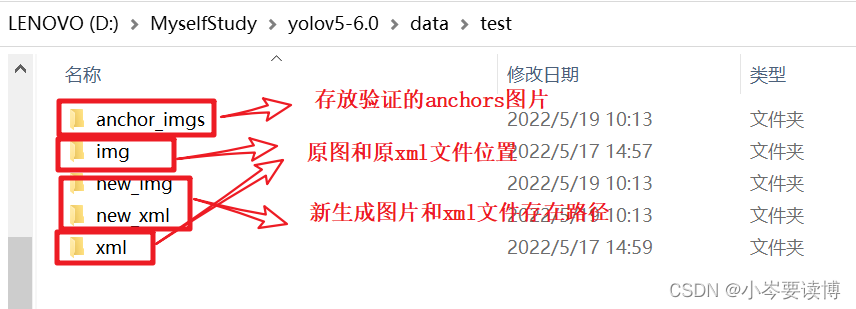
1.数据增强概述
- 海量数据是目标检测的基础,而针对于特定场景的数据往往需要自己获取和标注,往往需要耗费大量的人工成本和时间成本。而数据增强则能很好的解决这问题。
- 与简单的数据增强方法不同,目标检测的数据增强不仅要考虑图片的相应转变,还要实现图片内所标注坐标的转换,即目标检测的数据增强既要生成原图片的衍生图片,同时还需生成相应的xml文件(pascal voc数据集为例)。因此目标检测的数据增强与图像分类的数据增强有很大的不同。
- 往往目标检测的数据增强又分为在线数据增强和离线数据增强。大多的目标检测模型都默认带有在线数据增强,通过相关配置文件就能实现,优点是不占用本地内存方便实现,缺点是不够直观。而离线的数据增强则相反。而在刚起步学习阶段,可以通过离线数据增强的方式更直观的感受一下。
2.目标检测离线数据增强步骤(一定要先看,便于理解过程)
- 第一步针对标注好的数据(pascal voc数据集为例),通过相关python脚本将标注的矩形框画出来,检查标注时的准确性(随机挑选部分图片,可以不用全部照片)。
- 第二步使用几种数据增强方式对图片进行增强,这里主要使用了五种数据增强方法(图像旋转、高斯噪音、改变亮度、裁剪、平移),其中图像旋转有六种旋转角度(60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 270)。并且,在这几种方法中,添加高斯噪音和改变亮度xml文件与原图是相同的。
- 第三步在生成新的图片和xml文件后,与第一步相同验证新生成图像所生成xml文件的准确性。不正确就需要针对具体情况进行调整。
- 在扩充了数据集之后就开始对模型进行训练了。
3.数据增强代码
- 实现对标注好的数据集进行验证(验证标注情况的实际情况)
import os
import cv2 as cv
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def xml_jpg2labelled(imgs_path, xmls_path, labelled_path):
# k=0
imgs_list = os.listdir(imgs_path)
xmls_list = os.listdir(xmls_path)
nums = len(imgs_list)
for i in range(nums):
# k+=1
img_path = os.path.join(imgs_path, imgs_list[i])
xml_path = os.path.join(xmls_path, xmls_list[i])
img = cv.imread(img_path)
labelled = img
root = ET.parse(xml_path).getroot()
objects = root.findall('object')
for obj in objects:
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
xmin = int(float(bbox.find('xmin').text.strip()))
ymin = int(float(bbox.find('ymin').text.strip()))
xmax = int(float(bbox.find('xmax').text.strip()))
ymax = int(float(bbox.find('ymax').text.strip()))
labelled = cv.rectangle(labelled, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), (0, 0, 255), 1)
cv.imwrite('%s%s_labelled.jpg' % (labelled_path, imgs_list[i]), labelled)
# if k>=100:
# break
# cv.imshow('labelled', labelled)
# cv.imshow('origin', origin)
# cv.waitKey()
if __name__ == '__main__':
## 原图
# imgs_path='D:\MyselfStudy\yolov5-6.0\data\\test\img'#图片所在路径
# xmls_path ='D:\MyselfStudy\yolov5-6.0\data\\test\\xml'#xml所在路径
# labelled_path='D:\MyselfStudy\yolov5-6.0\data\\test\\anchor_imgs\yuan_img\\'#生成带有矩形框图片所在路径
# xml_jpg2labelled(imgs_path, xmls_path, labelled_path)
原图片生成anchors实验结果

2.图片增强(均在一个脚本内)
在实现图像增强时,将几种图片增强方法都放入了ImgAugemention这个类中,因此要调用相关方法时需先实例化ImgAugemention这个类。
#相关依赖包
import cv2
import math
import numpy as np
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import random
import xml.dom.minidom as DOC
from skimage import exposure
#ImgAugemention类
class ImgAugemention():
def __init__(self, crop_rate=0.5, shift_rate=0.5, change_light_rate=0.5, add_noise_rate=0.5, angle=90):
self.crop_rate = crop_rate
self.shift_rate = shift_rate
self.change_light_rate = change_light_rate
self.add_noise_rate = add_noise_rate
self.angle = angle # rotate_img
2.1图像水平旋转
def rotate_image(self, src, angle, scale=1.):
w = src.shape[1]
h = src.shape[0]
# convet angle into rad
rangle = np.deg2rad(angle) # angle in radians
# calculate new image width and height
nw = (abs(np.sin(rangle)*h) + abs(np.cos(rangle)*w))*scale
nh = (abs(np.cos(rangle)*h) + abs(np.sin(rangle)*w))*scale
# ask OpenCV for the rotation matrix
rot_mat = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((nw*0.5, nh*0.5), angle, scale)
# calculate the move from the old center to the new center combined
# with the rotation
rot_move = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(nw-w)*0.5, (nh-h)*0.5, 0]))
# the move only affects the translation, so update the translation
# part of the transform
rot_mat[0, 2] += rot_move[0]
rot_mat[1, 2] += rot_move[1]
# map
return cv2.warpAffine(
src, rot_mat, (int(math.ceil(nw)), int(math.ceil(nh))),
flags=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
def rotate_xml(self, src, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, angle, scale=1.):
w = src.shape[1]
h = src.shape[0]
rangle = np.deg2rad(angle) # angle in radians
# now calculate new image width and height
# get width and heigh of changed image
nw = (abs(np.sin(rangle)*h) + abs(np.cos(rangle)*w))*scale
nh = (abs(np.cos(rangle)*h) + abs(np.sin(rangle)*w))*scale
# ask OpenCV for the rotation matrix
rot_mat = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((nw*0.5, nh*0.5), angle, scale)
# calculate the move from the old center to the new center combined
# with the rotation
rot_move = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(nw-w)*0.5, (nh-h)*0.5, 0]))
