机器学习之MATLAB代码--基于VMD与SSA优化lssvm的功率预测(多变量)(七)
代码
先对外层代码的揭露,包括:顺序而下
1、
function s =Bounds( s, Lb, Ub)% Apply the lower bound vector
temp = s;
I = temp < Lb;temp(I)=Lb(I);% Apply the upper bound vector
J = temp > Ub;temp(J)=Ub(J);% Update thisnewmove
s = temp;
2、
function [in,out]=data_process(data,num)% 采用1-num的各种值为输入 第num+1的功率作为输出
n=length(data)-num;for i=1:nx(i,:,:)=data(i:i+num,:);
end
in=x(1:end-1,:);out=x(2:end,end);%功率是最后一列
3、
function y=fitness(x,train_x,train_y,test_x,test_y,typeID,kernelnamescell)
gam=x(1);
sig2=x(2);
model=initlssvm(train_x,train_y,typeID,gam,sig2,kernelnamescell);
model=trainlssvm(model);
y_pre_test=simlssvm(model,test_x);
y=mse(test_y-y_pre_test);
4、
clc;clear;close all
%%
lssvm=load('lssvm.mat');
ssa_lssvm=load('ssa_lssvm.mat');
vmd_lssvm=load('vmd_lssvm.mat');
vmd_ssa_lssvm=load('vmd_ssa_lssvm.mat');disp('结果分析-lssvm')
result(lssvm.true_value,lssvm.predict_value)fprintf('\n')disp('结果分析-ssa-lssvm')
result(ssa_lssvm.true_value,ssa_lssvm.predict_value)fprintf('\n')disp('结果分析-vmd-lssvm')
result(vmd_lssvm.true_value,vmd_lssvm.predict_value)fprintf('\n')disp('结果分析-vmd-ssa-lssvm')result(vmd_ssa_lssvm.true_value,vmd_ssa_lssvm.predict_value)figureplot(lssvm.true_value)holdon;grid onplot(lssvm.predict_value)plot(ssa_lssvm.predict_value)plot(vmd_lssvm.predict_value)plot(vmd_ssa_lssvm.predict_value)legend('真实值','lssvm预测','ssa-lssvm预测','vmd-lssvm预测','vmd-ssa-lssvm预测')title('各算法预测效果对比')ylabel('功率值')xlabel('测试集样本')
5、
%% 其他数据与功率数据一起作为输入,参看data_process.m
clc;clear;close alladdpath(genpath('LSSVMlabv1_8'));%%
data=xlsread('预测数据.xls','B2:K1000');[x,y]=data_process(data,24);%前24个时刻 预测下一个时刻
