文章目录
流程图
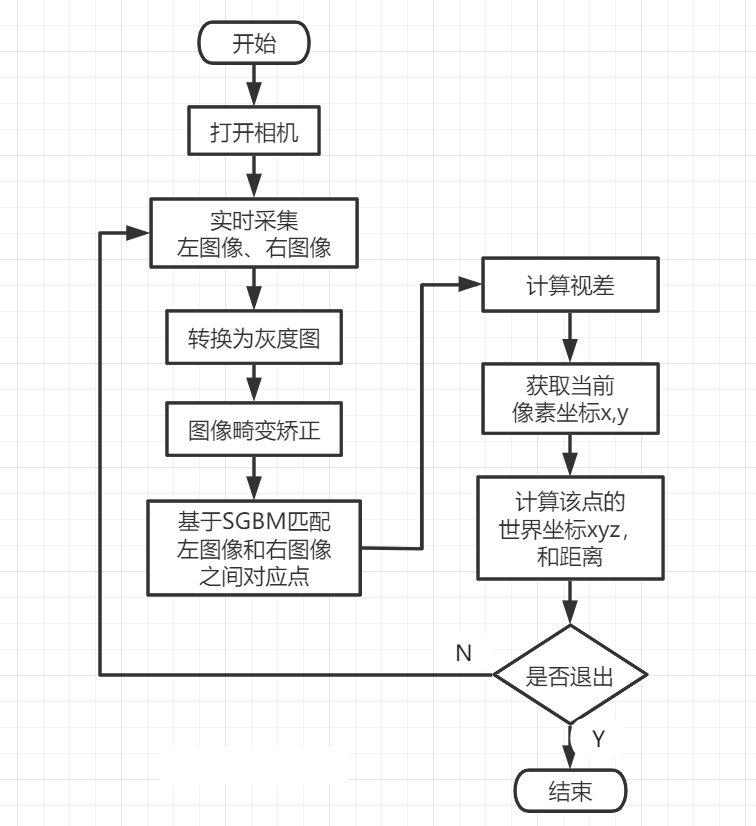
相机标定

参考链接:【开源 |教程 | 双目测距】双目相机的标定_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
自制的标定数据集,必须用自己相机拍摄照片制作数据集
标定板下载:pattern.png (1830×1330) (opencv.org)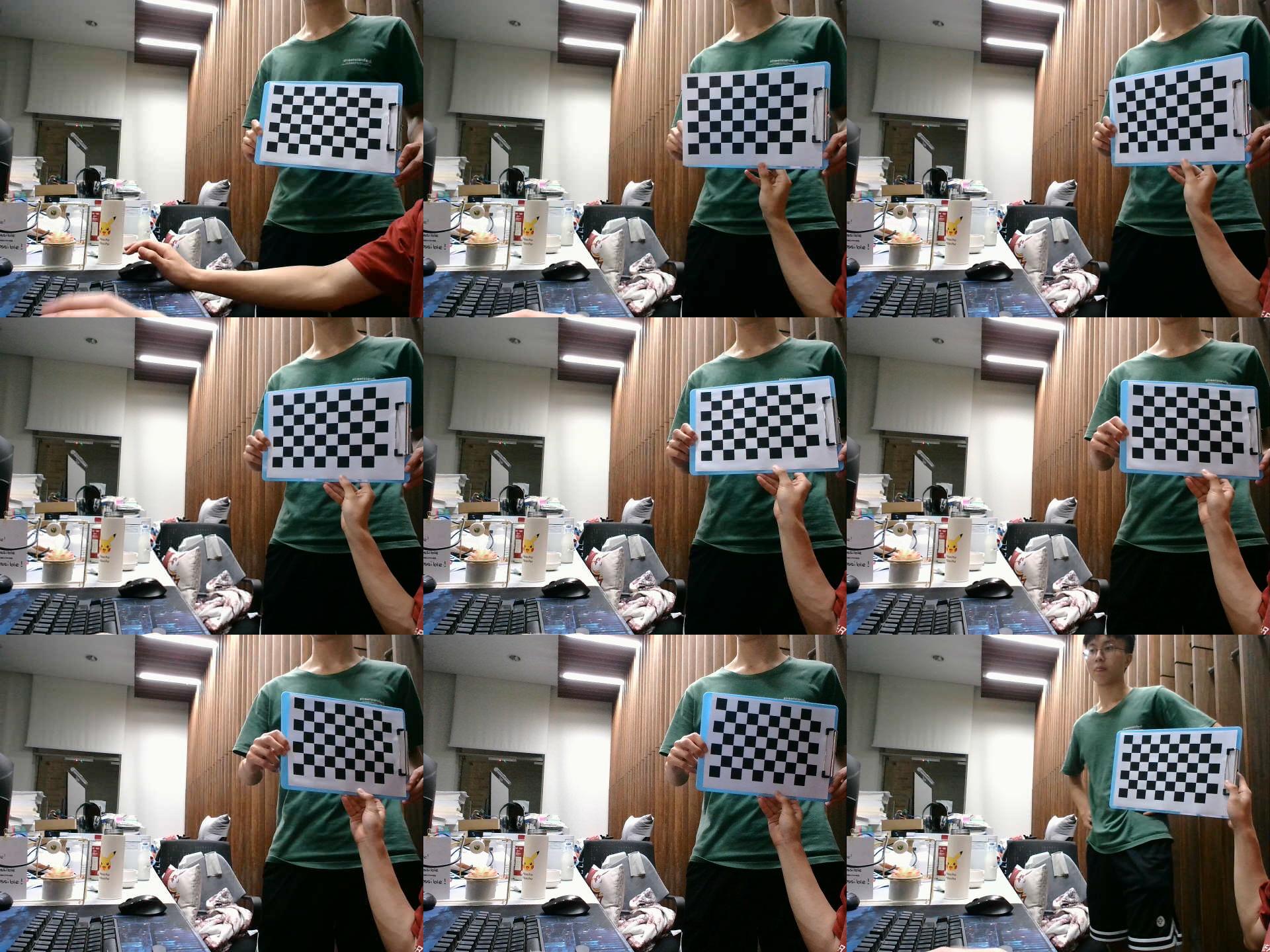
import cv2
import numpy as np
# -----------------------------------双目相机的基本参数---------------------------------------------------------# left_camera_matrix 左相机的内参矩阵# right_camera_matrix 右相机的内参矩阵## left_distortion 左相机的畸变系数 格式(K1,K2,P1,P2,0)# right_distortion 右相机的畸变系数# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------# 左镜头的内参,如焦距
left_camera_matrix = np.array([[516.5066236,-1.444673028,320.2950423],[0,516.5816117,270.7881873],[0.,0.,1.]])
right_camera_matrix = np.array([[511.8428182,1.295112628,317.310253],[0,513.0748795,269.5885026],[0.,0.,1.]])# 畸变系数,K1、K2、K3为径向畸变,P1、P2为切向畸变
left_distortion = np.array([[-0.046645194,0.077595167,0.012476819,-0.000711358,0]])
right_distortion = np.array([[-0.061588946,0.122384376,0.011081232,-0.000750439,0]])# 旋转矩阵
R = np.array([[0.999911333,-0.004351508,0.012585312],[0.004184066,0.999902792,0.013300386],[-0.012641965,-0.013246549,0.999832341]])# 平移矩阵
T = np.array([-120.3559901,-0.188953775,-0.662073075])
size =(640,480)
