一、前言
由于工程项目中需要对视频中的person进行关键点检测,我测试各个算法后,并没有采用比较应用化成熟的Openpose,决定采用检测精度更高的HRnet系列。但是由于官方给的算法只能测试数据集,需要自己根据算法模型编写实例化代码。
本文根据SimDR工程实现视频关键点检测。SimDR根据HRnet改进而来,整个工程既包括HRnet又包括改进后的算法,使用起来较为方便,而且本文仅在cpu上就可以跑通整个工程。
二、环境配置
python的环境主要就是按照工程中SimDR与yolov5的requirement.txt安装即可。总之缺啥装啥。
三、工程准备
1、克隆工程
git clone https://github.com/leeyegy/SimDR.git #克隆姿态估计工程
cd SimDR
git clone -b v5.0 https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git #在姿态估计工程中添加yolov5算法
2、目标检测
①添加权重文件
添加yolov5x.pt(见评论区网盘)到‘ SimDR/yolov5/weights/ ’文件夹下。
②获取边界框
在yolov5文件夹下新建YOLOv5.py,复制以下内容到文件中。注意:根据大家的反馈,不同的电脑,导入yolov5相关包时会不同的方式,代码中我是from yolov5.xxx import xxx,但是有些可以不用前面的yolov5,大家自行尝试哈。一般出现No module xxx 都是有关yolov5 的包导入出错哈。
import argparse
import time
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import cv2
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
from numpy import random
import sys
import os
from yolov5.models.experimental import attempt_load
from yolov5.utils.datasets import LoadStreams, LoadImages
from yolov5.utils.general import check_img_size, check_requirements, check_imshow, non_max_suppression, apply_classifier, \
scale_coords, xyxy2xywh, strip_optimizer, set_logging, increment_path
from yolov5.utils.plots import plot_one_box
from yolov5.utils.torch_utils import select_device, load_classifier, time_synchronized
from yolov5.utils.datasets import letterbox
class Yolov5():
def __init__(self, weights=None, opt=None, device=None):
"""
@param weights:
@param save_txt:
@param opt:
@param device:
"""
self.weights = weights
self.device = device
# save_dir = Path(increment_path(Path(opt.project) / opt.name, exist_ok=opt.exist_ok)) # increment run
# save_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir
self.img_size = 640
self.model = attempt_load(weights, map_location=self.device)
self.stride = int(self.model.stride.max())
self.names = self.model.module.names if hasattr(self.model, 'module') else self.model.names
self.colors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in self.names]
self.opt = opt
def detect(self,img0):
"""
@param img0: 输入图片 shape=[h,w,3]
@return:
"""
person_boxes = np.ones((6))
img = letterbox(img0, self.img_size, stride=self.stride)[0]
# Convert
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) # BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(self.device)
img = img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if img.ndimension() == 3:
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
pred = self.model(img, augment=self.opt.augment)[0]
# Apply NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, self.opt.conf_thres, self.opt.iou_thres, classes=self.opt.classes, agnostic=self.opt.agnostic_nms)
for i, det in enumerate(pred):
if len(det):
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], img0.shape).round()
boxes = reversed(det)
boxes = boxes.cpu().numpy() #2022.04.06修改,在GPU上跑boxes无法直接转numpy数据
#for i , box in enumerate(np.array(boxes)):
for i , box in enumerate(boxes):
if int(box[-1]) == 0 and box[-2]>=0.7:
person_boxes=np.vstack((person_boxes , box))
# label = f'{self.names[int(box[-1])]} {box[-2]:.2f}'
# print(label)
# plot_one_box(box, img0, label=label, color=self.colors[int(box[-1])], line_thickness=3)
# cv2.imwrite('result1.jpg',img0)
# print(s)
# print(person_boxes,np.ndim(person_boxes))
if np.ndim(person_boxes)>=2 :
person_boxes_result = person_boxes[1:]
boxes_result = person_boxes[1:,:4]
else:
person_boxes_result = []
boxes_result = []
return person_boxes_result,boxes_result
def yolov5test(opt,path = ''):
detector = Yolov5(weights='weights/yolov5x.pt',opt=opt,device=torch.device('cpu'))
img0 = cv2.imread(path)
personboxes ,boxes= detector.detect(img0)
for i,(x1,y1,x2,y2) in enumerate(boxes):
print(x1,y1,x2,y2)
print(personboxes,'\n',boxes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='object confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='IOU threshold for NMS')
parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3')
parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
parser.add_argument('--update', action='store_true', help='update all model')
parser.add_argument('--project', default='runs/detect', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save results to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
# check_requirements(exclude=('pycocotools', 'thop'))
with torch.no_grad():
yolov5test(opt,'data/images/zidane.jpg')
③路径问题
本文代码是在pycharm中运行,yolov5工程的加入导致有些文件夹名称相同,pycharm会搞混,可能会出现某些包找不到。这里需要先运行一下YOLOv5.py脚本,根据报错改一下import的内容。举个例子,./SimDR/yolov5/models/experimental.py 文件中会出现图片中的问题