%归一化
[xs,mappingx]=mapminmax(x',0,1);x=xs';[ys,mappingy]=mapminmax(y',0,1);y=ys';%划分数据
n=size(x,1);
m=round(n*0.7);%前70%训练,对最后30%进行预测
train_x=x(1:m,:);
test_x=x(m+1:end,:);
train_y=y(1:m,:);
test_y=y(m+1:end,:);%% lssvm 参数
gam=10;
sig2=1000;
typeID='function estimation';
kernelnamescell='RBF_kernel';
model=initlssvm(train_x,train_y,typeID,gam,sig2,kernelnamescell);
model=trainlssvm(model);
y_pre_test=simlssvm(model,test_x);% 反归一化
predict_value=mapminmax('reverse',y_pre_test',mappingy);
true_value=mapminmax('reverse',test_y',mappingy);
save lssvm predict_value true_valuedisp('结果分析')
rmse=sqrt(mean((true_value-predict_value).^2));disp(['根均方差(RMSE):',num2str(rmse)])
mae=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value));disp(['平均绝对误差(MAE):',num2str(mae)])
mape=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value)/true_value);disp(['平均相对百分误差(MAPE):',num2str(mape*100),'%'])fprintf('\n')figureplot(true_value,'-*','linewidth',3)
hold onplot(predict_value,'-s','linewidth',3)legend('实际值','预测值')
grid ontitle('LSSVM')
6、
clc;clear;close all;format compactaddpath(genpath('LSSVMlabv1_8'));%%
data=xlsread('预测数据.xls','B2:K1000');[x,y]=data_process(data,24);%前24个时刻 预测下一个时刻
%归一化
[xs,mappingx]=mapminmax(x',0,1);x=xs';[ys,mappingy]=mapminmax(y',0,1);y=ys';%划分数据
n=size(x,1);
m=round(n*0.7);%前70%训练,对最后30%进行预测
train_x=x(1:m,:);
test_x=x(m+1:end,:);
train_y=y(1:m,:);
test_y=y(m+1:end,:);%% ssa优化lssvm 参数
typeID='function estimation';
kernelnamescell='RBF_kernel';[x,trace]=ssa_lssvm(typeID,kernelnamescell,train_x,train_y,test_x,test_y);
