激光雷达点云与单图像配准/映射变为彩色点云
如果没有对pcl库进行配置,则需要先配置pcl:可重复使用的VS-PCL1.10.1环境配置
本文提供激光雷达采集的点云与单幅二维图像之间的配准方法,目的是实现点云到图像之间的映射,同时也可以将点云转变为彩色点云。
数据准备:
- point_cloud: 激光雷达点云数据;
- img: 与激光雷达对应的图像;
- camera_par: 相机内参 >> 相机坐标系到像素坐标系的变换矩阵
- D: 相机畸变系数
- t_word_to_cam: 激光雷达到相机位置的变换矩阵:世界坐标到相机坐标变换矩阵
关于激光雷达点云与图像之间的映射原理有网上给出了很多,但是具体转换的方法或开源的代码却较少。因此本文就以一副点云和一副图像进行介绍,并给出具体的实现过程。
这个中间具体的转换原理就不做介绍了,就给一个具体的转换思路。
转换过程:世界坐标 》相机坐标 》像素坐标 此时每个点云(x,y,z)就会对应到一个像素坐标(u,v),即对应一个颜色点(r,g,b)
具体的转换思路:
1、首先我们根据相机的畸变系数对图像去畸变,得到正确的图像。
2、然后将点云中的点 乘以 世界坐标到相机坐标变换矩阵 t_word_to_cam,目的是将世界坐标点转换为相机坐标点;
3、随后再将转换的相机坐标点乘以相机内参,目的是相机坐标点转换为平面像素坐标点。
4、最后将像素坐标点对应的颜色值赋予点云中的点,表现形式为:生成了彩色点云。
数据准备
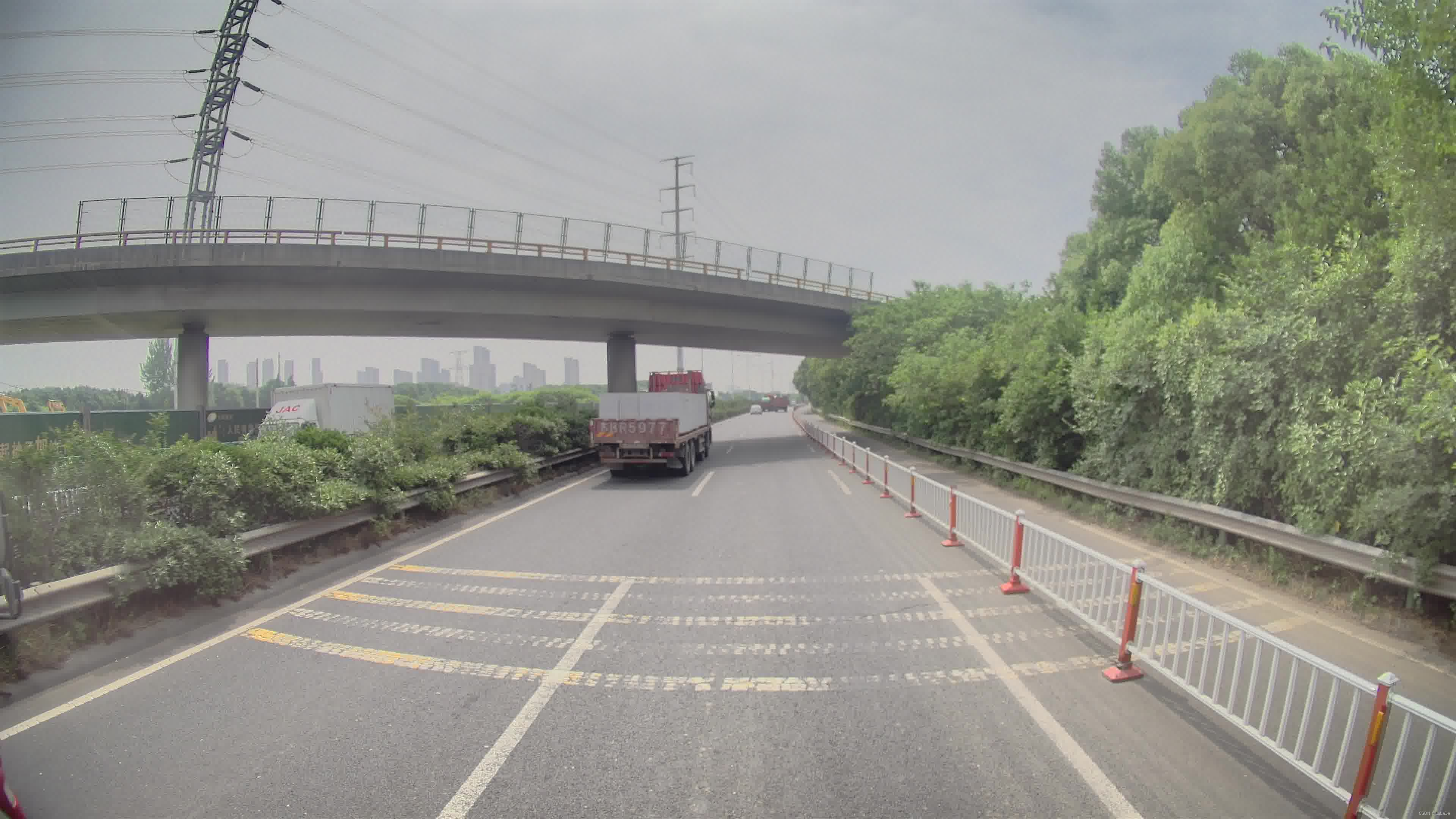

// 文件读取
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr point_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
std::string path ="2.pcd";
std::string imgPath ="2.jpeg";
pcl::io::loadPCDFile(path,*point_cloud);//PointCloudRoar(point_cloud, point_cloud_ptr);
Mat img =imread(imgPath);if(img.channels()!=3){
cout <<"RGB pics needed."<< endl;return0;}// 相机内参 3X3const Mat K =(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<1.9506592935364870e+03,0.0,1.9770478473401959e+03,0.0,1.9508117738745232e+03,1.0786204201895550e+03,0.0,0.0,1.);// 相机内参 3X4const Mat camera_par =(Mat_<double>(3,4)<<1.9506592935364870e+03,0.0,1.9770478473401959e+03,0,0.0,1.9508117738745232e+03,1.0786204201895550e+03,0,0.0,0.0,1.0,0);// 相机畸变参数const cv::Mat D =(cv::Mat_<double>(5,1)<<-0.050519061674533024,-0.007992982752507883,0.00970045657644595,-0.004354775040194558,0.0);// 世界坐标到相机坐标变换矩阵