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion,
right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, size, R,
T)# 校正查找映射表,将原始图像和校正后的图像上的点一一对应起来
left_map1, left_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion, R1, P1, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
right_map1, right_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, R2, P2, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)print(Q)
cv2.stereoRectify()函数
- 示例:
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion,right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, size, R, T)- 作用:为每个摄像头计算立体校正的映射矩阵R1, R2, P1, P2
- 参数: 1. left_camera_matrix:左相机内参2. left_distortion:左相机畸变系数3. right_camera_matrix:右相机内参4. right_distortion:右相机畸变系数5. size:单边相机的图片分辨率6. R:旋转矩阵7. T:平移矩阵
- 返回值: 1. R1, R2:R1-输出矩阵,第一个摄像机的校正变换矩阵(旋转变换);R2-输出矩阵,第二个摄像机的校正变换矩阵(旋转变换)2. P1, P2:P1-输出矩阵,第一个摄像机在新坐标系下的投影矩阵;P2-输出矩阵,第二个摄像机在新坐标系下的投影矩阵
立体匹配
import numpy as np
import cv2
import random
import math
# 加载视频文件
capture = cv2.VideoCapture("./car.avi")
WIN_NAME ='Deep disp'
cv2.namedWindow(WIN_NAME, cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)# 读取视频
fps =0.0
ret, frame = capture.read()while ret:# 开始计时
t1 = time.time()# 是否读取到了帧,读取到了则为True