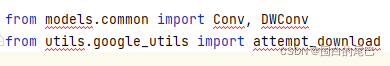
改成如下即可,其他的文件改法相同。
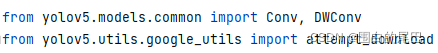
④添加SPPF模块

yolov5 v5.0工程中没有SPPF模块,此时我们需要在./SimDR/yolov5/models/common.py文件末尾加入以下代码。
import warnings
class SPPF(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1))
3、姿态估计
①添加权重
在SimDR文件夹下新建weight/hrnet文件夹,添加pose_hrnet_w48_384x288.pth等文件(见评论区网盘)
②修改yaml文件
SimDR/experiments/文件夹下是coco与mpii数据集的配置文件,本文以coco为例。

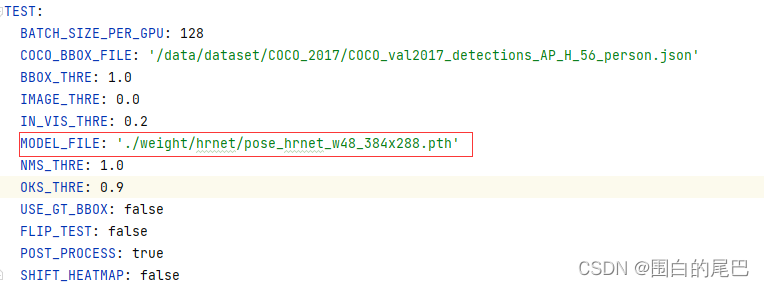
接下来,修改./SimDR/experiments/coco/hrnet/heatmap/w48_384x288_adam_lr1e-3.yaml文件中的TEST部分的MODEL_FILE路径,如图所示。(SimDR算法的配置文件同理改动。)
③获取关键点
在’ SimDR/ ‘文件夹下新建Point_detect.py ,复制以下内容到文件中。
注意:代码第12行的路径要改成自己yolov5工程的路径,有这条代码才能正常运行。
【2022.04.16更新:根据评论区的建议,为关键点增加置信度值,这个值我是根据模型输出经过softmax后取最大值(关键点坐标就是这个最大值的索引),仅供参考。根据这个置信度可以解决半身照也会绘制全部点的问题。】
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from torchvision.transforms import transforms
import torch.nn.functional as F
from lib.config import cfg
from yolov5.YOLOv5 import Yolov5
from lib.utils.transforms import flip_back_simdr,transform_preds,get_affine_transform
from lib import models
import argparse
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, 'D:\\Study\\Pose Estimation\\SimDR\\yolov5')
class Points():
def __init__(self,
model_name='sa-simdr',
resolution=(384,288),
opt=None,
yolo_weights_path="./yolov5/weights/yolov5x.pt",
):
"""
Initializes a new SimpleHRNet object.
HRNet (and YOLOv3) are initialized on the torch.device("device") and
its (their) pre-trained weights will be loaded from disk.
Args:
c (int): number of channels (when using HRNet model) or resnet size (when using PoseResNet model).
nof_joints (int): number of joints.
checkpoint_path (str): path to an official hrnet checkpoint or a checkpoint obtained with `train_coco.py`.
model_name (str): model name (HRNet or PoseResNet).
Valid names for HRNet are: `HRNet`, `hrnet`
Valid names for PoseResNet are: `PoseResNet`, `poseresnet`, `ResNet`, `resnet`
Default: "HRNet"
resolution (tuple): hrnet input resolution - format: (height, width).
Default: (384, 288)
interpolation (int): opencv interpolation algorithm.
Default: cv2.INTER_CUBIC
multiperson (bool): if True, multiperson detection will be enabled.
This requires the use of a people detector (like YOLOv3).
Default: True
return_heatmaps (bool): if True, heatmaps will be returned along with poses by self.predict.
Default: False
return_bounding_boxes (bool): if True, bounding boxes will be returned along with poses by self.predict.
Default: False
max_batch_size (int): maximum batch size used in hrnet inference.
Useless without multiperson=True.
Default: 16
yolo_model_def (str): path to yolo model definition file.
Default: "./model/detectors/yolo/config/yolov3.cfg"
yolo_class_path (str): path to yolo class definition file.
Default: "./model/detectors/yolo/data/coco.names"
yolo_weights_path (str): path to yolo pretrained weights file.
Default: "./model/detectors/yolo/weights/yolov3.weights.cfg"
device (:class:`torch.device`): the hrnet (and yolo) inference will be run on this device.
Default: torch.device("cpu")
"""
self.model_name = model_name
self.resolution = resolution # in the form (height, width) as in the original implementation
self.aspect_ratio = resolution[1]/resolution[0]
self.yolo_weights_path = yolo_weights_path
self.flip_pairs = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8],
[9, 10], [11, 12], [13, 14], [15, 16]]
self.device = torch.device(opt.device)
cfg.defrost()
if model_name in ('sa-simdr','sasimdr','sa_simdr'):
if resolution ==(384,288):
cfg.merge_from_file('./experiments/coco/hrnet/sa_simdr/w48_384x288_adam_lr1e-3_split1_5_sigma4.yaml')
elif resolution == (256,192):
cfg.merge_from_file('./experiments/coco/hrnet/sa_simdr/w48_256x192_adam_lr1e-3_split2_sigma4.yaml')
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong cfg file')
elif model_name in ('simdr'):
if resolution == (256, 192):
cfg.merge_from_file('./experiments/coco/hrnet/simdr/nmt_w48_256x192_adam_lr1e-3.yaml')
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong cfg file')
elif model_name in ('hrnet','HRnet','Hrnet'):
if resolution == (384,288):
cfg.merge_from_file('./experiments/coco/hrnet/heatmap/w48_384x288_adam_lr1e-3.yaml')
elif resolution == (256,192):
cfg.merge_from_file('./experiments/coco/hrnet/heatmap/w48_256x192_adam_lr1e-3.yaml')
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong cfg file')
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong model name.')