Mat t_word_to_cam =(Mat_<double>(4,4)<<2.4747462378258280e-02,-9.9955232303502073e-01,-1.6839925611563663e-02,-9.2541271346932907e-02,-1.3087302341509554e-02,1.6519577885364300e-02,-9.9977861656954914e-01,2.4302538338292576e+00,9.9960858363250360e-01,2.4962312041639460e-02,-1.2672595327247342e-02,-5.0924142692133323e+00,0.,0.,0.,1);
图像去畸变
cv::Mat UndistortImage;
cv::undistort(img, UndistortImage, K, D, K);
世界坐标》相机坐标》像素坐标
在坐标像素点映射的过程中我们只对位于图像像素范围内的点进行映射,超出图像范围的点将不做处理。
Mat word_h =Mat(4,1, CV_64FC1);
Mat p_result =Mat(3,1, CV_64FC1);
Mat cam_h =Mat(4,1, CV_64FC1);double p_u, p_v, p_w;//pics_uv1;(u for cols, v for lines!!!)double c_x, c_y, c_z, c_i;//clouds_xyz、intensity;for(int nIndex =0; nIndex < point_cloud->points.size(); nIndex++){
c_x = point_cloud->points[nIndex].x;
c_y = point_cloud->points[nIndex].y;
c_z = point_cloud->points[nIndex].z;
word_h =(Mat_<double>(4,1)<< c_x, c_y, c_z,1);// 矩阵计算 (3, 4) x (4, 4) x (4,1) = (3,1) 最后得到一个 3x1 的矩阵
p_result = camera_par * t_word_to_cam * word_h;
p_w = p_result.at<double>(2,0);
p_u =(int)((p_result.at<double>(0,0))/ p_w);
p_v =(int)((p_result.at<double>(1,0))/ p_w);// 判断当前点映射的像素点是否在图像像素范围内,如果在就将该像素点的颜色赋予世界坐标点if(p_u >=0&& p_u < cols && p_v >=0&& p_v < rows && p_w>0){/*cout << "--" << p_u << "--" << cols << endl;