figure;plot(trace);title('适应度曲线/mse')%% 利用寻优得到的参数重新训练lssvmdisp('寻优得到的参数分别是:')
gam=x(1)
sig2=x(2)
model=initlssvm(train_x,train_y,typeID,gam,sig2,kernelnamescell);
model=trainlssvm(model);
y_pre_test=simlssvm(model,test_x);% 反归一化
predict_value=mapminmax('reverse',y_pre_test',mappingy);
true_value=mapminmax('reverse',test_y',mappingy);
save ssa_lssvm predict_value true_valuedisp('结果分析')
rmse=sqrt(mean((true_value-predict_value).^2));disp(['根均方差(RMSE):',num2str(rmse)])
mae=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value));disp(['平均绝对误差(MAE):',num2str(mae)])
mape=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value)/true_value);disp(['平均相对百分误差(MAPE):',num2str(mape*100),'%'])fprintf('\n')figureplot(true_value,'-*','linewidth',3)
hold onplot(predict_value,'-s','linewidth',3)legend('实际值','预测值')
grid ontitle('SSA-LSSVM')
7、
clc;clear;format compact;close all;ticrng('default')%% 数据预处理
data=xlsread('预测数据.xls','B2:K1000');
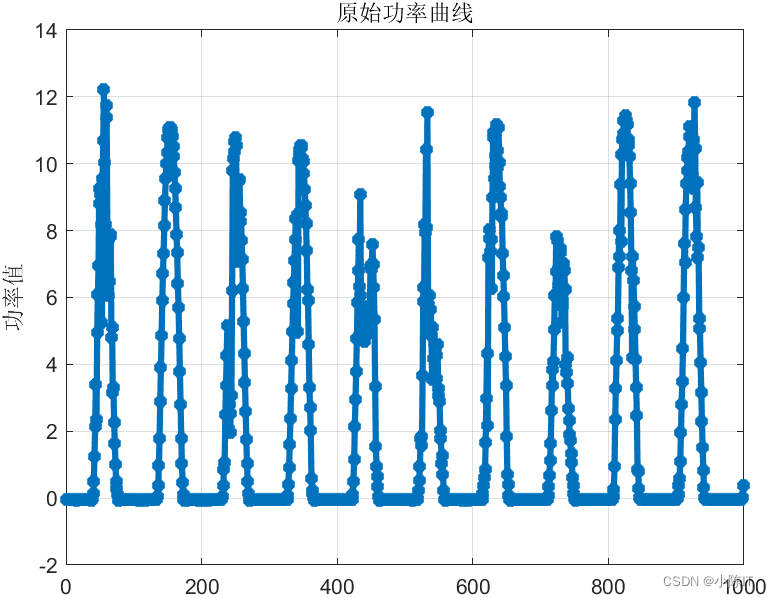
figure;plot(data(:,end),'-*','linewidth',3);title('原始功率曲线');gridon;ylabel('功率值')
alpha =2000;% moderate bandwidth constraint
tau =0;% noise-tolerance (no strict fidelity enforcement)
K =5;%3modes
DC =0;% no DC part imposed
init =1;% initialize omegas uniformly
tol =1e-7;[imf,u_hat,omega]=VMD(data(:,end), alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol);
figure
for i =1:size(imf,1)
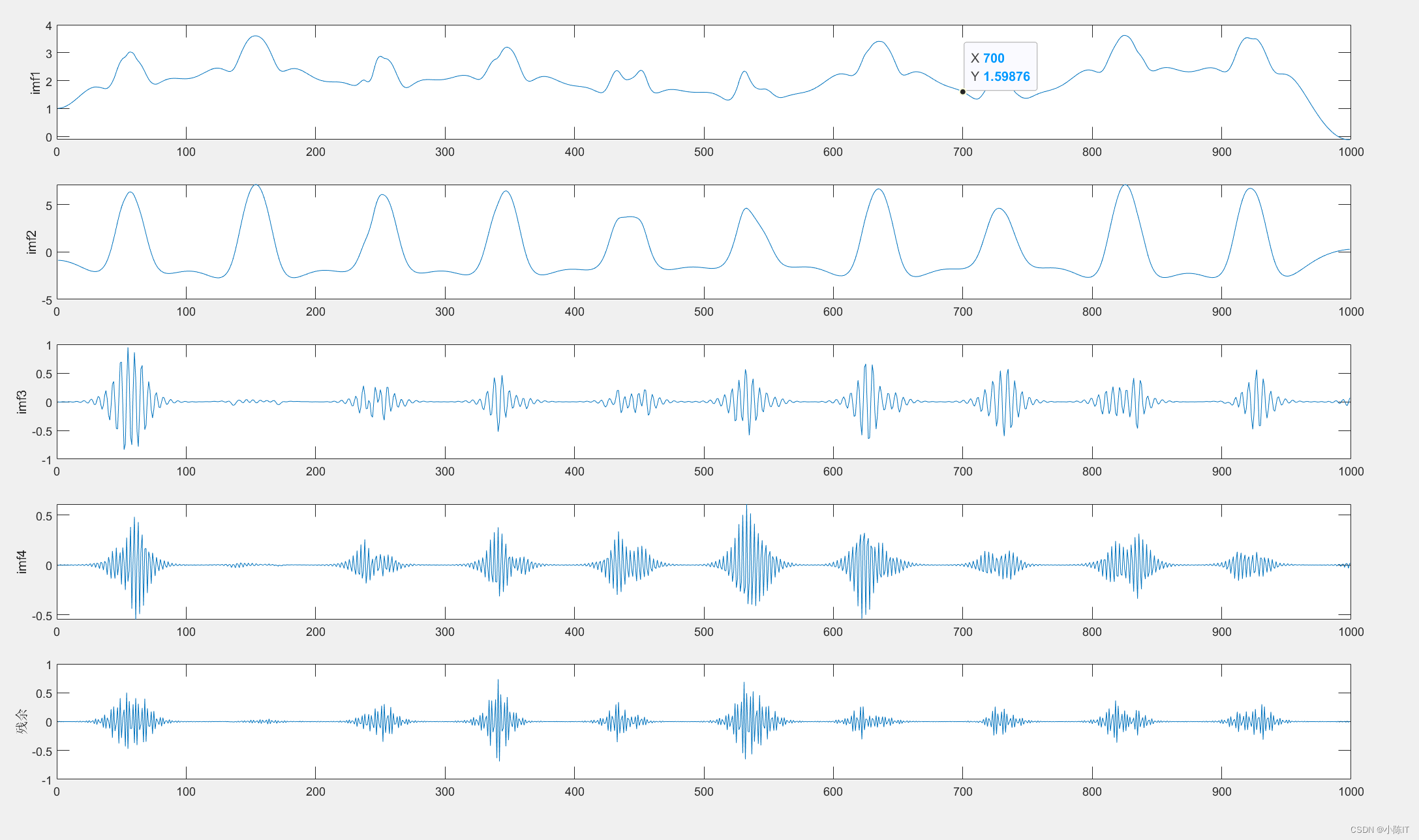
subplot(size(imf,1),1,i)plot(imf(i,:))ylabel(['imf',num2str(i)])endylabel('残余')suptitle('VMD')
c=size(imf,1);
pre_result=[];
true_result=[];%% 对每个分量建模