# the move only affects the translation, so update the translation
# part of the transform
rot_mat[0, 2] += rot_move[0]
rot_mat[1, 2] += rot_move[1]
# rot_mat: the final rot matrix
# get the four center of edges in the initial martix,and convert the coord
point1 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(xmin+xmax)/2, ymin, 1]))
point2 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([xmax, (ymin+ymax)/2, 1]))
point3 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(xmin+xmax)/2, ymax, 1]))
point4 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([xmin, (ymin+ymax)/2, 1]))
# concat np.array
concat = np.vstack((point1, point2, point3, point4))
# change type
concat = concat.astype(np.int32)
# print(concat)
rx, ry, rw, rh = cv2.boundingRect(concat)
return rx, ry, rw, rh
def process_img(self, imgs_path, xmls_path, img_save_path, xml_save_path, angle_list):
# assign the rot angles
for angle in angle_list:
for img_name in os.listdir(imgs_path):
# split filename and suffix
n, s = os.path.splitext(img_name)
# for the sake of use yolo model, only process '.jpg'
if s == ".jpg":
img_path = os.path.join(imgs_path, img_name)
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
rotated_img = self.rotate_image(img, angle)
save_name = n + "_" + str(angle) + ".jpg"
# 写入图像
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path + save_name, rotated_img)
# print("log: [%sd] %s is processed." % (angle, img))
xml_url = img_name.split('.')[0] + '.xml'
xml_path = os.path.join(xmls_path, xml_url)
tree = ET.parse(xml_path)
# file_name = tree.find('filename').text # it is origin name
# path = tree.find('path').text # it is origin path
# change name and path
tree.find('filename').text = save_name # change file name to rot degree name
# tree.find('path').text = save_name # change file path to rot degree name
root = tree.getroot()
# if angle in [90, 270], need to swap width and height
if angle in [90, 270]:
d = tree.find('size')
width = int(d.find('width').text)
height = int(d.find('height').text)
# swap width and height
d.find('width').text = str(height)
d.find('height').text = str(width)
for box in root.iter('bndbox'):
xmin = float(box.find('xmin').text)
ymin = float(box.find('ymin').text)
xmax = float(box.find('xmax').text)
ymax = float(box.find('ymax').text)
x, y, w, h = self.rotate_xml(img, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, angle)
# change the coord
box.find('xmin').text = str(x)
box.find('ymin').text = str(y)
box.find('xmax').text = str(x+w)
box.find('ymax').text = str(y+h)
box.set('updated', 'yes')
# write into new xml
tree.write(xml_save_path + n + "_" + str(angle) + ".xml")
2.2增加高斯噪音
# 高斯模糊
def addGaussi(self,img_path,xml_path,save_img,save_xml):
xml_save_path=save_xml+'GaussianBlur\\'
img_save_path=save_img+'GaussianBlur\\'
for imgs in os.listdir(img_path):
img = cv2.imread(img_path+imgs)
size = random.choice((5, 9, 11))
Gau_img=cv2.GaussianBlur(img, ksize=(size, size), sigmaX=0, sigmaY=0)
# 写入图像
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path + "Gau_img"+imgs, Gau_img)
xml=xml_path+imgs[:-4]+ ".xml"
tree = ET.parse(xml)
tree.write(xml_save_path + "Gau_img"+imgs[:-4]+ ".xml")
2.4改变亮度
# 调整亮度
def changeLight(self, img_path,xml_path,save_img,save_xml):
xml_save_path = save_xml +'changeLight'
img_save_path = save_img +'changeLight'
for imgs in os.listdir(img_path):
flag = random.uniform(0.6, 1.3) # flag>1为调暗,小于1为调亮
img = cv2.imread(img_path+imgs)
light_img=exposure.adjust_gamma(img, flag)
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path +'\\'+ "light_img" + imgs, light_img)
xml = xml_path + imgs[:-4] + ".xml"
tree = ET.parse(xml)
tree.write(xml_save_path + '\\'+"light_img" + imgs[:-4] + ".xml")
2.5平移和裁剪代码
以下时实现平移和裁剪所需的函数,不在ImgAugemention类中,不要将以下这段代码放到ImgAugemention类中。
# 从xml文件中提取bounding box信息, 格式为[[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name]]
def parse_xml(xml_path):
'''
输入:
xml_path: xml的文件路径
输出:
从xml文件中提取bounding box信息, 格式为[[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name]]
'''
tree = ET.parse(xml_path)
root = tree.getroot()
objs = root.findall('object')
coords = list()
for ix, obj in enumerate(objs):
name = obj.find('name').text
box = obj.find('bndbox')
x_min = int(box[0].text)
y_min = int(box[1].text)
x_max = int(box[2].text)
y_max = int(box[3].text)
coords.append([x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name])
return coords
