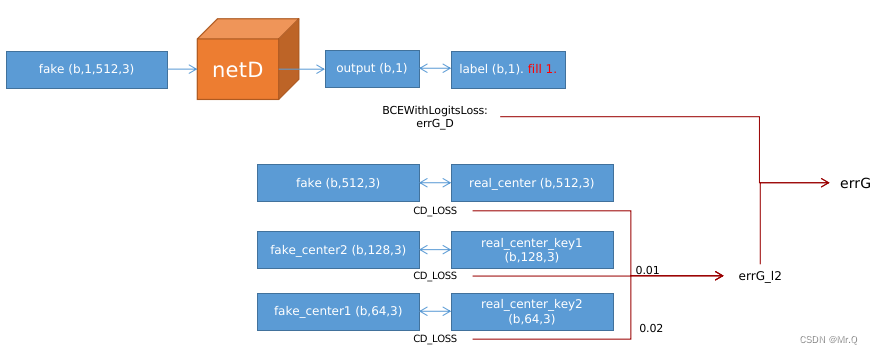
对图中生成的4个fake点云进行学习,降低损失函数。
############################
# (3) Update G network: maximize log(D(G(z)))
###########################
point_netG.zero_grad()
label.data.fill_(real_label) # (b,1). label赋值为1
# fake: (b,1,512,3). output: (b,1)。利用更新后的判别器再次判断fake数据
output = point_netD(fake)
errG_D = criterion(output, label) # tensor(0.5747)
# fake: (b,1,512,3) -> (b,512,3), real_center: (b,1,512,3) -> (b,512,3)
CD_LOSS = criterion_PointLoss(torch.squeeze(fake, 1), torch.squeeze(real_center, 1)) # 只是打印,没有参与训练
# 生成不同尺度下数据的损失CD
# fake and real_center: (b,1,512,3). 生成的假的被裁剪下来的点云、真的被裁剪下来的点云
# fake_center1 and real_center_key1: (b,64,3)
# fake_center2 and real_center_key2: (b,128,3)
errG_l2 = criterion_PointLoss(torch.squeeze(fake, 1), torch.squeeze(real_center, 1)) \
+ alpha1 * criterion_PointLoss(fake_center1, real_center_key1) \
+ alpha2 * criterion_PointLoss(fake_center2, real_center_key2)
errG = (1 - opt.wtl2) * errG_D + opt.wtl2 * errG_l2 # 0.05*errG_D + 0.95*errG_l2
errG.backward()
optimizerG.step()
3.4 判别器模型

对应到论文中的框架图:
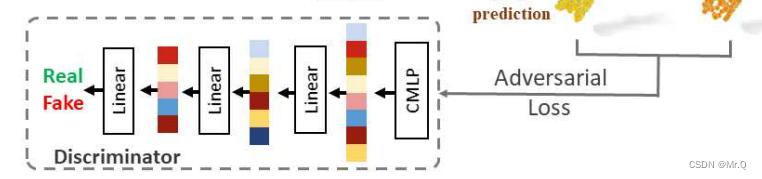
其中CMLP等于上图的conv2d+maxpool+conc组合操作。
(1) 输入生成的假的被裁剪下来的点云,四次卷积,缩小通道数,获得多尺度特征;
(2)分别对最后三个多尺度卷积结果进行最大池化,4维度变2维度特征;
(3)拼接多个尺度特征,再接4个全链接层。
class _netlocalD(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, crop_point_num):
super(_netlocalD, self).__init__()
self.crop_point_num = crop_point_num
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=64, kernel_size=(1, 3))
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 1)
self.conv4 = torch.nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 1)
self.maxpool = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(self.crop_point_num, 1), stride=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(448, 256)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(128, 16)
self.fc4 = nn.Linear(16, 1)
self.bn_1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
self.bn_2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
self.bn_3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(16)
def forward(self, x): # size: (2,1,512,3)
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) # (b,1,512,3) -> (2,64,512,1). conv2d+bn2d+relu
x_64 = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x))) # (b,64,512,1) -> (b,64,512,1)
x_128 = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x_64))) # (b,64,512,1) -> (b,128,512,1)
x_256 = F.relu(self.bn4(self.conv4(x_128))) # (b,128,512,1) -> (b,256,512,1)
x_64 = torch.squeeze(self.maxpool(x_64)) # (b,64,512,1) -> (b,64,1,1)->(b,64)
x_128 = torch.squeeze(self.maxpool(x_128)) # (b,128,512,1) -> (b,128,1,1)->(b,128)
x_256 = torch.squeeze(self.maxpool(x_256)) # (b,256,512,1) -> (b,256,1,1)->(b,256)
Layers = [x_256, x_128, x_64] # (b,64), (b,128), (b,256)
x = torch.cat(Layers, 1) # (b,448)
x = F.relu(self.bn_1(self.fc1(x))) # (b,448) -> (b,256)
x = F.relu(self.bn_2(self.fc2(x))) # (b,256) -> (b,128)
x = F.relu(self.bn_3(self.fc3(x))) # (b,128) -> (b,16)
x = self.fc4(x) # (b,1). real or fake
return x
3.5 生成器模型
3.5.1 CMLP
框架图中的CMLP代码如下,输入size: (b,num_points,3),输出size: (b,1024+512+256+128, 1).
class Convlayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, point_scales):
"""
CMLP: conv+max_pool+concat, 其中最大池化的核大小是动态的,使得最后输出的特征向量是固定大小
Parameters
----------
point_scales: int. 2048/1024/512. 用于最大池化核算子大小,相当与自适应最大池化,把特征图池化到1x1大小
"""
super(Convlayer, self).__init__()
self.point_scales = point_scales
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 64, (1, 3))
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 1)
self.conv4 = torch.nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 1)
self.conv5 = torch.nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 1)
self.conv6 = torch.nn.Conv2d(512, 1024, 1)
self.maxpool = torch.nn.MaxPool2d((self.point_scales, 1), 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
self.bn6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
def forward(self, x): # (b,num_point,3)
x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) # (b,num_point,3) -> (b,1,num_point,3)
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))
# 获取4个尺度的4维度特征
x_128 = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x)))
x_256 = F.relu(self.bn4(self.conv4(x_128)))
x_512 = F.relu(self.bn5(self.conv5(x_256)))
x_1024 = F.relu(self.bn6(self.conv6(x_512)))
# 4维度变2维度特征
x_128 = torch.squeeze(self.maxpool(x_128), 2) # (b,c,num_point,1) -> (b,c,1)
x_256 = torch.squeeze(self.maxpool(x_256), 2)
x_512 = torch.squeeze(self.maxpool(x_512), 2)
x_1024 = torch.squeeze(self.maxpool(x_1024), 2)
# 拼接多尺度特征
L = [x_1024, x_512, x_256, x_128] # (b,1024,1), (b,512,1),(b,256,1), (b,128,1)
x = torch.cat(L, 1) # (b,1024+512+256+128, 1)
return x
3.5.2 Final Feature Vector V
如下是框架中的特征向量Final feature vector V求取代码.
输入size: list. (b,2048,3)/(b,1024,3)/(b,512,3),输出size: (b,1920).
class Latentfeature(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_scales, each_scales_size, point_scales_list):
"""
Parameters
----------
num_scales: int. 3. number of scales.
each_scales_size: int. 1. each scales size. 即每个尺度的shape
point_scales_list: list. [2048, 1024, 512]. number of points in each scales.
"""
super(Latentfeature, self).__init__()
self.num_scales = num_scales
self.each_scales_size = each_scales_size
self.point_scales_list = point_scales_list
self.Convlayers1 = nn.ModuleList( # CMLP
[Convlayer(point_scales=self.point_scales_list[0]) for i in range(self.each_scales_size)])
self.Convlayers2 = nn.ModuleList(
[Convlayer(point_scales=self.point_scales_list[1]) for i in range(self.each_scales_size)])
self.Convlayers3 = nn.ModuleList(
[Convlayer(point_scales=self.point_scales_list[2]) for i in range(self.each_scales_size)])
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(3, 1, 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1)
def forward(self, x):
"""
Parameters
----------
x: list. (b,2048,3)/(b,1024,3)/(b,512,3)
Returns. (b,1920)
-------
"""
outs = []
# 1, CMLP. input (b,point_num,3), output latent vector.
for i in range(self.each_scales_size):
outs.append(self.Convlayers1[i](x[0])) # CMLP: (2,2048,3) -> (b,1024+512+256+128,1)
for j in range(self.each_scales_size):
outs.append(self.Convlayers2[j](x[1])) # CMLP: (2,1024,3) -> (b,1024+512+256+128,1)
for k in range(self.each_scales_size):
outs.append(self.Convlayers3[k](x[2])) # CMLP: (2,512,3) -> (b,1024+512+256+128,1)
# 2, CONCAT
latentfeature = torch.cat(outs, 2) # (b,1920,3). final latent map M
# 3, MLP
latentfeature = latentfeature.transpose(1, 2) # (b,1920,3) -> (b,3,1920)
latentfeature = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(latentfeature))) # (b,3,1920) -> (b,1,1920)
latentfeature = torch.squeeze(latentfeature, 1) # (b,1,1920) -> (b,1920)
return latentfeature
3.5.3 生成器主代码
class _netG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_scales, each_scales_size, point_scales_list, crop_point_num):
"""
Parameters
----------
num_scales: int. 3. number of scales.
