OpenFHE (原 PALISADE)
介绍
Duality Technologies 主导
- Duality Technologies 成立于 2016 年,总部位于美国马萨诸塞州剑桥市,由著名的密码专家和数据科学家联合创立。公司致力于研究大数据/云环境下的数据安全与隐私保护技术,为企业组织提供了一个安全的数字协作平台,目前在美国和以色列开展业务。目前获得了由 Team8 领导的 400 万美元投资。2019 年入选 RSA 大会的创新沙盒前十强,成为两家入选的数据安全公司之一(另一家是 Wirewheel 公司)
- Duality 使企业能够与他们的商业生态系统(客户、供应商和合作伙伴)安全地协作处理敏感数据。 通过实施隐私增强技术(PETs),Duality 实现了对加密数据的安全分析和人工智能,同时遵守数据隐私法规并保护宝贵的知识产权。领先的行业和政府组织与 Duality 合作,使其数据价值最大化,包括 DARPA、英特尔、丰业银行、甲骨文、IBM、世界经济论坛(WEF)等。
- PALISADE 库人员是联合创始人 +CTO,BGV 创始人(V)是首席密码学家
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-z7Y7Xerg-1666712451878)(static/boxcn2c58JLRy8h3wsq5FeDBdjg.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/677f741605f746e89013cdc73d179764.png)
- 以及其他公司参与

OpenFHE(2022 年 7 月发布)
- OpenFHE,一个新的开源 FHE 软件库,它结合了以前的 FHE 项目,如 PALISADE、HElib 和 HEAAN 的一些设计思想,并包括一些新的设计概念和思想。主要的新设计特点可以归纳为以下几点。(1 从一开始就假设所有实现的 FHE 方案将支持引导和方案切换;(2)OpenFHE 使用标准的硬件抽象层(HAL)支持多种硬件加速后端;(3)OpenFHE 包括用户友好模式和编译器友好模式,前者所有维护操作,如模数切换、密钥切换和引导-平移,都由库自动调用,后者由外部编译器做出这些决定。
- OpenFHE 专为可用性和性能而设计,提供更简单的 API、模块化、跨平台支持和硬件加速器集成。OpenFHE 支持所有主要的 FHE 方案,包括 BGV、BFV、CKKS、DM (FHEW) 和 CGGI (TFHE) 方案。我们支持多种引导设计,并且我们在积极开发中拥有更高效的引导方案。
- OpenFHE 是 PALISADE 的后继者由 PALISADE、HElib、HEAAN 和 FHEW 库的(部分)作者设计。OpenFHE 软件库结合了从这些先前的 FHE 项目中选择的设计理念,并包含几个新的设计理念和理念。有关该设计的更多信息,
- OpenFHE 得到 DARPA 的慷慨支持。 OpenFHE 是一个社区驱动的开源项目,由不同的贡献者群体开发。OpenFHE 正式隶属于 NumFocus 稳定的开源软件项目。
同态加密支持
全同态加密(FHE)是一个强大的加密基元,可以在不接触到秘密密钥的情况下对加密数据进行计算。OpenFHE 是一个开源的 FHE 库,包括所有常见 FHE 方案的有效实现:
- 整数算术的 Brakerski/Fan-Vercauteren(BFV)方案
- 用于整数算术的 Brakerski-Gentry-Vaikuntanathan(BGV)方案
- 用于实数算术的 Cheon-Kim-Kim-Song(CKKS)方案(包括近似的引导)。
- 用于布尔电路评估的 Ducas-Micciancio(DM/FHEW)和 Chillotti-Gama-Georgieva-Izabachene(CGGI/TFHE)方案
OpenFHE 还包括以下 FHE 的多方扩展:
- BGV、BFV 和 CKKS 方案的阈值 FHE
- BGV、BFV 和 CKKS 方案的代理重加密
OpenFHE 实现了高效的剩余数系统 (RNS) 算法以实现高性能。
google 应用(FHE C++ Transpiler)
- 据 Duality 技术公司的新闻稿,谷歌已将其在 GitHub 上开源的使用 XLS SDK 开发的开源项目完全同态加密(FHE)转译器与领先的开源完全同态加密(fully homomorphic encryption)库 OpenFHE 合并。通过使加密知识更简单、更容易接近,开发者对 FHE 的采用将增加。
- 同态加密(FHE)转译器(FHE C++ Transpiler)2022.9.14 整合
- FHE C++ Transpiler 是一项开源技术,将允许任何 C++ 开发人员在不解密的情况下对加密数据进行转换。这个转译器将谷歌的 XLS 库与多个 FHE 后端(目前是 TFHE 库和 OpenFHE 的 BinFHE 库)连接起来。它将允许开发者(包括那些没有密码学专业知识的人)编写在加密数据上运行的代码,而不透露数据内容或计算结果。这个系统应该有助于为实用 FHE 系统的进一步发展奠定基础。
- 该系统目前只支持 Linux,并需要 GCC 第 9 版(或更高)和 Bazel 4.0.0。这目前是一个探索性的概念验证。虽然它可以在实践中部署,但 FHE-C++ 操作的运行时间可能太长,目前还不实用。该转置器严重依赖所选择的 FHE 库来保证安全。由于 OpenFHE 和 TFHE 库都比较新,还没有强大的被广泛接受的密码分析。因此,在将该系统的输出纳入实时生产部署之前,请注意这两个库中可能存在尚未发现的漏洞。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4VEvWhBp-1666712451879)(static/boxcn0YDLk7X0fywq5YdfNPmPkg.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5c3c172b0bdf405eae75d355f83a31c2.png)