# 将bounding box信息写入xml文件中, bouding box格式为[[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name]]
def generate_xml(img_name, coords, img_size, out_root_path):
'''
输入:
img_name:图片名称,如a.jpg
coords:坐标list,格式为[[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name]],name为概况的标注
img_size:图像的大小,格式为[h,w,c]
out_root_path: xml文件输出的根路径
'''
doc = DOC.Document() # 创建DOM文档对象
annotation = doc.createElement('annotation')
doc.appendChild(annotation)
title = doc.createElement('folder')
title_text = doc.createTextNode('VOC2007')
title.appendChild(title_text)
annotation.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('filename')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(img_name)
title.appendChild(title_text)
annotation.appendChild(title)
source = doc.createElement('source')
annotation.appendChild(source)
title = doc.createElement('database')
title_text = doc.createTextNode('The VOC2007 Database')
title.appendChild(title_text)
source.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('annotation')
title_text = doc.createTextNode('PASCAL VOC2007')
title.appendChild(title_text)
source.appendChild(title)
size = doc.createElement('size')
annotation.appendChild(size)
title = doc.createElement('width')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(img_size[1]))
title.appendChild(title_text)
size.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('height')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(img_size[0]))
title.appendChild(title_text)
size.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('depth')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(img_size[2]))
title.appendChild(title_text)
size.appendChild(title)
for coord in coords:
object = doc.createElement('object')
annotation.appendChild(object)
title = doc.createElement('name')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(coord[4])
title.appendChild(title_text)
object.appendChild(title)
pose = doc.createElement('pose')
pose.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('Unspecified'))
object.appendChild(pose)
truncated = doc.createElement('truncated')
truncated.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('1'))
object.appendChild(truncated)
difficult = doc.createElement('difficult')
difficult.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('0'))
object.appendChild(difficult)
bndbox = doc.createElement('bndbox')
object.appendChild(bndbox)
title = doc.createElement('xmin')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(int(float(coord[0]))))
title.appendChild(title_text)
bndbox.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('ymin')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(int(float(coord[1]))))
title.appendChild(title_text)
bndbox.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('xmax')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(int(float(coord[2]))))
title.appendChild(title_text)
bndbox.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('ymax')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(int(float(coord[3]))))
title.appendChild(title_text)
bndbox.appendChild(title)
# 将DOM对象doc写入文件
f = open(os.path.join(out_root_path, "new_" + "_" + img_name[:-4] + '.xml'), 'w')
f.write(doc.toprettyxml(indent=''))
f.close()
平移和裁剪代码
# 平移
def shift_pic_bboxes(self,xml_path,img_path,img_save_path,save_path_xml):
img_save_path=img_save_path+'shift'
save_path_xml=save_path_xml+'shift'
for xmls in os.listdir(xml_path):
x=xml_path+xmls
coords = parse_xml(x)#读xml文件
img = cv2.imread(img_path+xmls[:-4] + ".jpg")
names = [coord[4] for coord in coords]
bboxes = [coord[:4] for coord in coords]
'''
平移后的图片要包含所有的框
输入:
img:图像array
bboxes:该图像包含的所有boundingboxs,一个list,每个元素为[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max,label],要确保是数值
输出:
shift_img:平移后的图像array
shift_bboxes:平移后的bounding box的坐标list
'''
# ---------------------- 平移图像 ----------------------
w = img.shape[1]
h = img.shape[0]
x_min = w # 裁剪后的包含所有目标框的最小的框
x_max = 0
y_min = h
y_max = 0
for bbox in bboxes:
x_min = min(x_min, bbox[0])
y_min = min(y_min, bbox[1])
x_max = max(x_max, bbox[2])
y_max = max(y_max, bbox[3])
d_to_left = x_min # 包含所有目标框的最大左移动距离
d_to_right = w - x_max # 包含所有目标框的最大右移动距离
d_to_top = y_min # 包含所有目标框的最大上移动距离
d_to_bottom = h - y_max # 包含所有目标框的最大下移动距离
x = random.uniform(-(d_to_left - 1) / 3, (d_to_right - 1) / 3)
y = random.uniform(-(d_to_top - 1) / 3, (d_to_bottom - 1) / 3)
M = np.float32([[1, 0, x], [0, 1, y]]) # x为向左或右移动的像素值,正为向右负为向左; y为向上或者向下移动的像素值,正为向下负为向上
