Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX,开放神经网络交换) 格式,是一个用于表示深度学习模型的标准,可使模型在不同框架之间进行转移
Torch 所定义的模型为动态图,其前向传播是由类方法定义和实现的
但是 Python 代码的效率是比较底下的,试想把动态图转化为静态图,模型的推理速度应当有所提升
Torch 框架中,torch.onnx.export 可以将父类为 nn.Module 的模型导出到 onnx 文件中,最重要的有三个参数:
- model:父类为 nn.Module 的模型
- args:传入 model 的 forward 方法的变量列表,类型应为 tuple
- f:onnx 文件名称的字符串
import torch
from torchvision.models import resnet50
file = 'resnet.onnx'
# 声明模型
resnet = resnet50(pretrained=False).eval()
image = torch.rand([1, 3, 224, 224])
# 导出为 onnx 文件
torch.onnx.export(resnet, (image,), file)
onnx 文件可被 Netron 打开,以查看模型结构
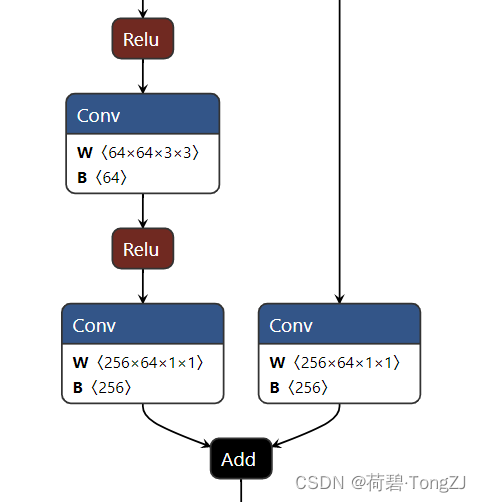
基本用法
要在 Python 中运行 onnx 模型,需要下载 onnxruntime
# 选其一即可
pip install onnxruntime # CPU 版本
pip install onnxruntime-gpu # GPU 版本
推理时需要借助其中的 InferenceSession,其中较为重要的实例方法有:
- get_inputs():得到输入变量的列表 (变量属性:name、shape、type)
- get_outputs():得到输入变量的列表 (变量属性:name、shape、type)
- run(output_names, input_feed):输入变量为 numpy.ndarray (注意 dtype 应为 float32),使用模型推理并返回输出
可得出 onnx 模型的基本用法:
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
file = 'resnet.onnx'
# 找到 GPU / CPU
provider = ort.get_available_providers()[
1 if ort.get_device() == 'GPU' else 0]
print('设备:', provider)
# 声明 onnx 模型
model = ort.InferenceSession(file, providers=[provider])
# 参考: ort.NodeArg
for node_list in model.get_inputs(), model.get_outputs():
for node in node_list:
attr = {'name': node.name,
'shape': node.shape,
'type': node.type}
print(attr)
print('-' * 60)
# 得到输入、输出结点的名称
input_node_name = model.get_inputs()[0].name
ouput_node_name = [node.name for node in model.get_outputs()]
image = np.random.random([1, 3, 224, 224]).astype(np.float32)
print(model.run(output_names=ouput_node_name,
input_feed={input_node_name: image}))
高级 API
为了简化使用步骤,使用类进行封装:
class Onnx_Module(ort.InferenceSession):
''' onnx 推理模型
provider: 优先使用 GPU'''
provider = ort.get_available_providers()[
1 if ort.get_device() == 'GPU' else 0]
def __init__(self, file):
super(Onnx_Module, self).__init__(file, providers=[self.provider])
# 参考: ort.NodeArg
self.inputs = [node_arg.name for node_arg in self.get_inputs()]
self.outputs = [node_arg.name for node_arg in self.get_outputs()]
def __call__(self, *arrays):
input_feed = {name: x for name, x in zip(self.inputs, arrays)}
return self.run(self.outputs, input_feed)
在 Torch 中,对于卷积神经网络 model 与图像 image,推理的代码为 "model(image)",而使用这个封装的类也是类似:
import numpy as np
file = 'resnet.onnx'
model = Onnx_Module(file)
image = np.random.random([1, 3, 224, 224]).astype(np.float32)
print(model(image))
为了方便观察 Torch 模型与 onnx 模型的速度差异,同时检查两个模型的输出是否一致,又编写了 test 函数
test 方法的参数与 torch.onnx.export 一致,其基本流程为:
- 得到 Torch 模型的输出,并 print 推断耗时
- 将 Torch 模型导出为 onnx 文件,将输入变量中的 torch.tensor 转化为 numpy.ndarray
- 初始化 onnx 模型,得到 onnx 模型的输出,并 print 推断耗时
- 计算 Torch 模型与 onnx 模型输出的绝对误差的均值
- 将 onnx 模型 return
class Timer:
repeat = 3
def __new__(cls, fun, *args, **kwargs):
import time
start = time.time()
for _ in range(cls.repeat): fun(*args, **kwargs)
cost = (time.time() - start) / cls.repeat
return cost * 1e3 # ms
class Onnx_Module(ort.InferenceSession):
''' onnx 推理模型
provider: 优先使用 GPU'''
provider = ort.get_available_providers()[
1 if ort.get_device() == 'GPU' else 0]
def __init__(self, file):
super(Onnx_Module, self).__init__(file, providers=[self.provider])
# 参考: ort.NodeArg
self.inputs = [node_arg.name for node_arg in self.get_inputs()]
self.outputs = [node_arg.name for node_arg in self.get_outputs()]
def __call__(self, *arrays):
input_feed = {name: x for name, x in zip(self.inputs, arrays)}
return self.run(self.outputs, input_feed)
@classmethod
def test(cls, model, args, file, **export_kwargs):
# 测试 Torch 的运行时间
torch_output = model(*args).data.numpy()
print(f'Torch: {Timer(model, *args):.2f} ms')
# model: Torch -> onnx
torch.onnx.export(model, args, file, **export_kwargs)
# data: tensor -> array
args = tuple(map(lambda tensor: tensor.data.numpy(), args))
onnx_model = cls(file)
# 测试 onnx 的运行时间
onnx_output = onnx_model(*args)
print(f'Onnx: {Timer(onnx_model, *args):.2f} ms')
# 计算 Torch 模型与 onnx 模型输出的绝对误差
abs_error = np.abs(torch_output - onnx_output).mean()
print(f'Mean Error: {abs_error:.2f}')
return onnx_model
对于 ResNet50 而言,Torch 模型的推断耗时为 172.67 ms,onnx 模型的推断耗时为 36.56 ms,onnx 模型的推断耗时仅为 Torch 模型的 21.17%
版权归原作者 荷碧TongZJ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。