hello,大家好。各位可点击左下方阅读原文,访问公众号官方店铺。谨防上当受骗,感谢各位支持!
今天为各位更新人工蜂群算法(Artificial Bee Colony,ABC)的Python代码,之前我们在MATLAB数学建模(十一) | 人工蜂群算法(附MATLAB代码)这篇推文讲解了ABC算法的基本思想,忘记ABC算法的小伙伴可以点击上述链接复习一下。
目录
1.ABC算法基本步骤
1)初始化各蜜源
X i X_i Xi ; 设定参数 N P NP NP、 l i m i t limit limit 以及最大迭代次数 m a x I t maxIt maxIt; 计数器初始化 i t = 1 it=1 it=1;2)为蜜源
X i X_i Xi分配一只引领蜂,按式 v i d = x i d + φ ( x i d − x j d ) v_{i d}=x_{i d}+\varphi\left(x_{i d}-x_{j d}\right) vid=xid+φ(xid−xjd)进行搜索,产生新蜜源 V i V_i Vi ;3)依据式
f i t i = { 1 / ( 1 + f i ) , f i ⩾ 0 1 + abs ( f i ) , otherwise f i t_{i}= \begin{cases}1 /\left(1+f_{i}\right), & f_{i} \geqslant 0 \\ 1+\operatorname{abs}\left(f_{i}\right), & \text { otherwise }\end{cases} fiti={1/(1+fi),1+abs(fi),fi⩾0 otherwise 评价 V i V_i Vi的适应度,根据贪婪选择的方法确定保留的蜜源;4)由式
p i = f i t i / ∑ i = 1 N P f i t i p_{i}=f i t_{i} / \sum_{i=1}^{N P} f i t_{i} pi=fiti/∑i=1NPfiti计算引领蜂找到的蜜源被跟随的概率;5)跟随峰采用与引领蜂相同的方式进行搜索,根据贪婪选择的方法确定保留的蜜源;
6)判断蜜源 是否满足被放弃的条件。如满足,对应的引领蜂角色变为侦察蜂,否则直接转到8);
7)侦察蜂根据式
X i t + 1 = { L d + rand ( 0 , 1 ) ( U d − L d ) , trial i ⩾ limit X i t , trial i < limit X_{i}^{t+1}=\left\{\begin{array}{l} L_{d}+\operatorname{rand}(0,1)\left(U_{d}-L_{d}\right), \operatorname{trial}_{i} \geqslant \text { limit } \\ X_{i}^{t}, \operatorname{trial}_{i}<\text { limit } \end{array}\right. Xit+1={Ld+rand(0,1)(Ud−Ld),triali⩾ limit Xit,triali< limit 随机产生新蜜源;8)
i t = i t + 1 it=it+1 it=it+1; 判断算法是否满足终止条件,若满足则终止,输出最优解,否则转到2)。
更多关于ABC算法详细内容详见MATLAB数学建模(十一) | 人工蜂群算法(附MATLAB代码)。
2.ABC算法Python代码
整个ABC算法Python代码共包含两个.py文件,即artificial_bee_colony.py和app.py。**这里需要注意的是,需要各位自行安装ypstruct库,安装方法可以参考https://pypi.org/project/ypstruct/**。
artificial_bee_colony.py文件如下所示:
import numpy as np
from ypstruct import structure
defrun(problem, params):# 函数信息
costfunc = problem.costfunc
nvar = problem.nvar
varmin = problem.varmin
varmax = problem.varmax
# 参数信息
maxit = params.maxit
npop = params.npop
nonlooker = params.nonlooker
limit =int(np.round(0.6*nvar*npop))
a = params.a
# 空的蜂群结构
empty_bee = structure()
empty_bee.position =None
empty_bee.cost =None# 临时蜂群结构
newbee = structure()
newbee.position =None
newbee.cost =None# 初始化全局最优解
bestsol = empty_bee.deepcopy()
bestsol.cost = np.inf
# 种群初始化
pop = empty_bee.repeat(npop)for i inrange(npop):
pop[i].position = np.random.uniform(varmin, varmax, nvar)
pop[i].cost = costfunc(pop[i].position)if pop[i].cost < bestsol.cost:
bestsol = pop[i].deepcopy()# 初始化每个个体的抛弃次数
count = np.empty(npop)# 记录每一代中全局最优个体目标函数值
bestcost = np.empty(maxit)# 人工蜂群算法主循环for it inrange(maxit):# 引领蜂for i inrange(npop):# 随机选择k,不等于i
K = np.append(np.arange(0,i),np.arange(i+1,npop))
k = K[np.random.randint(K.size)]# 定义加速系数
phi = a * np.random.uniform(-1,1, nvar)# 新的蜜蜂位置
newbee.position = pop[i].position + phi *(pop[i].position - pop[k].position)# 计算新蜜蜂目标函数值
