树的概念及结构
树的概念
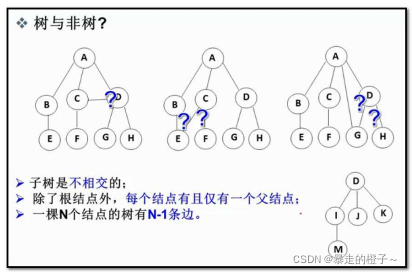
树是一种非线性的数据结构,它是由n(n>=0)个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。把它叫做树是因为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。
有一个特殊的结点,称为根结点,根节点没有前驱结点。
除根节点外,其余结点被分成M(M>0)个互不相交的集合T1、T2、……、Tm,其中每一个集合Ti(1<= i<= m)又是一棵结构与树类似的子树。每棵子树的根结点有且只有一个前驱,可以有0个或多个后继因此,树是递归定义的。

注意:树形结构中,子树之间不能有交集,否则就不是树形结构。
树的相关概念
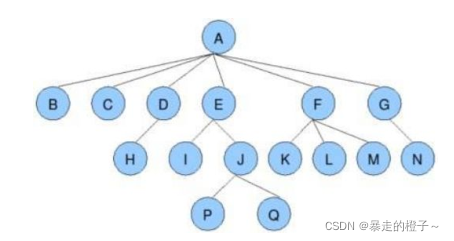
节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度; 如上图:A的为6
叶节点或终端节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点; 如上图:B、C、H、I...等节点为叶节点
非终端节点或分支节点:度不为0的节点; 如上图:D、E、F、G...等节点为分支节点
双亲节点或父节点:若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点; 如上图:A是B的父节点
孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点; 如上图:B是A的孩子节点
兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点; 如上图:B、C是兄弟节点
树的度:一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度; 如上图:树的度为6
节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推;
树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次; 如上图:树的高度为4
堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟;如上图:H、I互为兄弟节点
节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;如上图:A是所有节点的祖先
子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙。如上图:所有节点都是A的子孙
森林:由m(m>0)棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林;
二叉树概念
概念
一棵二叉树是结点的一个有限集合,该集合:
- 或者为空
- 由一个根节点加上两棵别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成
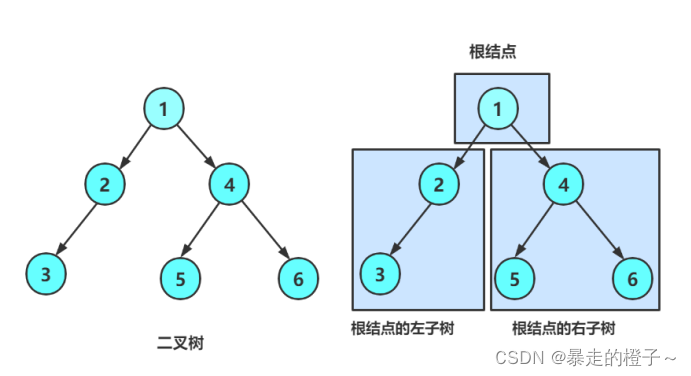
从上图可以看出:
- 二叉树不存在度大于2的结点
- 二叉树的子树有左右之分,次序不能颠倒,因此二叉树是有序树
注意:对于任意的二叉树都是由以下几种情况复合而成的: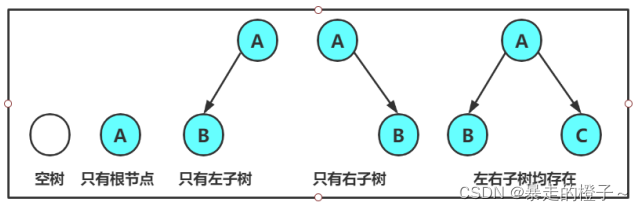
现实中的二叉树
特殊的二叉树
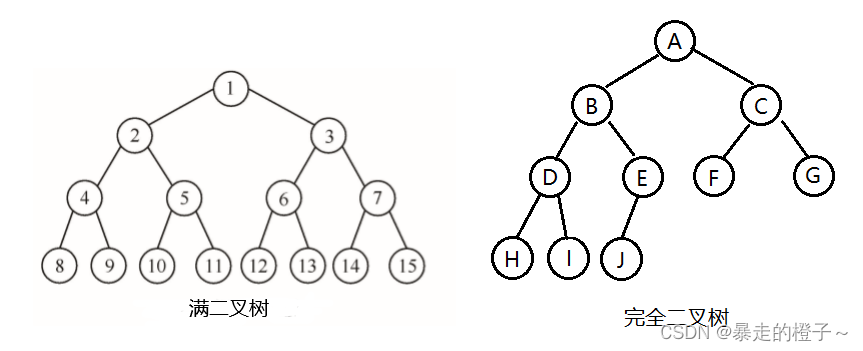
- 满二叉树:一个二叉树,如果每一个层的结点数都达到最大值,则这个二叉树就是满二叉 树。也就是说,如果一个二叉树的层数为K,且结点总数是 ,则它就是满二叉树。
- 完全二叉树:完全二叉树是效率很高的数据结构,完全二叉树是由满二叉树而引出来的。 对于深度为K的,有n个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为K的满二叉树中 编号从1至n的结点一一对应时称之为完全二叉树。 要注意的是满二叉树是一种特殊的完 全二叉树。
具体图形展示:
二叉树的性质
- 若规定根节点的层数为1,则一棵非空二叉树的第i层上最多有 2^(i-1)个结点.
- 若规定根节点的层数为1,则深度为h的二叉树的最大结点数是 2^h-1.
- 对任何一棵二叉树, 如果度为0其叶结点个数为n0 , 度为2的分支结点个数为n2 , 则有n0=n2+1
- 若规定根节点的层数为1,具有n个结点的满二叉树的深度,h= log2(n+1)(解释:是log以2
为底,n+1为对数)- 对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下从左至右的数组顺序对所有节点从0开 始编号,则对于序号为i的结点有:
- 若i>0,i位置节点的双亲序号:(i-1)/2;i=0,i为根节点编号,无双亲节点
- 若2i+1<n,左孩子序号:2i+1,2i+1>=n否则无左孩子
- 若2i+2<n,右孩子序号:2i+2,2i+2>=n否则无右孩子
有了以上的概念,接下来我们来用代码简单实现一下二叉树吧!
结构体初始化
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;
函数接口
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->left = NULL;
