MATLAB 支持向量机(SVM)详细解释(含代码)
基础
线性可分
简单来讲就是如何将两个数据用点、直线、平面分开。。。。。
二维空间中,要分开两个线性可分的点集合,我们需要找到一条分类直线即可,
最大间隔超平面
通俗来讲,在这个二维平面中,可以把两类点的分开的直线有很多条,那么这些直线中,哪一条才是最好的呢?也就是如何选择出一条最好的直线呢?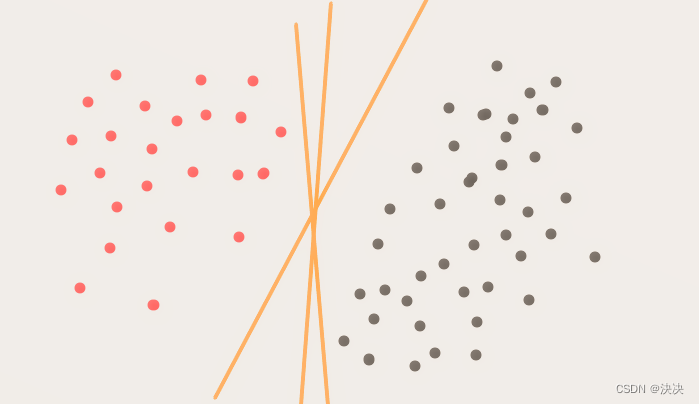
先看橙色的点,如果这些点到分类直线的距离越大,分类直线也就越远离橙色的点,那么再来一个新的点,如果这个点是依照橙色点集合的特性产生的(也就是它不是一个相对于橙色点集合很奇异的点),那么这个点也很可能和橙色的点集合一样,分布在直线的同一侧。分布在同一侧,表明它和橙色集合点属于同一个类别。用同样的思想,图4中,对于灰色的集合点,这条分类直线离它们的距离也要越远越好。所以找最优分类线,就是要找到这条一条直线,使它到两个类别点的距离越大越好。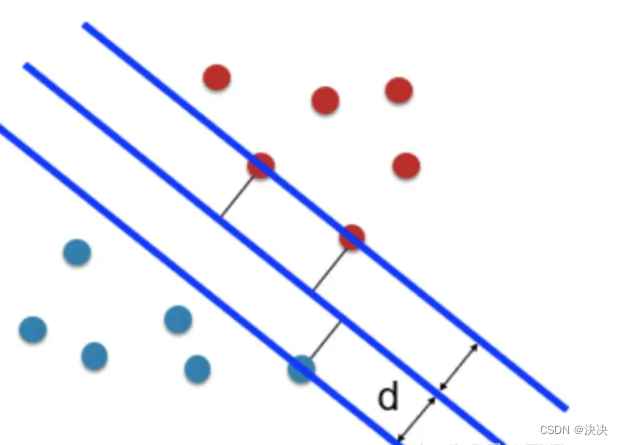
因此便可得到某根距离离两边都累计最远的直线,即最大分隔超平面。
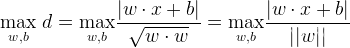
上述也叫硬间隔最最大化,能够用直线将两者分开。
SVM分类
基本代码和工具
工具:1、MATLAB 2020a;2、fitcsvm
二分类
fitcsvm:fitcsvm训练或交叉验证支持向量机(SVM)模型在低维或中维预测数据集上的一类和二类(binary)分类。fitcsvm支持使用核函数映射预测数据,并支持通过二次规划实现目标函数最小化的顺序最小优化(SMO,sequential minimal optimization)、迭代单数据算法(ISDA,iterative single data algorithm)或L1软边界最小化。
代码:
线性
clc
clear all
%设置两类不同数据
A=[3,7;6,6;4,6;5,6.5];B=[1,2;3,5;7,3;3,4;6,2.7;4,3;2,7];C=[A;B];%两类数据合并
%设置不同类别标签
table =[truetruetruetruefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalse];D=nominal(table);%%数据集和标签
sd=C;Y=D;%% 原始数据图像
subplot(1,2,1)gscatter(sd(:,1),sd(:,2),Y,'rg','+*');%%SVM
SVMModel=fitcsvm(sd,Y,'KernelFunction','linear');[lable,score]=predict(SVMModel,sd);%% 画图
subplot(1,2,2)
h =nan(3,1);h(1:2)=gscatter(sd(:,1),sd(:,2),Y,'rg','+*');
hold on
h(3)=plot(sd(SVMModel.IsSupportVector,1),sd(SVMModel.IsSupportVector,2),'ko');%画出支持向量
%画出决策边界
w=-SVMModel.Beta(1,1)/SVMModel.Beta(2,1);%斜率
b=-SVMModel.Bias/SVMModel.Beta(2,1);%截距
x_ =0:0.01:10;
y_ = w*x_+b;plot(x_,y_)
hold on
legend(h,{'-1','+1','Support Vectors'},'Location','Southeast');
axis equal
hold off
实验结果: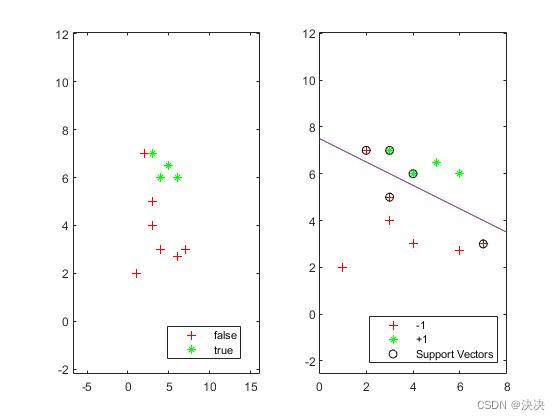
上述实验得到一个硬间隔最大化的分隔超平面
非线性
clc
clear all
%设置两类不同数据
A=[0.9,1;0.8,1.8;0.79,1.7;0.7,3;0.8,3.9;0.9,4.5;1.2,5.7;1.6,5.6;2.5,6.1;2.9,5.8;2.9,1;3.1,1.4;3.6,1.2;5,2;5.5,3.9;4.9,4.5;4.2,5.9;3.6,5.6;2.5,5.1;2.9,5.3];B=[2.5,3.1;3.5,2.6;4.5,3.2;3.5,2;2.4,2;3.5,2.5;4.3,3.7;2.6,2.8;2.4,3;3.6,3.1;4.4,3.3;2.5,4.0;3.5,4.1;4.5,4.2;1.5,4;2.4,4;3.5,4.5;4.3,3.7;3.6,3.8;2.4,3.5;3.6,3.7;4.4,3.3];C=[A;B];%两类数据合并
%设置不同类别标签
table =[truetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalsefalse];D=nominal(table);%%数据集和标签