ret, frame = capture.read()# 切割为左右两张图片
frame1 = frame[0:480,0:640]
frame2 = frame[0:480,640:1280]# 将BGR格式转换成灰度图片,用于畸变矫正
imgL = cv2.cvtColor(frame1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imgR = cv2.cvtColor(frame2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 重映射,就是把一幅图像中某位置的像素放置到另一个图片指定位置的过程。# 依据MATLAB测量数据重建无畸变图片,输入图片要求为灰度图
img1_rectified = cv2.remap(imgL, left_map1, left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
img2_rectified = cv2.remap(imgR, right_map1, right_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)# 转换为opencv的BGR格式
imageL = cv2.cvtColor(img1_rectified, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageR = cv2.cvtColor(img2_rectified, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)# ------------------------------------SGBM算法----------------------------------------------------------# blockSize 深度图成块,blocksize越低,其深度图就越零碎,0<blockSize<10# img_channels BGR图像的颜色通道,img_channels=3,不可更改# numDisparities SGBM感知的范围,越大生成的精度越好,速度越慢,需要被16整除,如numDisparities# 取16、32、48、64等# mode sgbm算法选择模式,以速度由快到慢为:STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY、# STEREO_SGBM_MODE_HH4、STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM、STEREO_SGBM_MODE_HH。精度反之# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