newnode->right = NULL;
newnode->data = x;
return newnode;
}
//创建树结点
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x) //返回值为BTNode,返回开辟好的树节点的地址
{
BTNode newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));//malloc一个结构体
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->left = NULL; //左子树置空
newnode->right = NULL;//右子树置空
newnode->data = x;//节点2上存数据
return newnode;//返回节点的地址
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* nodeA = BuyNode('A');
BTNode* nodeB = BuyNode('B');
BTNode* nodeC = BuyNode('C');
BTNode* nodeD = BuyNode('D');
BTNode* nodeE = BuyNode('E');
BTNode* nodeF = BuyNode('F');
BTNode* nodeG = BuyNode('G');
nodeA->left = nodeB;
nodeA->right = nodeC;
nodeB->left = nodeD;
nodeC->left = nodeE;
nodeC->right = nodeF;
nodeF->left = nodeG;
return nodeA;
}
//创建一个树,以下面创建的树为例,并作为测试用例
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* nodeA = BuyNode('A');
BTNode* nodeB = BuyNode('B');
BTNode* nodeC = BuyNode('C');
BTNode* nodeD = BuyNode('D');
BTNode* nodeE = BuyNode('E');
BTNode* nodeF = BuyNode('F');
BTNode* nodeG = BuyNode('G');
nodeA->left = nodeB;
nodeA->right = nodeC;
nodeB->left = nodeD;
nodeC->left = nodeE;
nodeC->right = nodeF;
nodeF->left = nodeG;
return nodeA;
}经过上面树的构建之后,二叉树的示意图:
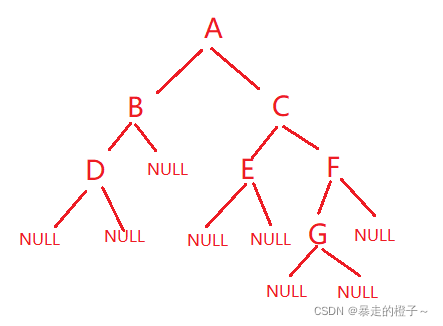
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL) //这里不用assert,否则遇到空时,就过不去了
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前
//前序遍历二叉树
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL) //这里不用assert,否则遇到空时,就过不去了
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->data);//打印根节点的数据
PrevOrder(root->left); //递归左子树
PrevOrder(root->right);//递归右子树
}部分递归展开图:
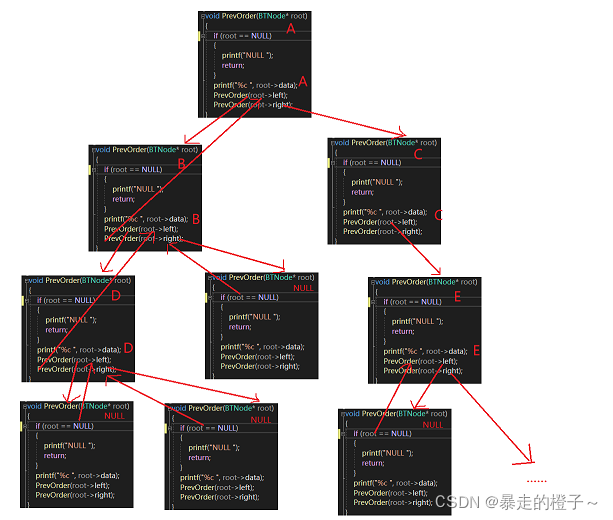
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)
//中序遍历二叉树
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);//遍历左子树
printf("%c ", root->data);//打印根节点的数据
InOrder(root->right);//遍历右子树
}部分递归展开图:
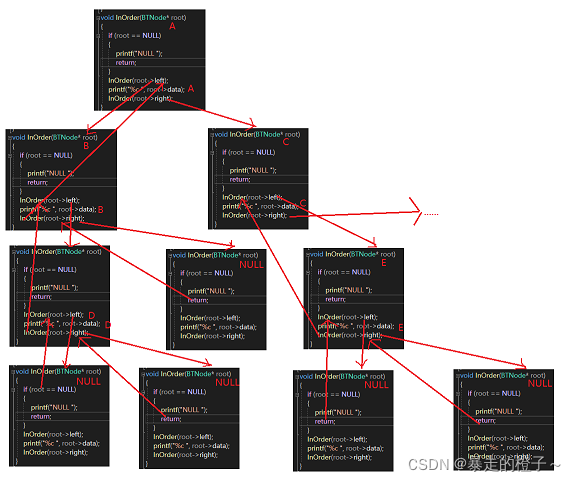
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}
后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后
//后序遍历二叉树
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);//遍历左子树
PostOrder(root->right);//遍历右子树
printf("%c ", root->data);//打印根节点
}部分递归展开图:

int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
//if (root == NULL)
//{
// return 0;
//}
//return BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//计算二叉树节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
//if (root == NULL)
//{
// return 0;
//}