BinFHE(Bootstrapping in FHEW-like Cryptosystems)
https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/086.pdf
- 摘要
FHEW 和 TFHE 是完全同态加密 (FHE) 密码系统,可以在每次门评估后通过自举来评估加密数据上的任意布尔电路。 FHEW 密码系统最初是基于标准(环形、循环安全)LWE 假设设计的,其初始实现能够在不到 1 秒的时间内运行自举。****TFHE 密码系统使用了一些更强的假设,例如(环,循环安全)LWE 在具有二进制秘密分布的环上,并应用了一些其他优化来将引导运行时间减少到小于 0.1 秒。
我们提出了一个统一的框架,包括 FHEW 和 TFHE 密码系统的原始和扩展变体,并在开源的 PALISADE 格密码学库中使用模块化算术来实现它。我们的分析表明,这些密码系统之间的主要区别在于所使用的引导程序。FHEW 的 Alperin-Sherif-Peikert(AP)与 TFHE 的 Gama-Izabachene-Nguyen-Xie(GINX)。TFHE 的所有其他算法优化同样适用于两个密码系统。GINX 的引导方法必须使用二进制秘密,不能直接应用于其他秘密分布。在比较这两种方案的过程中,我们提出了一种简单、轻量级的方法,将 GINX 引导法(例如 TFHE 所采用的方法)扩展到三元均匀和高斯秘密分布,这些秘密分布包括在 HE 社区安全标准中。我们对不同秘密分布的 AP 和 GINX 引导方法的比较表明,TFHE/GINX 密码系统对二元和三元秘密提供了更好的性能,而 FHEW/AP 对高斯秘密更快。我们建议考虑基于三元和高斯秘密的 FHEW 和 TFHE 密码系统的变体,以便由 HE 社区进行标准化。
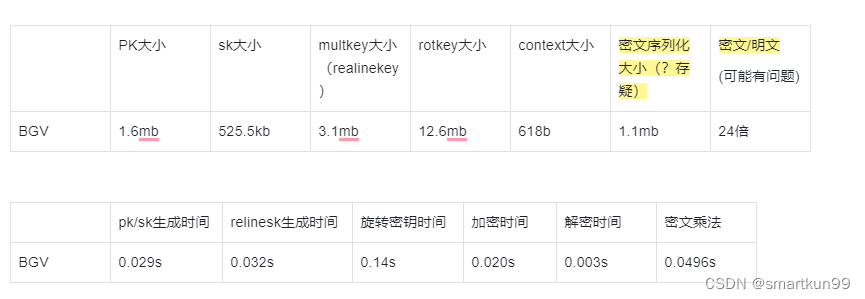
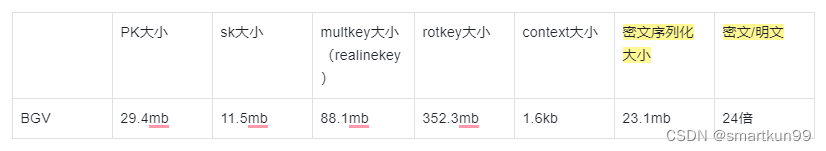
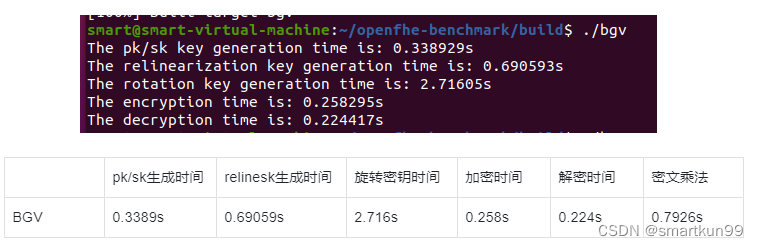
Benchmark
虚拟机运行(4 核 4gb 内存)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3ehItObK-1666712451880)(static/boxcnGHLlivAwi0afmLnscU6rtv.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1b0f07ae688a4d4e9a9fc9d94cd96ec0.png)
BGV
明文
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ArVjPztO-1666712451880)(static/boxcnGsnt1ldgdZd85C3zPlkofe.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3c89af7c79c74385bada1e1cd14d25cf.png)
// First plaintext vector is encoded
std::vector<int64_t> vectorOfInts1 ={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12};
Plaintext plaintext1 = cryptoContext->MakePackedPlaintext(vectorOfInts1);// The encoded vectors are encrypted
std::stringstream s2;//Serial::Serialize(plaintext1, s1, SerType::BINARY);Serial::Serialize(ciphertext1, s2, SerType::BINARY);//std::cout <<"good"<<std::endl;
std::cout <<"The extended times is "<<(double)(sizeof(s2)/sizeof(plaintext1))<<std::endl;//24
std::cout <<sizeof(s2)<<std::endl;//392//std::cout <<(double)(sizeof(s2)/sizeof(vectorOfInts1))<<std::endl;
密文参数(65537,乘法深度 2)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-LeLqOUm3-1666712451881)(static/boxcnkgV2fHJ5RZhUxBAr2rTM1d.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/04dc3187a82946baab0f69039cc4be9b.png)
密文参数(786433,乘法深度 20)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-WdZmjHsP-1666712451881)(static/boxcnSG2iPf2VhsHp0EQEIOJ9Ld.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/47d30d1c9c074dc0a488e10d6188e21a.png)