cfg.freeze()
self.model = eval('models.' + cfg.MODEL.NAME + '.get_pose_net')(
cfg, is_train=False)
print('=> loading model from {}'.format(cfg.TEST.MODEL_FILE))
checkpoint_path = cfg.TEST.MODEL_FILE
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path, map_location=self.device)
if 'model' in checkpoint:
self.model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model'])
else:
self.model.load_state_dict(checkpoint)
if 'cuda' in str(self.device):
print("device: 'cuda' - ", end="")
if 'cuda' == str(self.device):
# if device is set to 'cuda', all available GPUs will be used
print("%d GPU(s) will be used" % torch.cuda.device_count())
device_ids = None
else:
# if device is set to 'cuda:IDS', only that/those device(s) will be used
print("GPU(s) '%s' will be used" % str(self.device))
device_ids = [int(x) for x in str(self.device)[5:].split(',')]
elif 'cpu' == str(self.device):
print("device: 'cpu'")
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong device name.')
self.model = self.model.to(self.device)
self.model.eval()
self.detector = Yolov5(
weights=yolo_weights_path,
opt=opt ,
device=self.device)
self.transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToPILImage(),
transforms.Resize((self.resolution[0], self.resolution[1])), # (height, width)
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
def _box2cs(self, box):
x, y, w, h = box[:4]
return self._xywh2cs(x, y, w, h)
def _xywh2cs(self, x, y, w, h):
center = np.zeros((2), dtype=np.float32)
center[0] = x + w * 0.5
center[1] = y + h * 0.5
if w > self.aspect_ratio * h:
h = w * 1.0 / self.aspect_ratio
elif w < self.aspect_ratio * h:
w = h * self.aspect_ratio
scale = np.array(
[w * 1.0 / 200, h * 1.0 / 200],
dtype=np.float32)
if center[0] != -1:
scale = scale * 1.25
return center, scale
def predict(self, image):
"""
Predicts the human pose on a single image or a stack of n images.
Args:
image (:class:`np.ndarray`):
the image(s) on which the human pose will be estimated.
image is expected to be in the opencv format.
image can be:
- a single image with shape=(height, width, BGR color channel)
- a stack of n images with shape=(n, height, width, BGR color channel)
Returns:
:class:`np.ndarray` or list:
a numpy array containing human joints for each (detected) person.
Format:
if image is a single image:
shape=(# of people, # of joints (nof_joints), 3); dtype=(np.float32).
if image is a stack of n images:
list of n np.ndarrays with
shape=(# of people, # of joints (nof_joints), 3); dtype=(np.float32).
Each joint has 3 values: (y position, x position, joint confidence).
If self.return_heatmaps, the class returns a list with (heatmaps, human joints)
If self.return_bounding_boxes, the class returns a list with (bounding boxes, human joints)
If self.return_heatmaps and self.return_bounding_boxes, the class returns a list with
(heatmaps, bounding boxes, human joints)
"""
if len(image.shape) == 3:
return self._predict_single(image)
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong image format.')
def sa_simdr_pts(self,img,detection,images,boxes):
c, s = [], []
if detection is not None:
for i, (x1, y1, x2, y2) in enumerate(detection):
x1 = int(round(x1.item()))
x2 = int(round(x2.item()))
y1 = int(round(y1.item()))
y2 = int(round(y2.item()))
boxes[i] = [x1, y1, x2, y2]
w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
xx1 = np.max((0, x1))
yy1 = np.max((0, y1))
xx2 = np.min((img.shape[1] - 1, x1 + np.max((0, w - 1))))
yy2 = np.min((img.shape[0] - 1, y1 + np.max((0, h - 1))))
box = [xx1, yy1, xx2 - xx1, yy2 - yy1]
center, scale = self._box2cs(box)
c.append(center)
s.append(scale)
trans = get_affine_transform(center, scale, 0, np.array(cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE))
input = cv2.warpAffine(
img,
trans,
(int(self.resolution[1]), int(self.resolution[0])),
flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
images[i] = self.transform(input)
if images.shape[0] > 0:
images = images.to(self.device)
with torch.no_grad():
output_x, output_y = self.model(images)
if cfg.TEST.FLIP_TEST:
input_flipped = images.flip(3)
output_x_flipped_, output_y_flipped_ = self.model(input_flipped)
output_x_flipped = flip_back_simdr(output_x_flipped_.cpu().numpy(),
self.flip_pairs, type='x')
output_y_flipped = flip_back_simdr(output_y_flipped_.cpu().numpy(),
self.flip_pairs, type='y')
output_x_flipped = torch.from_numpy(output_x_flipped.copy()).to(self.device)
output_y_flipped = torch.from_numpy(output_y_flipped.copy()).to(self.device)
# feature is not aligned, shift flipped heatmap for higher accuracy
if cfg.TEST.SHIFT_HEATMAP:
output_x_flipped[:, :, 0:-1] = \
output_x_flipped.clone()[:, :, 1:]
output_x = F.softmax((output_x + output_x_flipped) * 0.5, dim=2)
output_y = F.softmax((output_y + output_y_flipped) * 0.5, dim=2)
else:
output_x = F.softmax(output_x, dim=2)
output_y = F.softmax(output_y, dim=2)