//return BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
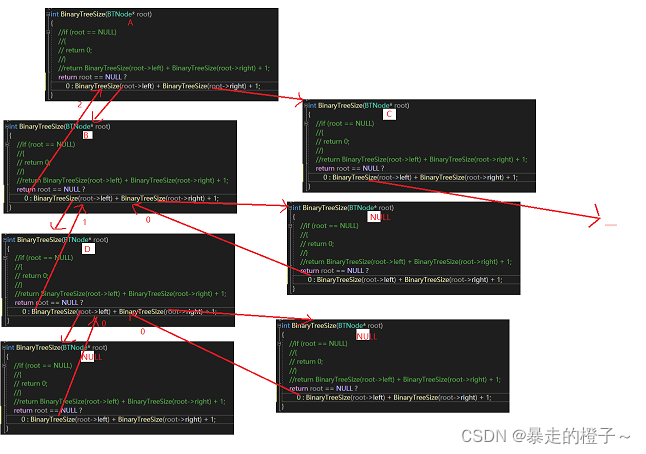
}//如果root为空,则返回0,如果不为空,递归左子树和右子树并且+1,这个1就相当于加上了当前结点的个数。部分递归展开图:
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL) //这个条件不能忘
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
//计算二叉树的叶子节点
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL) //这个条件不能忘,在这里根节点为空,说明就没有节点,就返回0
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) //一个节点的左子树和右子树都为空,则 该节点为叶子结点
{
return 1;
}
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);//递归左子树和 右子树得到返回值
}
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
//二叉树第K层结点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k >= 1);
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
int left = BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1);
int right = BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
return left + right;
//return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
//二叉树第K层结点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k >= 1);//判断第K层是否具有合法性,不能缺少
if (root == NULL) //当前递归到的结点为空时,返回0,这个条件必须放到下面判断条件前面
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1) //当递归到K==1时,则当前结点是第K层的结点,则返回1
{
return 1;
}
int left = BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1);//遍历左子树,每遍历一层,k-1
int right = BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);//遍历右子树,每遍历一层,k-1
return left + right;
//return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
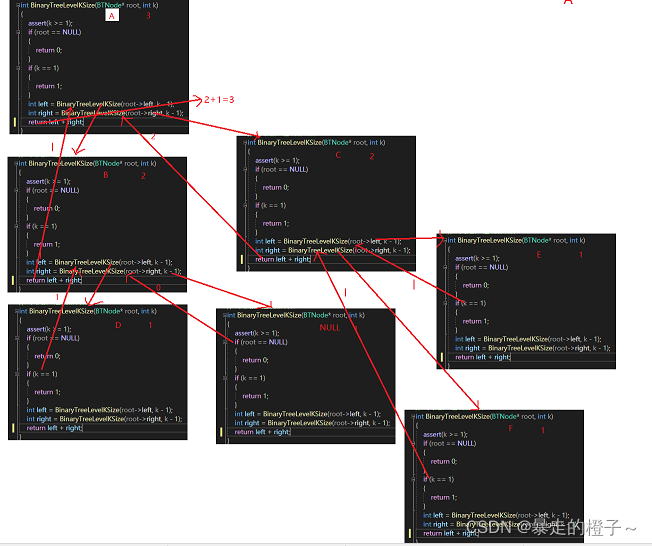
}**递归展开图: **
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root)
//二叉树的深度/高度
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = BinaryTreeDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = BinaryTreeDepth(root->right);
return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth + 1 : rightDepth + 1;
}
//二叉树的深度/高度
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = BinaryTreeDepth(root->left);//记录左子树的高度
int rightDepth = BinaryTreeDepth(root->right);//记录右子树的高度
return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth + 1 : rightDepth + 1;//左子树和右子树大的那一 个加1
}部分递归展开图:
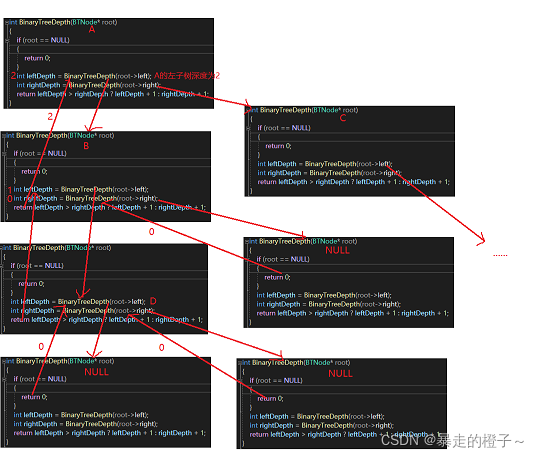
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == x)
{
return root;
}
BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
return NULL;
}
//查找某一个节点,并返回该节点的地址
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL) //如果节点为空,则返回空,表示没有找到
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == x)//找到节点时
{