sd=C;Y=D;%% 原始数据图像
subplot(1,2,1)gscatter(sd(:,1),sd(:,2),Y,'rg','+*');%% 原始数据图像
subplot(1,2,1)gscatter(sd(:,1),sd(:,2),Y,'rg','+*');%%SVM
SVMModel=fitcsvm(sd,Y,'BoxConstraint',10,'KernelFunction','rbf','KernelScale',2^0.5*2);%使用高斯核函数
%%SVMModel=fitcsvm(sd,Y,'KernelFunction','rbf','OptimizeHyperparameters',{'BoxConstraint','KernelScale'},'HyperparameterOptimizationOptions',struct('ShowPlots',false));%使用超参数优化
%% 画图
subplot(1,2,2)
h =nan(3,1);h(1:2)=gscatter(sd(:,1),sd(:,2),Y,'rg','+*');
hold on
h(3)=plot(sd(SVMModel.IsSupportVector,1),sd(SVMModel.IsSupportVector,2),'ko');%画出支持向量
%画出决策边界
h =0.2;[X1,X2]=meshgrid(min(sd(:,1)):h:max(sd(:,1)),min(sd(:,2)):h:max(sd(:,2)));%得到所有取点的矩阵
[lable,score]=predict(SVMModel,[X1(:),X2(:)]);
scoreGrid =reshape(score(:,2),size(X1,1),size(X2,2));contour(X1,X2,scoreGrid,[00]);%绘制等高线
hold on
legend('-1','+1','Support Vectors','分界线');
axis equal
hold off
实验结果: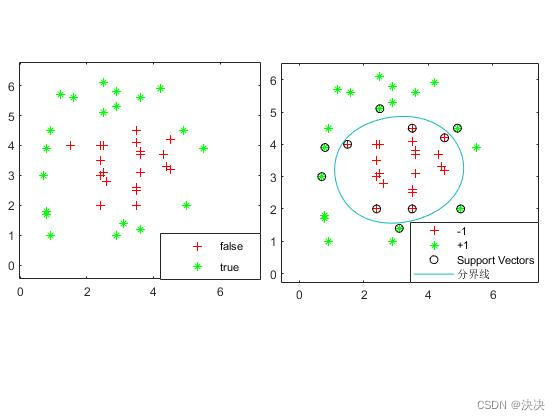
上述实验进行非线性的数据分类
多分类
详细解释
一对多法(one-versus-rest,简称OVR SVMs)
训练时依次把某个类别的样本归为一类,其他剩余的样本归为另一类,这样k个类别的样本就构造出了k个SVM。分类时将未知样本分类为具有最大分类函数值的那类。
假如我有四类要划分(也就是4个Label),他们是A、B、C、D。
于是我在抽取训练集的时候,分别抽取
(1)A所对应的向量作为正集,B,C,D所对应的向量作为负集;
(2)B所对应的向量作为正集,A,C,D所对应的向量作为负集;
(3)C所对应的向量作为正集,A,B,D所对应的向量作为负集;
(4)D所对应的向量作为正集,A,B,C所对应的向量作为负集;
使用这四个训练集分别进行训练,然后的得到四个训练结果文件。在测试的时候,把对应的测试向量分别利用这四个训练结果文件进行测试。最后每个测试都有一个结果f1(x),f2(x),f3(x),f4(x)。于是最终的结果便是这四个值中最大的一个作为分类结果。
数据链接: [https://pan.baidu.com/s/1QUNknb-AV-cPt0hM_jSs_Q ]提取码:http
代码:
clc;
clear;
close all;%%导入数据:训练集、测试集、训练标签、测试标签
train_data=xlsread('train_data.xls');
group_train=xlsread('group_train.xls');
test_data=xlsread('test_data.xls');
test_labels=xlsread('test_labels.xls');%%绘数据分布图
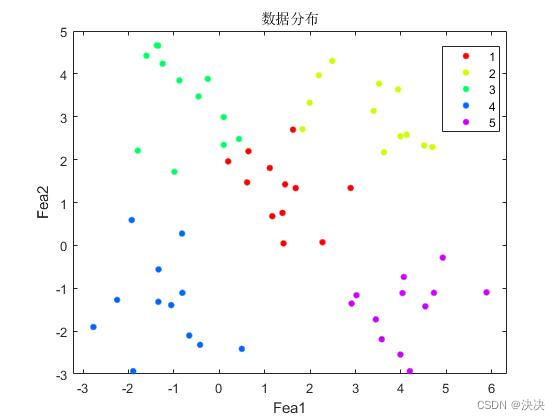
gscatter(train_data(:,1),train_data(:,2),group_train);title('数据分布');xlabel('Fea1');ylabel('Fea2');%%% 训练数据分为5类
% 类别i的 正样本 选择类别i的全部,负样本 从其余类别中随机选择(个数与正样本相同)
%%% 类别1
class1_p =train_data(1:12,:);%randperm(n,k)是从1到n的序号中随机返回k个
index1 =randperm(48,12);
train_data_c = train_data;train_data_c(1:12,:)=[];%正样本
class1_n =train_data_c(index1,:);%负样本
train_features1 =[class1_p;class1_n];% 正类表示为1,负类表示为-1
train_labels1 =[ones(12,1);-1*ones(12,1)];%% 类别2