BFV
明文
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-RXxBbFuz-1666712451882)(static/boxcnvSq4nin0SmyMpg16rjonrf.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3e58e73e08b64feba76a77b57bd23a4d.png)
密文参数(65537,乘法深度 2)
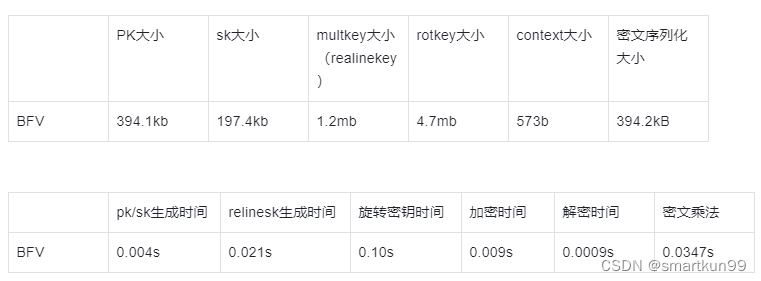
密文参数(786433,乘法深度20)
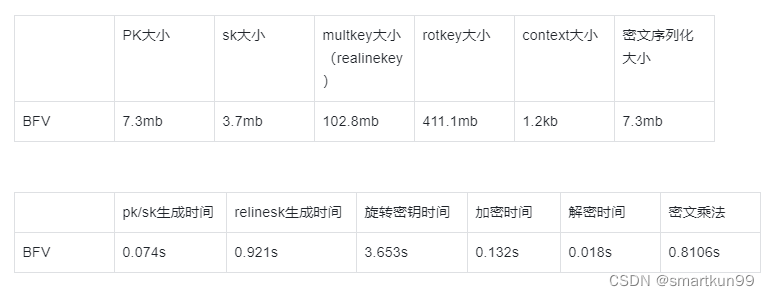
CKKS
明文
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-bODP9ldE-1666712451882)(static/boxcnVExuYOSlR240sPBWhACRzb.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b3d601afe8274c489383f94448a49389.png)
密文参数(浮点数精度 50,乘法深度 1,向量长度 8)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-pMhkQZYi-1666712451883)(static/boxcnyMrcDgxYOgZ5MfbqxyRldc.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3f425a8155284fa9b0ae63f72b560db1.png)
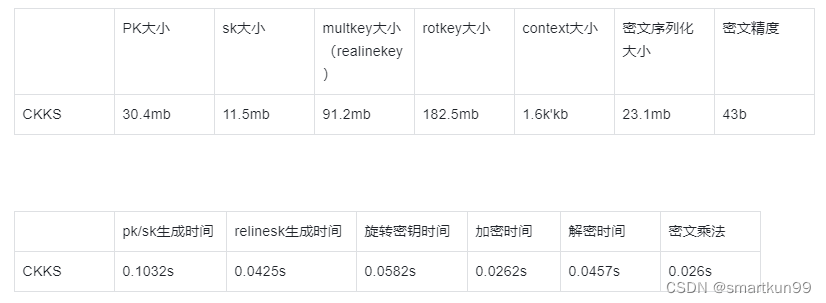
密文参数(浮点数精度 50,乘法深度 20,向量长度 8)
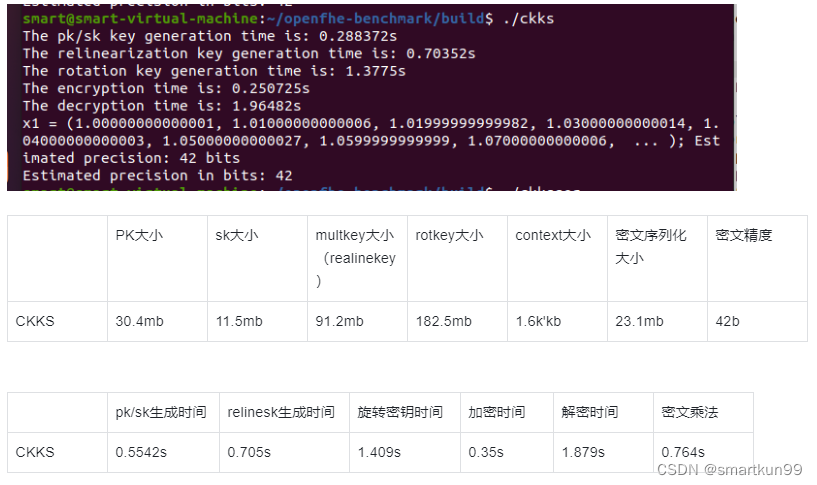
FHEW
安全系数:TOY, MEDIUM, STD128, STD192, and STD256
安全系数(TOY)
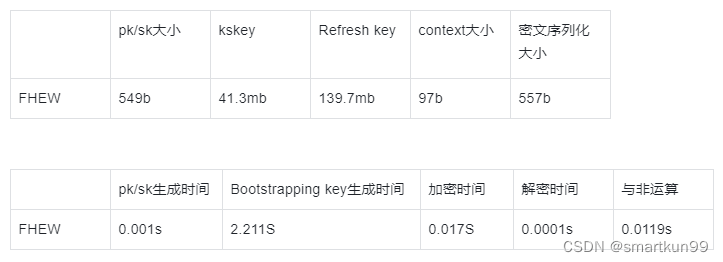
安全系数(STD128)——进程被杀死——密钥过大
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-PM31mFgu-1666712451883)(static/boxcnbl0v2n1JLBFLYKu1Qgttet.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dc4acf39bc674014a246db62e9983f59.png)
TFHE(使用 GINX bootstrapping 的 FHEW)
- 不算正宗 TFHE
- bootstrapping as described in TFHE: Fast Fully Homomorphic Encryption over the Torus and in Bootstrapping in FHEW-like Cryptosystems
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-uVQeHYCL-1666712451884)(static/boxcn8N3tLlPC2mRA4OrjifUzud.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d4770034bc3f4158987019953e237e83.png)
安全系数(TOY)
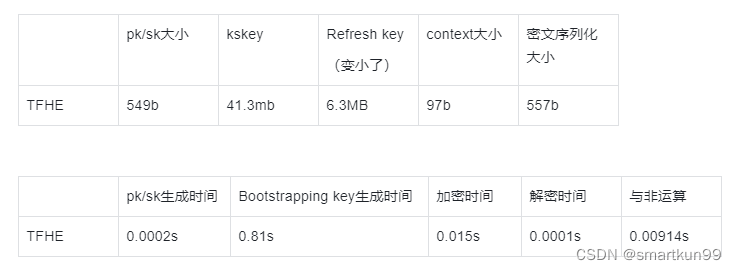
安全系数(STD128)
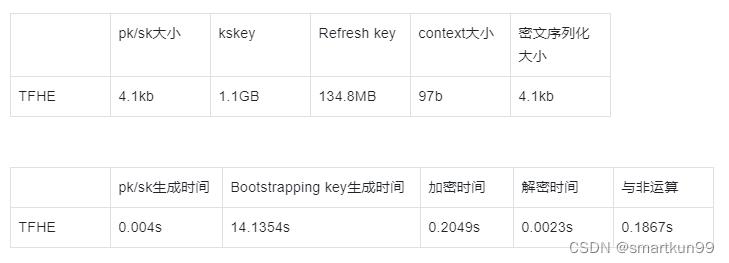
多密钥阈值 BGV/BFV/CKKS
多密钥阈值BGV(3方)
代码
voidRunBGVrnsAdditive(){
CCParams<CryptoContextBGVRNS> parameters;
parameters.SetPlaintextModulus(65537);
CryptoContext<DCRTPoly> cc =GenCryptoContext(parameters);// Enable features that you wish to use//启动模块
cc->Enable(PKE);
cc->Enable(KEYSWITCH);
cc->Enable(LEVELEDSHE);
cc->Enable(ADVANCEDSHE);
cc->Enable(MULTIPARTY);// Set-up of parameters// Print out the parameters//输出参数
std::cout <<"p = "<< cc->GetCryptoParameters()->GetPlaintextModulus()<< std::endl;
std::cout <<"n = "<< cc->GetCryptoParameters()->GetElementParams()->GetCyclotomicOrder()/2<< std::endl;