return root; //返回结点的地址
}
BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);//递归遍历左子树
BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);//递归遍历右子树
return NULL;
}
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueHead(&q);
QueuePop(&q);//Pop掉的是存放树节点的地址,而不是把树节点Pop掉了
printf("%c ", front->data);
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)//root为空时,说明二叉树第一个结点为空,则二叉树为空,不用遍历
{
return;
}
Queue q;//利用队列的性质来遍历二叉树
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, root);//首先,把二叉树头结点放入队列中
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueHead(&q);
QueuePop(&q);//Pop掉的是存放树节点的地址,而不是把树节点Pop掉了
printf("%c ", front->data);
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
** 条件while (!QueueEmpty(&q)):依次类推,当队列为空时就终止遍历。**
在这里队列的实现就不再赘述,详细请看博客:
队列的模拟实现(单链链表模拟)_暴走的橙子~的博客-CSDN博客
只不过在这里队列在头文件进行这样的修改。
struct BinaryTreeNode;//声明出来节点的类型
typedef struct BinaryTreeNoide* QDataType;//每个data存放的是每个节点的地址
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueHead(&q);//front是存放树节点的指针,树节点为空,front不一定为空
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
else
{
//NULL也放入
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueHead(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
//判断是不是完全二叉树
//思想就是用一个队列来存放二叉树的结点地址,空地址也用data存放,直到遍历到data==NULL时,就终止第一次循环。接着遍历剩下队列的data,如果剩下的data全部为空,则返回true,说明时完全二叉树;反之,返回false,说明不是完全二叉树。
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{/ /遍历剩下队列中的data地址。
BTNode* front = QueueHead(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
void BinaryTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
void BinaryTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
//后序遍历
BinaryTreeDestroy(root->left);
BinaryTreeDestroy(root->right);
free(root);
root = NULL;
//前序遍历
/*BTNode* lf = root->left;
BTNode* rt = root->right;
free(root);
root = NULL;
BinaryTreeDestroy(lf);
BinaryTreeDestroy(rt);*/
}
在这里推荐后序遍历方式销毁空间。代码的可读性会更高,另外,root是会被置空的。
而前序遍历销毁空间是,root在这里还没有置空,还需要在函数外面置空,比较麻烦。
完整代码
Binary.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x);
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree();
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root);
void InOrder(BTNode* root);
void PostOrder(BTNode* root);
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root);
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root);
//二叉树第K层结点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k);
//二叉树的深度/高度
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root);
