1.简介
Canopy聚类算法是一个将对象分组到类的简单、快速、精确地方法。每个对象用多维特征空间里的一个点来表示。这个算法使用一个快速近似距离度量和两个距离阈值T1 > T2 处理。
Canopy聚类很少单独使用, 一般是作为k-means前不知道要指定k为何值的时候,用Canopy聚类来判断k的取值
2.算法步骤
输入:所有点的集合D, 超参数:T1 , T2 , 且 T1 > T2
输出:聚类好的集合

注意
- 当T1过大时,会使许多点属于多个Canopy,可能会造成各个簇的中心点间距离较近,各簇间区别不明显;
- 当T2过大时,增加强标记数据点的数量,会减少簇个个数;
- T2过小,会增加簇的个数,同时增加计算时间;
一幅图说明算法:
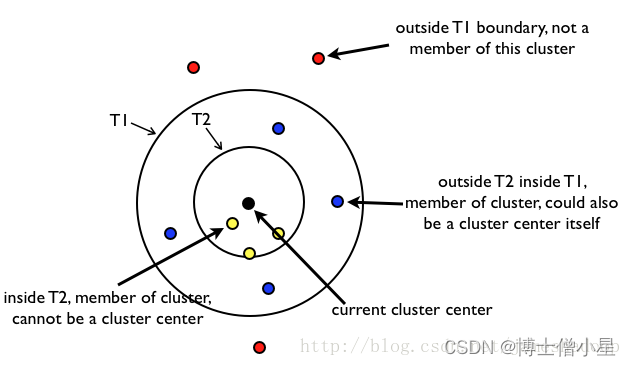
内圈的一定属于该类, 外圈的一定不属于该类, 中间层的可能属于别的类(因为不止一个聚类中心, 他可能属于别的类的内圈);
3.python实现
对iris数据集做Canopy聚类, 半径分别设置为1和2
#%% Canopy聚类
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import copy
class Solution(object):
def Canopy(self, x, t1, t2):
'''
Parameters
----------
x : array
数据集.
t1 : float
外圈半径.
t2 : float
内圈半径.
Returns
-------
result: list.
聚好类的数据集
'''
if t1 < t2:
return print("t1 应该大于 t2")
x = copy.deepcopy(x)
result = [] # 用于存放最终结果
index = np.zeros((len(x),)) # 用于标记外圈外的点 1表示强标记, 2表示弱标记
while (index == np.zeros((len(x),))).any():
alist = [] # 用于存放某一类的数据集
choice_index = None
for i, j in enumerate(index):
if j == 0:
choice_index = i
break
C = copy.deepcopy(x[choice_index])
alist.append(C)
x[choice_index] = np.zeros((1, len(x[0])))
index[choice_index] = 1
for i,a in enumerate(x):
if index[i] != 1:
distant = (((a-C)**2).sum())**(1/2)
if distant <= t2: # 打上强标记
alist.append(copy.deepcopy(x[i]))
x[i] = np.zeros((1, len(x[0])))
index[i] = 1
elif distant <= t1:
index[i] = 2
result.append(alist)
return result
def pint(r, x, y, c):
# 点的横坐标为a
a = np.arange(x-r,x+r,0.0001)
# 点的纵坐标为b
b = np.sqrt(np.power(r,2)-np.power((a-x),2))
plt.plot(a,y+b,color=c,linestyle='-')
plt.plot(a,y-b,color=c,linestyle='-')
plt.scatter(x, y, c='r',marker='*')
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = pd.read_csv(r'C:/Users/潘登/Documents/python全系列/人工智能/iris.csv')
X = np.array(data.iloc[:, 2:4])
Y = data['species']
result = Solution().Canopy(X, 2, 1)
x1 = []
y1 = []
for i in result[0]:
x1.append(i[0])
y1.append(i[1])
x2 = []
y2 = []
for i in result[1]:
x2.append(i[0])
y2.append(i[1])
x3 = []
y3 = []
for i in result[2]:
x3.append(i[0])
y3.append(i[1])
plt.figure(figsize=(16,12))
plt.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], s=50, c='violet', marker='s')
plt.scatter(x1, y1, s=50, c='orange', marker='s')
plt.scatter(x2, y2, s=50, c='lightblue', marker='s')
plt.scatter(x3, y3, s=50, c='blue', marker='s')
pint(2, x1[0], y1[0], 'b')
pint(1, x1[0], y1[0], 'y')
pint(2, x2[0], y2[0], 'b')
pint(1, x2[0], y2[0], 'y')
pint(2, x3[0], y3[0], 'b')
pint(1, x3[0], y3[0], 'y')
plt.xlim([0, 8])
plt.ylim([-3, 5])
plt.show()
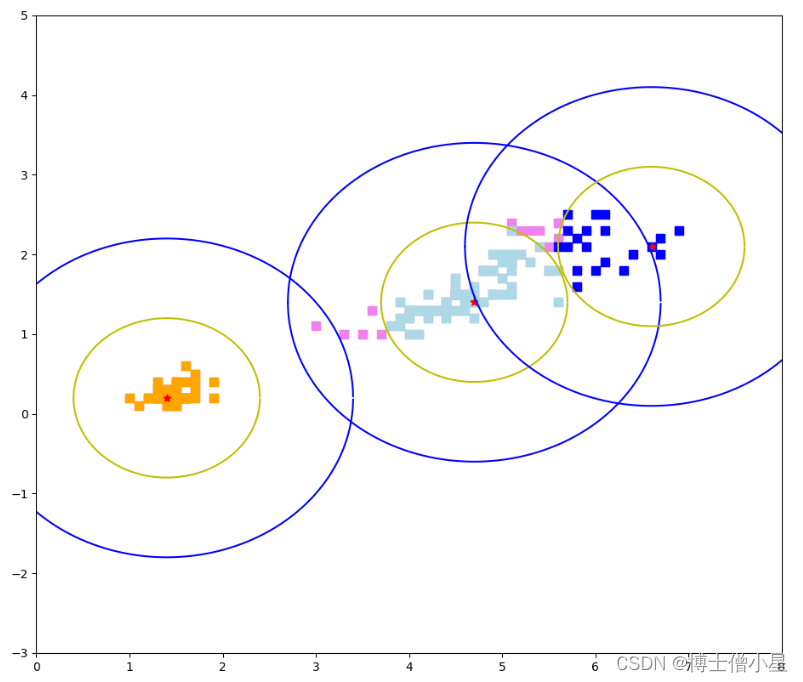
+结果如下:
版权归原作者 博士僧小星 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。