此文章仅大致讲解yolov5神经网络结构,具体理论知识请自行学习神经网络。(电脑阅读体验更佳)
目录
在解析yolo文件之前,我们需要先了解yolov5的网络结构是怎么样的:
yolov5s.yaml:
(这个文件其实只是指导我们搭建模型的配置文件的说明书,供我们参考,我们可以参考此文件配置自己的模型文件)
先如图了解yolov5网络结构:
我们先了解一下中间的Backone,Head是什么东西:
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
backbone: 仅仅表示数字的含义
# 0-P1/2 第一层
from:-1表示该输入从上一层传过来,【-1,6】表示从11和6层传过来
number:表示模块结构数量,若number>1,则数量=number*depth_multiple
module:模块结构(Conv、C3等),卷积层结构,定义于(**common.py**)
args: 传入参数,需要联系到common各网络层模型类别确定各参数含义
P1: 第一层
/2: 步长为2,图片长宽尺寸分别除以2(图片分辨率要求长宽为32倍数的原因)
# 1-P2/4 第二层:
依次往下逐层叠加
head: 这里和backbone一样也是由各网络层组成
**nn.Upsample**: 上采样层
**Concat**: 综合各层传出特征的网络层
** Detect: ** 推理检测层
我们留意到这里一共有24层神经网络层,那么这24层是怎么相互叠加的呢,是简单的逐层叠加吗?
答案显然不是,实际上的网络结构是这样的:(网上多处的网络结构解析backbone都是从上往下叠加的,这里我是从B站up:480920279那里取经得到的从下往上的神经网络结构)
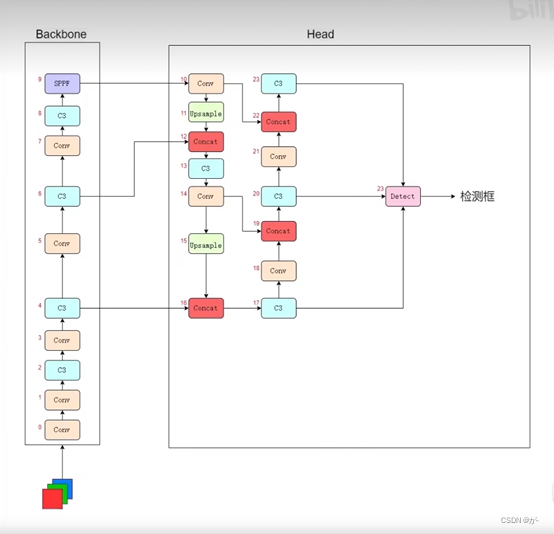
这个图的意思是,我们往神经网络中传入一个RGB三通道的图片,经Backbone10层网络后,进入Head进行上采样,综合特征处理等,最终有3个C3网络层输出到Detect层,这3个C3层从上到下就是我们说的高层特征层、中层特征层、低层特征层。
这些特征层区别在于低层检测小目标,中层检测中型目标,高层检测大目标,综合起来预测目标。
# Parameters
nc: 6 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
nc: (number of classes)目标类别数
Anchors: 三层对应不同的特征层级
[10,13, 16,30, 33,23] 低层3个anchor,10×13,16×30,33×23
[30,61, 62,45, 59,119] 中层3个anchor
depth_multiple: 模型深度倍数,创建模型时number* depth_multiple
width_multiple: 通道倍数,每层通道参数* width_multiple=传出通道数,深度宽度参数相乘不为整向下取整
depth_multiple,width_multiple决定模型复杂程度,值越大越复杂准确率越高,耗时长
对于各种模型文件的准确率:n<s<m<l<x(准确率越高,耗时越长)(这些文件的区别也仅仅是深度倍数和通道倍数的不同而已)
因此,我们可以参照此说明书自己写一个模型配置文件。
了解神经网络结构后,我们到yolo.py中看看神经网络是怎么实现的:
yolo.py:
if __name:
**create model**: **创建yolov5模型**
(这里可能会出现有几种写法):
第一种:
# Create model
im = torch.rand(opt.batch_size,3,640,640).to(device)
model = Model(opt.cfg).to(device)
第二种:
# Create model
model = Model(opt.cfg).to(device)
model.train()
# Profile
if opt.profile:
img = torch.rand(8 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 1, 3, 640, 640).to(device)
y = model(img, profile=True)
im(g): 随机定义一张图片
y=model: 定义模型(——>Model)
(Options):
Model:
init: 搭建网络结构
def __init__(self, cfg='yolov5s.yaml', ch=3, nc=None, anchors=None): # model, input channels, number of classes
super().__init__()
if isinstance(cfg, dict):
self.yaml = cfg # model dict
else: # is *.yaml
import yaml # for torch hub
self.yaml_file = Path(cfg).name
with open(cfg, encoding='ascii', errors='ignore') as f:
self.yaml = yaml.safe_load(f) # model dict
cfg: 配置文件(yolov5s.yaml)
ch: 输入图片通道数
super().init: 加载配置文件
判断传入的是否为字符串
self.yaml_file 获取文件名
with: 开始加载文件,关键元素以字典形式存放
Define model: 定义模型
# Define model
ch = self.yaml['ch'] = self.yaml.get('ch', ch) # input channels
if nc and nc != self.yaml['nc']: # 判断该值和yaml中的值是否一样
LOGGER.info(f"Overriding model.yaml nc={self.yaml['nc']} with nc={nc}")
self.yaml['nc'] = nc # override yaml value
if anchors:
LOGGER.info(f'Overriding model.yaml anchors with anchors={anchors}')
self.yaml['anchors'] = round(anchors) # override yaml value
self.model, self.save = parse_model(deepcopy(self.yaml), ch=[ch]) # model, savelist
self.names = [str(i) for i in range(self.yaml['nc'])] # default names
self.inplace = self.yaml.get('inplace', True)
ch: 定义通道数
nc、anchor: 校正类数量
.model: 搭建模型(——>parse_model)
.names: 类别名
.inplace: 加载关键字
Build:
# Build strides, anchors
m = self.model[-1] # Detect()
if isinstance(m, Detect):
s = 256 # 2x min stride
m.inplace = self.inplace
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in self.forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward:[8, 16, 32]
m.anchors /= m.stride.view(-1, 1, 1)
check_anchor_order(m)
self.stride = m.stride
self._initialize_biases() # only run once
判断model上一层是否为detect层
m.stride: 将s*s图片放入低中高特征层次中预测,将原尺寸除以预测层尺寸 获得步长
m.anchors /=: anchors除以步长
check_anchor: 检验传入的anchor顺序
forward: 对输入图片预测
parse_model:
LOGGER.info(f"\n{'':>3}{'from':>18}{'n':>3}{'params':>10} {'module':<40}{'arguments':<30}")
anchors, nc, gd, gw = d['anchors'], d['nc'], d['depth_multiple'], d['width_multiple']
na = (len(anchors[0]) // 2) if isinstance(anchors, list) else anchors # number of anchors
no = na * (nc + 5) # number of outputs = anchors * (classes + 5)
layers, save, c2 = [], [], ch[-1] # layers, savelist, ch out
.info: 打印信息
获取yaml参数:
na: anchor数量
no: 输出通道,nc(80),5(矩形框四点+置信度),值为255
layers(存储创建的每层网络),save(统计要保存的特征层)
for i, (f, n, m, args) in enumerate(d['backbone'] + d['head']): # from, number, module, args
# 获取模型,这里主要是作者防止格式错误而不采取直接赋值
m = eval(m) if isinstance(m, str) else m # eval strings
for j, a in enumerate(args):
try:
# 同理防止格式错误而不直接赋值
args[j] = eval(a) if isinstance(a, str) else a # eval strings, [64, 6, 2, 2]
except NameError:
pass
获取模型和args,这里这样写可能是因为作者防止格式错误而不采用直接赋值
接下来就是判断当前网络层是卷积层还是上采样层,检测层等,然后相应的进行不同处理
# n>1就乘以深度倍数
n = n_ = max(round(n * gd), 1) if n > 1 else n # depth gain
if m in [Conv, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, MixConv2d, Focus, CrossConv,
BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3SPP, C3Ghost]:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no: # if not output
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]] # args[3, 32, 6, 2, 2]
if m in [BottleneckCSP, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost]:
args.insert(2, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f)
elif m is Detect:
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if isinstance(args[1], int): # number of anchors
args[1] = [list(range(args[1] * 2))] * len(f)
elif m is Contract:
c2 = ch[f] * args[0] ** 2
elif m is Expand:
c2 = ch[f] // args[0] ** 2
else:
c2 = ch[f]
If m: 判断结构类型
卷积层: 判断通道数是否为255否则乘以通道倍数,判断是否为8倍数(8的倍数对GPU计算更加友好)
C3层:
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type, m_.np = i, f, t, np # attach index, 'from' index, type, number params
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>18}{n_:>3}{np:10.0f} {t:<40}{str(args):<30}') # print
save.extend(x % i for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
save.extend: 保存所需特征层,【4,6,10,14,17,20, 23】
ch.append(c2): 存储各层通道数,将上层输出通道作为该层输入通道
common.py:
以Conv为例简单了解:
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = nn.SiLU() if act is True else (act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity())
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
Conv:
init:
c1: 输入该层通道数
c2: 输出该层通道数
k=1: 卷积核的大小
s=1: 卷积层滑动的步长
C3:
本人才疏学浅,若各位读者发现文章内容有误,烦请不吝赐教,本人将不胜感激。
版权归原作者 が- 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。