本文介绍了傅里叶变换处理,离散余弦变换,灰度增强,图像翻转,线性变换,对数变换,直方图均衡化,直方图规定化,均值和中值滤波和低通滤波
傅里叶变换处理图像
代码:
I = imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\3.png'); %读入图像
imshow(I); %显示图像
I1 = fft2(I); %计算2维傅里叶变换
I2 = fftshift(I1); %直流分量移至中心
figure;imshow(log(abs(I2)+1),[0,10]); %对数变换
结果:
测试不同图像结果:
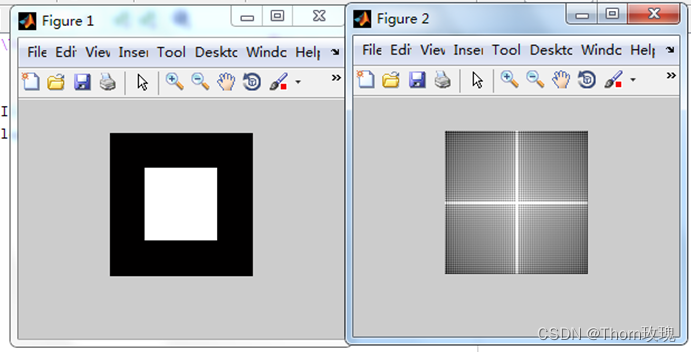
离散余弦变换
代码:
I = imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\3.png') %读入图像
I1 = dct2(I) %做dct变换
figure;imshow(I) %显示原图像
figure;imshow(log(abs(I1)),[0,5]); %显示dct变换结果
结果:
不同图像结果:


灰度增强
程序
x = imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\4.png')
subplot(221);
imshow(x);
subplot(222);
imshow(x.*3);
subplot(223);
imshow(x.*4.5);
subplot(224);
imshow(x.*5);
结果:
不同图像结果:
图像反转
程序:
x = imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\lena.png')
subplot(121);
imshow(x);
subplot(122);
imshow(255-x);
结果: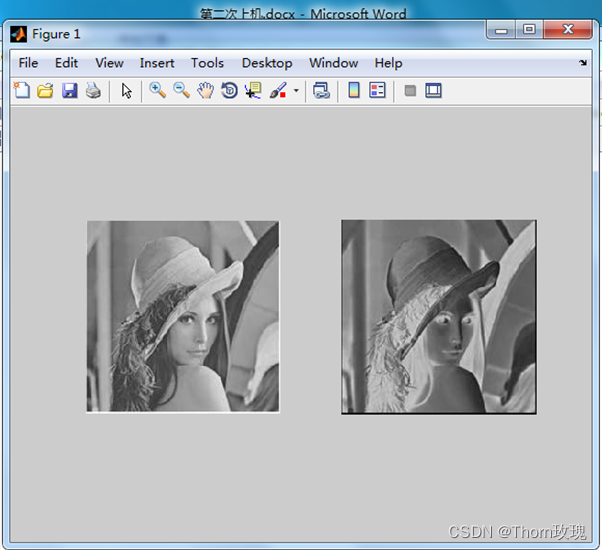
不同图像结果:


线性变换
程序:
x = imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\hjh.jpg');
subplot(131);
imshow(x);
subplot(132);
imhist(x);
y = imadjust(x,[0.2,0.8],[0,1]);
subplot(133);
imshow(y);
结果:

对数变换
程序:
x=imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\men.bmp');
g=fft2(double(x));
fg=abs(fftshift(g)); %幅度谱
subplot(121);
imshow(fg,[]);
title('傅里叶谱');
subplot(122);
imshow(log(fg+1),[]);
title('傅里叶频谱对数变换结果');
结果:
直方图均衡化
程序:
I=imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\men.bmp');
subplot(221);
imshow(I);
subplot(222);
imhist(I); %显示图像直方图
[J,T]=histeq(I,64); %图像灰度扩展到0-255,但是只有64个灰度级
subplot(223);
imshow(J);
subplot(224);
imhist(J);
结果:
直方图规定化
程序:
clc;clear;
h=imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\men.bmp');
subplot(321);imshow(h);
subplot(322);imhist(h);
g=histeq(h,256);
subplot(323);imshow(g);
subplot(324);imhist(g,256);
r=[0.05,zeros(1,9),0.05,zeros(1,9),0.05,zeros(1,9),0.05,zeros(1,9),0.05,zeros(1,9),0.05,zeros(1,9),0.05,zeros(1,39),0.05,zeros(1,19),0.05,zeros(1,19),0.05,zeros(1,19),ones(1,80).*0.0045,ones(1,66).*0.0088];
k=histeq(h,r);
subplot(325);
imshow(k);
subplot(326);
imhist(k);
结果:
均值和中值滤波
程序:
clc;clear;close
I=imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\lena.png');
% I=I(:,:,2); %将lena图从3维转化为2维
subplot(221);
imshow(I,[]);
f=imnoise(I,'salt & pepper',0.04); %加噪(此处为椒盐噪声)
subplot(222);
imshow(f);
H0=ones(3,3)/9; %3*3邻域模板
g=imfilter(f,H0); %均值滤波
subplot(223);
imshow(g,[]);
g2=medfilt2(f,[3,3]); %中值滤波
subplot(224);
imshow(g2)
结果:

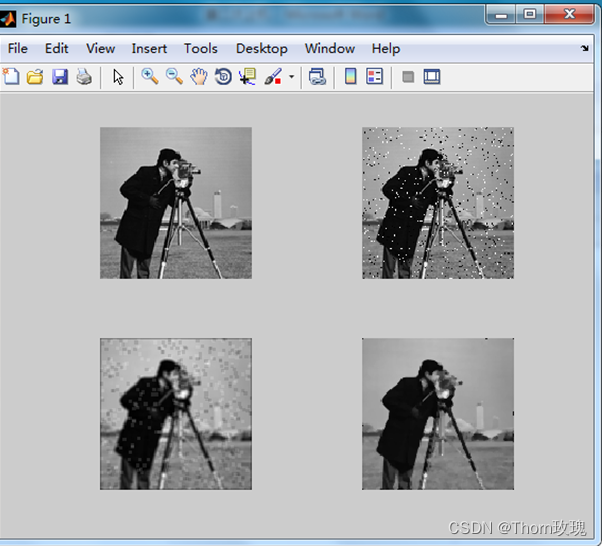
低通滤波
程序:
clc;clear;close;
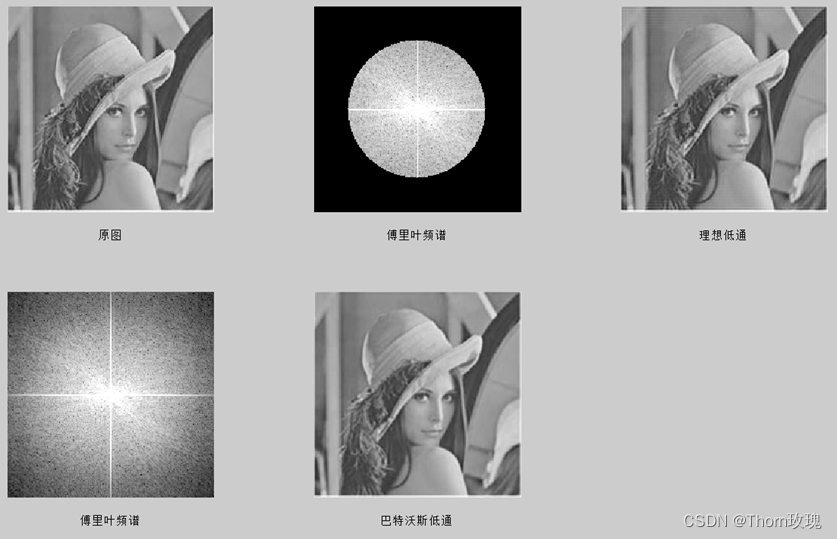
%理想低通滤波
I1=imread('C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\test\图片\lena.png');
I1=I1(:,:,2); %将lena三维转二维
subplot(231);
imshow(I1);
xlabel('原图');
f=double(I1); %matlab不支持图像的无符号整形的计算
g=fft2(f); %傅里叶变换
g=fftshift(g); %平移至中心
[N1,N2]=size(g); %取得对象g的行数和列数
d0=68; %改变d0的值,可以观察到滤波的不同效果
n1=fix(N1/2); %fix为取整,取接近0的整数
n2=fix(N2/2);
% 理想滤波器处理傅里叶图
for i=1:N1
for j=1:N2
d=sqrt((i-n1)^2+(j-n2)^2);
if d<=d0
h=1;
else
h=0;
end %计算理想低通滤波响应函数
result(i,j)=h*g(i,j);
end
end
subplot(232);
imshow(log(abs(result)+1),[0,10]); %显示傅里叶图对应的滤波器通过部分
xlabel('傅里叶频谱');
result=ifftshift(result);
x2=ifft2(result);
x3=uint8(real(x2)); %real为取实部
subplot(233);
imshow(x3);
xlabel('理想低通');
% 2阶巴特沃斯滤波器处理傅里叶图
n=2; %n为巴特沃斯阶数,此处取2阶
for i=1:N1
for j=1:N2
d=sqrt((i-n1)^2+(j-n2)^2);
h=1/(1+(d/d0)^(2*n));
result(i,j)=h*g(i,j);
end
end
subplot(234);
imshow(log(abs(result)+1),[0,10]); %显示傅里叶图对应的滤波器通过部分
xlabel('傅里叶频谱');
result=ifftshift(result);
x2=ifft2(result);
x3=uint8(real(x2)); %real为取实部
subplot(235);
imshow(x3);
xlabel('巴特沃斯低通');
结果:

版权归原作者 Thorn玫瑰 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。