max_val_x, preds_x = output_x.max(2, keepdim=True)
max_val_y, preds_y = output_y.max(2, keepdim=True)
mask = max_val_x > max_val_y
max_val_x[mask] = max_val_y[mask]
maxvals = max_val_x * 10.0
output = torch.ones([images.size(0), preds_x.size(1), 3])
output[:, :, 0] = torch.squeeze(torch.true_divide(preds_x, cfg.MODEL.SIMDR_SPLIT_RATIO))
output[:, :, 1] = torch.squeeze(torch.true_divide(preds_y, cfg.MODEL.SIMDR_SPLIT_RATIO))
# output[:, :, 2] = maxvals.squeeze(2)
output = output.cpu().numpy()
preds = output.copy()
for i in range(output.shape[0]):
preds[i] = transform_preds(
output[i], c[i], s[i], [cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE[0], cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE[1]]
)
preds[:, :, 2] = maxvals.squeeze(2)
else:
preds = np.empty((0, 0, 3), dtype=np.float32)
return preds
def simdr_pts(self,img,detection,images,boxes):
c, s = [], []
if detection is not None:
for i, (x1, y1, x2, y2) in enumerate(detection):
x1 = int(round(x1.item()))
x2 = int(round(x2.item()))
y1 = int(round(y1.item()))
y2 = int(round(y2.item()))
boxes[i] = [x1, y1, x2, y2]
w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
xx1 = np.max((0, x1))
yy1 = np.max((0, y1))
xx2 = np.min((img.shape[1] - 1, x1 + np.max((0, w - 1))))
yy2 = np.min((img.shape[0] - 1, y1 + np.max((0, h - 1))))
box = [xx1, yy1, xx2 - xx1, yy2 - yy1]
center, scale = self._box2cs(box)
c.append(center)
s.append(scale)
trans = get_affine_transform(center, scale, 0, np.array(cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE))
input = cv2.warpAffine(
img,
trans,
(int(self.resolution[1]), int(self.resolution[0])),
flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
images[i] = self.transform(input)
if images.shape[0] > 0:
images = images.to(self.device)
with torch.no_grad():
output_x, output_y = self.model(images)
if cfg.TEST.FLIP_TEST:
input_flipped = images.flip(3)
output_x_flipped_, output_y_flipped_ = self.model(input_flipped)
output_x_flipped = flip_back_simdr(output_x_flipped_.cpu().numpy(),
self.flip_pairs, type='x')
output_y_flipped = flip_back_simdr(output_y_flipped_.cpu().numpy(),
self.flip_pairs, type='y')
output_x_flipped = torch.from_numpy(output_x_flipped.copy()).to(self.device)
output_y_flipped = torch.from_numpy(output_y_flipped.copy()).to(self.device)
# feature is not aligned, shift flipped heatmap for higher accuracy
if cfg.TEST.SHIFT_HEATMAP:
output_x_flipped[:, :, 0:-1] = \
output_x_flipped.clone()[:, :, 1:]
output_x = (F.softmax(output_x, dim=2) + F.softmax(output_x_flipped, dim=2)) * 0.5
output_y = (F.softmax(output_y, dim=2) + F.softmax(output_y_flipped, dim=2)) * 0.5
else:
output_x = F.softmax(output_x, dim=2)
output_y = F.softmax(output_y, dim=2)
max_val_x, preds_x = output_x.max(2, keepdim=True)
max_val_y, preds_y = output_y.max(2, keepdim=True)
mask = max_val_x > max_val_y
max_val_x[mask] = max_val_y[mask]
maxvals = max_val_x * 10.0
output = torch.ones([images.size(0), preds_x.size(1), 3])
output[:, :, 0] = torch.squeeze(torch.true_divide(preds_x, cfg.MODEL.SIMDR_SPLIT_RATIO))
output[:, :, 1] = torch.squeeze(torch.true_divide(preds_y, cfg.MODEL.SIMDR_SPLIT_RATIO))
output = output.cpu().numpy()
preds = output.copy()
for i in range(output.shape[0]):
preds[i] = transform_preds(
output[i], c[i], s[i], [cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE[0], cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE[1]]
)
preds[:, :, 2] = maxvals.squeeze(2)
else:
preds = np.empty((0, 0, 3), dtype=np.float32)
return preds
def hrnet_pts(self,img,detection,images,boxes):
if detection is not None:
for i, (x1, y1, x2, y2) in enumerate(detection):
x1 = int(round(x1.item()))
x2 = int(round(x2.item()))
y1 = int(round(y1.item()))
y2 = int(round(y2.item()))
# Adapt detections to match HRNet input aspect ratio (as suggested by xtyDoge in issue #14)
correction_factor = self.resolution[0] / self.resolution[1] * (x2 - x1) / (y2 - y1)
if correction_factor > 1:
# increase y side
center = y1 + (y2 - y1) // 2
length = int(round((y2 - y1) * correction_factor))
y1 = max(0, center - length // 2)
y2 = min(img.shape[0], center + length // 2)
elif correction_factor < 1:
# increase x side
center = x1 + (x2 - x1) // 2
length = int(round((x2 - x1) * 1 / correction_factor))
x1 = max(0, center - length // 2)
x2 = min(img.shape[1], center + length // 2)
boxes[i] = [x1, y1, x2, y2]
images[i] = self.transform(img[y1:y2, x1:x2, ::-1])
if images.shape[0] > 0:
images = images.to(self.device)
with torch.no_grad():
out = self.model(images)
out = out.detach().cpu().numpy()
pts = np.empty((out.shape[0], out.shape[1], 3), dtype=np.float32)
# For each human, for each joint: y, x, confidence
for i, human in enumerate(out):
for j, joint in enumerate(human):
pt = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(joint), (self.resolution[0] // 4, self.resolution[1] // 4))