std::cout <<"log2 q = "<<log2(cc->GetCryptoParameters()->GetElementParams()->GetModulus().ConvertToDouble())<< std::endl;// Initialize Public Key Containers for 3 parties//初始化三个密钥
KeyPair<DCRTPoly> kp1;
KeyPair<DCRTPoly> kp2;
KeyPair<DCRTPoly> kp3;
KeyPair<DCRTPoly> kpMultiparty;// Perform Key Generation Operation
std::cout <<"Running key generation (used for source data)..."<< std::endl;// generate the public key for first share//生成第一个密钥kp1
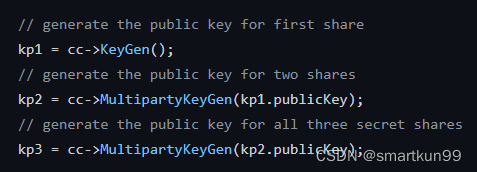
kp1 = cc->KeyGen();// generate the public key for two shares//利用kp1的公钥生成密钥kp2
kp2 = cc->MultipartyKeyGen(kp1.publicKey);// generate the public key for all three secret shares//利用kp2的公钥生成密钥kp3
kp3 = cc->MultipartyKeyGen(kp2.publicKey);if(!kp1.good()){
std::cout <<"Key generation failed!"<< std::endl;exit(1);}if(!kp2.good()){
std::cout <<"Key generation failed!"<< std::endl;exit(1);}if(!kp3.good()){
std::cout <<"Key generation failed!"<< std::endl;exit(1);}// Encode source data
std::vector<int64_t> vectorOfInts1 ={1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0};
std::vector<int64_t> vectorOfInts2 ={1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
std::vector<int64_t> vectorOfInts3 ={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,0,0};
Plaintext plaintext1 = cc->MakePackedPlaintext(vectorOfInts1);
Plaintext plaintext2 = cc->MakePackedPlaintext(vectorOfInts2);
Plaintext plaintext3 = cc->MakePackedPlaintext(vectorOfInts3);// Encryption//加密
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertext1;
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertext2;
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertext3;//全部都用kp3来加密明文
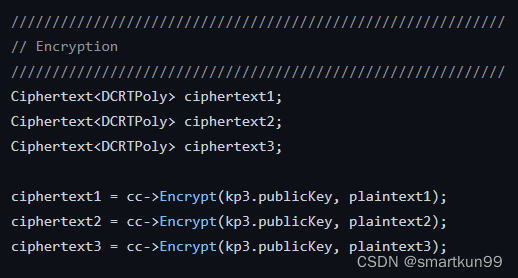
ciphertext1 = cc->Encrypt(kp3.publicKey, plaintext1);
ciphertext2 = cc->Encrypt(kp3.publicKey, plaintext2);
ciphertext3 = cc->Encrypt(kp3.publicKey, plaintext3);// EvalAdd Operation on Re-Encrypted Data
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertextAdd12;
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertextAdd123;
ciphertextAdd12 = cc->EvalAdd(ciphertext1, ciphertext2);
ciphertextAdd123 = cc->EvalAdd(ciphertextAdd12, ciphertext3);// Decryption after Accumulation Operation on Encrypted Data with Multiparty
Plaintext plaintextAddNew1;
Plaintext plaintextAddNew2;
Plaintext plaintextAddNew3;
DCRTPoly partialPlaintext1;
DCRTPoly partialPlaintext2;
DCRTPoly partialPlaintext3;
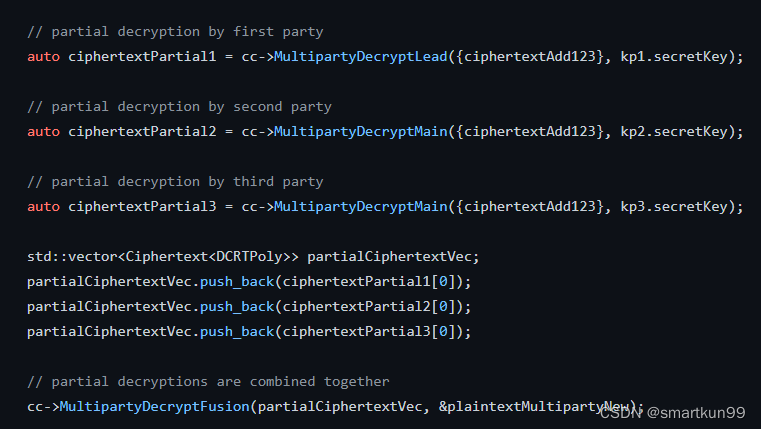