cout << "***" << p_v << "--" << rows << endl;*/float r = UndistortImage.at<Vec3b>(p_v, p_u)[2];float g = UndistortImage.at<Vec3b>(p_v, p_u)[1];float b = UndistortImage.at<Vec3b>(p_v, p_u)[0];
point_cloud->points[nIndex].r = r;
point_cloud->points[nIndex].g = g;
point_cloud->points[nIndex].b = b;}else{
point_cloud->points[nIndex].r =255;
point_cloud->points[nIndex].g =255;
point_cloud->points[nIndex].b =255;}}
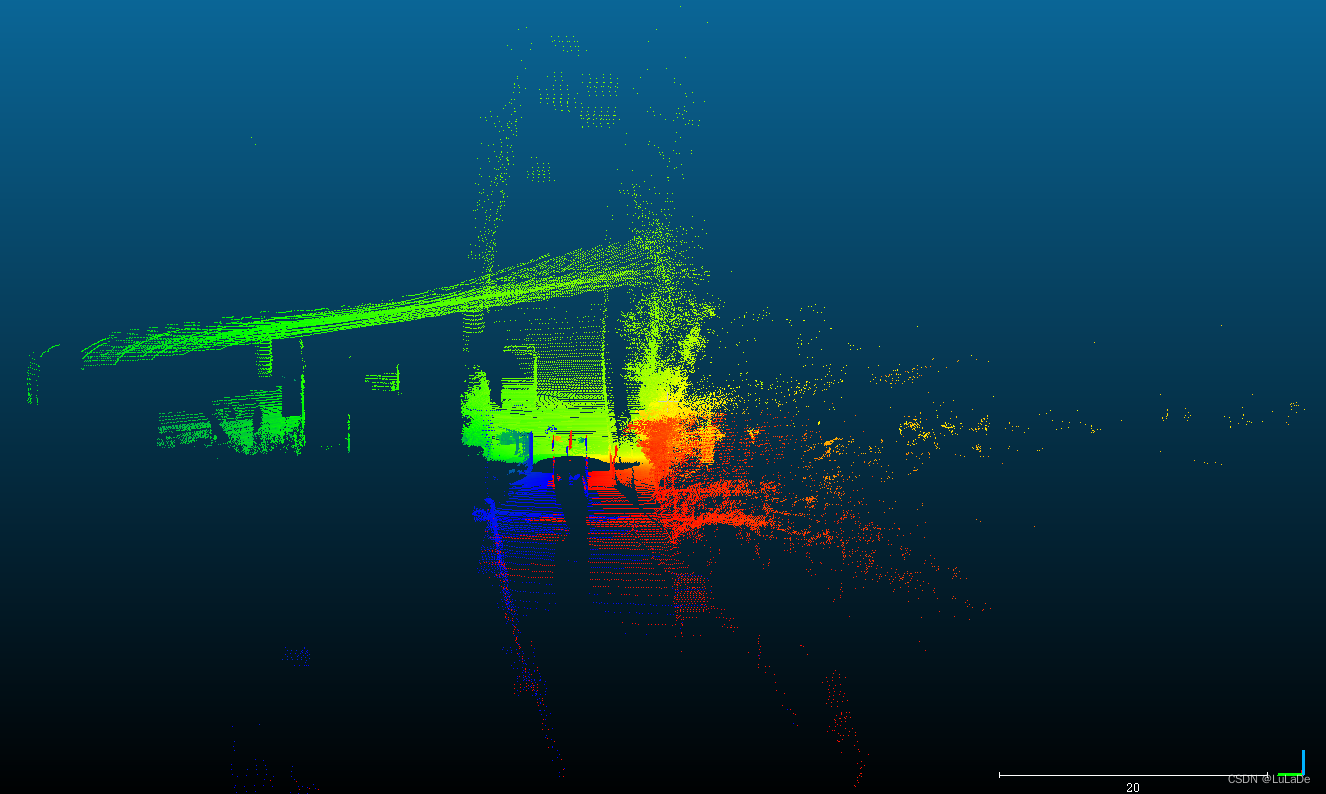
映射结果
从结果中可见车,围栏、路边的树木,地面都进行了准确映射。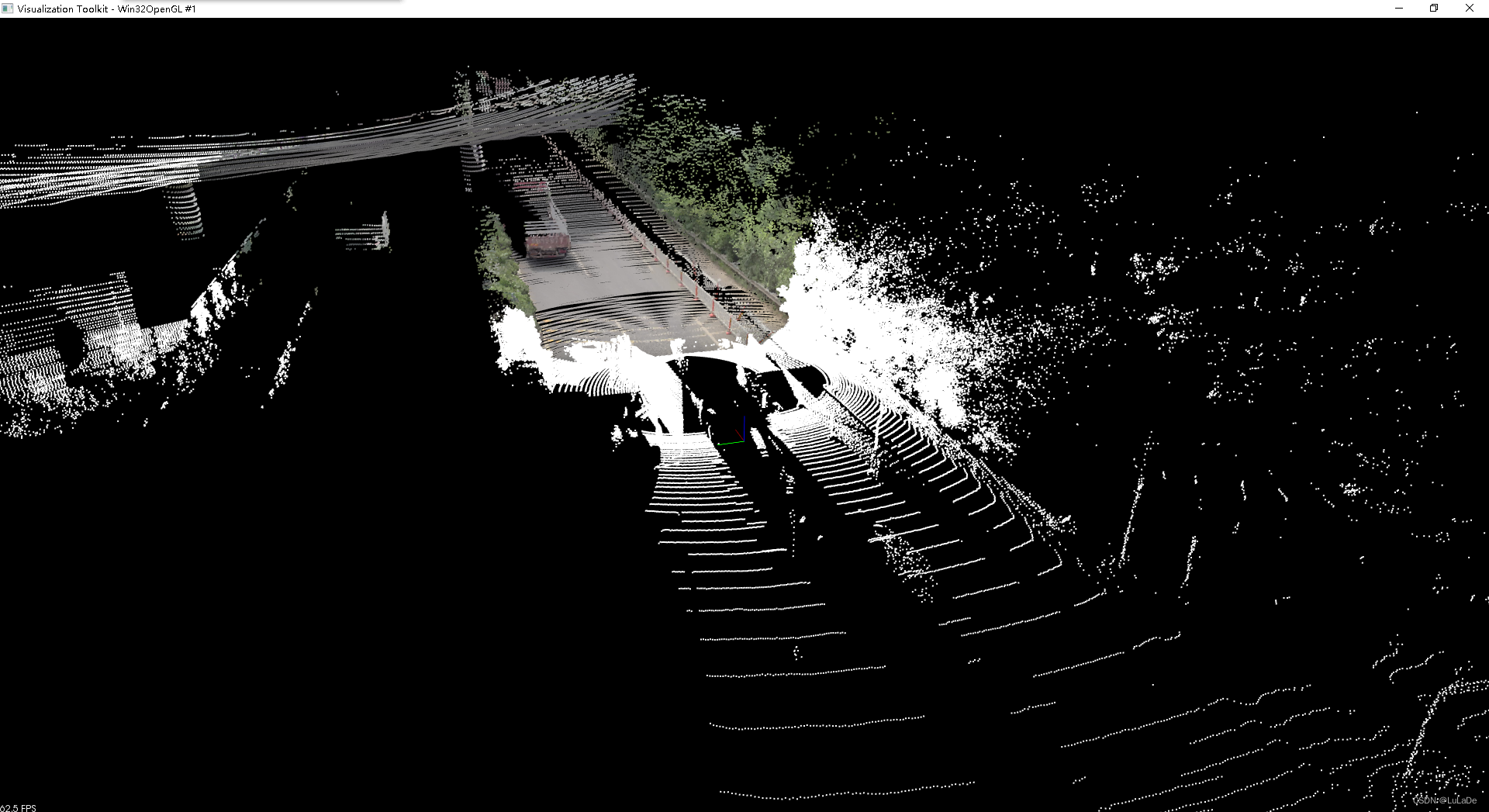
文件下载
本文所使用的测试点云和图像文件可从此处免费下载
资源:点云数据,二维图像
全部代码
#include<iostream>#include<boost/thread/thread.hpp>#include<pcl/common/common_headers.h>#include<pcl/common/common_headers.h>#include<pcl/features/normal_3d.h>#include<pcl/io/pcd_io.h>#include<pcl/io/io.h>#include<pcl/point_types.h>#include<pcl/registration/icp.h>#include<pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>#include<pcl/console/parse.h>#include<pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>//点云查看窗口头文件#include"opencv2/highgui.hpp"#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>#include<opencv2/core/eigen.hpp>#include<Eigen/Dense>usingnamespace cv;usingnamespace std;//RGB colour visualisation example
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer>rgbVis(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::ConstPtr cloud){//创建3D窗口并添加点云
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer>viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3D Viewer"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0,0,0);