# 0: pt_x / (height // 4) * (bb_y2 - bb_y1) + bb_y1
# 1: pt_y / (width // 4) * (bb_x2 - bb_x1) + bb_x1
# 2: confidences
pts[i, j, 0] = pt[1] * 1. / (self.resolution[1] // 4) * (boxes[i][2] - boxes[i][0]) + boxes[i][0]
pts[i, j, 1] = pt[0] * 1. / (self.resolution[0] // 4) * (boxes[i][3] - boxes[i][1]) + boxes[i][1]
pts[i, j, 2] = joint[pt]
else:
pts = np.empty((0, 0, 3), dtype=np.float32)
return pts
def _predict_single(self, image):
_,detections = self.detector.detect(image)
nof_people = len(detections) if detections is not None else 0
boxes = np.empty((nof_people, 4), dtype=np.int32)
images = torch.empty((nof_people, 3, self.resolution[0], self.resolution[1])) # (height, width)
if self.model_name in ('sa-simdr','sasimdr'):
pts=self.sa_simdr_pts(image,detections,images,boxes)
elif self.model_name in ('hrnet','HRnet','hrnet'):
pts = self.hrnet_pts(image, detections, images, boxes)
elif self.model_name in ('simdr'):
pts = self.simdr_pts(image, detections, images, boxes)
return pts
# c,s=[],[]
# if detections is not None:
# for i, (x1, y1, x2, y2) in enumerate(detections):
# x1 = int(round(x1.item()))
# x2 = int(round(x2.item()))
# y1 = int(round(y1.item()))
# y2 = int(round(y2.item()))
# boxes[i] = [x1,y1,x2,y2]
# w ,h= x2-x1,y2-y1
# xx1 = np.max((0, x1))
# yy1 = np.max((0, y1))
# xx2 = np.min((image.shape[1] - 1, x1 + np.max((0, w - 1))))
# yy2 = np.min((image.shape[0] - 1, y1 + np.max((0, h - 1))))
# box = [xx1, yy1, xx2-xx1, yy2-yy1]
# center,scale = self._box2cs(box)
# c.append(center)
# s.append(scale)
#
# trans = get_affine_transform(center, scale, 0, np.array(cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE))
# input = cv2.warpAffine(
# image,
# trans,
# (int(self.resolution[1]), int(self.resolution[0])),
# flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# images[i] = self.transform(input)
# if images.shape[0] > 0:
# images = images.to(self.device)
# with torch.no_grad():
# output_x,output_y = self.model(images)
# if cfg.TEST.FLIP_TEST:
# input_flipped = images.flip(3)
# output_x_flipped_, output_y_flipped_ = self.model(input_flipped)
# output_x_flipped = flip_back_simdr(output_x_flipped_.cpu().numpy(),
# self.flip_pairs, type='x')
# output_y_flipped = flip_back_simdr(output_y_flipped_.cpu().numpy(),
# self.flip_pairs, type='y')
# output_x_flipped = torch.from_numpy(output_x_flipped.copy()).to(self.device)
# output_y_flipped = torch.from_numpy(output_y_flipped.copy()).to(self.device)
#
# # feature is not aligned, shift flipped heatmap for higher accuracy
# if cfg.TEST.SHIFT_HEATMAP:
# output_x_flipped[:, :, 0:-1] = \
# output_x_flipped.clone()[:, :, 1:]
# output_x = F.softmax((output_x + output_x_flipped) * 0.5, dim=2)
# output_y = F.softmax((output_y + output_y_flipped) * 0.5, dim=2)
# else:
# output_x = F.softmax(output_x, dim=2)
# output_y = F.softmax(output_y, dim=2)
# max_val_x, preds_x = output_x.max(2, keepdim=True)
# max_val_y, preds_y = output_y.max(2, keepdim=True)
#
# mask = max_val_x > max_val_y
# max_val_x[mask] = max_val_y[mask]
# maxvals = max_val_x.cpu().numpy()
#
# output = torch.ones([images.size(0), preds_x.size(1), 2])
# output[:, :, 0] = torch.squeeze(torch.true_divide(preds_x, cfg.MODEL.SIMDR_SPLIT_RATIO))
# output[:, :, 1] = torch.squeeze(torch.true_divide(preds_y, cfg.MODEL.SIMDR_SPLIT_RATIO))
#
# output = output.cpu().numpy()
# preds = output.copy()
# for i in range(output.shape[0]):
# preds[i] = transform_preds(
# output[i], c[i], s[i], [cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE[0], cfg.MODEL.IMAGE_SIZE[1]]
# )
# else:
# preds = np.empty((0, 0, 2), dtype=np.float32)
# return preds
# parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='object confidence threshold')
# parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='IOU threshold for NMS')
# parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3')
# parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')
# parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
# parser.add_argument('--update', action='store_true', help='update all model')
# parser.add_argument('--project', default='runs/detect', help='save results to project/name')
# parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save results to project/name')
# parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
# opt = parser.parse_args()
# model = Points(model_name='hrnet',opt=opt)
# img0 = cv2.imread('./data/test1.jpg')
# pts = model.predict(img0)
# print(pts.shape)
# for point in pts[0]:
# image = cv2.circle(img0, (int(point[0]), int(point[1])), 3, [255,0,255], -1 , lineType= cv2.LINE_AA)
# cv2.imwrite('./data/test11_result.jpg',image)
④绘制骨骼关键点
根据以上步骤,我们已经得到了关键点的坐标值,接下来需要在图片中描绘出来,以便展示检测结果。
首先在’ ./SimDR/lib/utils/ ‘文件夹下新建visualization.py文件,将以下内容复制到文件中。骨架绘制代码结合了simple-hrnet与Openpose工程。
【2022.04.16更新:由于之前的绘制代码被我魔改过,现在恢复成所有点与骨骼都绘制的模样,但是总觉得好丑,没有openpose那种美观,如果有人绘制出比较美观的骨架,希望能分享一下哈,共同进步!】
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
import torchvision
import ffmpeg