shift_img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (img.shape[1], img.shape[0]))
# ---------------------- 平移boundingbox ----------------------
shift_bboxes = list()
for bbox in bboxes:
i=0
shift_bboxes.append([bbox[0] + x, bbox[1] + y, bbox[2] + x, bbox[3] + y,names[i]])
i+=1
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path + '\\' + "shift_img" +xmls[:-4] + ".jpg", shift_img)
file=xmls[:-4] + ".jpg"
auged_img=shift_img
auged_bboxes = shift_bboxes
generate_xml(file, auged_bboxes, list(auged_img.shape), save_path_xml)
# 裁剪
def crop_img_bboxes(self,xml_path,img_path,img_save_path,save_path_xml):
'''
裁剪后的图片要包含所有的框
输入:
img:图像array
bboxes:该图像包含的所有boundingboxs,一个list,每个元素为[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max,label],要确保是数值
输出:
crop_img:裁剪后的图像array
crop_bboxes:裁剪后的bounding box的坐标list
'''
# ---------------------- 裁剪图像 ----------------------
img_save_path=img_save_path+'crop'
save_path_xml=save_path_xml+'crop'
for imgs in os.listdir(img_path):
imgPath=img_path+imgs
img=cv2.imread(img_path+imgs)
w = img.shape[1]
h = img.shape[0]
x_min = w # 裁剪后的包含所有目标框的最小的框
x_max = 0
y_min = h
y_max = 0
xmlPath=xml_path+imgs[:-4] + ".xml"
coords = parse_xml(xmlPath) # 读xml文件
names = [coord[4] for coord in coords]
bboxes = [coord[:4] for coord in coords]
for bbox in bboxes:
x_min = min(x_min, bbox[0])
y_min = min(y_min, bbox[1])
x_max = max(x_max, bbox[2])
y_max = max(y_max, bbox[3])
d_to_left = x_min # 包含所有目标框的最小框到左边的距离
d_to_right = w - x_max # 包含所有目标框的最小框到右边的距离
d_to_top = y_min # 包含所有目标框的最小框到顶端的距离
d_to_bottom = h - y_max # 包含所有目标框的最小框到底部的距离
# 随机扩展这个最小框
crop_x_min = int(x_min - random.uniform(0, d_to_left))
crop_y_min = int(y_min - random.uniform(0, d_to_top))
crop_x_max = int(x_max + random.uniform(0, d_to_right))
crop_y_max = int(y_max + random.uniform(0, d_to_bottom))
# 确保不要越界
crop_x_min = max(0, crop_x_min)
crop_y_min = max(0, crop_y_min)
crop_x_max = min(w, crop_x_max)
crop_y_max = min(h, crop_y_max)
crop_img = img[crop_y_min:crop_y_max, crop_x_min:crop_x_max]
# ---------------------- 裁剪boundingbox ----------------------
# 裁剪后的boundingbox坐标计算
crop_bboxes = list()
for bbox in bboxes:
i=0
crop_bboxes.append([bbox[0] - crop_x_min, bbox[1] - crop_y_min, bbox[2] - crop_x_min, bbox[3] - crop_y_min,names[i]])
i+=1
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path + '\\' + "crop_img" + imgs, crop_img)
auged_img = crop_img
auged_bboxes = crop_bboxes
generate_xml(imgs, auged_bboxes, list(auged_img.shape), save_path_xml)
4.代码运行
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_aug = ImgAugemention()
#原图像路径
imgs_path='D:\MyselfStudy\yolov5-6.0\data\\test\img\\'
##原xml文件路径
xmls_path='D:\MyselfStudy\yolov5-6.0\data\\test\\xml\\'
#新生成图像存储路径
save_xml='D:\MyselfStudy\yolov5-6.0\data\\test\\new_xml\\'
##新生成xml文件存储路径
save_img='D:\MyselfStudy\yolov5-6.0\data\\test\\new_img\\'
#要实现相应图像增强方式,去掉注释即可
#旋转
# angle_list = [60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 270]
# img_aug.process_img(imgs_path, xmls_path, save_img, save_xml, angle_list)
#高斯噪音
# img_aug.addGaussi(imgs_path, xmls_path, save_img, save_xml)
#改变亮度
# img_aug.changeLight(imgs_path, xmls_path, save_img, save_xml)
#平移
# img_aug.shift_pic_bboxes(xmls_path, imgs_path, save_img, save_xml)
#裁剪
img_aug.crop_img_bboxes(xmls_path, imgs_path, save_img, save_xml)
5.完整代码
路径改为自己的即可
import cv2
import math
import numpy as np
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import random
import xml.dom.minidom as DOC
from skimage import exposure
# 从xml文件中提取bounding box信息, 格式为[[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name]]
def parse_xml(xml_path):
'''
输入:
xml_path: xml的文件路径
输出:
从xml文件中提取bounding box信息, 格式为[[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name]]
'''
tree = ET.parse(xml_path)
root = tree.getroot()
objs = root.findall('object')
coords = list()
for ix, obj in enumerate(objs):
name = obj.find('name').text
box = obj.find('bndbox')
x_min = int(box[0].text)
y_min = int(box[1].text)
x_max = int(box[2].text)
y_max = int(box[3].text)
coords.append([x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name])
return coords
# 将bounding box信息写入xml文件中, bouding box格式为[[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name]]
def generate_xml(img_name, coords, img_size, out_root_path):
'''
输入:
img_name:图片名称,如a.jpg
coords:坐标list,格式为[[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, name]],name为概况的标注
img_size:图像的大小,格式为[h,w,c]
