基于yolo目标检测算法实现的车前道路中的车辆和行人检测,并且可以估测出目标与本车之间的距离
一、视频展示
yolo车距1
二、单目测距原理
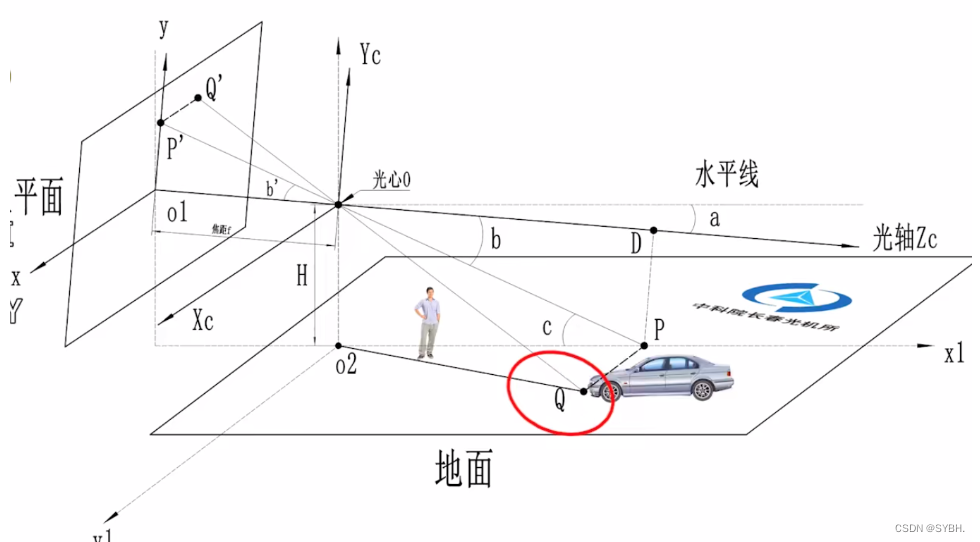

图中有一个车辆,且车辆在地面上,其接地点Q必定在地面上。那么Q点的深度便可以求解出来。具体求解步骤懒得打公式了,就截图了。在单目测距过程中,实际物体上的Q点在成像的图片上对应Q’点,Q’点距离o1点沿y轴的距离为o1p’。这个距离o1p’除以y轴像素焦距fy (单位为pixel) ,再求arctan即可得到角度b’。然后按图中步骤很容易理解了。
三、准备工作
参考我这篇文章:AI识别教程 yolov5 (穿越火线,csgo等FPS游戏识别)_SYBH.的博客-CSDN博客_yolo对游戏画面实时检测
第一步:将整个代码从github上下载下来,
网址:GitHub - ultralytics/yolov5: YOLOv5 🚀 in PyTorch > ONNX > CoreML > TFLite
也可以直接到GitHub上搜yolov5
主要是安装版本与配置声明中所需在库。
matplotlib>=3.2.2
numpy>=1.18.5
opencv-python>=4.1.2
Pillow
PyYAML>=5.3.1
scipy>=1.4.1
torch>=1.7.0
torchvision>=0.8.1
tqdm>=4.41.0
tensorboard>=2.4.1
seaborn>=0.11.0
pandas
pycocotools>=2.0 # COCO mAP
albumentations>=1.0.2
(1)安装pytorch(建议安装gpu版本cpu版本太慢)
这些库中可能就pytorch比较难安装,其他库用pip install 基本能实现。
可直接在Anaconda Prompt里输入:
pip install torch==1.7.0+cu101 torchvision==0.8.1+cu101 torchaudio===0.7.0 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
1.运行检测
下载完yolov5后,运行detect,可以帮助我们检查上面的环境是不是安装成功。
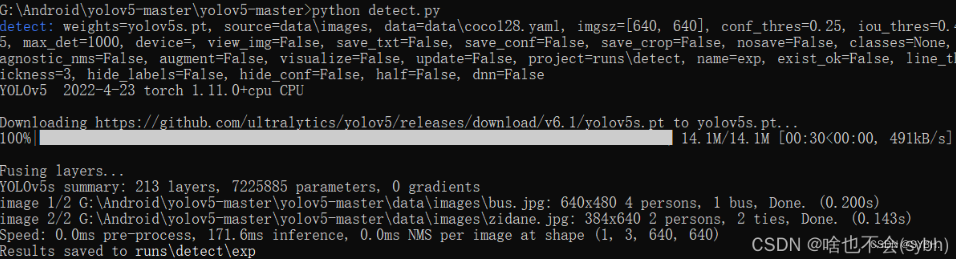
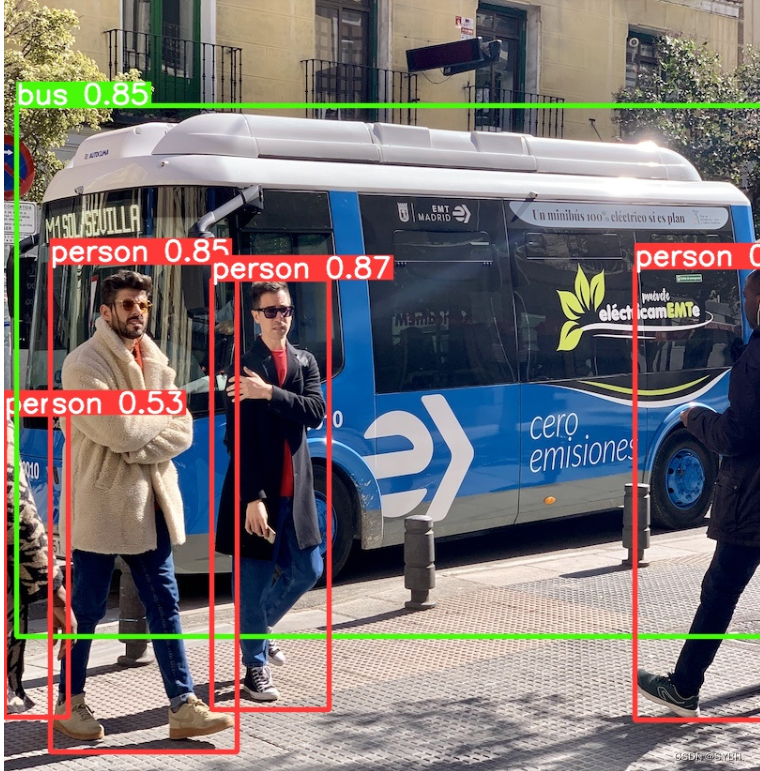
如果运行不报错,我们会在runs//detect//exp 文件夹下看到两张已经预测出的照片。
四、如果用双目检测
要想将双目测距的代码加入到YOLO v5中,就需要将YOLO v5检测目标的代码看懂,这部分学起来对我来说是比较吃力的。
我这里的结合用的比较简单,就是把双目测距的代码加入到了yolov5的
detect.py
中。具体加在了打印目标框的位置,如下代码所示。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import argparse
import time
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
from numpy import random
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.datasets import LoadStreams, LoadImages
from utils.general import check_img_size, check_requirements, check_imshow, non_max_suppression, apply_classifier, \
scale_coords, xyxy2xywh, strip_optimizer, set_logging, increment_path
from utils.plots import plot_one_box
from utils.torch_utils import select_device, load_classifier, time_synchronized
from stereo.dianyuntu_yolo import preprocess, undistortion, getRectifyTransform, draw_line, rectifyImage,\
stereoMatchSGBM, hw3ToN3, DepthColor2Cloud, view_cloud
from stereo import stereoconfig_040_2
num = 210 #207 209 210 211
def detect(save_img=False):
num = 210
source, weights, view_img, save_txt, imgsz = opt.source, opt.weights, opt.view_img, opt.save_txt, opt.img_size
webcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith('.txt') or source.lower().startswith(
('rtsp://', 'rtmp://', 'http://') )
# Directories
save_dir = Path( increment_path(Path(opt.project) / opt.name, exist_ok=opt.exist_ok) ) # increment run
(save_dir / 'labels' if save_txt else save_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir
# Initialize
set_logging()
device = select_device(opt.device)
half = device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA
# Load model
model = attempt_load(weights, map_location=device) # load FP32 model
stride = int(model.stride.max()) # model stride
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=stride) # check img_size
if half:
model.half() # to FP16
# Second-stage classifier
classify = False
if classify:
modelc = load_classifier(name='resnet101', n=2) # initialize