import random
import math
import copy
def plot_one_box(x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=3):
# Plots one bounding box on image img
tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
if label:
tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3
cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
return img
def joints_dict():
joints = {
"coco": {
"keypoints": {
0: "nose",
1: "left_eye",
2: "right_eye",
3: "left_ear",
4: "right_ear",
5: "left_shoulder",
6: "right_shoulder",
7: "left_elbow",
8: "right_elbow",
9: "left_wrist",
10: "right_wrist",
11: "left_hip",
12: "right_hip",
13: "left_knee",
14: "right_knee",
15: "left_ankle",
16: "right_ankle"
},
"skeleton": [
# # [16, 14], [14, 12], [17, 15], [15, 13], [12, 13], [6, 12], [7, 13], [6, 7], [6, 8],
# # [7, 9], [8, 10], [9, 11], [2, 3], [1, 2], [1, 3], [2, 4], [3, 5], [4, 6], [5, 7]
# [15, 13], [13, 11], [16, 14], [14, 12], [11, 12], [5, 11], [6, 12], [5, 6], [5, 7],
# [6, 8], [7, 9], [8, 10], [1, 2], [0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 3], [2, 4], [3, 5], [4, 6]
[15, 13], [13, 11], [16, 14], [14, 12], [11, 12], [5, 11], [6, 12], [5, 6], [5, 7],
[6, 8], [7, 9], [8, 10], [1, 2], [0, 1], [0, 2], [1, 3], [2, 4], # [3, 5], [4, 6]
[0, 5], [0, 6]
# [15, 13], [13, 11], [16, 14], [14, 12], [11, 12], [5, 11], [6, 12], [5, 6], [5, 7],
# [6, 8], [7, 9], [8, 10], [0, 3], [0, 4], [1, 3], [2, 4], # [3, 5], [4, 6]
# [0, 5], [0, 6]
]
},
"mpii": {
"keypoints": {
0: "right_ankle",
1: "right_knee",
2: "right_hip",
3: "left_hip",
4: "left_knee",
5: "left_ankle",
6: "pelvis",
7: "thorax",
8: "upper_neck",
9: "head top",
10: "right_wrist",
11: "right_elbow",
12: "right_shoulder",
13: "left_shoulder",
14: "left_elbow",
15: "left_wrist"
},
"skeleton": [
# [5, 4], [4, 3], [0, 1], [1, 2], [3, 2], [13, 3], [12, 2], [13, 12], [13, 14],
# [12, 11], [14, 15], [11, 10], # [2, 3], [1, 2], [1, 3], [2, 4], [3, 5], [4, 6], [5, 7]
[5, 4], [4, 3], [0, 1], [1, 2], [3, 2], [3, 6], [2, 6], [6, 7], [7, 8], [8, 9],
[13, 7], [12, 7], [13, 14], [12, 11], [14, 15], [11, 10],
]
},
}
return joints
def draw_points(image, points, color_palette='tab20', palette_samples=16, confidence_threshold=0.1,color=None):
"""
Draws `points` on `image`.
Args:
image: image in opencv format
points: list of points to be drawn.
Shape: (nof_points, 3)
Format: each point should contain (y, x, confidence)
color_palette: name of a matplotlib color palette
Default: 'tab20'
palette_samples: number of different colors sampled from the `color_palette`
Default: 16
confidence_threshold: only points with a confidence higher than this threshold will be drawn. Range: [0, 1]
Default: 0.1
Returns:
A new image with overlaid points
"""
circle_size = max(2, int(np.sqrt(np.max(np.max(points, axis=0) - np.min(points, axis=0)) // 16)))
for i, pt in enumerate(points):
if pt[2] >= confidence_threshold:
image = cv2.circle(image, (int(pt[0]), int(pt[1])), circle_size, color[i] ,-1, lineType= cv2.LINE_AA)
return image
def draw_skeleton(image, points, skeleton, color_palette='Set2', palette_samples=8, person_index=0,
confidence_threshold=0.1,sk_color=None):
"""
Draws a `skeleton` on `image`.
Args:
image: image in opencv format
points: list of points to be drawn.
Shape: (nof_points, 3)
Format: each point should contain (y, x, confidence)
skeleton: list of joints to be drawn
Shape: (nof_joints, 2)
Format: each joint should contain (point_a, point_b) where `point_a` and `point_b` are an index in `points`
color_palette: name of a matplotlib color palette
Default: 'Set2'
palette_samples: number of different colors sampled from the `color_palette`
Default: 8
person_index: index of the person in `image`
Default: 0
confidence_threshold: only points with a confidence higher than this threshold will be drawn. Range: [0, 1]
Default: 0.1
Returns:
A new image with overlaid joints
"""
canvas = copy.deepcopy(image)
cur_canvas = canvas.copy()
for i, joint in enumerate(skeleton):
pt1, pt2 = points[joint]
if pt1[2] >= confidence_threshold and pt2[2]>= confidence_threshold :
length = ((pt1[0] - pt2[0]) ** 2 + (pt1[1] - pt2[1]) ** 2) ** 0.5
angle = math.degrees(math.atan2(pt1[1] - pt2[1],pt1[0] - pt2[0]))
polygon = cv2.ellipse2Poly((int(np.mean((pt1[0],pt2[0]))), int(np.mean((pt1[1],pt2[1])))), (int(length / 2), 2), int(angle), 0, 360, 1)
cv2.fillConvexPoly(cur_canvas, polygon, sk_color[i],lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
# cv2.fillConvexPoly(cur_canvas, polygon, sk_color,lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
canvas = cv2.addWeighted(canvas, 0.4, cur_canvas, 0.6, 0)
return canvas
def draw_points_and_skeleton(image, points, skeleton, points_color_palette='tab20', points_palette_samples=16,
skeleton_color_palette='Set2', skeleton_palette_samples=8, person_index=0,
confidence_threshold=0.1,color=None,sk_color=None):
"""
Draws `points` and `skeleton` on `image`.
