一、算法原理
1.关于伪距单点定位
GPS伪距单点定位的原理比较简单,主要是利用空间距离的后方交会,用一台接收机同时接受四颗卫星的位置坐标和卫星与接收机的距离,运用后方交会原理解算出接收机的三维坐标。其中,如果接收机观测的卫星的数目多于四颗,则采用最小二乘法进行平差计算,求解出接收机坐标。
2.伪距单点定位的具体原理
(1)伪距观测方程
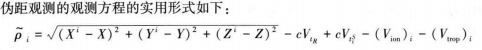
若得到了测站的近似坐标,则可以使用泰勒展开得到线性化方程如下。
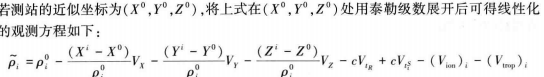
(2)列写伪距观测方程,线性化后,得到误差方程:

(3)计算信号发射时刻卫星i的位置与信号到达时接收机的近似距离之间的距离。


3.伪距单点定位程序的计算步骤
1.读取RINEX N文件,将所有星历放置到一个列表ephlst(数组)中。
2.读取RINEX O文件,读取一个历元观测值epoch。
3.数据预处理
根据数组中的卫星号和历元时刻T在ephlst查找相应的卫星星历,
准则

4.程序初始化,设置测站概略位置为Xr,接受机钟差dtr。



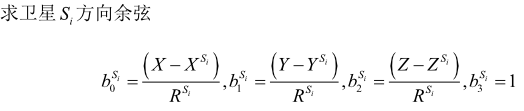
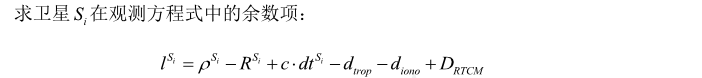



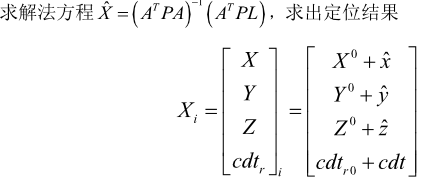

14.输出该历元定位结果
二、程序设计
1.读取文件及数据准备
# 数据处理
import numpy
def donfile(path):
with open(path, 'r') as f:
# 获取行数
lines_n = f.readlines()
Ndata = []
# 获取数据组数
data_line_num = int(len(lines_n) / 8)
print(data_line_num)
Ndataitemkeys = ['IODE', 'Crs', 'Delta_n', 'M0', 'Cuc', 'e', 'Cus', 'sqrt_A', 'TEO', 'Cic', 'OMEGA_A0', 'Cis', 'i0',
'Crc',
'omega', 'OMEGA_DOT', 'IDOT', 'L2Codes', 'GPSWEEK', 'L2PCODE', '卫星精度', '卫星健康状态', 'TGD', 'IODC',
'电文发送时刻', '拟合区间', '备用1', '备用2']
# 遍历
for i in range(data_line_num):
Ndataitem = {}
k = 0
for j in range(8):
data_countent = lines_n[8 * i + j]
Ndataitem['数据组号'] = i + 1
if j == 0:
Ndataitem['卫星PRN号'] = data_countent.strip('\n')[0:3]
Ndataitem['历元'] = data_countent.strip('\n')[4:23]
I = data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42] # [:-4]+ 'e' + data_countent.strip('\n')[24:42][-3:]
Ndataitem['卫星钟差参数s'] = str(float(
(data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42][:-4].strip()) + 'e' + data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42][-3:]))
Ndataitem['卫星钟漂参数s/s'] = str(float(data_countent.strip('\n')[42:61][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0, -int( data_countent.strip( '\n')[42:61][-2:])))
Ndataitem['卫星钟漂速度参数s/s/s'] = str( float(data_countent.strip('\n')[61:80][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0,int(data_countent.strip('\n')[62:80][-2:])))
IB = data_countent.strip('\n')[2:22][-4] # 1-1.731250000000
elif 0 < j < 7:
if data_countent.strip('\n')[4:23][-3] == '-':
Ndataitem[Ndataitemkeys[k]] = str(
float(data_countent.strip('\n')[4:23][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0, -int(
data_countent.strip('\n')[4:23][-2:])))
else:
Ndataitem[Ndataitemkeys[k]] = str(
float(data_countent.strip('\n')[4:23][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0,
int(data_countent.strip('\n')[