out_root_path: xml文件输出的根路径
'''
doc = DOC.Document() # 创建DOM文档对象
annotation = doc.createElement('annotation')
doc.appendChild(annotation)
title = doc.createElement('folder')
title_text = doc.createTextNode('VOC2007')
title.appendChild(title_text)
annotation.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('filename')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(img_name)
title.appendChild(title_text)
annotation.appendChild(title)
source = doc.createElement('source')
annotation.appendChild(source)
title = doc.createElement('database')
title_text = doc.createTextNode('The VOC2007 Database')
title.appendChild(title_text)
source.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('annotation')
title_text = doc.createTextNode('PASCAL VOC2007')
title.appendChild(title_text)
source.appendChild(title)
size = doc.createElement('size')
annotation.appendChild(size)
title = doc.createElement('width')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(img_size[1]))
title.appendChild(title_text)
size.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('height')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(img_size[0]))
title.appendChild(title_text)
size.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('depth')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(img_size[2]))
title.appendChild(title_text)
size.appendChild(title)
for coord in coords:
object = doc.createElement('object')
annotation.appendChild(object)
title = doc.createElement('name')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(coord[4])
title.appendChild(title_text)
object.appendChild(title)
pose = doc.createElement('pose')
pose.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('Unspecified'))
object.appendChild(pose)
truncated = doc.createElement('truncated')
truncated.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('1'))
object.appendChild(truncated)
difficult = doc.createElement('difficult')
difficult.appendChild(doc.createTextNode('0'))
object.appendChild(difficult)
bndbox = doc.createElement('bndbox')
object.appendChild(bndbox)
title = doc.createElement('xmin')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(int(float(coord[0]))))
title.appendChild(title_text)
bndbox.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('ymin')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(int(float(coord[1]))))
title.appendChild(title_text)
bndbox.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('xmax')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(int(float(coord[2]))))
title.appendChild(title_text)
bndbox.appendChild(title)
title = doc.createElement('ymax')
title_text = doc.createTextNode(str(int(float(coord[3]))))
title.appendChild(title_text)
bndbox.appendChild(title)
# 将DOM对象doc写入文件
f = open(os.path.join(out_root_path, "new_" + "_" + img_name[:-4] + '.xml'), 'w')
f.write(doc.toprettyxml(indent=''))
f.close()
class ImgAugemention():
def __init__(self, crop_rate=0.5, shift_rate=0.5, change_light_rate=0.5, add_noise_rate=0.5,
cutout_rate=0.5, cut_out_length=50, cut_out_holes=1, cut_out_threshold=0.5, angle=90):
self.crop_rate = crop_rate
self.shift_rate = shift_rate
self.change_light_rate = change_light_rate
# self.cutout_rate = cutout_rate
self.add_noise_rate = add_noise_rate
# self.cut_out_length = cut_out_length
# self.cut_out_holes = cut_out_holes
# self.cut_out_threshold = cut_out_threshold
self.angle = angle # rotate_img
# rotate_img
def rotate_image(self, src, angle, scale=1.):
w = src.shape[1]
h = src.shape[0]
# convet angle into rad
rangle = np.deg2rad(angle) # angle in radians
# calculate new image width and height
nw = (abs(np.sin(rangle)*h) + abs(np.cos(rangle)*w))*scale
nh = (abs(np.cos(rangle)*h) + abs(np.sin(rangle)*w))*scale
# ask OpenCV for the rotation matrix
rot_mat = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((nw*0.5, nh*0.5), angle, scale)
# calculate the move from the old center to the new center combined
# with the rotation
rot_move = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(nw-w)*0.5, (nh-h)*0.5, 0]))
# the move only affects the translation, so update the translation
# part of the transform
rot_mat[0, 2] += rot_move[0]
rot_mat[1, 2] += rot_move[1]
# map
return cv2.warpAffine(
src, rot_mat, (int(math.ceil(nw)), int(math.ceil(nh))),
flags=cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
def rotate_xml(self, src, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, angle, scale=1.):