for i=1:cdisp(['对第',num2str(i),'个分量建模'])[x,y]=data_process([data(:,1:end-1)imf(i,:)'],24);%每个序列和原始的几列数据合并 然后划分
%归一化
[xs,mappingx]=mapminmax(x',0,1);x=xs';[ys,mappingy]=mapminmax(y',0,1);y=ys';%划分数据
n=size(x,1);
m=round(n*0.7);%前70%训练,对最后30%进行预测
train_x=x(1:m,:);
test_x=x(m+1:end,:);
train_y=y(1:m,:);
test_y=y(m+1:end,:);%%
gam=100;
sig2=1000;
typeID='function estimation';
kernelnamescell='RBF_kernel';
model=initlssvm(train_x,train_y,typeID,gam,sig2,kernelnamescell);
model=trainlssvm(model);
pred=simlssvm(model,test_x);
pre_value=mapminmax('reverse',pred',mappingy);
true_value=mapminmax('reverse',test_y',mappingy);
pre_result=[pre_result;pre_value];
true_result=[true_result;true_value];
end
%% 各分量预测的结果相加
true_value=sum(true_result);
predict_value=sum(pre_result);
save vmd_lssvm predict_value true_value
%%
load vmd_lssvmdisp('结果分析')
rmse=sqrt(mean((true_value-predict_value).^2));disp(['根均方差(RMSE):',num2str(rmse)])
mae=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value));disp(['平均绝对误差(MAE):',num2str(mae)])
mape=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value)/true_value);disp(['平均相对百分误差(MAPE):',num2str(mape*100),'%'])fprintf('\n')figureplot(true_value,'-*','linewidth',3)
hold onplot(predict_value,'-s','linewidth',3)legend('实际值','预测值')
grid ontitle('VMD-LSSVM')
8、
clc;clear;format compact;close all;ticrng('default')%% 数据预处理
data=xlsread('预测数据.xls','B2:K1000');
figure;plot(data(:,end),'-*','linewidth',3);title('原始功率曲线');gridon;ylabel('功率值')
alpha =2000;% moderate bandwidth constraint
tau =0;% noise-tolerance (no strict fidelity enforcement)
K =5;%3modes
DC =0;% no DC part imposed
init =1;% initialize omegas uniformly