each_scales_size: int. 1. each scales size. 即每个尺度的shape
point_scales_list: list. [2048, 1024, 512]. number of points in each scale.
crop_point_num: int. 512. 裁剪多少个点下来
"""
super(_netG, self).__init__()
self.crop_point_num = crop_point_num
self.latentfeature = Latentfeature(num_scales, each_scales_size, point_scales_list)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1920, 1024)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.fc1_1 = nn.Linear(1024, 128 * 512)
self.fc2_1 = nn.Linear(512, 64 * 128) # nn.Linear(512,64*256) !
self.fc3_1 = nn.Linear(256, 64 * 3)
self.conv1_1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(512, 512, 1) # torch.nn.Conv1d(256,256,1) !
self.conv1_2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(512, 256, 1)
self.conv1_3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(256, int((self.crop_point_num * 3) / 128), 1)
self.conv2_1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 6, 1) # torch.nn.Conv1d(256,12,1) !
def forward(self, x):
"""
Parameters
----------
x: list. (b,2048,3)/(b,1024,3)/(b,512,3)
Returns (b,64,3), (b,128,3), (b,512,3).
-------
"""
# final feature vector V
x = self.latentfeature(x) # list -> (b,1920)
# FPN
# fc1, fc2, fc3
x_1 = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) # (b,1920) -> (b,1024)
x_2 = F.relu(self.fc2(x_1)) # (b,1024) -> (b,512)
x_3 = F.relu(self.fc3(x_2)) # (b,512) -> (b,256)
# x_3: fc+reshape. 少了论文中的一个conv
pc1_feat = self.fc3_1(x_3) # (b,256) -> (b,192)
pc1_xyz = pc1_feat.reshape(-1, 64, 3) # (b,192) -> (b,64,3). 64x3 center1. 64个点
# x_2: fc+reshape+conv1d
pc2_feat = F.relu(self.fc2_1(x_2)) # (b,192) -> (b,8192)
pc2_feat = pc2_feat.reshape(-1, 128, 64) # (b,8192) -> (b,128,64)
pc2_xyz = self.conv2_1(pc2_feat) # (b,128,64) -> (b,6,64). 6x64 center2
# x_1: fc_reshape+conv1d+conv1d+conv1d
pc3_feat = F.relu(self.fc1_1(x_1)) # (b,1024) -> (b,65536)
pc3_feat = pc3_feat.reshape(-1, 512, 128) # (b,65536) -> (b,512,128)
pc3_feat = F.relu(self.conv1_1(pc3_feat)) # (b,512,128) -> (b,512,128)
pc3_feat = F.relu(self.conv1_2(pc3_feat)) # (b,512,128) -> (b,256,128)
pc3_xyz = self.conv1_3(pc3_feat) # (b,256,128) -> (b,12,128). 12x128 fine
# plus: scale 1 + scale 2
pc1_xyz_expand = torch.unsqueeze(pc1_xyz, 2) # (b,64,3) -> (b,64,1,3)
pc2_xyz = pc2_xyz.transpose(1, 2) # (b,6,64) -> (b,64,6)
pc2_xyz = pc2_xyz.reshape(-1, 64, 2, 3) # (b,64,6) -> (b,64,2,3)
pc2_xyz = pc1_xyz_expand + pc2_xyz # (b,64,1,3) + (b,64,2,3) = (b,64,2,3)
pc2_xyz = pc2_xyz.reshape(-1, 128, 3) # (b,64,2,3) -> (b,128,3)
# plus: scale 2 + scale 3
pc2_xyz_expand = torch.unsqueeze(pc2_xyz, 2) # (b,128,3) -> (b,128,1,3)
pc3_xyz = pc3_xyz.transpose(1, 2) # (b,12,128) -> (b,12,128)
pc3_xyz = pc3_xyz.reshape(-1, 128, int(self.crop_point_num / 128), 3) # (b,12,128) -> (b,128,4,3)
pc3_xyz = pc2_xyz_expand + pc3_xyz # (b,128,1,3) + (b,128,4,3) = (b,128,4,3)
pc3_xyz = pc3_xyz.reshape(-1, self.crop_point_num, 3) # (b,128,4,3) -> (b,512,3)
return pc1_xyz, pc2_xyz, pc3_xyz # (b,64,3), (b,128,3), (b,512,3). center1, center2, fine
3.6 测试效果

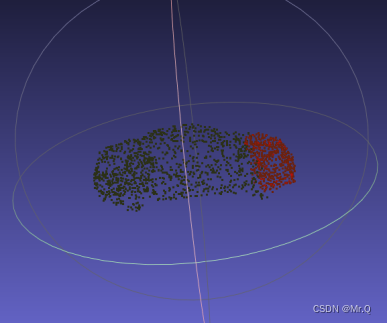
测试代码
# 1. init model
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