w = src.shape[1]
h = src.shape[0]
rangle = np.deg2rad(angle) # angle in radians
# now calculate new image width and height
# get width and heigh of changed image
nw = (abs(np.sin(rangle)*h) + abs(np.cos(rangle)*w))*scale
nh = (abs(np.cos(rangle)*h) + abs(np.sin(rangle)*w))*scale
# ask OpenCV for the rotation matrix
rot_mat = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((nw*0.5, nh*0.5), angle, scale)
# calculate the move from the old center to the new center combined
# with the rotation
rot_move = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(nw-w)*0.5, (nh-h)*0.5, 0]))
# the move only affects the translation, so update the translation
# part of the transform
rot_mat[0, 2] += rot_move[0]
rot_mat[1, 2] += rot_move[1]
# rot_mat: the final rot matrix
# get the four center of edges in the initial martix,and convert the coord
point1 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(xmin+xmax)/2, ymin, 1]))
point2 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([xmax, (ymin+ymax)/2, 1]))
point3 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([(xmin+xmax)/2, ymax, 1]))
point4 = np.dot(rot_mat, np.array([xmin, (ymin+ymax)/2, 1]))
# concat np.array
concat = np.vstack((point1, point2, point3, point4))
# change type
concat = concat.astype(np.int32)
# print(concat)
rx, ry, rw, rh = cv2.boundingRect(concat)
return rx, ry, rw, rh
def process_img(self, imgs_path, xmls_path, img_save_path, xml_save_path, angle_list):
# xml_save_path = xml_save_path + 'rotate\\'
# img_save_path = img_save_path + 'rotate\\'
# assign the rot angles
for angle in angle_list:
for img_name in os.listdir(imgs_path):
# split filename and suffix
n, s = os.path.splitext(img_name)
# for the sake of use yolo model, only process '.jpg'
if s == ".jpg":
img_path = os.path.join(imgs_path, img_name)
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
rotated_img = self.rotate_image(img, angle)
save_name = n + "_" + str(angle) + ".jpg"
# 写入图像
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path +'/'+ save_name, rotated_img)
# print("log: [%sd] %s is processed." % (angle, img))
xml_url = img_name.split('.')[0] + '.xml'
xml_path = os.path.join(xmls_path, xml_url)
tree = ET.parse(xml_path)
# file_name = tree.find('filename').text # it is origin name
# path = tree.find('path').text # it is origin path
# change name and path
tree.find('filename').text = save_name # change file name to rot degree name
# tree.find('path').text = save_name # change file path to rot degree name
root = tree.getroot()
# if angle in [90, 270], need to swap width and height
if angle in [90, 270]:
d = tree.find('size')
width = int(d.find('width').text)
height = int(d.find('height').text)
# swap width and height
d.find('width').text = str(height)
d.find('height').text = str(width)
for box in root.iter('bndbox'):
xmin = float(box.find('xmin').text)
ymin = float(box.find('ymin').text)
xmax = float(box.find('xmax').text)
ymax = float(box.find('ymax').text)
x, y, w, h = self.rotate_xml(img, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, angle)
# change the coord
box.find('xmin').text = str(x)
box.find('ymin').text = str(y)
box.find('xmax').text = str(x+w)
box.find('ymax').text = str(y+h)
box.set('updated', 'yes')
# write into new xml
tree.write(xml_save_path +'/'+ n + "_" + str(angle) + ".xml")
# print("[%s] %s is processed." % (angle, img_name))
# 高斯模糊
def addGaussi(self,img_path,xml_path,img_save_path,xml_save_path):
# xml_save_path=xml_save_path+'GaussianBlur\\'
# img_save_path=img_save_path+'GaussianBlur\\'
for imgs in os.listdir(img_path):
img = cv2.imread(img_path+'/'+ imgs)
size = random.choice((5, 9, 11))
Gau_img=cv2.GaussianBlur(img, ksize=(size, size), sigmaX=0, sigmaY=0)
# 写入图像
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path +'/'+ "Gau_img"+imgs, Gau_img)
xml=xml_path+'/'+imgs[:-4]+ ".xml"
tree = ET.parse(xml)
tree.write(xml_save_path + "Gau_img"+imgs[:-4]+ ".xml")
# 调整亮度
def changeLight(self, img_path,xml_path,img_save_path,xml_save_path):
# xml_save_path = xml_save_path +'changeLight'
# img_save_path = img_save_path +'changeLight'
for imgs in os.listdir(img_path):
flag = random.uniform(0.6, 1.3) # flag>1为调暗,小于1为调亮
img = cv2.imread(img_path+'/'+imgs)
light_img=exposure.adjust_gamma(img, flag)
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path +'/'+"light_img" + imgs, light_img)
xml = xml_path+'/' + imgs[:-4] + ".xml"