4:23][-2:])))
if data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42][-3] == '-':
Ndataitem[Ndataitemkeys[k + 1]] = str(
float(data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0, -int(
data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42][-2:])))
# IB = data_countent.strip('\n')[2:22][-4] # 1-1.731250000000
else:
B = data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42][:-4]
Ndataitem[Ndataitemkeys[k + 1]] = str(
float(data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0, int(data_countent.strip('\n')[23:42][-2:])))
if data_countent.strip('\n')[42:61][-3] == '-':
Ndataitem[Ndataitemkeys[k + 2]] = str(float(data_countent.strip('\n')[42:61][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0, -int(data_countent.strip('\n')[42:61][-2:])))
else:
Ndataitem[Ndataitemkeys[k + 2]] = str(
float(data_countent.strip('\n')[42:61][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0,int(data_countent.strip( '\n')[42:61][-2:])))
if data_countent.strip('\n')[61:80][-3] == '-':
Ndataitem[Ndataitemkeys[k + 3]] = str(float(data_countent.strip('\n')[61:80][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0, -int(data_countent.strip('\n')[61:80][-2:])))
else:
Ndataitem[Ndataitemkeys[k + 3]] = str( float(data_countent.strip('\n')[61:80][:-4].strip()) * numpy.power(10.0, int(data_countent.strip('\n')[61:80][-2:])))
k = k + 4
if len(Ndataitem) > 4:
Ndata.append(Ndataitem)
return Ndata
def head_num(lines_n):
for i in range(len(lines_n)):
if lines_n[i].find('END OF HEADER') != -1:
data_num = i + 1
return data_num
2.卫星位置以及迭代计算
import math
import numpy
from numpy import *
def nfilecompute(Ndata):
#计算xyz的三维坐标
xyzs = []
A1=[]
L1=[]
#初值测站坐标-2424425.1013 5377188.1768 2418617.7454
#初值化
X0=mat([[0],[0],[0],[0]])
sum=1
#导入C1码数据即伪距观测值
C1=[21937747.840,24275893.980,21322965.800,22097191.620,24075984.740, 21068789.740,20803383.780 ]
C2 = [float(1/21937747.84), float(1/24275893.98), float(1/21322965.8), float(1/24606230.92), float(1/22097191.62),float( 1/24075984.74), float(1/21068789.74)]
while True:
for ii in range(len(Ndata)):
xyz = []
#系数矩阵
A=[]
c = 299792458 # 光速常数
u = 3.986004418e14#地球引力常数
a = numpy.power(float(Ndata[ii]['sqrt_A']) ,2)#卫星轨道长半径a
n0 = numpy.sqrt(u/numpy.power(a , 3))#参考时刻TOE平均角速度n0
n = n0 + float(Ndata[ii]['Delta_n'])#时刻未定的平均角速度n
e = float(Ndata[ii]['e'])#椭圆轨道偏心率
we = 7.2921151467e-5
cal=[]
cal.append(int(Ndata[ii]['历元'][:4])) #年
cal.append(int(Ndata[ii]['历元'][5:7]))#月
cal.append(int(Ndata[ii]['历元'][9:10]))#日