tol =1e-7;[imf,u_hat,omega]=VMD(data(:,end), alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol);
figure
for i =1:size(imf,1)
subplot(size(imf,1),1,i)plot(imf(i,:))ylabel(['imf',num2str(i)])endylabel('残余')suptitle('VMD')
c=size(imf,1);
pre_result=[];
true_result=[];%% 对每个分量建模
for i=1:cdisp(['对第',num2str(i),'个分量建模'])[x,y]=data_process([data(:,1:end-1)imf(i,:)'],24);%归一化
[xs,mappingx]=mapminmax(x',0,1);x=xs';[ys,mappingy]=mapminmax(y',0,1);y=ys';%划分数据
n=size(x,1);
m=round(n*0.7);%前70%训练,对最后30%进行预测
train_x=x(1:m,:);
test_x=x(m+1:end,:);
train_y=y(1:m,:);
test_y=y(m+1:end,:);%%
typeID='function estimation';
kernelnamescell='RBF_kernel';[x,trace]=ssa_lssvm(typeID,kernelnamescell,train_x,train_y,test_x,test_y);
gam=x(1);
sig2=x(2);
model=initlssvm(train_x,train_y,typeID,gam,sig2,kernelnamescell);
model=trainlssvm(model);
pred=simlssvm(model,test_x);
pre_value=mapminmax('reverse',pred',mappingy);
true_value=mapminmax('reverse',test_y',mappingy);
pre_result=[pre_result;pre_value];
true_result=[true_result;true_value];
end
%% 各分量预测的结果相加
true_value=sum(true_result);
predict_value=sum(pre_result);
save vmd_ssa_lssvm predict_value true_value
%%
load vmd_ssa_lssvmdisp('结果分析')
rmse=sqrt(mean((true_value-predict_value).^2));disp(['根均方差(RMSE):',num2str(rmse)])
mae=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value));disp(['平均绝对误差(MAE):',num2str(mae)])
mape=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value)/true_value);disp(['平均相对百分误差(MAPE):',num2str(mape*100),'%'])fprintf('\n')figureplot(true_value,'-*','linewidth',3)
hold onplot(predict_value,'-s','linewidth',3)legend('实际值','预测值')
