大家好,我是微学AI,今天给大家介绍一下人工智能(pytorch)搭建模型12-pytorch搭建BiGRU模型,利用正态分布数据训练该模型。本文将介绍一种基于PyTorch的BiGRU模型应用项目。我们将首先解释BiGRU模型的原理,然后使用PyTorch搭建模型,并提供模型代码和数据样例。接下来,我们将加载数据到模型中进行训练,打印损失值与准确率,并在训练完成后进行测试。最后,我们将提供完整的文章目录结构和全套实现代码。
目录
- BiGRU模型原理
- 使用PyTorch搭建BiGRU模型
- 数据样例
- 模型训练
- 模型测试
- 完整代码
1. BiGRU模型原理
BiGRU(双向门控循环单元)是一种改进的循环神经网络(RNN)结构,它由两个独立的GRU层组成,一个沿正向处理序列,另一个沿反向处理序列。这种双向结构使得BiGRU能够捕捉到序列中的长距离依赖关系,从而提高模型的性能。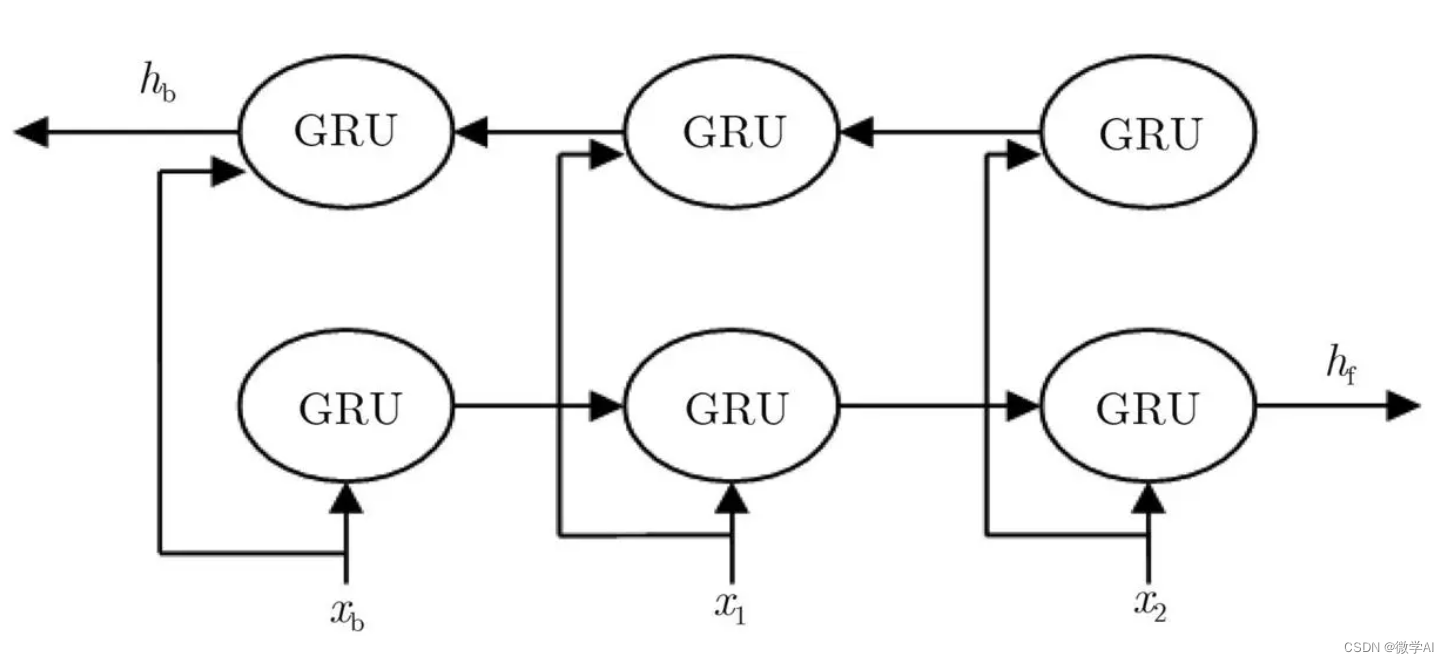
GRU(门控循环单元)是一种RNN变体,它通过引入更新门和重置门来解决传统RNN中的梯度消失问题。更新门负责确定何时更新隐藏状态,而重置门负责确定何时允许过去的信息影响当前隐藏状态。
BiGRU模型的数学原理可以用以下公式表示:
首先,对于一个输入序列
X
=
x
1
x
2
,
.