cal.append(int(Ndata[ii]['历元'][12:13]))#时
cal.append(int(Ndata[ii]['历元'][14:16]))#分
cal.append(int(Ndata[ii]['历元'][17:19]))#秒
#计算参考时刻的时间
t_oc = cal2gps(cal)#将UTC转换为GPS周内秒
#计算观测时间(历元时刻)
t=cal2gps([2022,3,9,0,0])
#卫星钟差改正
a_0=float(Ndata[ii]['卫星钟差参数s'])
a_1=float(Ndata[ii]['卫星钟漂参数s/s'])
a_2=float(Ndata[ii]['卫星钟漂速度参数s/s/s'])
#观测时刻2022,3,9,0,0,计算卫星钟差δt
δt = a_0 + a_1*(t[1] - t_oc[1]) + a_2*((t[1]-t_oc[1])^2)
# dtr = C1[ii] / c #dtr
#接收机钟差
dtr = float(X0[3][0])/c
# print(dtr)
dtsi = δt # 卫星钟差
#while True:
# 选择数据中的一颗卫星的观测值设伪距为C1[ii](需要迭代)
# 计算卫星Sii的信号发射的概略时刻,Tsii
# (a)计算卫星Sii的信号传播时间dtsii
dtsii = C1[ii] / c - dtr + dtsi
Tr = t[1] # Tr历元时刻
# (b)计算卫星Sii的信号发射时刻Tsii
Tsii = Tr - dtsii
t2 = Tsii - δt
#计算dtr
while True:
tk = t2 - float(Ndata[ii]['TEO']) # 规划时间
M = float(Ndata[ii]['M0']) + n*tk#观测卫星瞬间平近点角M TOE参考时刻 t接收机接收卫星信号时刻(变量)
E = computeE(M,e)#利用迭代方式解算偏近点角E
f = 2 * math.atan(numpy.sqrt((1+e)/(1-e))*math.tan(E/2))
_theta = f + float(Ndata[ii]['omega'])
g_theta , g_r , g_i = sdgz(float(Ndata[ii]['Cuc']) , float(Ndata[ii]['Cus']) , float(Ndata[ii]['Crc']) , float(Ndata[ii]['Crs']) , float(Ndata[ii]['Cic']) , float(Ndata[ii]['Cis']) , _theta)
theta = _theta + g_theta
r = a * (1 - e * math.cos(E)) + g_r
i = float(Ndata[ii]['i0']) + g_i + float(Ndata[ii]['IDOT']) * tk
x = r * math.cos(theta)#卫星在轨道平面坐标系中的x
y = r * math.sin(theta)#卫星在轨道平面坐标系中的y
OMEGA = float(Ndata[ii]['OMEGA_A0']) + (float(Ndata[ii]['OMEGA_DOT']) - we)*t[1] - (float(Ndata[ii]['OMEGA_DOT']) * float(Ndata[ii]['TEO']))
#计算地心地固坐标
X1 = x * math.cos(OMEGA) - y * math.cos(i) * math.sin(OMEGA)
Y1 = x * math.sin(OMEGA) + y * math.cos(i) * math.cos(OMEGA)
Z1 = y * math.sin(i)
#初始化,置测站概略位置为xyz_0,接受机钟差初值为dtr
#xyz_0_coord = [0,0,0]
x_0 = float(X0[0][0])
y_0 = float(X0[1][0])
z_0 = float(X0[2][0])
# (c)计算卫星sii在Tsi的位置
#计算发射时刻的卫星坐标(近似坐标),并且对卫星坐标进行地球自传改正
tch=C1[ii]/c
X=X1*cos(we*tch)+Y1*sin(we*tch)
Y=-sin(we*tch)*X1+Y1*cos(we*tch)
Z=Z1
#计算近似卫星在接受时刻的坐标
#计算卫星和测站的近似几何距离
disct0 = numpy.sqrt(numpy.power((X - x_0), 2) + numpy.power((Y - y_0), 2) + numpy.power((Z- z_0), 2))
#几何距离 求信号传播时间
dts1ii=disct0/c
g=dts1ii-dtsii
if(abs(dts1ii-dtsii)<10.0e-7):
break
else:
dtsii=dts1ii
sum=sum+1
#rs
b0=-(X-x_0)/disct0
b1=-(Y-y_0)/disct0
b2=-(Z-z_0)/disct0
b3=1
#获取系数矩阵A
A.append(b0)
A.append(b1)
A.append(b2)
A.append(b3)
#计算lso和L矩阵
L=[]
rs=disct0#卫星si到测站的几何距离
psi=C1[ii]#卫星si的伪距观测值
cdtsi=δt#以米表示的卫星si的钟差
dtrop=0#对流层延迟改正量,单位米,用简化的 模型计算对流层延迟改正量,单位米,用简化的模型计算
diono=0#电离层延迟改正量,单位为米,采用无电离层组合观测值时,此处为0