grid ontitle('VMD-SSA-LSSVM')
9、
clear;close all;
clc;
format compactaddpath('vmd-verify')
data=xlsread('预测数据.xls','B2:K1000');
f=data(:,end);% some sample parameters forVMD
alpha =2000;% moderate bandwidth constraint
tau =0;% noise-tolerance (no strict fidelity enforcement)
K =5;%3modes
DC =0;% no DC part imposed
init =1;% initialize omegas uniformly
tol =1e-7;%--------------- Run actual VMD code
[u, u_hat, omega]=VMD(f, alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol);figureplot(f)title('原始')
figure
for i=1:K
subplot(K,1,i)plot(u(i,:))ylabel(['IMF_',num2str(i)])endylabel('res')
10、
function result(true_value,predict_value)
rmse=sqrt(mean((true_value-predict_value).^2));disp(['根均方差(RMSE):',num2str(rmse)])
mae=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value));disp(['平均绝对误差(MAE):',num2str(mae)])
mape=mean(abs(true_value-predict_value)/true_value);disp(['平均相对百分误差(MAPE):',num2str(mape*100),'%'])
11、
function [bestX,Convergence_curve]=ssa_lssvm(typeID,Kernel_type,inputn_train,label_train,inputn_test,label_test)%% 麻雀优化
pop=10;% 麻雀数
M=10;% Maximum numbef of iterations
c=1;
d=10000;
dim=2;
P_percent =0.2;% The population size of producers accounts for"P_percent" percent of the total population size
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
pNum =round( pop * P_percent );% The population size of the producers
lb= c.*ones(1,dim );% Lower limit/bounds/ a vector
ub= d.*ones(1,dim );% Upper limit/bounds/ a vector
%Initialization
for i =1:popx( i,:)= lb +(ub - lb).*rand(1, dim );fit( i )=fitness(x(i,:),inputn_train,label_train,inputn_test,label_test,typeID,Kernel_type);end