Plaintext plaintextMultipartyNew;const std::shared_ptr<CryptoParametersBase<DCRTPoly>> cryptoParams = kp1.secretKey->GetCryptoParameters();const std::shared_ptr<typenameDCRTPoly::Params> elementParams = cryptoParams->GetElementParams();//部分解密// partial decryption by first party//kp1用kp1私钥解密part1(kp1解密叫Lead,kp2\kp3解密叫Main)auto ciphertextPartial1 = cc->MultipartyDecryptLead({ciphertextAdd123}, kp1.secretKey);// partial decryption by second party//kp2用kp2私钥解密part2auto ciphertextPartial2 = cc->MultipartyDecryptMain({ciphertextAdd123}, kp2.secretKey);// partial decryption by third party//kp3用kp3私钥解密part3auto ciphertextPartial3 = cc->MultipartyDecryptMain({ciphertextAdd123}, kp3.secretKey);
std::vector<Ciphertext<DCRTPoly>> partialCiphertextVec;
partialCiphertextVec.push_back(ciphertextPartial1[0]);
partialCiphertextVec.push_back(ciphertextPartial2[0]);
partialCiphertextVec.push_back(ciphertextPartial3[0]);// partial decryptions are combined together// 合并所有的part
cc->MultipartyDecryptFusion(partialCiphertextVec,&plaintextMultipartyNew);
std::cout <<"\n Original Plaintext: \n"<< std::endl;
std::cout << plaintext1 << std::endl;
std::cout << plaintext2 << std::endl;
std::cout << plaintext3 << std::endl;
plaintextMultipartyNew->SetLength(plaintext1->GetLength());
std::cout <<"\n Resulting Fused Plaintext adding 3 ciphertexts: \n"<< std::endl;
std::cout << plaintextMultipartyNew << std::endl;
std::cout <<"\n";}
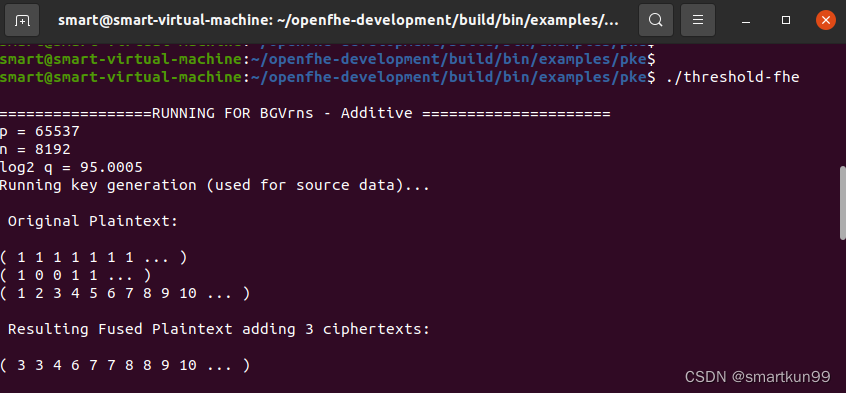
生成密钥
加密(统一用kp3.publickey)
运算
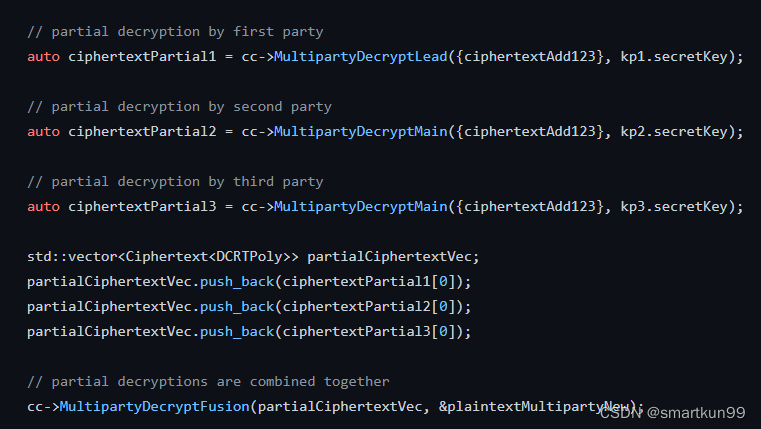
运算(部分解密,再合并)
- kp1解密叫Lead,kp2\kp3解密叫Main)
多密钥阈值CKKS(两方)
voidRunCKKS(){
usint batchSize =16;
CCParams<CryptoContextCKKSRNS> parameters;
parameters.SetMultiplicativeDepth(3);
parameters.SetScalingModSize(50);
parameters.SetBatchSize(batchSize);
CryptoContext<DCRTPoly> cc =GenCryptoContext(parameters);// enable features that you wish to use//启动模块
cc->Enable(PKE);
cc->Enable(KEYSWITCH);
cc->Enable(LEVELEDSHE);
cc->Enable(ADVANCEDSHE);
cc->Enable(MULTIPARTY);// Set-up of parameters// 设置参数// Output the generated parameters
std::cout <<"p = "<< cc->GetCryptoParameters()->GetPlaintextModulus()<< std::endl;
std::cout <<"n = "<< cc->GetCryptoParameters()->GetElementParams()->GetCyclotomicOrder()/2<< std::endl;
std::cout <<"log2 q = "<<log2(cc->GetCryptoParameters()->GetElementParams()->GetModulus().ConvertToDouble())<< std::endl;// Initialize Public Key Containers
KeyPair<DCRTPoly> kp1;
KeyPair<DCRTPoly> kp2;
KeyPair<DCRTPoly> kpMultiparty;// Perform Key Generation Operation// 密钥生成
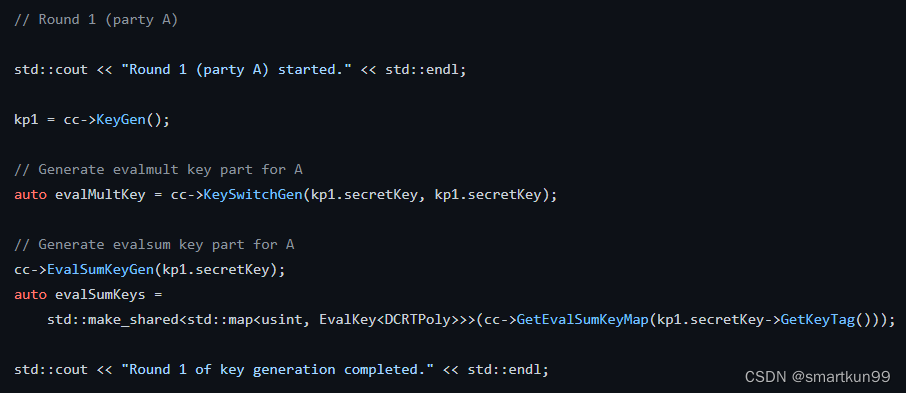