newbee.cost = costfunc(newbee.position)# 通过比较目标函数值,更新第i个蜜蜂的位置if newbee.cost < pop[i].cost:
pop[i]= newbee.deepcopy()else:
count[i]+=1# 计算适应度值和选择概率
fit = np.empty(npop)
meancost = np.mean([pop[i].cost for i inrange(npop)])for i inrange(npop):
fit[i]= np.exp(-pop[i].cost/meancost)#将目标函数值转换为适应度值
probs = fit / np.sum(fit)# 跟随蜂for m inrange(nonlooker):# 通过轮盘赌的方式选择蜜源
i = roulette_wheel_selection(probs)# 随机选择k,不等于i
K = np.append(np.arange(0, i), np.arange(i +1, npop))
k = K[np.random.randint(K.size)]# 定义加速系数
phi = a * np.random.uniform(-1,1, nvar)# 新的蜜蜂位置
newbee.position = pop[i].position + phi *(pop[i].position - pop[k].position)# 计算新蜜蜂目标函数值
newbee.cost = costfunc(newbee.position)# 通过比较目标函数值,更新第i个蜜蜂的位置if newbee.cost < pop[i].cost:
pop[i]= newbee.deepcopy()else:
count[i]+=1# 侦察蜂for i inrange(npop):if count[i]> limit:
pop[i].position = np.random.uniform(varmin, varmax, nvar)
pop[i].cost = costfunc(pop[i].position)
count[i]=0# 更新全局最优解for i inrange(npop):if pop[i].cost < bestsol.cost:
bestsol = pop[i].deepcopy()# 存储每一代全局最优解的目标函数值
bestcost[it]= bestsol.cost
# 展示迭代信息print("Iteration {}: Best Cost = {}".format(it, bestcost[it]))# 返回值
out = structure()
out.pop = pop
out.bestsol = bestsol
out.bestcost = bestcost
return out
defroulette_wheel_selection(p):
c = np.cumsum(p)
r =sum(p)* np.random.rand()
ind = np.argwhere(r <= c)return ind[0][0]
app.py文件如下所示:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from ypstruct import structure
import time
import artificial_bee_colony
start = time.time()#运行开始时刻# 测试函数defsphere(x):returnsum(x**2)# 问题定义
problem = structure()
problem.costfunc = sphere
problem.nvar =10
problem.varmin =-100* np.ones(10)
problem.varmax =100* np.ones(10)# ABC参数
params = structure()
params.maxit =500
params.npop =100
params.nonlooker =100
params.a =1# 运行ABC
out = artificial_bee_colony.run(problem, params)# 运行结果
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['KaiTi']#设置字体为楷体
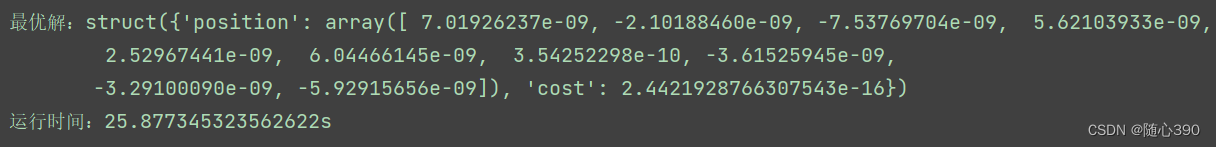
plt.plot(out.bestcost)print("最优解:{}".format(out.bestsol))
end = time.time()# 运行结束时刻print('运行时间:{}s'.format(end-start))
plt.xlim(0, params.maxit)
plt.xlabel('迭代次数')
plt.ylabel('全局最优目标函数值')
plt.title('人工蜂群算法')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
3.ABC算法实例验证
测试函数如下:
min
f
(
x
)
=
∑
i
=
1
10
x
i
2
−
100
≤
x
i
≤
100
\min f\left ( x \right ) =\sum_{i=1}^{10} x_{i}^2 \quad -100\le x_{i} \le 100
minf(x)=i=1∑10xi2−100≤xi≤100
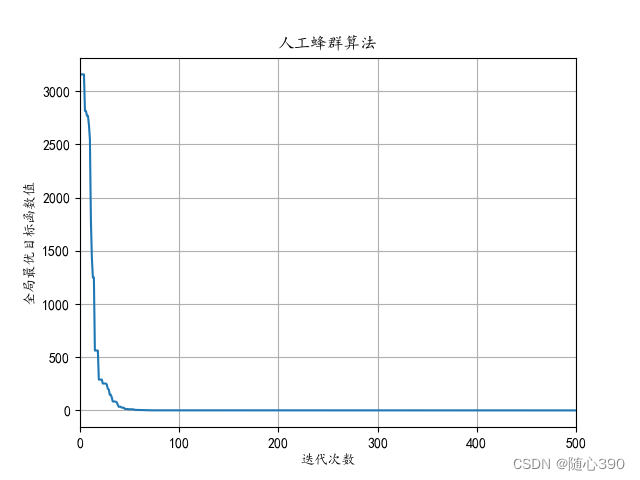
运行app.py文件,运行结果如下:
参考文献
[1] 秦全德, 程适, 李丽, 等. 人工蜂群算法研究综述[J]. 2014
OK,今天就到这里啦,各位可点击下方图片留言。
我们已经推出粉丝QQ交流群,各位小伙伴赶快加入吧!!!

咱们下期再见
近期你可能错过了的好文章
新书上架 | 《MATLAB智能优化算法:从写代码到算法思想》
优化算法 | 灰狼优化算法(文末有福利)
优化算法 | 鲸鱼优化算法
遗传算法(GA)求解带时间窗的车辆路径(VRPTW)问题MATLAB代码
粒子群优化算法(PSO)求解带时间窗的车辆路径问题(VRPTW)MATLAB代码
知乎 | bilibili | CSDN:随心390
版权归原作者 随心390 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。