pFit = fit;
pX = x;% The individual's best position corresponding to the pFit
[ fMin, bestI ]=min( fit );% fMin denotes the global optimum fitness value
bestX =x( bestI,:);% bestX denotes the global optimum position corresponding to fMin
for t =1: M
[ ans, sortIndex ]=sort( pFit );% Sort.[fmax,B]=max( pFit );
worse=x(B,:);
r2=rand(1);%%%%%%%%%%%%%5%%%%%%这一部位为发现者(探索者)的位置更新%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%if(r2<0.8)%预警值较小,说明没有捕食者出现
for i =1: pNum %r2小于0.8的发现者的改变(1-20) % Equation (3)
r1=rand(1);x(sortIndex( i ),:)=pX(sortIndex( i ),:)*exp(-(i)/(r1*M));%对自变量做一个随机变换
x(sortIndex( i ),:)=Bounds(x(sortIndex( i ),:), lb, ub );%对超过边界的变量进行去除
fit(sortIndex( i ))=fitness(x(sortIndex( i ),:),inputn_train,label_train,inputn_test,label_test,typeID,Kernel_type);
end
else%预警值较大,说明有捕食者出现威胁到了种群的安全,需要去其它地方觅食
for i =1: pNum %r2大于0.8的发现者的改变
x(sortIndex( i ),:)=pX(sortIndex( i ),:)+randn(1)*ones(1,dim);x(sortIndex( i ),:)=Bounds(x(sortIndex( i ),:), lb, ub );fit(sortIndex( i ))=fitness(x(sortIndex( i ),:),inputn_train,label_train,inputn_test,label_test,typeID,Kernel_type);
end
end
[ fMMin, bestII ]=min( fit );
bestXX =x( bestII,:);%%%%%%%%%%%%%5%%%%%%这一部位为加入者(追随者)的位置更新%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%for i =( pNum +1): pop %剩下20-100的个体的变换 % Equation (4)
A=floor(rand(1,dim)*2)*2-1;if( i>(pop/2))%这个代表这部分麻雀处于十分饥饿的状态(因为它们的能量很低,也是是适应度值很差),需要到其它地方觅食
x(sortIndex(i ),:)=randn(1)*exp((worse-pX(sortIndex( i ),:))/(i)^2);else%这一部分追随者是围绕最好的发现者周围进行觅食,其间也有可能发生食物的争夺,使其自己变成生产者