class2_p =train_data(13:24,:);%randperm(n,k)是从1到n的序号中随机返回k个
index1 =randperm(48,12);
train_data_c = train_data;train_data_c(13:24,:)=[];%正样本
class2_n =train_data_c(index1,:);%负样本
train_features2 =[class2_p;class2_n];% 正类表示为1,负类表示为-1
train_labels2 =[ones(12,1);-1*ones(12,1)];%% 类别3
class3_p =train_data(25:36,:);%randperm(n,k)是从1到n的序号中随机返回k个
index1 =randperm(48,12);
train_data_c = train_data;train_data_c(25:36,:)=[];%正样本
class3_n =train_data_c(index1,:);%负样本
train_features3 =[class3_p;class3_n];% 正类表示为1,负类表示为-1
train_labels3 =[ones(12,1);-1*ones(12,1)];%% 类别4
class4_p =train_data(37:48,:);%randperm(n,k)是从1到n的序号中随机返回k个
index1 =randperm(48,12);
train_data_c = train_data;train_data_c(37:48,:)=[];%正样本
class4_n =train_data_c(index1,:);%负样本
train_features4 =[class4_p;class4_n];% 正类表示为1,负类表示为-1
train_labels4 =[ones(12,1);-1*ones(12,1)];%% 类别5
class5_p =train_data(49:60,:);%randperm(n,k)是从1到n的序号中随机返回k个
index1 =randperm(48,12);
train_data_c = train_data;train_data_c(49:60,:)=[];%正样本
class5_n =train_data_c(index1,:);%负样本
train_features5 =[class5_p;class5_n];% 正类表示为1,负类表示为-1
train_labels5 =[ones(12,1);-1*ones(12,1)];%%% 分别训练5个类别的SVM模型
model1 =fitcsvm(train_features1,train_labels1,'ClassNames',{'-1','1'});
model2 =fitcsvm(train_features2,train_labels2,'ClassNames',{'-1','1'});
model3 =fitcsvm(train_features3,train_labels3,'ClassNames',{'-1','1'});
model4 =fitcsvm(train_features4,train_labels4,'ClassNames',{'-1','1'});
model5 =fitcsvm(train_features5,train_labels5,'ClassNames',{'-1','1'});%%% label是n*1的矩阵,每一行是对应测试样本的预测标签;
% score是n*2的矩阵,第一列为预测为“负”的得分,第二列为预测为“正”的得分。
% 用训练好的5个SVM模型分别对测试样本进行预测分类,得到5个预测标签
[label1,score1]=predict(model1,test_data);[label2,score2]=predict(model2,test_data);[label3,score3]=predict(model3,test_data);[label4,score4]=predict(model4,test_data);[label5,score5]=predict(model5,test_data);% 求出测试样本在5个模型中预测为“正”得分的最大值,作为该测试样本的最终预测标签
score =[score1(:,2),score2(:,2),score3(:,2),score4(:,2),score5(:,2)];% 最终预测标签为k*1矩阵,k为预测样本的个数
final_labels =zeros(20,1);for i =1:size(final_labels,1)% 返回每一行的最大值和其位置
[m,p]=max(score(i,:));% 位置即为标签
final_labels(i,:)= p;
end
% 分类评价指标

版权归原作者 決决 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。