modelc.load_state_dict(torch.load('weights/resnet101.pt', map_location=device)['model']).to(device).eval()
# Set Dataloader
vid_path, vid_writer = None, None
if webcam:
view_img = check_imshow()
cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference
dataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride)
else:
save_img = True
dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride)
print("img_size:")
print(imgsz)
# Get names and colors
names = model.module.names if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.names
colors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in names]
# Run inference
if device.type != 'cpu':
model(torch.zeros(1, 3, imgsz, imgsz).to(device).type_as(next(model.parameters()))) # run once
t0 = time.time()
for path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset:
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if img.ndimension() == 3:
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
# Inference
t1 = time_synchronized()
pred = model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0]
# Apply NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, opt.conf_thres, opt.iou_thres, classes=opt.classes, agnostic=opt.agnostic_nms)
t2 = time_synchronized()
# Apply Classifier
if classify:
pred = apply_classifier(pred, modelc, img, im0s)
# Process detections
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # detections per image
if webcam: # batch_size >= 1
p, s, im0, frame = path[i], '%g: ' % i, im0s[i].copy(), dataset.count
else:
p, s, im0, frame = path, '', im0s, getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0)
p = Path(p) # to Path
save_path = str(save_dir / p.name) # img.jpg
txt_path = str(save_dir / 'labels' / p.stem) + ('' if dataset.mode == 'image' else f'_{frame}') # img.txt
s += '%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:] # print string
gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results
for c in det[:, -1].unique():
n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class
s += f"{n} {names[int(c)]} {'s' * (n > 1)} , " # add to string
# Write results
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
if save_txt: # Write to file
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywh
print("xywh x : %d, y : %d"%(xywh[0],xywh[1]) )
line = (cls, *xywh, conf) if opt.save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label format
with open(txt_path + '.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')
if save_img or view_img: # Add bbox to image
label = f'{names[int(cls)]} {conf:.2f} '
plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=3)
##print label x,y zuobiao
x = (xyxy[0] + xyxy[2]) / 2
y = (xyxy[1] + xyxy[3]) / 2
#print(" %s is x: %d y: %d " %(label,x,y) )
height_0, width_0 = im0.shape[0:2]
if (x <= int(width_0/2) ):
t3 = time_synchronized()
################################
#stereo code
p = num
string = ''
#print("P is %d" %p )
# 读取数据集的图片
#iml = cv2.imread('./stereo/yolo/zuo/%szuo%d.bmp' %(string,p) ) # 左图
#imr = cv2.imread('./stereo/yolo/you/%syou%d.bmp' %(string,p) ) # 右图
#iml = cv2.imread('./stereo/yolo/zuo/%szuo%d.bmp' %(string,p) ) # 左图