x(sortIndex( i ),:)=bestXX+(abs((pX(sortIndex( i ),:)-bestXX)))*(A'*(A*A')^(-1))*ones(1,dim);endx(sortIndex( i ),:)=Bounds(x(sortIndex( i ),:), lb, ub );%判断边界是否超出
fit(sortIndex( i ))=fitness(x(sortIndex( i ),:),inputn_train,label_train,inputn_test,label_test,typeID,Kernel_type);
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%5%%%%%%这一部位为意识到危险(注意这里只是意识到了危险,不代表出现了真正的捕食者)的麻雀的位置更新%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
c=randperm(numel(sortIndex));%%%%%%%%%这个的作用是在种群中随机产生其位置(也就是这部分的麻雀位置一开始是随机的,意识到危险了要进行位置移动,
%处于种群外围的麻雀向安全区域靠拢,处在种群中心的麻雀则随机行走以靠近别的麻雀)
b=sortIndex(c(1:10));for j =1:length(b)% Equation (5)if(pFit(sortIndex(b(j)))>(fMin))%处于种群外围的麻雀的位置改变
x(sortIndex(b(j)),:)=bestX+(randn(1,dim)).*(abs((pX(sortIndex(b(j)),:)-bestX)));else%处于种群中心的麻雀的位置改变
x(sortIndex(b(j)),:)=pX(sortIndex(b(j)),:)+(2*rand(1)-1)*(abs(pX(sortIndex(b(j)),:)-worse))/(pFit(sortIndex(b(j)))-fmax+1e-50);endx(sortIndex(b(j)),:)=Bounds(x(sortIndex(b(j)),:), lb, ub );fit(sortIndex(b(j)))=fitness(x(sortIndex(b(j)),:),inputn_train,label_train,inputn_test,label_test,typeID,Kernel_type);
end
for i =1: pop
if(fit( i )<pFit( i ))pFit( i )=fit( i );pX( i,:)=x( i,:);
end
if(pFit( i )< fMin )
fMin=pFit( i );
bestX =pX( i,:);
end
endConvergence_curve(t,:)=[fMinmean(pFit)];
end
接下来是内嵌代码,就是下面两个文件夹的代码,实在是太多,想要的留言吧!
数据
数据是由时间、风速、风向等等因素组成的文件。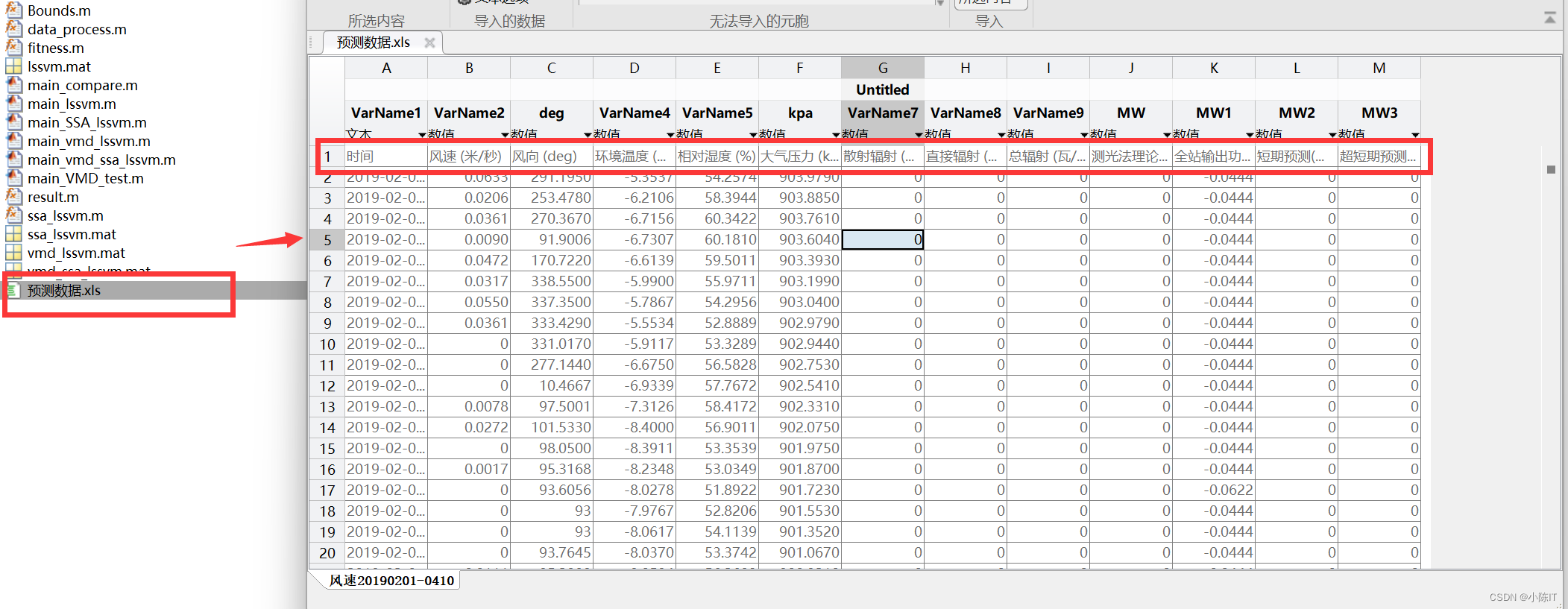
结果
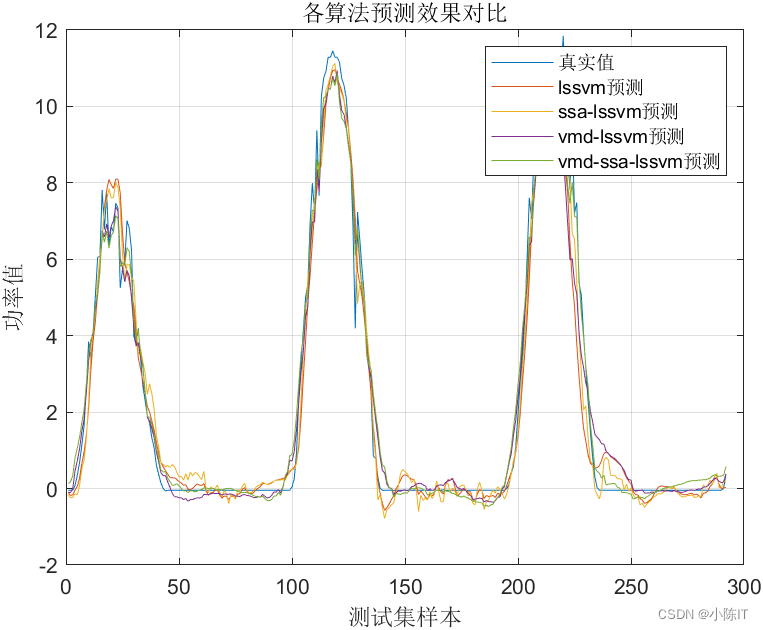
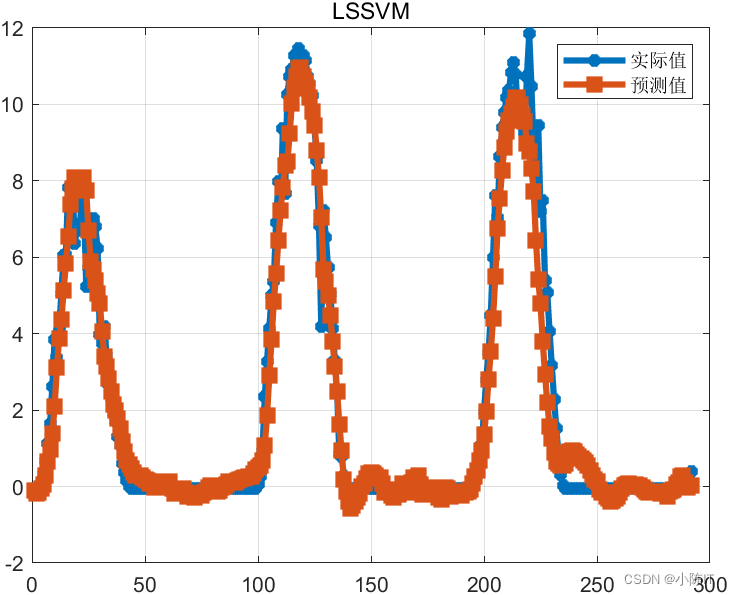
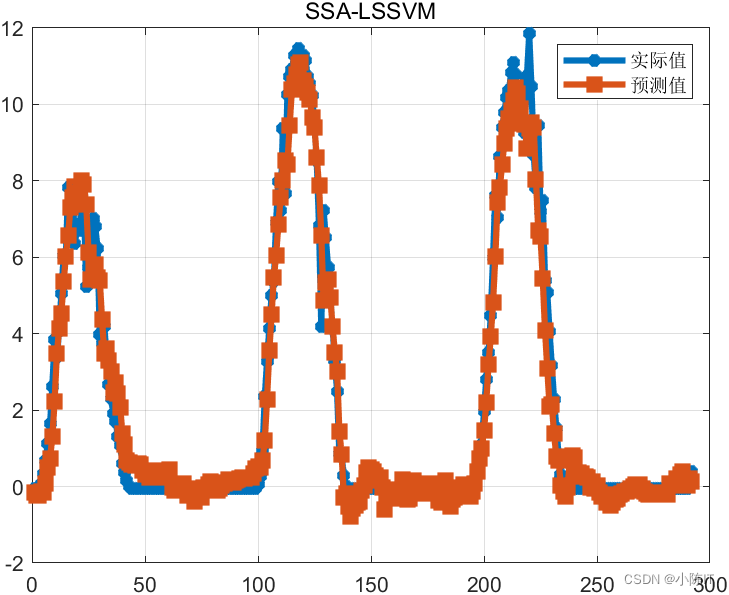
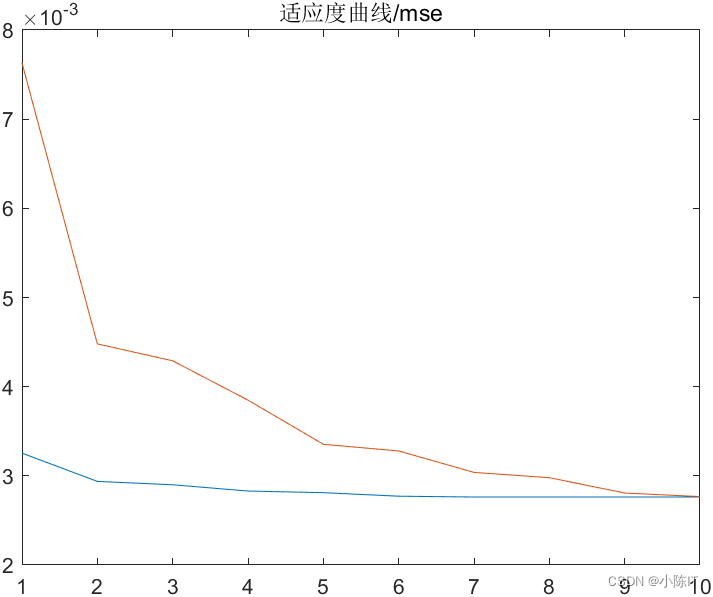
结果图太多,就先给出这么多,如有需要代码和数据的同学请在评论区发邮箱,一般一天之内会回复,请点赞+关注谢谢!!
版权归原作者 小陈IT 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。