简洁概要:
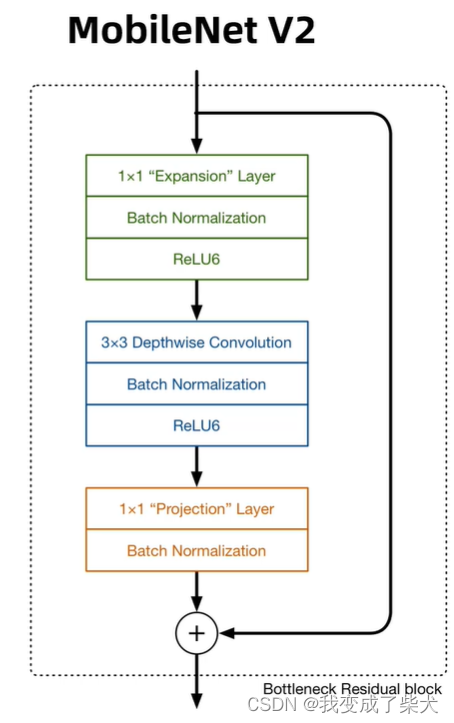
MobileNetV2主要采用了深度可分离卷积,在MobileNetv1的基础上引用了残差模块以及Relu6的激活函数,用1n,n1的思想代替了n*n的矩阵,计算量会更小。
修改主干网络:
一:添加自己主干网络
yolov5 6.1的版本中,在models/common中添加MobilenetV2作为backbone
class ConvBNReLU(nn.Sequential): # 该函数主要做卷积 池化 ReLU6激活操作
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1):
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 # 池化 = (步长-1)整除2
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__( # 调用ConvBNReLU父类添加模块
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride, padding, bias=False, groups=groups), # bias默认为False
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True))
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module): # 该模块主要实现了倒残差模块
def __init__(self, inp, oup, stride, expand_ratio): # inp 输入 oup 输出 stride步长 exoand_ratio 按比例扩张
super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
assert stride in [1, 2]
hidden_dim = int(round(inp * expand_ratio)) # 由于有到残差模块有1*1,3*3的卷积模块,所以可以靠expand_rarton来进行升维
self.use_res_connect = self.stride == 1 and inp == oup # 残差连接的判断条件:当步长=1且输入矩阵与输出矩阵的shape相同时进行
layers = []
if expand_ratio != 1: # 如果expand_ratio不等于1,要做升维操作,对应图中的绿色模块
# pw
layers.append(ConvBNReLU(inp, hidden_dim, kernel_size=1)) # 这里添加的是1*1的卷积操作
layers.extend([
# dw
ConvBNReLU(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, stride=stride, groups=hidden_dim),
# 这里做3*3的卷积操作,步长可能是1也可能是2,groups=hidden_dim表示这里使用了分组卷积的操作,对应图上的蓝色模块
# pw-linear
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False), # 对应图中的黄色模块
nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
])
self.conv = nn.Sequential(*layers) # 将layers列表中的元素解开依次传入nn.Sequential
def forward(self, x):
if self.use_res_connect: # 如果使用了残差连接,就会进行一个x+的操作
return x + self.conv(x)
else:
return self.conv(x) # 否则不做操作
二:在yolo.py中添加common中的两个函数
if m in (Conv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, MixConv2d, Focus, CrossConv,
BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost, nn.ConvTranspose2d, DWConvTranspose2d, C3x,
ConvBNReLU, InvertedResidual): # 添加 common中新加的两个模块 ConvBNReLU和InvertedResidual
三:制作mobilenetv2的yaml配置文件
# Parameters
nc: 1 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 1.0 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.0 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [ 10,13, 16,30, 33,23 ] # P3/8
- [ 30,61, 62,45, 59,119 ] # P4/16
- [ 116,90, 156,198, 373,326 ] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[ [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 32, 3, 2 ] ], # 0-P1/2 32x320x320
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 16, 1, 1 ] ], # 1 16x320x320
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 24, 2, 6 ] ], # 2-P2/4 24x160x160