.
.
,
x
T
X = {x_1 x_2, ..., x_T}
X=x1x2,...,xT,BiGRU模型的前向计算可以表示为:
h
t
→
=
GRU
(
h
t
−
1
→
,
x
t
)
\overrightarrow{h_t} = \text{GRU}(\overrightarrow{h_{t-1}}, x_t)
ht=GRU(ht−1,xt)
h
t
←
=
GRU
(
h
t
+
1
←
,
x
t
)
\overleftarrow{h_t} = \text{GRU}(\overleftarrow{h_{t+1}}, x_t)
ht=GRU(ht+1,xt)
其中,
h
t
→
\overrightarrow{h_t}
ht 和
h
t
←
\overleftarrow{h_t}
ht 分别表示从左到右和从右到左的隐藏状态,
GRU
\text{GRU}
GRU 表示GRU单元,
x
t
x_t
xt 表示输入序列中的第
t
t
t 个元素。
然后,将两个方向的隐藏状态拼接在一起,得到最终的隐藏状态
h
t
h_t
ht:
h
t
=
[
h
t
→
;
h
t
←
]
h_t = [\overrightarrow{h_t}; \overleftarrow{h_t}]
ht=[ht;ht]
其中,
[
⋅
;
⋅
]
[\cdot;\cdot]
[⋅;⋅] 表示向量的拼接操作。
最后,将隐藏状态
h
t
h_t
ht 传递给一个全连接层,得到输出
y
t
y_t
yt:
y
t
=
softmax
(
W
h
t
+
b
)
y_t = \text{softmax}(W h_t + b)
yt=softmax(Wht+b)
其中,
W
W
W 和
b
b
b 分别表示全连接层的权重和偏置,
softmax
\text{softmax}
softmax 表示
softmax
\text{softmax}
softmax激活函数。
2. 使用PyTorch搭建BiGRU模型
首先,我们需要导入所需的库:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
接下来,我们定义BiGRU模型类:
classBiGRU(nn.Module):def__init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes):super(BiGRU, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size *2, num_classes)defforward(self, x):# 初始化隐藏状态
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers *2, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(device)# 双向GRU
out, _ = self.gru(x, h0)
out = out[:,-1,:]# 全连接层
out = self.fc(out)return out
3. 数据样例
为了简化问题,我们将使用一个简单的人造数据集。数据集包含10个样本,每个样本有8个时间步长,每个时间步长有一个特征。标签是一个二分类问题。
# 生成数据样例import numpy as np
# 均值为1的正态分布随机数
data_0 = np.random.randn(50,20,1)+1# 均值为-1的正态分布随机数
data_1 = np.random.randn(50,20,1)-1# 合并为总数据集
data = np.concatenate([data_0, data_1], axis=0)# 将 labels 修改为对应大小的数组
labels = np.concatenate([np.zeros((50,1)), np.ones((50,1))], axis=0)
4. 模型训练
首先,我们需要将数据转换为PyTorch张量,并将其分为训练集和验证集。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(data, labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
X_train = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32)
y_train = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.long)
X_val = torch.tensor(X_val, dtype=torch.float32)
y_val = torch.tensor(y_val, dtype=torch.long)
接下来,我们定义训练和验证函数:
deftrain(model, device, X_train, y_train, optimizer, criterion):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(X_train.to(device))
loss = criterion(output, y_train.squeeze().to(device))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()return loss.item()defvalidate(model, device, X_val, y_val, criterion):
model.eval()with torch.no_grad():
output = model(X_val.to(device))
loss = criterion(output, y_val.squeeze().to(device))return loss.item()
现在,我们可以开始训练模型:
device = torch.device("cuda"if torch.cuda.is_available()else"cpu")
input_size =1
hidden_size =32
num_layers =1
num_classes =2
num_epochs =10
learning_rate =0.01
model = BiGRU(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes).to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)for epoch inrange(num_epochs):
train_loss = train(model, device, X_train, y_train, optimizer, criterion)
val_loss = validate(model, device, X_val, y_val, criterion)print(f"Epoch [{epoch +1}/{num_epochs}], Train Loss: {train_loss:.4f}, Validation Loss: {val_loss:.4f}")
5. 模型测试
在训练完成后,我们可以使用测试数据集评估模型的性能。这里,我们将使用训练过程中的验证数据作为测试数据。
deftest(model, device, X_test, y_test):
model.eval()with torch.no_grad():
output = model(X_test.to(device))
_, predicted = torch.max(output.data,1)
correct =(predicted == y_test.squeeze().to(device)).sum().item()
accuracy = correct / y_test.size(0)return accuracy