Args:
image: image in opencv format
points: list of points to be drawn.
Shape: (nof_points, 3)
Format: each point should contain (y, x, confidence)
skeleton: list of joints to be drawn
Shape: (nof_joints, 2)
Format: each joint should contain (point_a, point_b) where `point_a` and `point_b` are an index in `points`
points_color_palette: name of a matplotlib color palette
Default: 'tab20'
points_palette_samples: number of different colors sampled from the `color_palette`
Default: 16
skeleton_color_palette: name of a matplotlib color palette
Default: 'Set2'
skeleton_palette_samples: number of different colors sampled from the `color_palette`
Default: 8
person_index: index of the person in `image`
Default: 0
confidence_threshold: only points with a confidence higher than this threshold will be drawn. Range: [0, 1]
Default: 0.1
Returns:
A new image with overlaid joints
"""
colors1 = [[255, 0, 0], [255, 85, 0], [255, 170, 0], [255, 255, 0], [170, 255, 0], [85, 255, 0], [0, 255, 0],
[0, 255, 85], [0, 255, 170], [0, 255, 255], [0, 170, 255], [0, 85, 255], [0, 0, 255], [85, 0, 255],
[170, 0, 255], [255, 0, 255], [255, 0, 170], [255, 0, 85], [255, 0, 85]]
image = draw_skeleton(image, points, skeleton, color_palette=skeleton_color_palette,
palette_samples=skeleton_palette_samples, person_index=person_index,
confidence_threshold=confidence_threshold,sk_color=colors1)
image = draw_points(image, points, color_palette=points_color_palette, palette_samples=points_palette_samples,
confidence_threshold=confidence_threshold,color=colors1)
return image
def save_images(images, target, joint_target, output, joint_output, joint_visibility, summary_writer=None, step=0,
prefix=''):
"""
Creates a grid of images with gt joints and a grid with predicted joints.
This is a basic function for debugging purposes only.
If summary_writer is not None, the grid will be written in that SummaryWriter with name "{prefix}_images" and
"{prefix}_predictions".
Args:
images (torch.Tensor): a tensor of images with shape (batch x channels x height x width).
target (torch.Tensor): a tensor of gt heatmaps with shape (batch x channels x height x width).
joint_target (torch.Tensor): a tensor of gt joints with shape (batch x joints x 2).
output (torch.Tensor): a tensor of predicted heatmaps with shape (batch x channels x height x width).
joint_output (torch.Tensor): a tensor of predicted joints with shape (batch x joints x 2).
joint_visibility (torch.Tensor): a tensor of joint visibility with shape (batch x joints).
summary_writer (tb.SummaryWriter): a SummaryWriter where write the grids.
Default: None
step (int): summary_writer step.
Default: 0
prefix (str): summary_writer name prefix.
Default: ""
Returns:
A pair of images which are built from torchvision.utils.make_grid
"""
# Input images with gt
images_ok = images.detach().clone()
images_ok[:, 0].mul_(0.229).add_(0.485)
images_ok[:, 1].mul_(0.224).add_(0.456)
images_ok[:, 2].mul_(0.225).add_(0.406)
for i in range(images.shape[0]):
joints = joint_target[i] * 4.
joints_vis = joint_visibility[i]
for joint, joint_vis in zip(joints, joints_vis):
if joint_vis[0]:
a = int(joint[1].item())
b = int(joint[0].item())
# images_ok[i][:, a-1:a+1, b-1:b+1] = torch.tensor([1, 0, 0])
images_ok[i][0, a - 1:a + 1, b - 1:b + 1] = 1
images_ok[i][1:, a - 1:a + 1, b - 1:b + 1] = 0
grid_gt = torchvision.utils.make_grid(images_ok, nrow=int(images_ok.shape[0] ** 0.5), padding=2, normalize=False)
if summary_writer is not None:
summary_writer.add_image(prefix + 'images', grid_gt, global_step=step)
# Input images with prediction
images_ok = images.detach().clone()
images_ok[:, 0].mul_(0.229).add_(0.485)
images_ok[:, 1].mul_(0.224).add_(0.456)
images_ok[:, 2].mul_(0.225).add_(0.406)
for i in range(images.shape[0]):
joints = joint_output[i] * 4.