blockSize =8
img_channels =3
stereo = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(minDisparity=1,
numDisparities=64,
blockSize=blockSize,
P1=8* img_channels * blockSize * blockSize,
P2=32* img_channels * blockSize * blockSize,
disp12MaxDiff=-1,
preFilterCap=1,
uniquenessRatio=10,
speckleWindowSize=100,
speckleRange=100,
mode=cv2.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_HH)# 计算视差
disparity = stereo.compute(img1_rectified, img2_rectified)# 归一化函数算法,生成深度图(灰度图)
disp = cv2.normalize(disparity, disparity, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)# 生成深度图(颜色图)
dis_color = disparity
dis_color = cv2.normalize(dis_color,None, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
dis_color = cv2.applyColorMap(dis_color,2)# 计算三维坐标数据值
threeD = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disparity, Q, handleMissingValues=True)# 计算出的threeD,需要乘以16,才等于现实中的距离
threeD = threeD *16# 鼠标回调事件
cv2.setMouseCallback("depth", onmouse_pick_points, threeD)#完成计时,计算帧率
fps =(fps +(1./(time.time()- t1)))/2
frame = cv2.putText(frame,"fps= %.2f"%(fps),(0,40), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,1,(0,255,0),2)
cv2.imshow("depth", dis_color)
cv2.imshow("left", frame1)
