本次推荐三个插件。
Verilog-HDL/SystemVerilog/Bluespec SystemVerilog
可实现功能:
- 语法高亮
- 自动例化
- 代码提示和跳转
- 自动补全
插件配置
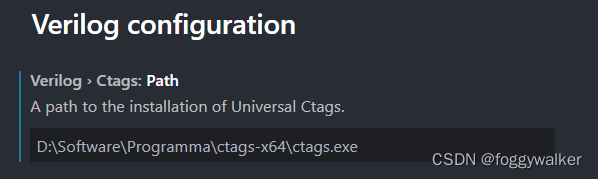
如Verilog HDL/SystemVerilog插件欢迎页的说明,支持Ctags功能:

配置步骤:
- 下载最新版ctags,旧版的有些功能不够齐全;windows可选x64版本;
- 将ctags.exe的路径设置到系统环境变量中;
- 插件设置中配置ctags路径;
- 重启VSCode即可;
可以选择不同的编译器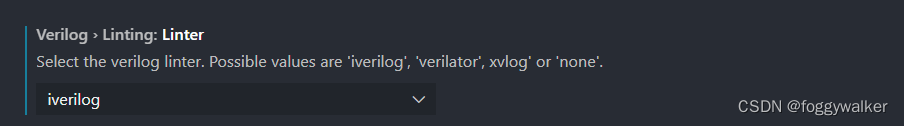
包括:
- iverilog
- xvlog(vivado)
- modelsim
功能展示
 支持verilog、SV等语法高亮。
支持verilog、SV等语法高亮。

shift+ctrl+p输入verilog,可以直接自动例化模块。
 鼠标放在信号上,就会有声明显示在悬浮框中。Ctrl+左键,点击信号名,自动跳转到声明处。光标放在信号处,右键选择查看定义(快捷键可自行绑定),可以在此处展开声明处的代码,用于修改声明十分方便,就不用再来回跳转了。
鼠标放在信号上,就会有声明显示在悬浮框中。Ctrl+左键,点击信号名,自动跳转到声明处。光标放在信号处,右键选择查看定义(快捷键可自行绑定),可以在此处展开声明处的代码,用于修改声明十分方便,就不用再来回跳转了。
Verilog_Testbench
可实现功能:
- 自动生成testbench
shift+ctrl+p输入testbench,可以直接生成tb。然后在终端复制即可。
SystemVerilog and Verilog Formatter
 这款工具由谷歌推出,同时支持Verilog和System Verilog,效果非常好,支持自定义的格式化参数也很丰富。个人认为比verilog format好用。
这款工具由谷歌推出,同时支持Verilog和System Verilog,效果非常好,支持自定义的格式化参数也很丰富。个人认为比verilog format好用。
可实现功能
- 自动格式化文件
- 自动格式化选定内容
- 自定义格式
自定义参数设置表
verible-verilog-format: usage: bazel-bin/verilog/tools/formatter/verible-verilog-format [options] <file> [<file...>]
To pipe from stdin, use '-' as <file>.Flags from common/formatting/basic_format_style_init.cc:
--column_limit (Target line length limit to stay under when formatting.);
default: 100;
--indentation_spaces (Each indentation level adds this many spaces.);
default: 2;
--line_break_penalty (Penalty added to solution for each introduced line
break.); default: 2;
--over_column_limit_penalty (For penalty minimization, this represents the
baseline penalty value of exceeding the column limit. Additional penalty
of 1 is incurred for each character over this limit); default: 100;
--wrap_spaces (Each wrap level adds this many spaces. This applies when the
first element after an open-group section is wrapped. Otherwise, the
indentation level is set to the column position of the open-group
operator.); default: 4;Flags from external/com_google_absl/absl/flags/parse.cc:
--flagfile (comma-separated list of files to load flags from); default: ;
--fromenv (comma-separated list of flags to set from the environment [use
'export FLAGS_flag1=value']); default: ;
--tryfromenv (comma-separated list of flags to try to set from the
environment if present); default: ;
--undefok (comma-separated list of flag names that it is okay to specify on
the command line even if the program does not define a flag with that
name); default: ;Flags from verilog/formatting/format_style_init.cc:
--assignment_statement_alignment (Format various assignments:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--case_items_alignment (Format case items:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--class_member_variable_alignment (Format class member variables:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--compact_indexing_and_selections (Use compact binary expressions inside
indexing / bit selection operators); default: true;
--distribution_items_alignment (Aligh distribution items:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--enum_assignment_statement_alignment (Format assignments with enums:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--expand_coverpoints (If true, always expand coverpoints.); default: false;
--formal_parameters_alignment (Format formal parameters:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--formal_parameters_indentation (Indent formal parameters: {indent,wrap});