point_netG = _netG(opt.num_scales, opt.each_scales_size, opt.point_scales_list, opt.crop_point_num)
point_netG = torch.nn.DataParallel(point_netG)
point_netG.to(device)
point_netG.load_state_dict(torch.load(opt.netG, map_location=lambda storage, location: storage)['state_dict'])
point_netG.eval()
# 2. load incomplete point cloud
input_cropped1 = np.loadtxt(opt.infile, delimiter=',') # (1536,3). csv文件
input_cropped1 = torch.FloatTensor(input_cropped1) # (1536,3)
input_cropped1 = torch.unsqueeze(input_cropped1, 0) # (1,1536,3)
Zeros = torch.zeros(1, 512, 3) # (1,512,3)
input_cropped1 = torch.cat((input_cropped1, Zeros), 1) # (1,1536+512,3) = (1,2048,3)
# 2. preprocess
# 获得多尺度输入: [input_cropped1, input_cropped2, input_cropped3]. (1,2048,3)/(1,1024,3)/(1,512,3)
input_cropped2_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(input_cropped1, opt.point_scales_list[1], RAN=True)
input_cropped2 = utils.index_points(input_cropped1, input_cropped2_idx) # (1,1024,3)
input_cropped3_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(input_cropped1, opt.point_scales_list[2], RAN=False)
input_cropped3 = utils.index_points(input_cropped1, input_cropped3_idx) # (1,512,3)
# input_cropped4_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(input_cropped1, 256, RAN=True)
# input_cropped4 = utils.index_points(input_cropped1, input_cropped4_idx) # (1,256,3). 没啥用
# to cuda
input_cropped2 = input_cropped2.to(device) # (1,1024,3)
input_cropped3 = input_cropped3.to(device) # (1,512,3)
input_cropped = [input_cropped1, input_cropped2, input_cropped3]
# 3. infer. fake.size: (1,512,3)
fake_center1, fake_center2, fake = point_netG(input_cropped)
# fake = fake.cuda() # 返回的本来就在cuda设备上
# fake_center1 = fake_center1.cuda()
# fake_center2 = fake_center2.cuda()
# 4. post-process
# input_cropped2 = input_cropped2.cpu()
# input_cropped3 = input_cropped3.cpu()
# input_cropped4 = input_cropped4.cpu()
# np_crop2 = input_cropped2[0].detach().numpy()
# np_crop3 = input_cropped3[0].detach().numpy()
# np_crop4 = input_cropped4[0].detach().numpy()
# # 真实被裁剪下来的点云,并生成多尺度真实点云
# real = np.loadtxt(opt.infile_real, delimiter=',')
# real = torch.FloatTensor(real)
# real = torch.unsqueeze(real, 0)
# real2_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(real, 64, RAN=False)
# real2 = utils.index_points(real, real2_idx)
# real3_idx = utils.farthest_point_sample(real, 128, RAN=True)
# real3 = utils.index_points(real, real3_idx)
#
# real2 = real2.cpu()
# real3 = real3.cpu()
#
# np_real2 = real2[0].detach().numpy()
# np_real3 = real3[0].detach().numpy()
fake = fake.cpu()
# fake_center1 = fake_center1.cpu()
# fake_center2 = fake_center2.cpu()
np_fake = fake[0].detach().numpy() # (1,512,3) -> (512,3)
# np_fake1 = fake_center1[0].detach().numpy()
# np_fake2 = fake_center2[0].detach().numpy()
input_cropped1 = input_cropped1.cpu()
np_crop = input_cropped1[0].numpy() # (1,2048,3) -> (2048,3)
np.savetxt('test_one/crop_ours' + '.csv', np_crop, fmt="%f,%f,%f")
np.savetxt('test_one/fake_ours' + '.csv', np_fake, fmt="%f,%f,%f")
np.savetxt('test_one/crop_ours_txt' + '.txt', np_crop, fmt="%f,%f,%f")
np.savetxt('test_one/fake_ours_txt' + '.txt', np_fake, fmt="%f,%f,%f")
版权归原作者 Mr.Q 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。