test_accuracy = test(model, device, X_val, y_val)print(f"Test Accuracy: {test_accuracy *100:.2f}%")
6. 完整代码
以下是本文中提到的完整代码:
# 导入库import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 定义BiGRU模型classBiGRU(nn.Module):def__init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes):super(BiGRU, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.gru = nn.GRU(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size *2, num_classes)defforward(self, x):
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers *2, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(device)
out, _ = self.gru(x, h0)
out = out[:,-1,:]
out = self.fc(out)return out
# 生成数据样例# 均值为1的正态分布随机数
data_0 = np.random.randn(50,20,1)+1# 均值为-1的正态分布随机数
data_1 = np.random.randn(50,20,1)-1# 合并为总数据集
data = np.concatenate([data_0, data_1], axis=0)# 将 labels 修改为对应大小的数组
labels = np.concatenate([np.zeros((50,1)), np.ones((50,1))], axis=0)# 划分训练集和验证集
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(data, labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
X_train = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32)
y_train = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.long)
X_val = torch.tensor(X_val, dtype=torch.float32)
y_val = torch.tensor(y_val, dtype=torch.long)# 定义训练和验证函数deftrain(model, device, X_train, y_train, optimizer, criterion):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(X_train.to(device))
loss = criterion(output, y_train.squeeze().to(device))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()return loss.item()defvalidate(model, device, X_val, y_val, criterion):
model.eval()with torch.no_grad():
output = model(X_val.to(device))
loss = criterion(output, y_val.squeeze().to(device))return loss.item()# 训练模型
device = torch.device("cuda"if torch.cuda.is_available()else"cpu")
input_size =1
hidden_size =32
num_layers =1
num_classes =2
num_epochs =10
learning_rate =0.01
model = BiGRU(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes).to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)for epoch inrange(num_epochs):
train_loss = train(model, device, X_train, y_train, optimizer, criterion)
val_loss = validate(model, device, X_val, y_val, criterion)print(f"Epoch [{epoch +1}/{num_epochs}], Train Loss: {train_loss:.4f}, Validation Loss: {val_loss:.4f}")# 测试模型deftest(model, device, X_test, y_test):
model.eval()with torch.no_grad():
output = model(X_test.to(device))
_, predicted = torch.max(output.data,1)
correct =(predicted == y_test.squeeze().to(device)).sum().item()
accuracy = correct / y_test.size(0)return accuracy
test_accuracy = test(model, device, X_val, y_val)print(f"Test Accuracy: {test_accuracy *100:.2f}%")
运行结果:
Epoch [1/10], Train Loss:0.7157, Validation Loss:0.6330
Epoch [2/10], Train Loss:0.6215, Validation Loss:0.5666
Epoch [3/10], Train Loss:0.5390, Validation Loss:0.4980
Epoch [4/10], Train Loss:0.4613, Validation Loss:0.4214
Epoch [5/10], Train Loss:0.3825, Validation Loss:0.3335
Epoch [6/10], Train Loss:0.2987, Validation Loss:0.2357
Epoch [7/10], Train Loss:0.2096, Validation Loss:0.1381
Epoch [8/10], Train Loss:0.1230, Validation Loss:0.0644
Epoch [9/10], Train Loss:0.0581, Validation Loss:0.0273
Epoch [10/10], Train Loss:0.0252, Validation Loss:0.0125
Test Accuracy:100.00%
本文介绍了一个基于PyTorch的BiGRU模型应用项目的完整实现。我们详细介绍了BiGRU模型的原理,并使用PyTorch搭建了模型。我们还提供了模型代码和数据样例,并展示了如何加载数据到模型中进行训练和测试。希望能帮助大家理解和实现BiGRU模型。
版权归原作者 微学AI 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。