default: wrap;
--module_net_variable_alignment (Format net/variable declarations:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--named_parameter_alignment (Format named actual parameters:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--named_parameter_indentation (Indent named parameter assignments:
{indent,wrap}); default: wrap;
--named_port_alignment (Format named port connections:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--named_port_indentation (Indent named port connections: {indent,wrap});
default: wrap;
--port_declarations_alignment (Format port declarations:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--port_declarations_indentation (Indent port declarations: {indent,wrap});
default: wrap;
--port_declarations_right_align_packed_dimensions (If true, packed
dimensions in contexts with enabled alignment are aligned to the right.);
default: false;
--port_declarations_right_align_unpacked_dimensions (If true, unpacked
dimensions in contexts with enabled alignment are aligned to the right.);
default: false;
--struct_union_members_alignment (Format struct/union members:
{align,flush-left,preserve,infer}); default: infer;
--try_wrap_long_lines (If true, let the formatter attempt to optimize line
wrapping decisions where wrapping is needed, else leave them unformatted.
This is a short-term measure to reduce risk-of-harm.); default: false;Flags from verilog/parser/verilog_parser.cc:
--verilog_trace_parser (Trace verilog parser); default: false;Flags from verilog/tools/formatter/verilog_format.cc:
--failsafe_success (If true, always exit with 0 status, even if there were
input errors or internal errors. In all error conditions, the original
text is always preserved. This is useful in deploying services where
fail-safe behaviors should be considered a success.); default: true;
--inplace (If true, overwrite the input file on successful conditions.);
default: false;
--lines (Specific lines to format, 1-based, comma-separated, inclusive N-M
ranges, N is short for N-N. By default, left unspecified, all lines are
enabled for formatting. (repeatable, cumulative)); default: ;
--max_search_states (Limits the number of search states explored during line
wrap optimization.); default: 100000;
--show_equally_optimal_wrappings (If true, print when multiple optimal
solutions are found (stderr), but continue to operate normally.);
default: false;
--show_inter_token_info (If true, along with show_token_partition_tree,
include inter-token information such as spacing and break penalties.);
default: false;
--show_largest_token_partitions (If > 0, print token partitioning and then
exit without formatting output.); default: 0;
--show_token_partition_tree (If true, print diagnostics after token
partitioning and then exit without formatting output.); default: false;
--stdin_name (When using '-' to read from stdin, this gives an alternate
name for diagnostic purposes. Otherwise this is ignored.);
default: "<stdin>";
--verbose (Be more verbose.); default: false;
--verify_convergence (If true, and not incrementally formatting with
--lines, verify that re-formatting the formatted output yields no further
changes, i.e. formatting is convergent.); default: true;Try --helpfull to get a list of all flags or --help=substring shows help for
flags which include specified substring in either in the name, or description or
path.