joints_vis = joint_visibility[i]
for joint, joint_vis in zip(joints, joints_vis):
if joint_vis[0]:
a = int(joint[1].item())
b = int(joint[0].item())
# images_ok[i][:, a-1:a+1, b-1:b+1] = torch.tensor([1, 0, 0])
images_ok[i][0, a - 1:a + 1, b - 1:b + 1] = 1
images_ok[i][1:, a - 1:a + 1, b - 1:b + 1] = 0
grid_pred = torchvision.utils.make_grid(images_ok, nrow=int(images_ok.shape[0] ** 0.5), padding=2, normalize=False)
if summary_writer is not None:
summary_writer.add_image(prefix + 'predictions', grid_pred, global_step=step)
# Heatmaps
# ToDo
# for h in range(0,17):
# heatmap = torchvision.utils.make_grid(output[h].detach(), nrow=int(np.sqrt(output.shape[0])),
# padding=2, normalize=True, range=(0, 1))
# summary_writer.add_image('train_heatmap_%d' % h, heatmap, global_step=step + epoch*len_dl_train)
return grid_gt, grid_pred
def check_video_rotation(filename):
# thanks to
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/53097092/frame-from-video-is-upside-down-after-extracting/55747773#55747773
# this returns meta-data of the video file in form of a dictionary
meta_dict = ffmpeg.probe(filename)
# from the dictionary, meta_dict['streams'][0]['tags']['rotate'] is the key
# we are looking for
rotation_code = None
try:
if int(meta_dict['streams'][0]['tags']['rotate']) == 90:
rotation_code = cv2.ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE
elif int(meta_dict['streams'][0]['tags']['rotate']) == 180:
rotation_code = cv2.ROTATE_180
elif int(meta_dict['streams'][0]['tags']['rotate']) == 270:
rotation_code = cv2.ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE
else:
raise ValueError
except KeyError:
pass
return rotation_code
4、测试算法
①主程序
在SimDR文件夹下新建main.py ,复制以下代码到文件中,修改parser参数source的默认值,运行代码。
import argparse
import time
import os
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from pathlib import Path
from Point_detect import Points
from lib.utils.visualization import draw_points_and_skeleton,joints_dict
def image_detect(opt):
skeleton = joints_dict()['coco']['skeleton']
hrnet_model = Points(model_name='hrnet', opt=opt,resolution=(384,288)) #resolution = (384,288) or (256,192)
# simdr_model = Points(model_name='simdr', opt=opt,resolution=(256,192)) #resolution = (256,192)
# sa_simdr_model = Points(model_name='sa-simdr', opt=opt,resolution=(384,288)) #resolution = (384,288) or (256,192)
img0 = cv.imread(opt.source)
frame = img0.copy()
#predict
pred = hrnet_model.predict(img0)
# pred = simdr_model.predict(frame)
# pred = sa_simdr_model.predict(frame)
#vis
for i, pt in enumerate(pred):
frame = draw_points_and_skeleton(frame, pt, skeleton)
#save
cv.imwrite('test_result.jpg', frame)
def video_detect(opt):
hrnet_model = Points(model_name='hrnet', opt=opt, resolution=(384, 288)) # resolution = (384,288) or (256,192)
# simdr_model = Points(model_name='simdr', opt=opt,resolution=(256,192)) #resolution = (256,192)
# sa_simdr_model = Points(model_name='sa-simdr', opt=opt,resolution=(384,288)) #resolution = (384,288) or (256,192)
skeleton = joints_dict()['coco']['skeleton']
cap = cv.VideoCapture(opt.source)
if opt.save_video:
fourcc = cv.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'MJPG')
out = cv.VideoWriter('data/runs/{}_out.avi'.format(os.path.basename(opt.source).split('.')[0]), fourcc, 24, (int(cap.get(3)), int(cap.get(4))))
while cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
pred = hrnet_model.predict(frame)
# pred = simdr_model.predict(frame)
# pred = sa_simdr_model.predict(frame)
for pt in pred:
frame = draw_points_and_skeleton(frame,pt,skeleton)
if opt.show:
cv.imshow('result', frame)
if opt.save_video:
out.write(frame)
if cv.waitKey(1) == 27:
break
out.release()
cap.release()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
# video_detect(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default='./data/images/test1.jpg', help='source') # file/folder, 0 for webcam
parser.add_argument('--detect_weight', type=str, default="./yolov5/weights/yolov5x.pt", help='e.g "./yolov5/weights/yolov5x.pt"')
parser.add_argument('--save_video', action='store_true', default=False,help='save results to *.avi')
parser.add_argument('--show', action='store_true', default=True, help='save results to *.avi')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cpu', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='object confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='IOU threshold for NMS')
parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3')
parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
opt = parser.parse_args()
image_detect(opt)
②结果展示
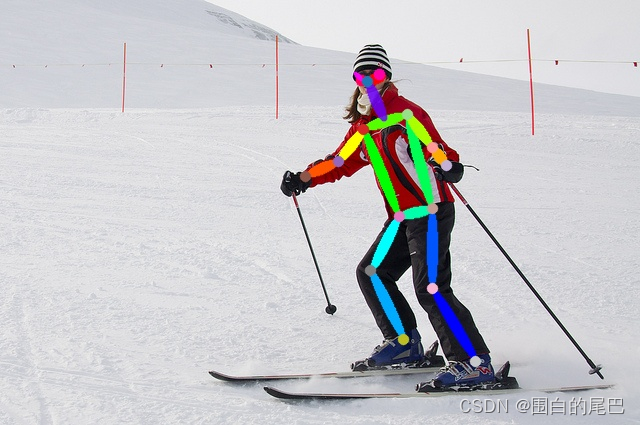


四、总结
全文较长,主要都是些代码,整个工程从跑数据集到实际检测需要对代码工程有一定的理解,整个项目不难,主要考验类的构造。如果需要整个工程可以私聊我。由于我也是刚入门的萌新,所以代码格式写法或者理论看法有很多错误,欢迎指正,共同进步,如果有帮助欢迎点赞评论,万分感谢。
五、参考内容
1、GitHub - leeyegy/SimDR: PyTorch implementation for: Is 2D Heatmap Representation Even Necessary for Human Pose Estimation? (http://arxiv.org/abs/2107.03332)
2、https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
3、GitHub - GreenTeaHua/simple-HRNet: Multi-person Human Pose Estimation with HRNet in Pytorch
版权归原作者 围白的尾巴 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。