tree = ET.parse(xml)
tree.write(xml_save_path +'/'+"light_img" + imgs[:-4] + ".xml")
# 平移
def shift_pic_bboxes(self,xml_path,img_path,img_save_path,save_path_xml):
# img_save_path=img_save_path+'shift'
# save_path_xml=save_path_xml+'shift'
for xmls in os.listdir(xml_path):
x=xml_path+'/'+xmls
coords = parse_xml(x)#读xml文件
img = cv2.imread(img_path+'/'+xmls[:-4] + ".jpg")
names = [coord[4] for coord in coords]
bboxes = [coord[:4] for coord in coords]
'''
平移后的图片要包含所有的框
输入:
img:图像array
bboxes:该图像包含的所有boundingboxs,一个list,每个元素为[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max,label],要确保是数值
输出:
shift_img:平移后的图像array
shift_bboxes:平移后的bounding box的坐标list
'''
# ---------------------- 平移图像 ----------------------
w = img.shape[1]
h = img.shape[0]
x_min = w # 裁剪后的包含所有目标框的最小的框
x_max = 0
y_min = h
y_max = 0
for bbox in bboxes:
x_min = min(x_min, bbox[0])
y_min = min(y_min, bbox[1])
x_max = max(x_max, bbox[2])
y_max = max(y_max, bbox[3])
d_to_left = x_min # 包含所有目标框的最大左移动距离
d_to_right = w - x_max # 包含所有目标框的最大右移动距离
d_to_top = y_min # 包含所有目标框的最大上移动距离
d_to_bottom = h - y_max # 包含所有目标框的最大下移动距离
x = random.uniform(-(d_to_left - 1) / 3, (d_to_right - 1) / 3)
y = random.uniform(-(d_to_top - 1) / 3, (d_to_bottom - 1) / 3)
M = np.float32([[1, 0, x], [0, 1, y]]) # x为向左或右移动的像素值,正为向右负为向左; y为向上或者向下移动的像素值,正为向下负为向上
shift_img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (img.shape[1], img.shape[0]))
# ---------------------- 平移boundingbox ----------------------
shift_bboxes = list()
for bbox in bboxes:
i=0
shift_bboxes.append([bbox[0] + x, bbox[1] + y, bbox[2] + x, bbox[3] + y,names[i]])
i+=1
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path +'/'+ "shift_img" +xmls[:-4] + ".jpg", shift_img)
file=xmls[:-4] + ".jpg"
auged_img=shift_img
auged_bboxes = shift_bboxes
generate_xml(file, auged_bboxes, list(auged_img.shape), save_path_xml)
# 裁剪
def crop_img_bboxes(self,xml_path,img_path,img_save_path,save_path_xml):
'''
裁剪后的图片要包含所有的框
输入:
img:图像array
bboxes:该图像包含的所有boundingboxs,一个list,每个元素为[x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max,label],要确保是数值
输出:
crop_img:裁剪后的图像array
crop_bboxes:裁剪后的bounding box的坐标list
'''
# ---------------------- 裁剪图像 ----------------------
# img_save_path=img_save_path+'crop'
# save_path_xml=save_path_xml+'crop'
for imgs in os.listdir(img_path):
imgPath=img_path+imgs
img=cv2.imread(img_path+'/'+imgs)
w = img.shape[1]
h = img.shape[0]
x_min = w # 裁剪后的包含所有目标框的最小的框
x_max = 0
y_min = h
y_max = 0
xmlPath=xml_path+'/'+imgs[:-4] + ".xml"
coords = parse_xml(xmlPath) # 读xml文件
names = [coord[4] for coord in coords]
bboxes = [coord[:4] for coord in coords]
for bbox in bboxes:
x_min = min(x_min, bbox[0])
y_min = min(y_min, bbox[1])
x_max = max(x_max, bbox[2])
y_max = max(y_max, bbox[3])
d_to_left = x_min # 包含所有目标框的最小框到左边的距离
d_to_right = w - x_max # 包含所有目标框的最小框到右边的距离
d_to_top = y_min # 包含所有目标框的最小框到顶端的距离
d_to_bottom = h - y_max # 包含所有目标框的最小框到底部的距离
# 随机扩展这个最小框
crop_x_min = int(x_min - random.uniform(0, d_to_left))
crop_y_min = int(y_min - random.uniform(0, d_to_top))
crop_x_max = int(x_max + random.uniform(0, d_to_right))
crop_y_max = int(y_max + random.uniform(0, d_to_bottom))
# 确保不要越界
crop_x_min = max(0, crop_x_min)
crop_y_min = max(0, crop_y_min)
crop_x_max = min(w, crop_x_max)
crop_y_max = min(h, crop_y_max)
crop_img = img[crop_y_min:crop_y_max, crop_x_min:crop_x_max]
# ---------------------- 裁剪boundingbox ----------------------
# 裁剪后的boundingbox坐标计算
crop_bboxes = list()
for bbox in bboxes:
i=0
crop_bboxes.append([bbox[0] - crop_x_min, bbox[1] - crop_y_min, bbox[2] - crop_x_min, bbox[3] - crop_y_min,names[i]])
i+=1
cv2.imwrite(img_save_path +'/'+ "crop_img" + imgs, crop_img)
auged_img = crop_img
auged_bboxes = crop_bboxes
generate_xml(imgs, auged_bboxes, list(auged_img.shape), save_path_xml)
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_aug = ImgAugemention()
#路径修改为自己的
imgs_path='./weed_cron_data/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/JPEGImages'
xmls_path='./weed_cron_data/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations'
save_xml='./new/new_xmls'
save_img='./new/new_imgs'
print("start rorate!!!")
angle_list = [60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 270]
img_aug.process_img(imgs_path, xmls_path, save_img, save_xml, angle_list)
print("start addGaussi!!!")
img_aug.addGaussi(imgs_path, xmls_path, save_img, save_xml)
print("start changeLight!!!")
