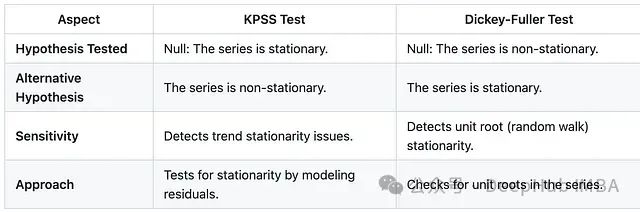
在进行时间序列分析之前,确定序列的平稳性是一个关键步骤。平稳性指的是时间序列的统计特性(如均值和方差)在时间维度上保持不变。本文将详细介绍如何运用 KPSS 检验和 Dickey-Fuller 检验来验证序列的平稳性。这两种检验方法基于不同的统计假设:KPSS 检验的原假设是数据非平稳,而 Dickey-Fuller 检验则假设数据平稳。
时间序列平稳性的基本概念
时间序列的平稳性主要体现在三个方面:
- 均值稳定性:序列的期望值在时间维度上保持恒定
- 方差稳定性:数据波动范围保持相对稳定
- 无周期性:数据不存在明显的周期性波动或循环模式
平稳性是许多时间序列模型(如 ARIMA)的基本假设条件,对模型的有效性具有重要影响。
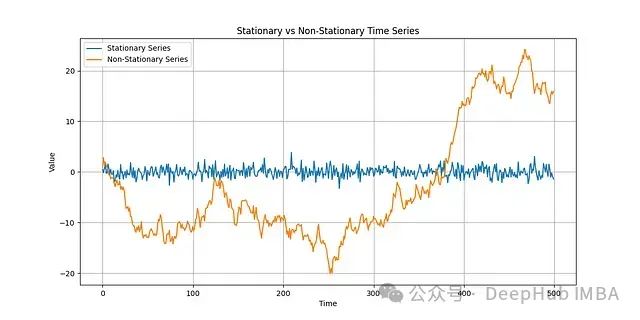
以下我们将通过构造平稳序列和非平稳序列来演示这两种检验方法的应用。
importnumpyasnp
importpandasaspd
importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt
fromstatsmodels.tsa.stattoolsimportadfuller, kpss
# 构造平稳时间序列(白噪声过程)
np.random.seed(42)
stationary_series=np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=500)
# 构造非平稳时间序列(随机游走过程)
non_stationary_series=np.cumsum(np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=500))
# 创建数据框用于后续分析
data=pd.DataFrame({
"Stationary": stationary_series,
"Non-Stationary": non_stationary_series
})
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(data['Stationary'], label='Stationary Series')
plt.plot(data['Non-Stationary'], label='Non-Stationary Series')
plt.title('Stationary vs Non-Stationary Time Series')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.savefig('stationary_vs_non_stationary.png')
plt.show()
![]
defkpss_test(series):
statistic, p_value, _, critical_values=kpss(series, regression='c')
print("KPSS Test:")
print(f"Statistic: {statistic:.4f}")
print(f"P-Value: {p_value:.4f}")
print("Critical Values:")
forkey, valueincritical_values.items():
print(f"{key}: {value:.4f}")
print(f"Conclusion: {'Stationary'ifp_value>0.05else'Non-Stationary'}\n")
defadf_test(series):
statistic, p_value, _, _, critical_values, _=adfuller(series)
print("Dickey-Fuller Test:")
print(f"Statistic: {statistic:.4f}")
print(f"P-Value: {p_value:.4f}")
print("Critical Values:")
forkey, valueincritical_values.items():
print(f"{key}: {value:.4f}")
print(f"Conclusion: {'Stationary'ifp_value<0.05else'Non-Stationary'}\n")
print("Testing the Stationary Series:\n")
kpss_test(data['Stationary'])
adf_test(data['Stationary'])
print("Testing the Non-Stationary Series:\n")
kpss_test(data['Non-Stationary'])
adf_test(data['Non-Stationary'])
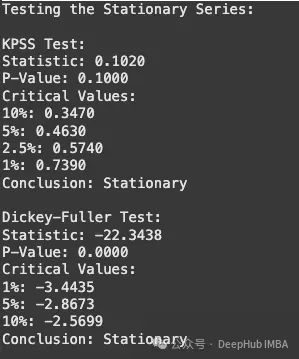
平稳序列检验结果分析:
- KPSS 检验结果显示 p 值大于显著性水平 0.05,未能拒绝序列平稳的原假设
- Dickey-Fuller 检验的 p 值小于 0.05,拒绝序列存在单位根的原假设,证实序列平稳性
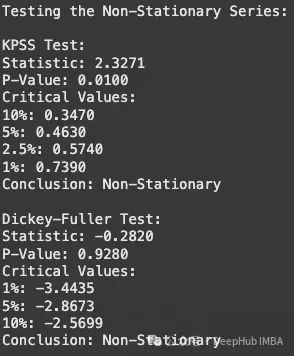
非平稳序列检验结果分析:
- KPSS 检验的 p 值小于 0.05,拒绝平稳性假设,表明序列非平稳
- Dickey-Fuller 检验的 p 值大于 0.05,未能拒绝单位根假设,同样证实序列非平稳性
总结
时间序列的平稳性检验是建模过程中的重要环节。KPSS 和 Dickey-Fuller 检验提供了两种互补的统计方法,可以帮助研究者准确评估序列的平稳性特征,并为后续的数据转换(如差分处理)提供依据。
- KPSS 检验适用于验证时间序列是否围绕确定性趋势呈现平稳特性
- Dickey-Fuller 检验主要用于检验序列是否存在单位根,尤其适用于 ARIMA 建模前的平稳性验证
由于这两种检验方法基于不同的统计假设,在实际应用中通常建议同时使用两种方法进行交叉验证,以获得更可靠的结论。