std::cout <<"Running key generation (used for source data)..."<< std::endl;// Round 1 (party A)// 第一轮(A产生)
std::cout <<"Round 1 (party A) started."<< std::endl;// 生成 kp1
kp1 = cc->KeyGen();// Generate evalmult key part for A// 由kp1的secretKey生成evalMultKeyauto evalMultKey = cc->KeySwitchGen(kp1.secretKey, kp1.secretKey);// Generate evalsum key part for A// 由kp1的secretKey生成evalsum key——evalsum表示向量求后面所有值的和
cc->EvalSumKeyGen(kp1.secretKey);auto evalSumKeys =
std::make_shared<std::map<usint, EvalKey<DCRTPoly>>>(cc->GetEvalSumKeyMap(kp1.secretKey->GetKeyTag()));
std::cout <<"Round 1 of key generation completed."<< std::endl;// Round 2 (party B)// 第二轮(B产生)
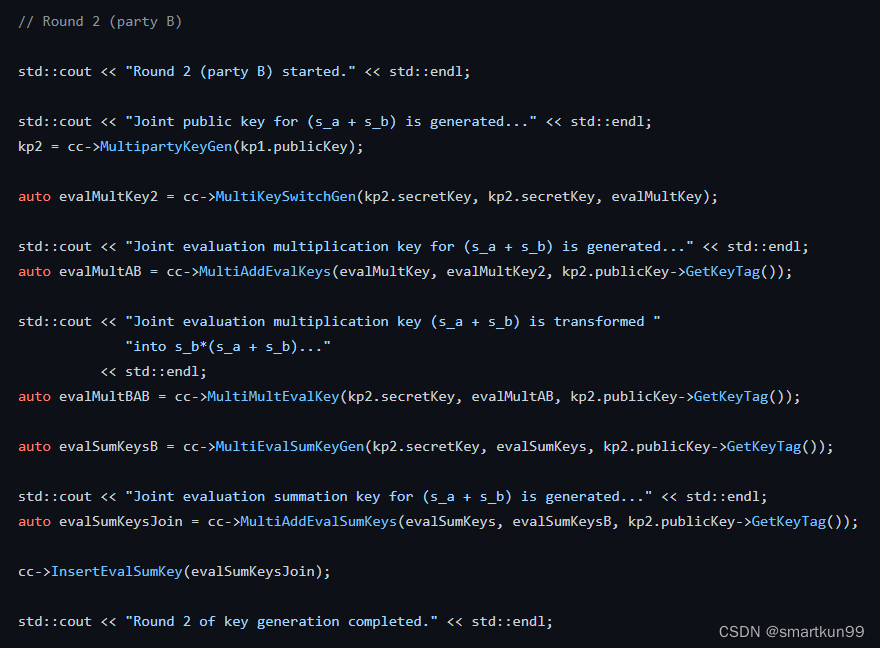
std::cout <<"Round 2 (party B) started."<< std::endl;
std::cout <<"Joint public key for (s_a + s_b) is generated..."<< std::endl;// 由kp1的publicKey生成kp2
kp2 = cc->MultipartyKeyGen(kp1.publicKey);// 由kp2的secretKey生成 evalMultKey2auto evalMultKey2 = cc->MultiKeySwitchGen(kp2.secretKey, kp2.secretKey, evalMultKey);
std::cout <<"Joint evaluation multiplication key for (s_a + s_b) is generated..."<< std::endl;// 由kp2的evalMultKey2和kp1的evalMultKey生成 evalMultABauto evalMultAB = cc->MultiAddEvalKeys(evalMultKey, evalMultKey2, kp2.publicKey->GetKeyTag());
std::cout <<"Joint evaluation multiplication key (s_a + s_b) is transformed ""into s_b*(s_a + s_b)..."<< std::endl;//由kp2的secretKey和publickey把evalMultAB 转换为 evalMultBABauto evalMultBAB = cc->MultiMultEvalKey(kp2.secretKey, evalMultAB, kp2.publicKey->GetKeyTag());//由kp2的secretKey和publickey 由kp1的evalSumKeys 生成 evalSumKeysBauto evalSumKeysB = cc->MultiEvalSumKeyGen(kp2.secretKey, evalSumKeys, kp2.publicKey->GetKeyTag());
std::cout <<"Joint evaluation summation key for (s_a + s_b) is generated..."<< std::endl;//由kp2的evalSumKeysB和publickey 以及 kp1的evalSumKeys 生成最终的 evalSumKeysJoin keyauto evalSumKeysJoin = cc->MultiAddEvalSumKeys(evalSumKeys, evalSumKeysB, kp2.publicKey->GetKeyTag());
cc->InsertEvalSumKey(evalSumKeysJoin);
std::cout <<"Round 2 of key generation completed."<< std::endl;// 第三轮(A产生)
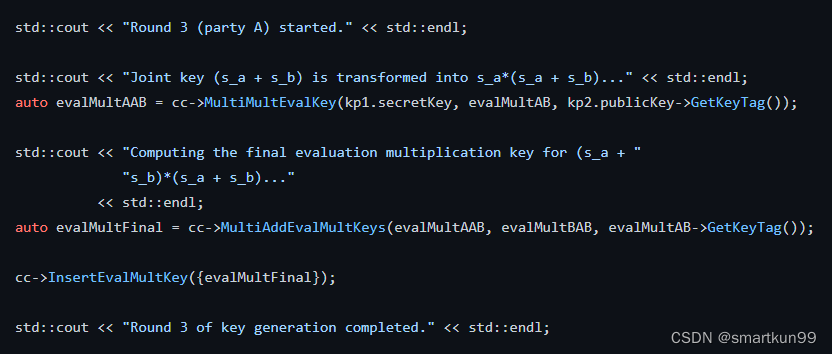
std::cout <<"Round 3 (party A) started."<< std::endl;
std::cout <<"Joint key (s_a + s_b) is transformed into s_a*(s_a + s_b)..."<< std::endl;//由kp1的secretKey和kp2的publickey把evalMultAB 转换为 evalMultAABauto evalMultAAB = cc->MultiMultEvalKey(kp1.secretKey, evalMultAB, kp2.publicKey->GetKeyTag());