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 24, 1, 6 ] ], # 3-P2/4 24x160x160
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 32, 2, 6 ] ], # 4-P3/8 32x80x80
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 32, 1, 6 ] ], # 5-P3/8 32x80x80
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 32, 1, 6 ] ], # 6-P3/8 32x80x80
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 64, 2, 6 ] ], # 7-P4/16 64x40x40
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 64, 1, 6 ] ], # 8-P4/16 64x40x40
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 64, 1, 6 ] ], # 9-P4/16 64x40x40
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 64, 1, 6 ] ], # 10-P4/16 64x40x40
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 96, 1, 6 ] ], # 11 96X40X40
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 96, 1, 6 ] ], # 12 96X40X40
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 96, 1, 6 ] ], # 13 96X40X40
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 160, 2, 6 ] ], # 14-P5/32 160X20X20
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 160, 1, 6 ] ], # 15-P5/32 160X20X20
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 160, 1, 6 ] ], # 16-P5/32 160X20X20
[ -1, 1, InvertedResidual, [ 320, 1, 6 ] ], # 17 320X20X20
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[ [ -1, 1, Conv, [ 160, 1, 1 ] ],
[ -1, 1, nn.Upsample, [ None, 2, 'nearest' ] ],
[ [ -1, 13 ], 1, Concat, [ 1 ] ], # cat backbone P4
[ -1, 1, C3, [ 160, False ] ], # 21
[ -1, 1, Conv, [ 80, 1, 1 ] ],
[ -1, 1, nn.Upsample, [ None, 2, 'nearest' ] ],
[ [ -1, 6 ], 1, Concat, [ 1 ] ], # cat backbone P3
[ -1, 1, C3, [ 80, False ] ], # 25 (P3/8-small)
[ -1, 1, Conv, [ 80, 3, 2 ] ],
[ [ -1, 22 ], 1, Concat, [ 1 ] ], # cat head P4
[ -1, 1, C3, [ 160, False ] ], # 28 (P4/16-medium)
[ -1, 1, Conv, [ 160, 3, 2 ] ],
[ [ -1, 18 ], 1, Concat, [ 1 ] ], # cat head P5
[ -1, 1, C3, [ 320, False ] ], # 31 (P5/32-large)
[ [ 25, 28, 31 ], 1, Detect, [ nc, anchors ] ], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
四:制作数据集VOC的yaml配置文件
# YOLOv5 by Ultralytics, GPL-3.0 license
# PASCAL VOC dataset http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC by University of Oxford
# Example usage: python train.py --data VOC.yaml
# parent
# ├── yolov5
# └── datasets
# └── VOC ← downloads here (2.8 GB)
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
path: E:\yolov5-6.1\VOCdevkit
train: # train images (relative to 'path') 16551 images
- images/train
val: # val images (relative to 'path') 4952 images
- images/val
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes
nc: 1 # number of classes