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x);
//层序遍历
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root);
//判断是不是完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root);
void BinaryTreeDestroy(BTNode* root);
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
struct BinaryTreeNode;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNoide* QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
QDataType QueueTail(Queue* q);
QDataType QueueHead(Queue* q);
Binary.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Binary.h"
#include"Queue.h"
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->left = NULL;
newnode->right = NULL;
newnode->data = x;
return newnode;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* nodeA = BuyNode('A');
BTNode* nodeB = BuyNode('B');
BTNode* nodeC = BuyNode('C');
BTNode* nodeD = BuyNode('D');
BTNode* nodeE = BuyNode('E');
BTNode* nodeF = BuyNode('F');
BTNode* nodeG = BuyNode('G');
nodeA->left = nodeB;
nodeA->right = nodeC;
nodeB->left = nodeD;
nodeC->left = nodeE;
nodeC->right = nodeF;
nodeF->left = nodeG;
return nodeA;
}
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL) //这里不用assert,否则遇到空时,就过不去了
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
//if (root == NULL)
//{
// return 0;
//}
//return BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL) //这个条件不能忘
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
//二叉树第K层结点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k >= 1);
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
int left = BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1);
int right = BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
return left + right;
//return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
//二叉树的深度/高度
int BinaryTreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = BinaryTreeDepth(root->left);
int rightDepth = BinaryTreeDepth(root->right);
return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth + 1 : rightDepth + 1;
}
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == x)
{
return root;
}
BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
return NULL;
}
//层序遍历
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueHead(&q);
QueuePop(&q);//Pop掉的是存放树节点的地址,而不是把树节点Pop掉了
printf("%c ", front->data);
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
//判断是不是完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueHead(&q);//front是存放树节点的指针,树节点为空,front不一定为空
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