插件配置
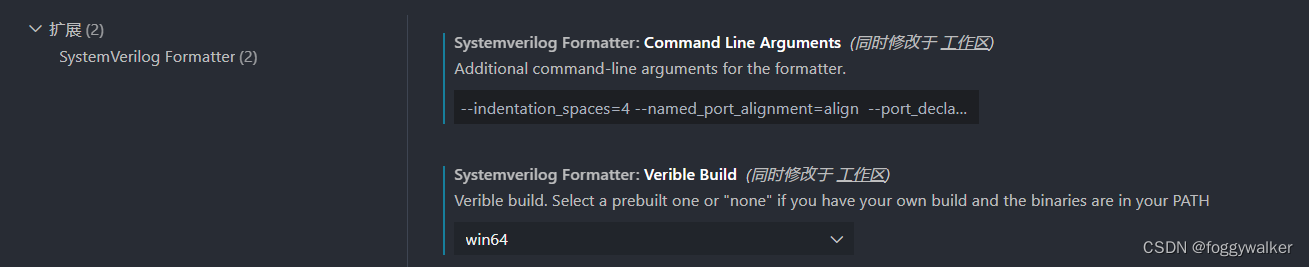
如果是windows,systemverilogFormatter.veribleBuild设置为win64
systemverilogFormatter.commandLineArguments可以自定义格式化参数,下面放上我自己用的参数,可以实现大部分常用代码段实现对齐。
--indentation_spaces=4 --named_port_alignment=align --ort_declarations_alignment=align --module_net_variable_alignment=align
如何使用?如何格式化?
和vscode内置格式化一样,直接shift+ctrl+f就可以格式化文件,ctrl+k可以格式化选定内容。
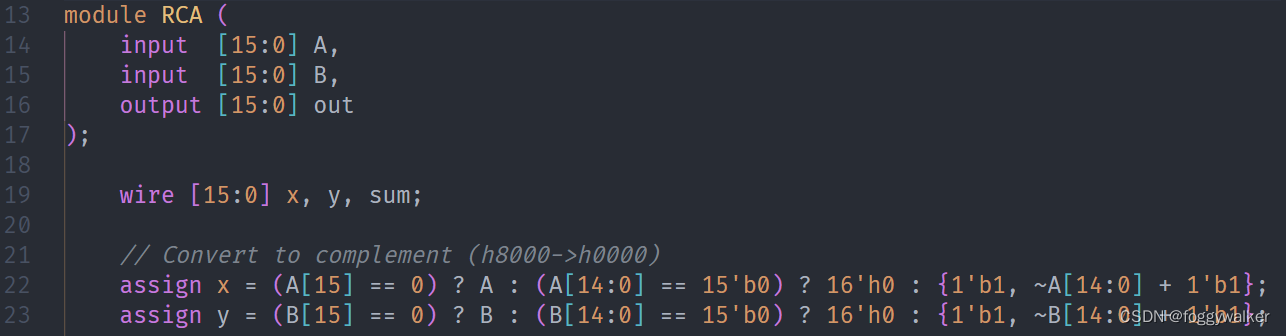 值得注意的是,由于这个插件也是在完善中,还是存在部分问题的。
值得注意的是,由于这个插件也是在完善中,还是存在部分问题的。
比如else不会换行。
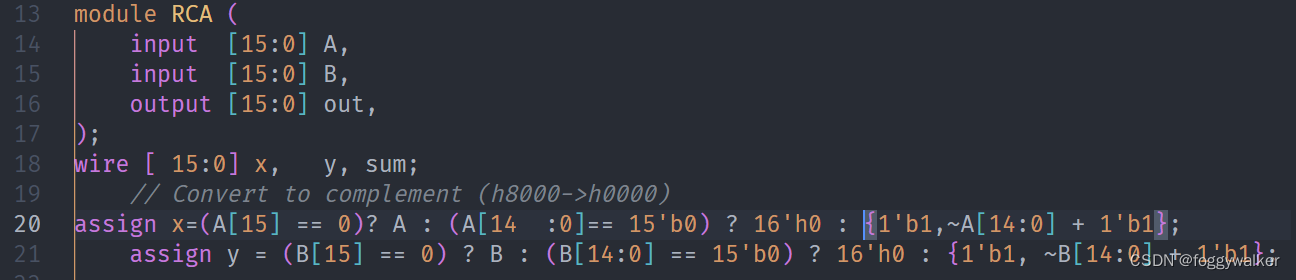
 比如,存在语法问题,或者不能识别语法的时候,格式化会使用不了。这里我将最后一个端口加上","就不能格式化了。
比如,存在语法问题,或者不能识别语法的时候,格式化会使用不了。这里我将最后一个端口加上","就不能格式化了。
版权归原作者 foggywalker 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。