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>(cloud,"sample cloud");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE,2,"sample cloud");
viewer->addCoordinateSystem(1.0);
viewer->initCameraParameters();return(viewer);}intmain(){// 文件读取
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr point_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
std::string path ="2.pcd";
std::string imgPath ="2.jpeg";
pcl::io::loadPCDFile(path,*point_cloud);//PointCloudRoar(point_cloud, point_cloud_ptr);
Mat img =imread(imgPath);if(img.channels()!=3){
cout <<"RGB pics needed."<< endl;return0;}// 相机内参 3X3const Mat K =(Mat_<double>(3,3)<<1.9506592935364870e+03,0.0,1.9770478473401959e+03,0.0,1.9508117738745232e+03,1.0786204201895550e+03,0.0,0.0,1.);// 相机内参 3X4const Mat camera_par =(Mat_<double>(3,4)<<1.9506592935364870e+03,0.0,1.9770478473401959e+03,0,0.0,1.9508117738745232e+03,1.0786204201895550e+03,0,0.0,0.0,1.0,0);// 相机畸变参数const cv::Mat D =(cv::Mat_<double>(5,1)<<-0.050519061674533024,-0.007992982752507883,0.00970045657644595,-0.004354775040194558,0.0);
cv::Mat UndistortImage;
cv::undistort(img, UndistortImage, K, D, K);int rows = UndistortImage.rows;int cols = UndistortImage.cols;// 世界坐标到相机坐标变换矩阵
Mat t_word_to_cam =(Mat_<double>(4,4)<<2.4747462378258280e-02,-9.9955232303502073e-01,-1.6839925611563663e-02,-9.2541271346932907e-02,-1.3087302341509554e-02,1.6519577885364300e-02,-9.9977861656954914e-01,2.4302538338292576e+00,9.9960858363250360e-01,2.4962312041639460e-02,-1.2672595327247342e-02,-5.0924142692133323e+00,0.,0.,0.,1);