names: [ 'ball' ] # class names
# Download script/URL (optional) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
download: |
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from tqdm import tqdm
from utils.general import download, Path
def convert_label(path, lb_path, year, image_id):
def convert_box(size, box):
dw, dh = 1. / size[0], 1. / size[1]
x, y, w, h = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1, (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1, box[1] - box[0], box[3] - box[2]
return x * dw, y * dh, w * dw, h * dh
in_file = open(path / f'VOC{year}/Annotations/{image_id}.xml')
out_file = open(lb_path, 'w')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls in yaml['names'] and not int(obj.find('difficult').text) == 1:
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
bb = convert_box((w, h), [float(xmlbox.find(x).text) for x in ('xmin', 'xmax', 'ymin', 'ymax')])
cls_id = yaml['names'].index(cls) # class id
out_file.write(" ".join([str(a) for a in (cls_id, *bb)]) + '\n')
# Download
dir = Path(yaml['path']) # dataset root dir
url = 'https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v1.0/'
urls = [f'{url}VOCtrainval_06-Nov-2007.zip', # 446MB, 5012 images
f'{url}VOCtest_06-Nov-2007.zip', # 438MB, 4953 images
f'{url}VOCtrainval_11-May-2012.zip'] # 1.95GB, 17126 images
download(urls, dir=dir / 'images', delete=False, curl=True, threads=3)
# Convert
path = dir / 'images/VOCdevkit'
for year, image_set in ('2007', 'train'), ('2007', 'val'), ('2007', 'test'):
imgs_path = dir / 'images' / f'{image_set}{year}'
lbs_path = dir / 'labels' / f'{image_set}{year}'
imgs_path.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
lbs_path.mkdir(exist_ok=True, parents=True)
with open(path / f'VOC{year}/ImageSets/Main/{image_set}.txt') as f:
image_ids = f.read().strip().split()
for id in tqdm(image_ids, desc=f'{image_set}{year}'):
f = path / f'VOC{year}/JPEGImages/{id}.jpg' # old img path
lb_path = (lbs_path / f.name).with_suffix('.txt') # new label path
f.rename(imgs_path / f.name) # move image
convert_label(path, lb_path, year, id) # convert labels to YOLO format
五:启用训练
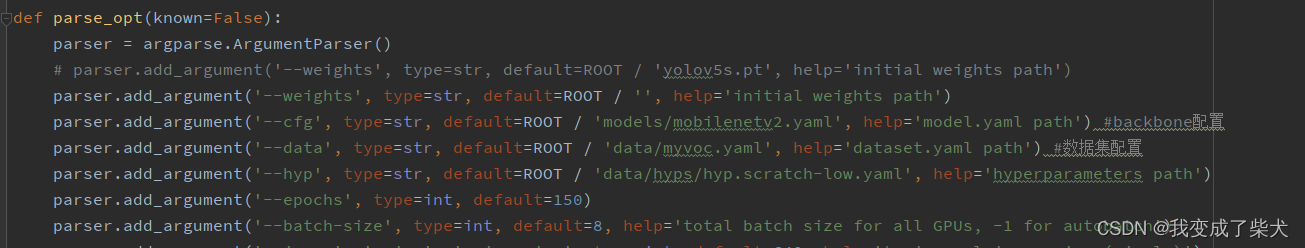 由于修改了网络所以不能加载预训练模型进行
由于修改了网络所以不能加载预训练模型进行
预训练模型的作用:加快模型训练初期的超参数训练时间
weights修改为空
cfg修改为自己网络模型的配置文件
data修改为自己VOC数据集的配置文件
六:性能检测
修改val.py的参数,与上一步一致
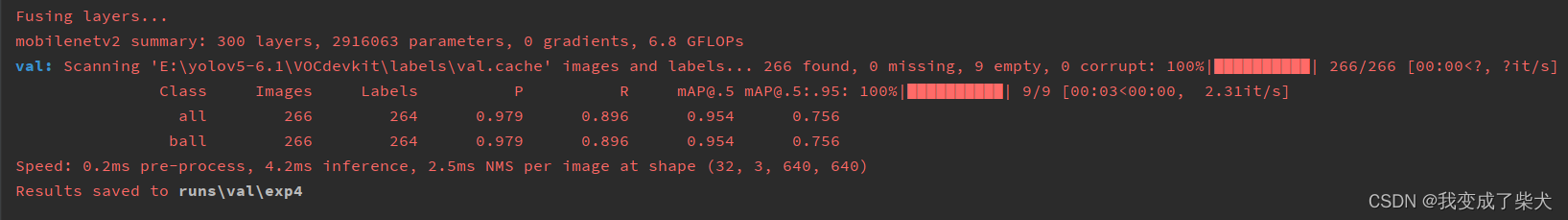
这里分别用了V5s,V5n,以及mobilenetV2分别做了150批次训练来对比
mobilenetV2
V5s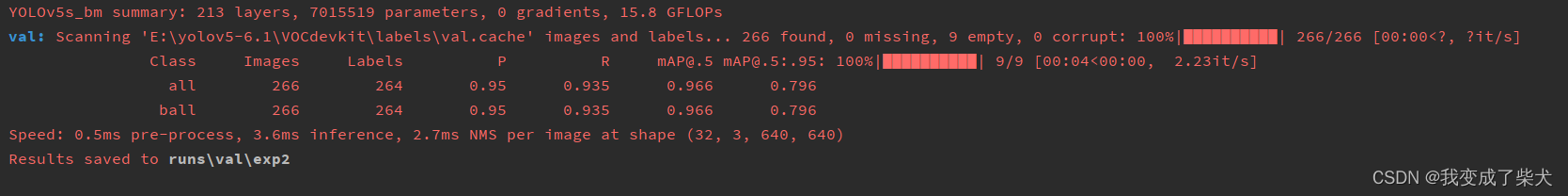
V5n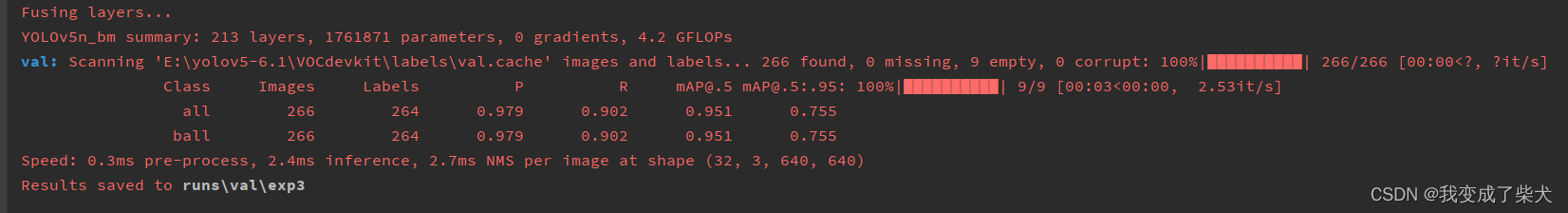
对比可以发现 V5n与mobilenetV2的相差并不大,相比较于这两个模型,V5s的精度稍微高一些,但是它模型的复杂度会略微大一丢丢,推理时间略大一点。
版权归原作者 我变成了柴犬 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。