std::cout <<"Computing the final evaluation multiplication key for (s_a + ""s_b)*(s_a + s_b)..."<< std::endl;//由kp1的evalMultAAB和kp2的evalMultBAB 以及公开的evalMultAB 转换为 evalMultFinalauto evalMultFinal = cc->MultiAddEvalMultKeys(evalMultAAB, evalMultBAB, evalMultAB->GetKeyTag());
cc->InsertEvalMultKey({evalMultFinal});
std::cout <<"Round 3 of key generation completed."<< std::endl;// Encode source data
std::vector<double> vectorOfInts1 ={1,2,3,4,5,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
std::vector<double> vectorOfInts2 ={1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
std::vector<double> vectorOfInts3 ={2,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,0,0};
Plaintext plaintext1 = cc->MakeCKKSPackedPlaintext(vectorOfInts1);
Plaintext plaintext2 = cc->MakeCKKSPackedPlaintext(vectorOfInts2);
Plaintext plaintext3 = cc->MakeCKKSPackedPlaintext(vectorOfInts3);// Encryption
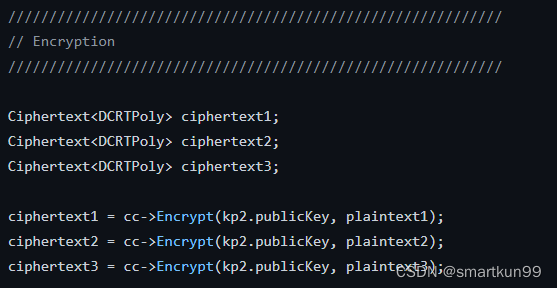
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertext1;
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertext2;
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertext3;// 用kp2.publickey加密
ciphertext1 = cc->Encrypt(kp2.publicKey, plaintext1);
ciphertext2 = cc->Encrypt(kp2.publicKey, plaintext2);
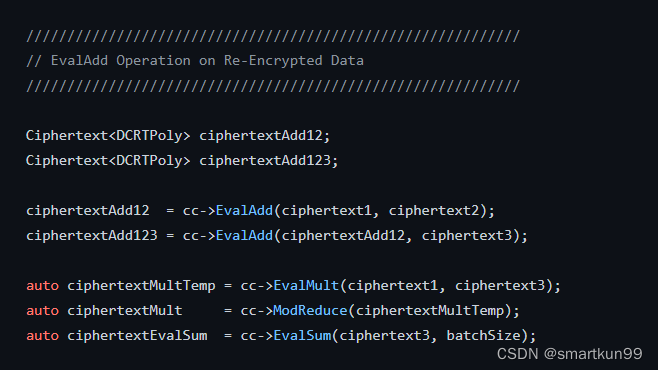
ciphertext3 = cc->Encrypt(kp2.publicKey, plaintext3);// EvalAdd Operation on Re-Encrypted Data
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertextAdd12;
Ciphertext<DCRTPoly> ciphertextAdd123;
ciphertextAdd12 = cc->EvalAdd(ciphertext1, ciphertext2);
ciphertextAdd123 = cc->EvalAdd(ciphertextAdd12, ciphertext3);auto ciphertextMultTemp = cc->EvalMult(ciphertext1, ciphertext3);auto ciphertextMult = cc->ModReduce(ciphertextMultTemp);auto ciphertextEvalSum = cc->EvalSum(ciphertext3, batchSize);// Decryption after Accumulation Operation on Encrypted Data with Multiparty
Plaintext plaintextAddNew1;
Plaintext plaintextAddNew2;
Plaintext plaintextAddNew3;
DCRTPoly partialPlaintext1;
DCRTPoly partialPlaintext2;
DCRTPoly partialPlaintext3;
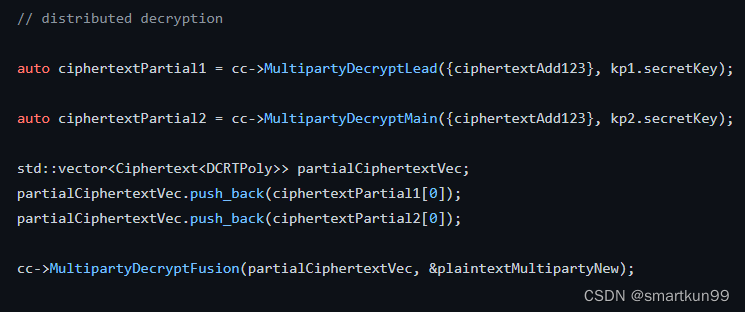
Plaintext plaintextMultipartyNew;const std::shared_ptr<CryptoParametersBase<DCRTPoly>> cryptoParams = kp1.secretKey->GetCryptoParameters();const std::shared_ptr<typenameDCRTPoly::Params> elementParams = cryptoParams->GetElementParams();// distributed decryption//各自用自己的secretkey解密(kp1解密叫Lead,kp2解密叫Main)auto ciphertextPartial1 = cc->MultipartyDecryptLead({ciphertextAdd123}, kp1.secretKey);auto ciphertextPartial2 = cc->MultipartyDecryptMain({ciphertextAdd123}, kp2.secretKey);