Mat word_h =Mat(4,1, CV_64FC1);
Mat p_result =Mat(3,1, CV_64FC1);
Mat cam_h =Mat(4,1, CV_64FC1);double p_u, p_v, p_w;//pics_uv1;(u for cols, v for lines!!!)double c_x, c_y, c_z, c_i;//clouds_xyz、intensity;for(int nIndex =0; nIndex < point_cloud->points.size(); nIndex++){
c_x = point_cloud->points[nIndex].x;
c_y = point_cloud->points[nIndex].y;
c_z = point_cloud->points[nIndex].z;
word_h =(Mat_<double>(4,1)<< c_x, c_y, c_z,1);
p_result = camera_par * t_word_to_cam * word_h;
p_w = p_result.at<double>(2,0);
p_u =(int)((p_result.at<double>(0,0))/ p_w);
p_v =(int)((p_result.at<double>(1,0))/ p_w);if(p_u >=0&& p_u < cols && p_v >=0&& p_v < rows && p_w>0){/*cout << "--" << p_u << "--" << cols << endl;
cout << "***" << p_v << "--" << rows << endl;*/float r = UndistortImage.at<Vec3b>(p_v, p_u)[2];float g = UndistortImage.at<Vec3b>(p_v, p_u)[1];float b = UndistortImage.at<Vec3b>(p_v, p_u)[0];
point_cloud->points[nIndex].r = r;
point_cloud->points[nIndex].g = g;
point_cloud->points[nIndex].b = b;}else{
point_cloud->points[nIndex].r =255;
point_cloud->points[nIndex].g =255;
point_cloud->points[nIndex].b =255;}}
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer;
viewer =rgbVis(point_cloud);// 主循环 while(!viewer->wasStopped()){
viewer->spinOnce(100);}}
版权归原作者 LuLaDe 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。