Drtcm=0#对伪距的差分改正值,此处为0
lso=psi-rs+cdtsi*c-dtrop-diono+Drtcm
#将计算后lso添加进L
L.append(lso)
xyz.append(X)
xyz.append(Y)
xyz.append(Z)
xyzs.append(xyz)
A1.append(A)
L1.append(L)
#将数组转为矩阵
A2=mat(A1)
L2=mat(L1)
#计算权阵
mat_P = mat(diag(C2))
#加入权阵后
mat_mid = A2.T * mat_P *A2
ary_mid_tr = around(mat_mid.astype(float), decimals=20)
mat_mid_tr = mat(ary_mid_tr)
x2 = mat_mid_tr.I * A2.T * mat_P * L2
Xi=X0+x2
if abs(float(x2[0][0]))>0.001 and abs(float(x2[1][0]))>0.001 and abs(float(x2[2][0]))>0.001 :#or abs(float(x2[3][0]))<0.001:
X0=Xi
A=[]
A1=[]
xyzs=[]
xyz=[]
L=[]
L1=[]
else:
X0=Xi
print("最终的接收机坐标结果为:\n",X0)
resultx=(abs(-2424425.1013-X0[0,0])/abs(-2424425.1013))*100
resulty=(abs(5377188.1768-X0[1,0]) /abs(5377188.1768))*100
resultz=(abs(2418617.7454-X0[2,0])/abs(2418617.7454))*100
print("误差分析:\n")
print("X坐标误差为百分之:{}".format(resultx))
print("Y坐标误差为百分之:{}".format(resulty))
print("Z坐标误差为百分之:{}".format(resultz))
break
return [xyzs,A1,L1,Xi]
def computeE(M,e):
E = 0.0
while True:
E0 = E
E = M + e*math.sin(E0)
if abs(E - E0) <0.001:
break
return E
def sdgz(Cuc , Cus , Crc , Crs , Cic , Cis , theta):
g_theta = Cuc * math.cos(2*theta) + Cus * math.sin(2 * theta)
g_r = Crc * math.cos(2*theta) + Crs * math.sin(2 * theta)
g_i = Cic * math.cos(2*theta) + Cis * math.sin(2 * theta)
return g_theta , g_r , g_i
def cal2gps(cal):
# cal2gps 将公历GPS时间转换到GPS周和周内的秒
# 返回列表,周和周内秒
mjd=cal2mjd(cal)
#GPS从MJD44244开始
e=mjd-44244
week=math.floor(e/7)
e=e-week*7
return [week,round(e*86400)]
def cal2mjd(cal):
# cal2jd 将公历年月日时分秒转换到简化儒略日。
# 输入公历时间列表,返回儒略日
if (len(cal) < 6):
for i in range(len(cal), 6):
cal.append(0)
year = cal[0]
month = cal[1]
day = cal[2] + (cal[3] * 3600 + cal[4] * 60 + cal[5]) / 86400;
y = year + 4800
m = month
if (year < 0):
print('Year is wrong')
return False
if (m <= 2):
# 1,2月视为前一年13,14月
m = m + 12
y = y - 1
e = math.floor(30.6 * (m + 1))
a = math.floor(y / 100)
# 教皇格雷戈里十三世于1582年2月24日以教皇训令颁布,将1582年10月5日至14抹掉。1582年10月4日过完后第二天是10月15日
if (year < 1582) or (year == 1582 and month < 10) or (year == 1582 and month == 10 and day < 15):
b = -38
else:
b = math.floor((a / 4) - a)
c = math.floor(365.25 * y)
jd = b + c + e + day - 32167.5
mjd = jd - 2400000.5
return mjd
3.主函数编写
from data import donfile
from 卫星位置 import nfilecompute
filename="C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\GPS!.txt"
nfilecompute(donfile(filename))
三、总结
在程序编写中,没有进行电离层改正等误差改正,没有完善模型,计算误差在米级,误差较小,可以使用,供交流学习。
版权归原作者 学测绘的小杨 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。