#imr = cv2.imread('./stereo/yolo/you/%syou%d.bmp' %(string,p) ) # 右图
#height_0, width_0 = im0.shape[0:2]
#print("width_0 = %d " % width_0)
#print("height_0 = %d " % height_0)
iml = im0[0:int(height_0), 0:int(width_0/2)]
imr = im0[0:int(height_0), int(width_0/2):int(width_0) ]
height, width = iml.shape[0:2]
#cv2.imshow("iml",iml)
#cv2.imshow("imr",im0)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
#print("width = %d " % width)
#print("height = %d " % height)
# 读取相机内参和外参
config = stereoconfig_040_2.stereoCamera()
# 立体校正
map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y, Q = getRectifyTransform(height, width, config) # 获取用于畸变校正和立体校正的映射矩阵以及用于计算像素空间坐标的重投影矩阵
#print("Print Q!")
#print("Q[2,3]:%.3f"%Q[2,3])
iml_rectified, imr_rectified = rectifyImage(iml, imr, map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y)
# 绘制等间距平行线,检查立体校正的效果
line = draw_line(iml_rectified, imr_rectified)
#cv2.imwrite('./yolo/%s检验%d.png' %(string,p), line)
# 消除畸变
iml = undistortion(iml, config.cam_matrix_left, config.distortion_l)
imr = undistortion(imr, config.cam_matrix_right, config.distortion_r)
# 立体匹配
iml_, imr_ = preprocess(iml, imr) # 预处理,一般可以削弱光照不均的影响,不做也可以
iml_rectified_l, imr_rectified_r = rectifyImage(iml_, imr_, map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y)
disp, _ = stereoMatchSGBM(iml_rectified_l, imr_rectified_r, True)
#cv2.imwrite('./yolo/%s视差%d.png' %(string,p), disp)
# 计算像素点的3D坐标(左相机坐标系下)
points_3d = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disp, Q) # 可以使用上文的stereo_config.py给出的参数
#points_3d = points_3d
'''
#print("x is :%.3f" %points_3d[int(y), int(x), 0] )
print('点 (%d, %d) 的三维坐标 (x:%.3fcm, y:%.3fcm, z:%.3fcm)' % (int(x), int(y),
points_3d[int(y), int(x), 0]/10,
points_3d[int(y), int(x), 1]/10,
points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2]/10) )
'''
count = 0
#try:
while( (points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2] < 0) | (points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2] > 2500) ):
count += 1
x += count
if( 0 < points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2] < 2300 ):
break
y += count
if( 0 < points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2] < 2300 ):
break
count += 1
x -= count
if( 0 < points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2] < 2300 ):
break
y -= count
if( 0 < points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2] < 2300 ):
break
#if(count%2==1):
# x += 1
#else:
# y += 1
text_cxy = "*"
cv2.putText(im0, text_cxy, (x, y) , cv2.FONT_ITALIC, 1.2, (0,0,255), 3)
#print("count is %d" %count)
print('点 (%d, %d) 的三维坐标 (x:%.1fcm, y:%.1fcm, z:%.1fcm)' % (int(x), int(y),
points_3d[int(y), int(x), 0]/10,
points_3d[int(y), int(x), 1]/10,
points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2]/10) )
dis = ( (points_3d[int(y), int(x), 0] ** 2 + points_3d[int(y), int(x), 1] ** 2 + points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2] **2) ** 0.5 ) / 10
print('点 (%d, %d) 的 %s 距离左摄像头的相对距离为 %0.1f cm' %(x, y,label, dis) )
text_x = "x:%.1fcm" %(points_3d[int(y), int(x), 0]/10)