cv2.imshow(WIN_NAME, disp)# 显示深度图的双目画面# 若键盘按下q则退出播放if cv2.waitKey(20)&0xff==ord('q'):break# 释放资源
capture.release()# 关闭所有窗口
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
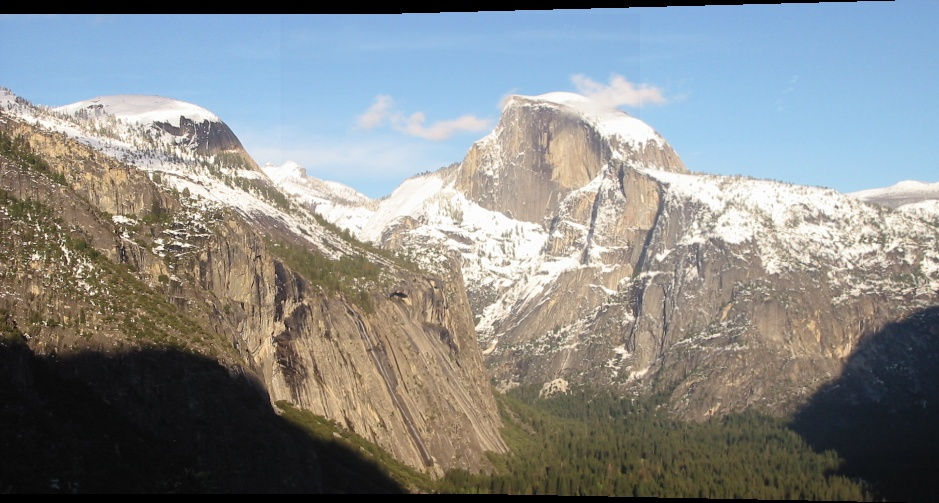
img1_rectified = cv2.remap(imgL, left_map1, left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR):重映射,即把一幅图像内的像素点放置到另外一幅图像内的指定位置,俗称“拼接”我们可以通过cv.remap()函数来将img2映射到img1对应位置上并合成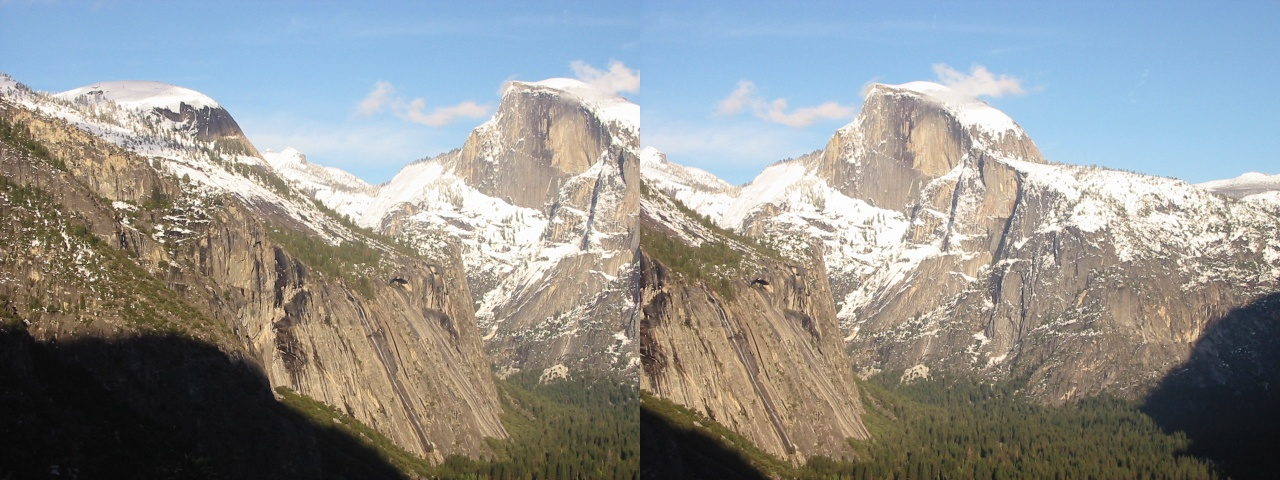

cv2.StereoSGBM_create()函数为opencv集成的算法;我们只需关注blockSize。 使用方法为: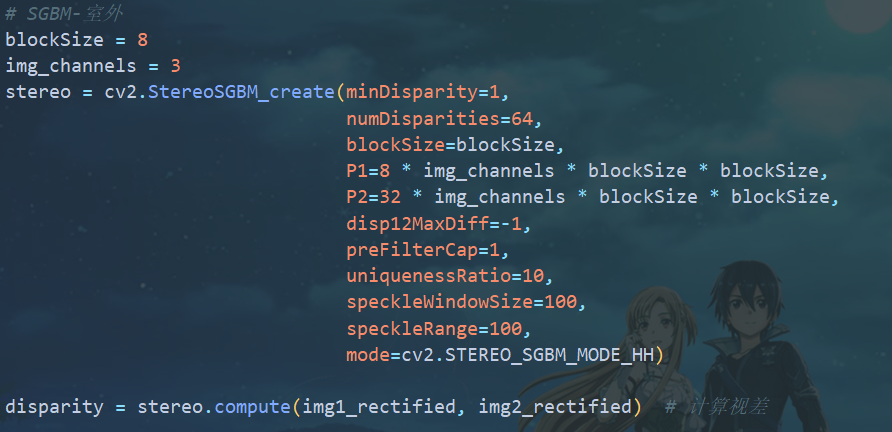 其中,调小
其中,调小numDisparities会降低精度,但提高速度。注意:numDisparities需能被16整除mode可以设置为STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY,STEREO_SGBM_MODE_HH,STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM,STEREO_SGBM_MODE_HH4四种模式,它们的精度和速度呈反比,可根据情况来选择不同的模式.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_HH4的速度最快,STEREO_SGBM_MODE_HH的精度最好
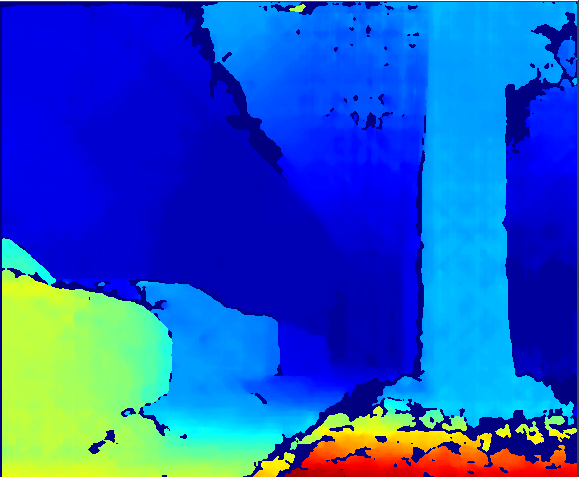
效果
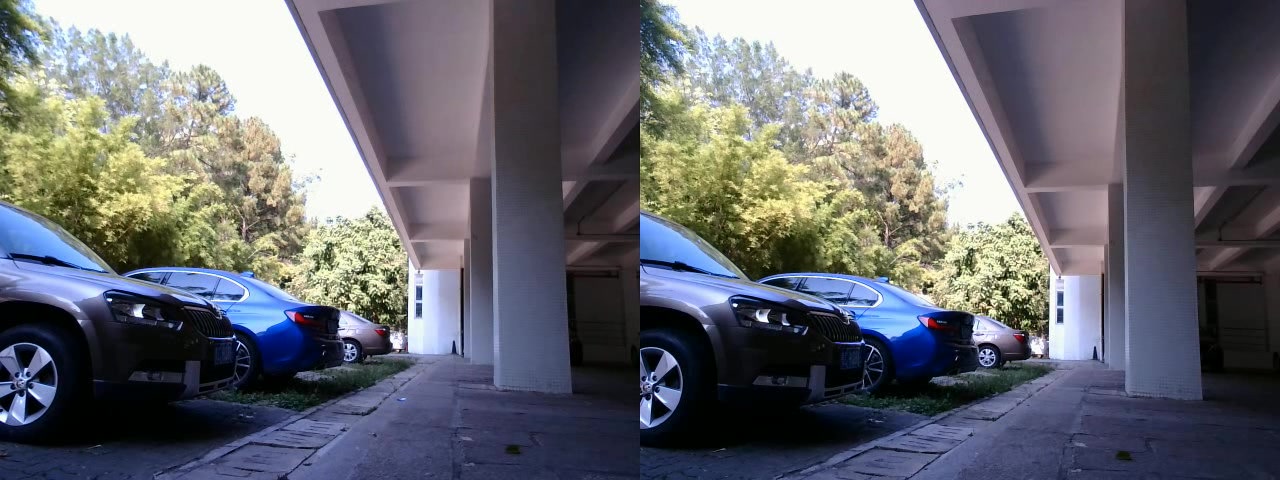
1.原图像

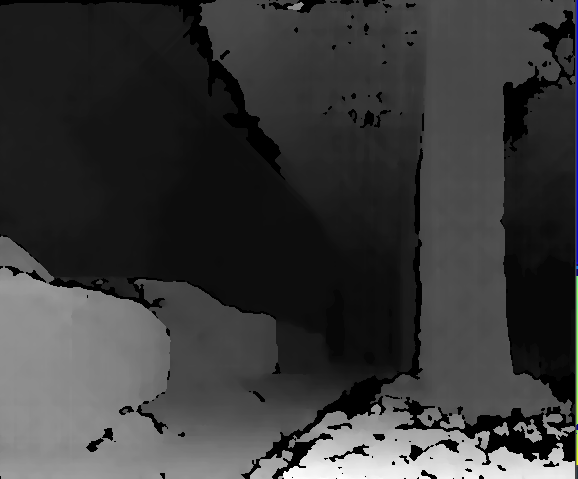
2.深度图

3.代码链接
本文转载自: https://blog.csdn.net/henghuizan2771/article/details/126463140
版权归原作者 什么都只会一点 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
版权归原作者 什么都只会一点 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。