else
{
//NULL也放入
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueHead(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
void BinaryTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
//后序遍历
BinaryTreeDestroy(root->left);
BinaryTreeDestroy(root->right);
free(root);
root = NULL;
//前序遍历
/*BTNode* lf = root->left;
BTNode* rt = root->right;
free(root);
root = NULL;
BinaryTreeDestroy(lf);
BinaryTreeDestroy(rt);*/
}
Queue.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
q->head = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
QNode* cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
q->head=q->tail = NULL;//在这里头结点和尾结点要置空
}
//队尾插入数据
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x)
{
assert(q);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (q->head == NULL)
{
q->head = q->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
q->tail->next = newnode;
q->tail = newnode;
}
}
//队头删除数据
void QueuePop(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
if (q->head == q->tail)
{
free(q->head);
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = q->head->next;
free(q->head);
q->head = next;
}
//方法二
//QNode* next = q->head->next;
//free(q->head);
//q->head = next;
//if (q->head == NULL)
//{
// q->tail = NULL;
//}
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
return q->head == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = q->head;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
QDataType QueueTail(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->tail->data;
}
QDataType QueueHead(Queue* q)
{
assert(q);
assert(!QueueEmpty(q));
return q->head->data;
}
测试代码test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Binary.h"
void BinaryTest1()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
PrevOrder(root);
printf("\n");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
PostOrder(root);
printf("\n");
int size = BinaryTreeSize(root);//节点个数
printf("%d\n", size);
int LeafSize = BinaryTreeLeafSize(root);
printf("%d\n", LeafSize);
int sizeK = BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root, 3);
printf("%d\n", sizeK);
int depth = BinaryTreeDepth(root);
printf("%d\n", depth);
BinaryTreeLevelOrder(root);
printf("%d\n",BinaryTreeComplete(root));
BinaryTreeDestroy(root);
root = NULL;
}
int main()
{
BinaryTest1();
return 0;
}
测试结果
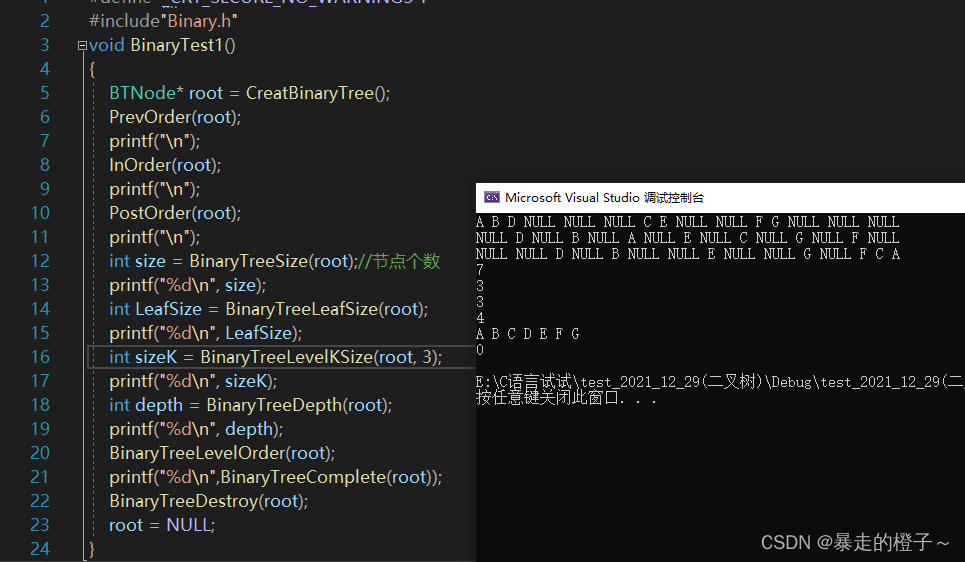
版权归原作者 暴走的橙子~ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。