text_y = "y:%.1fcm" %(points_3d[int(y), int(x), 1]/10)
text_z = "z:%.1fcm" %(points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2]/10)
text_dis = "dis:%.1fcm" %dis
cv2.rectangle(im0,(xyxy[0]+(xyxy[2]-xyxy[0]),xyxy[1]),(xyxy[0]+(xyxy[2]-xyxy[0])+5+220,xyxy[1]+150),colors[int(cls)],-1);
cv2.putText(im0, text_x, (xyxy[0]+(xyxy[2]-xyxy[0])+5, xyxy[1]+30), cv2.FONT_ITALIC, 1.2, (255,255,255), 3)
cv2.putText(im0, text_y, (xyxy[0]+(xyxy[2]-xyxy[0])+5, xyxy[1]+65), cv2.FONT_ITALIC, 1.2, (255, 255, 255), 3)
cv2.putText(im0, text_z, (xyxy[0]+(xyxy[2]-xyxy[0])+5, xyxy[1]+100), cv2.FONT_ITALIC, 1.2, (255, 255, 255), 3)
cv2.putText(im0, text_dis, (xyxy[0]+(xyxy[2]-xyxy[0])+5, xyxy[1]+145), cv2.FONT_ITALIC, 1.2, (255, 255, 255), 3)
t4 = time_synchronized()
print(f'Done. ({t4 - t3:.3f}s)')
# Print time (inference + NMS)
print(f'{s}Done. ({t2 - t1:.3f}s)')
# Stream results
if view_img:
cv2.imshow(str(p), im0)
cv2.waitKey(1) # 1 millisecond
# Save results (image with detections)
if save_img:
if dataset.mode == 'image':
cv2.imwrite(save_path, im0)
else: # 'video'
if vid_path != save_path: # new video
vid_path = save_path
if isinstance(vid_writer, cv2.VideoWriter):
vid_writer.release() # release previous video writer
fourcc = 'mp4v' # output video codec
fps = vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
w = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
h = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*fourcc), fps, (w, h))
vid_writer.write(im0)
if save_txt or save_img:
s = f"\n{len(list(save_dir.glob('labels/*.txt')))} labels saved to {save_dir / 'labels'}" if save_txt else ''
print(f"Results saved to {save_dir}{s}")
print(f'Done. ({time.time() - t0:.3f}s)')
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default='last_dead_fish_1000.pt', help='model.pt path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default='./shuangmu_dead_fish_011.mp4' , help='source') # file/folder, 0 for webcam
parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=640, help='inference size (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='object confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='IOU threshold for NMS')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--view-img', action='store_true', help='display results')
parser.add_argument('--save-txt', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--save-conf', action='store_true', help='save confidences in --save-txt labels')
parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3')
parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
parser.add_argument('--update', action='store_true', help='update all models')
parser.add_argument('--project', default='runs/detect', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
check_requirements()
with torch.no_grad():
if opt.update: # update all models (to fix SourceChangeWarning)
for opt.weights in ['yolov5s.pt', 'yolov5m.pt', 'yolov5l.pt', 'yolov5x.pt']:
detect()
strip_optimizer(opt.weights)
else:
detect()
五、完整代码
下载后直接运行
detect_and_stereo_video_003.py
即可开始识别定位
版权归原作者 SYBH. 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。