std::vector<Ciphertext<DCRTPoly>> partialCiphertextVec;
partialCiphertextVec.push_back(ciphertextPartial1[0]);
partialCiphertextVec.push_back(ciphertextPartial2[0]);//合并密钥
cc->MultipartyDecryptFusion(partialCiphertextVec,&plaintextMultipartyNew);
std::cout <<"\n Original Plaintext: \n"<< std::endl;
std::cout << plaintext1 << std::endl;
std::cout << plaintext2 << std::endl;
std::cout << plaintext3 << std::endl;
plaintextMultipartyNew->SetLength(plaintext1->GetLength());
std::cout <<"\n Resulting Fused Plaintext: \n"<< std::endl;
std::cout << plaintextMultipartyNew << std::endl;
std::cout <<"\n";
Plaintext plaintextMultipartyMult;//(kp1解密叫Lead,kp2解密叫Main)
ciphertextPartial1 = cc->MultipartyDecryptLead({ciphertextMult}, kp1.secretKey);
ciphertextPartial2 = cc->MultipartyDecryptMain({ciphertextMult}, kp2.secretKey);
std::vector<Ciphertext<DCRTPoly>> partialCiphertextVecMult;
partialCiphertextVecMult.push_back(ciphertextPartial1[0]);
partialCiphertextVecMult.push_back(ciphertextPartial2[0]);
cc->MultipartyDecryptFusion(partialCiphertextVecMult,&plaintextMultipartyMult);
plaintextMultipartyMult->SetLength(plaintext1->GetLength());
std::cout <<"\n Resulting Fused Plaintext after Multiplication of plaintexts 1 ""and 3: \n"<< std::endl;
std::cout << plaintextMultipartyMult << std::endl;
std::cout <<"\n";
Plaintext plaintextMultipartyEvalSum;
ciphertextPartial1 = cc->MultipartyDecryptLead({ciphertextEvalSum}, kp1.secretKey);
ciphertextPartial2 = cc->MultipartyDecryptMain({ciphertextEvalSum}, kp2.secretKey);
std::vector<Ciphertext<DCRTPoly>> partialCiphertextVecEvalSum;
partialCiphertextVecEvalSum.push_back(ciphertextPartial1[0]);
partialCiphertextVecEvalSum.push_back(ciphertextPartial2[0]);
cc->MultipartyDecryptFusion(partialCiphertextVecEvalSum,&plaintextMultipartyEvalSum);
plaintextMultipartyEvalSum->SetLength(plaintext1->GetLength());
std::cout <<"\n Fused result after the Summation of ciphertext 3: ""\n"<< std::endl;
std::cout << plaintextMultipartyEvalSum << std::endl;}
生成密钥
第一轮——A 生成公钥、乘法计算密钥、加法计算密钥(A的)
第二轮——B利用A的公钥,生成公钥和乘法计算密钥,加法计算密钥
- 由kp1.publickey生成公钥:Joint public key for (s_a + s_b)
- 乘法计算密钥:Joint evaluation multiplication key for (s_a + s_b)
- 转化乘法计算密钥为:把 (s_a + s_b) 转化为 s_b*(s_a + s_b)
- 生成加法计算密钥为:Joint evaluation summation key for (s_a + s_b)
第三轮——A最后生成最终的乘法计算密钥
- 转化乘法计算密钥为:把 (s_a + s_b) 转化为 s_a*(s_a + s_b)
- 生成最终的乘法计算密钥为 (s_a + s_b) * (s_a + s_b)
加密(统一用kp2.publickey)
运算
解密(部分解密再合并)
版权归原作者 smartkun99 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。