一、问题描述
旅行商问题(Travelling Salesman Problem, 简记TSP,亦称货郎担问题):设有n个城市和距离矩阵D=[dij],其中dij表示城市i到城市j的距离,i,j=1,2 … n,则问题是要找出遍访每个城市恰好一次的一条回路并使其路径长度为最短。
初始问题图像如下:
近似理想结果图像如下:
二、算法设计
2.1 GA遗传算法
遗传算法(GeneticAlgorithm)是模拟达尔文生物进化论的自然选择和遗传学机理的生物进化过程的计算模型,通过模拟自然进化过程搜索最优解。遗传算法首先初始化一个种群,然后根据适应性函数确定个体的适应度,由适应度来选择父代个体进行交叉产生子代种群,再以某种概率让后代个体进行变异,从而不断选出适应度高的个体,进而更新种群,最终得到近似最优解情况。
2.2 算法伪代码
—————————————————————————————————
Algorithm 1 算法伪代码
—————————————————————————————————
function GA_TSP
确定种群规模M,迭代次数T,变异概率Pm,源点,交叉概率Pc等
产生初始种群(初始化路径城市序列)
while t<T
计算个体适应度
选择高适应度个体作为父代
交叉产生子代种群
变异得到新子代种群
更新种群得到新一代群体
end while
输出适应度最高的个体
end function
—————————————————————————————————
三、程序代码
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
import random
#读取城市数据defread_data():
data = pd.read_csv('city.csv')
city_name = data['city'].values
city_position_x = data['x'].values
city_position_y = data['y'].values
#原始问题图
plt.scatter(city_position_x, city_position_y)for i inrange(len(city_position_x)):
plt.annotate(city_name[i], xy=(city_position_x[i], city_position_y[i]), xytext=(city_position_x[i]+0.1, city_position_y[i]+0.1))# xy是需要标记的坐标,xytext是对应的标签坐标
plt.show()return city_name, city_position_x, city_position_y
#计算不同城市间距离矩阵defdistances(city_name, city_position_x, city_position_y):global city_count, city_distance
#城市总数量
city_count =len(city_name)#城市距离矩阵初始化
city_distance = np.zeros([city_count, city_count])for i inrange(city_count):for j inrange(city_count):
city_distance[i][j]= math.sqrt((city_position_x[i]- city_position_x[j])**2+(city_position_y[i]- city_position_y[j])**2)return city_count, city_distance
#计算一条路径的总长度defpath_length(path,origin):#具体路径,出发源点
distance =0
distance += city_distance[origin][path[0]]for i inrange(len(path)):if i ==len(path)-1:
distance += city_distance[origin][path[i]]else:
distance += city_distance[path[i]][path[i +1]]return distance
#改良defimprove(path,improve_count,origin):#具体路径,改良迭代次数
distance = path_length(path,origin)for i inrange(improve_count):#随机选择两个城市
u = random.randint(0,len(path)-1)
v = random.randint(0,len(path)-1)if u != v:
new_path = path.copy()
t = new_path[u]
new_path[u]= new_path[v]
new_path[v]= t
new_distance = path_length(new_path,origin)if new_distance < distance:# 保留更优解
distance = new_distance
path = new_path.copy()return path
#环境选择父代种群defselection(population, retain_rate, live_rate,origin):#种群,适者比例, 生命强度# 对总距离进行从小到大排序
graded =[[path_length(path,origin), path]for path in population]
graded =[path[1]for path insorted(graded)]# 选出适应性强的染色体
retain_length =int(len(graded)* retain_rate)
parents = graded[: retain_length]# 保留适应性强的染色体#保留一定存活程度强的个体for weak in graded[retain_length:]:if random.random()< live_rate:
parents.append(weak)return parents
#使用常规匹配交叉获得子代#随机选取一个交配位,子代1交配位之前的基因选自父代1交配位之前,交配位之后按父代2顺序选择没有在子代1中出现的基因#子代2交配位之前的基因选自父代2交配位之前,交配位之后按父代1顺序选择没有在子代2中出现的基因defcrossover(parents,population_num):#存活的父代种群,种群总数# 生成子代的个数
children_count = population_num -len(parents)# 孩子列表
children =[]whilelen(children)< children_count:# 在父母种群中随机选择父母
male_index = random.randint(0,len(parents)-1)
female_index = random.randint(0,len(parents)-1)if male_index != female_index:
male = parents[male_index]
female = parents[female_index]
position = random.randint(0,len(male)-1)#随机产生一个交配位
child1 = male[:position]
child2 = female[:position]for i in female:if i notin child1:
child1.append(i)for i in male:if i notin child2:
child2.append(i)
children.append(child1)
children.append(child2)return children
#变异:随机交换路径中两个城市位置defmutation(children,mutation_rate):#孩子种群,变异率for i inrange(len(children)):if random.random()< mutation_rate:# 变异
child = children[i]
u = random.randint(0,len(child)-2)
v = random.randint(u +1,len(child)-1)
tmp = child[u]
child[u]= child[v]
child[v]= tmp
children[i]=child
return children
#得到当前代种群最优个体defget_result(population,origin):
graded =[[path_length(path,origin), path]for path in population]
graded =sorted(graded)return graded[0][0], graded[0][1]# 返回种群的最优解#结果可视化defplt_magin(iters,distance,result_path,origin,city_name,city_position_x,city_position_y):print("进化次数为",iters,"时的最佳路径长度为:", distance)
result_path =[origin]+ result_path +[origin]# print("最佳路线为:")# for i, index in enumerate(result_path):# print(city_name[index] + "(" + str(index) + ")", end=' ')# if i % 9 == 0:# print()
X =[]
Y =[]for i in result_path:
X.append(city_position_x[i])
Y.append(city_position_y[i])
plt.figure()
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']# 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.plot(X, Y,'-o')
plt.xlabel('经度')
plt.ylabel('纬度')
plt.title("GA_TSP")for i inrange(len(X)):
plt.annotate(city_name[result_path[i]], xy=(X[i], Y[i]), xytext=(X[i]+0.1, Y[i]+0.1))# xy是需要标记的坐标,xytext是对应的标签坐标
plt.show()#遗传算法总流程defGA_TSP(origin,population_num,improve_count,iter_count,retain_rate,live_rate,mutation_rate):#源点,种群个体数,改良迭代数,进化次数,适者概率,生命强度,变异率
city_name, city_position_x, city_position_y = read_data()
city_count, city_distance = distances(city_name, city_position_x, city_position_y)list=[i for i inrange(city_count)]list.remove(origin)
population =[]for i inrange(population_num):# 随机生成个体
path =list.copy()
random.shuffle(path)#随机打乱
path = improve(path,improve_count,origin)#使用改良方案尽量提高初始化种群多样性
population.append(path)
every_gen_best =[]# 存储每一代最好的
distance, result_path = get_result(population,origin)for i inrange(iter_count):# 选择繁殖个体群
parents = selection(population, retain_rate, live_rate,origin)# 交叉繁殖
children = crossover(parents,population_num)# 变异
children = mutation(children,mutation_rate)# 更新种群,采用杰出选择
population = parents + children
distance, result_path = get_result(population,origin)
every_gen_best.append(distance)if(i%500==0):
plt_magin(i,distance,result_path,origin,city_name,city_position_x,city_position_y)
plt_magin(i,distance,result_path,origin,city_name,city_position_x,city_position_y)
plt.plot(range(len(every_gen_best)), every_gen_best)
plt.show()if __name__ =='__main__':
GA_TSP(10,300,200,10000,0.3,0.5,0.01)#源点,种群个数,改良次数,进化次数,适者概率,生命强度,变异率
四、结果展示
城市个数为中国省会城市为34个,种群大小选择300,选择0.3比例的作为精英个体保留,并将其作为父代个体交叉变异产生子代种群,在变异概率为0.01的情况下,最佳路径长度随迭代次数的变化情况如下图所示:
迭代次数为500,1000,2000,6000时路线情况如下图所示:




城市信息如下: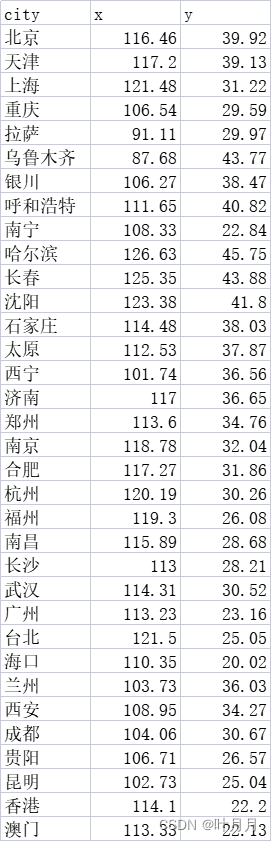
版权归原作者 叶月月 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。