img_aug.changeLight(imgs_path, xmls_path, save_img, save_xml)
print("start shift_pic_bboxes!!!")
img_aug.shift_pic_bboxes(xmls_path, imgs_path, save_img, save_xml)
print("start crop_img_bboxes!!!")
img_aug.crop_img_bboxes(xmls_path, imgs_path, save_img, save_xml)
6.结果展示
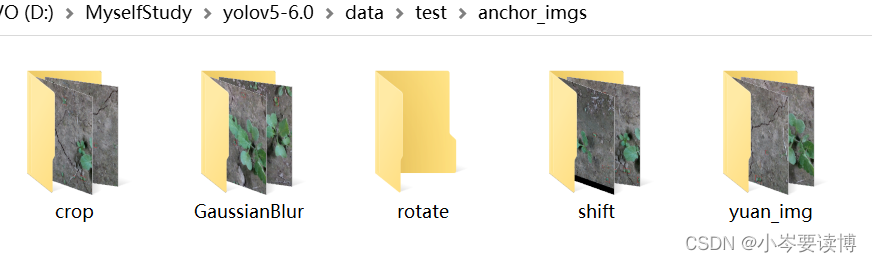
- anchor_imgs内记录了各种生成方法的anchors图片
以shift(平移)为例子(原图和平移后的带anchors图片)
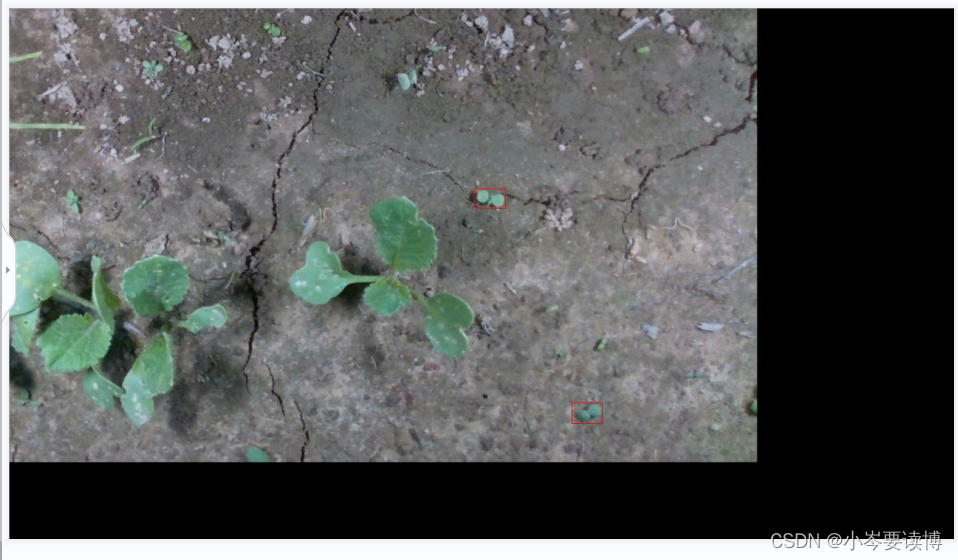
 很显然,图像增强后的anchor准确,经得起验证。
很显然,图像增强后的anchor准确,经得起验证。
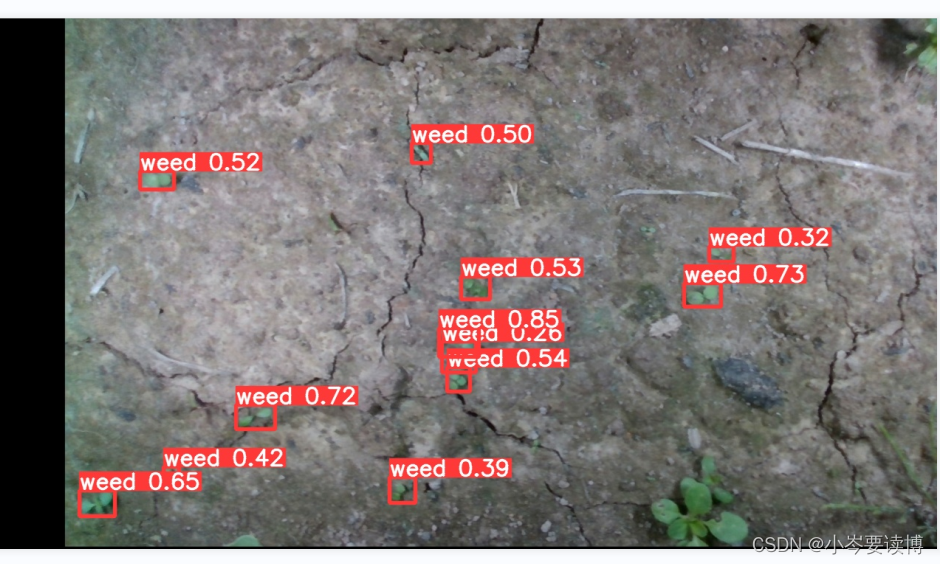
最后附上近期实现yolov5模型实现的杂草检测结果(小岑还要继续努力)。

版权归原作者 小岑要努力 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。