5 键控状态
5.1 键控状态
在 Flink 中有如下 5 种键控状态(Keyed State),这些状态仅能在键控数据流(Keyed Stream)的算子(operator)上使用。键控流使用键(key)对数据流中的记录进行分区,同时也会对状态进行分区。要创建键控流,只需要在 DataStream 上使用
keyBy()
方法指定键即可。
具体地,这 5 种键控状态如下:
ValueState<T>:保存一个值;这个值可以通过update(T)进行更新,通过T value()进行检索。MapState<UK, UV>:保存一个映射列表;可以使用put(UK, UV)或putAll(Map<UK, UV>)添加映射,使用get(UK)来检索特定的 key,使用entires()、keys()、values()分别检索映射、键和值的可迭代视图,使用isEmpty()判断是否包含任何键值对。ListState<T>:保存一个元素的列表;可以通过add(T)或者addAll(List<T>)添加元素,通过Iterable<T> get()获取整个列表,通过update(List<T>)覆盖当前的列表。ReducingState<T>:保存一个值,表示添加到状态的所有值聚合后的结果;使用add(T)添加元素,并使用提供的reduceFunction进行聚合。AggregatingState<IN, OUT>:保存一个值,表示添加到状态的所有值聚合后的结果;使用add(T)添加元素,并使用提供的AggregateFunction进行聚合。与ReducingState不同的时,聚合类型可能与添加到状态的元素类型不同。
所有的类型状态还有一个
clear()
方法,用于清除当前键的状态数据。
键控状态具有如下特性:
- 实现以上 5 个接口的状态对象仅用于与状态交互,状态本身不一定存储在内存中,还可能在磁盘或其他位置。
- 从状态中获取的值取决于输入元素所代表的 Key,在不同 key 上调用同一个接口,可能得到不同的值。
5.2 键控状态的源码
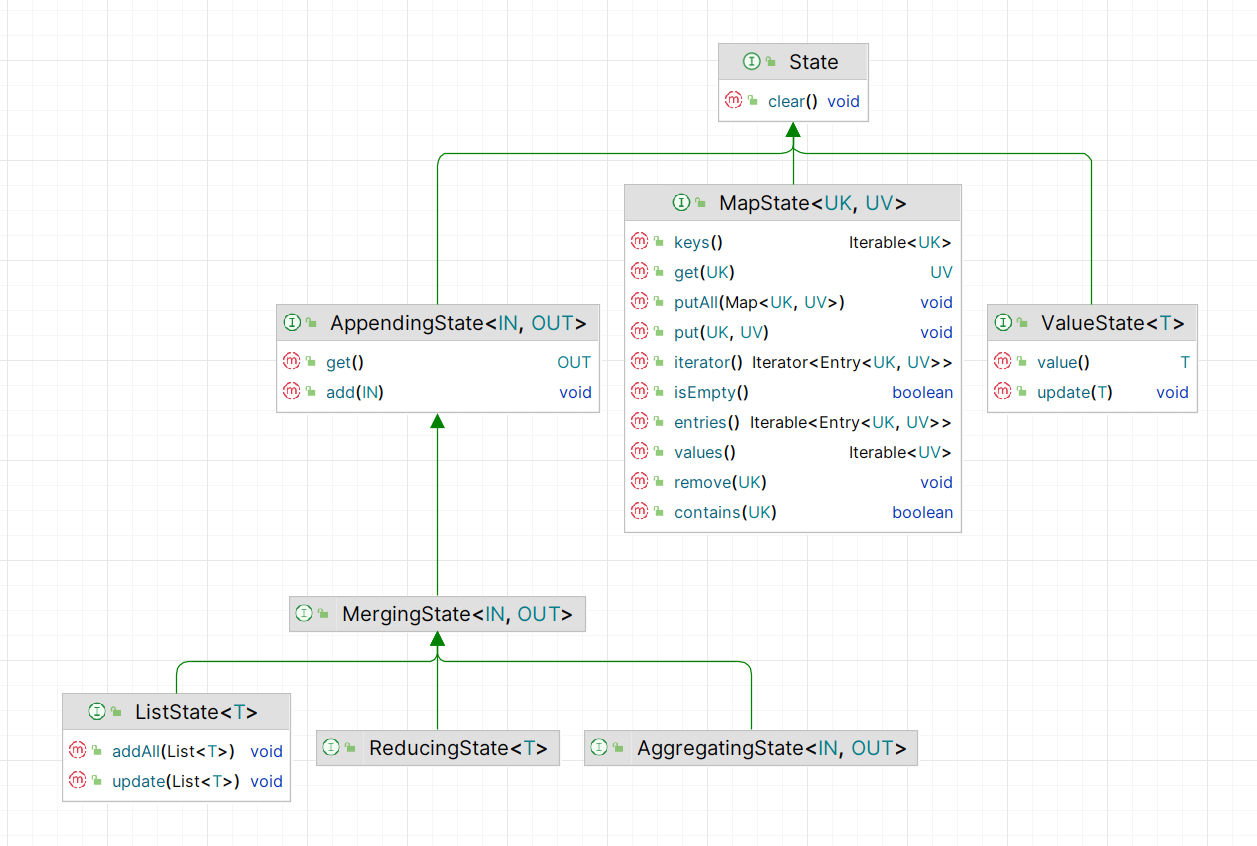
5.2.1
State
State
接口是所有状态接口的基类,其中只定义了一个
clear()
方法,用于移除当前 key 下的状态。
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.State
@PublicEvolvingpublicinterfaceState{/** Removes the value mapped under the current key. */voidclear();}
5.2.2
ValueState
:每个 key 存储一个值
ValueState<T>
接口是用于保存一个值的状态,其中定义了
value()
方法和
update(T value)
方法用于查询和更新当前 key 的状态;泛型
V
是存储的值的类型。
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueState
@PublicEvolvingpublicinterfaceValueState<T>extendsState{Tvalue()throwsIOException;voidupdate(T value)throwsIOException;}
5.2.3
MapState
:每个 key 存储一个映射
MapState<UK, UV>
接口用于保存一个映射,泛型
UK
是映射的键的类型,泛型
UV
是映射的值的类型。其方法与 Java 的
Map
接口类似,具体包含如下方法:
get(UK key):获取状态中key对应的值put(UK key, UV value):将键值对key/value写入到状态中putAll(Map<UK, UV> map):将map中的所有键值对写入到状态中remove(UK key):移除状态中key及其对应的值contains(UK key):查询状态中是否包含keyentries()/iterator():遍历状态中的所有键值对keys():遍历状态中的所有键values():遍历状态中的所有值isEmpty():查询状态的映射是否为空
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.MapState
@PublicEvolvingpublicinterfaceMapState<UK, UV>extendsState{UVget(UK key)throwsException;voidput(UK key,UV value)throwsException;voidputAll(Map<UK, UV> map)throwsException;voidremove(UK key)throwsException;booleancontains(UK key)throwsException;Iterable<Map.Entry<UK, UV>>entries()throwsException;Iterable<UK>keys()throwsException;Iterable<UV>values()throwsException;Iterator<Map.Entry<UK, UV>>iterator()throwsException;booleanisEmpty()throwsException;}
5.2.4
AppendingState
及其子类:每个 key 存储一个累加状态
AppendingState<IN, OUT>
接口定义了一个具有类似累加器性质的状态,其泛型
IN
为每次添加元素的类型,
OUT
为结果的类型。其中包含 2 个方法,
add(IN value)
方法用于向累加器添加元素,
get()
方法用于获取当前累加器的值。
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.AppendingState
@PublicEvolvingpublicinterfaceAppendingState<IN, OUT>extendsState{OUTget()throwsException;voidadd(IN value)throwsException;}
MergingState<IN, OUT>
接口继承了
AppendingState<IN, OUT>
接口,要求在实现时支持类似累加器的合并运算,即将两个
MergingState
实例合并为包含 2 个实例信息的 1 个
MergingState
实例。
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.MergingState
@PublicEvolvingpublicinterfaceMergingState<IN, OUT>extendsAppendingState<IN, OUT>{}
ListState<T>
、
ReducingState<T>
和
AggregatingState<IN, OUT>
均继承了
MergingState<IN, OUT>
。
5.2.4.1
ListState
:输入元素,输出可迭代对象
ListState<T>
的
add(T value)
接受一个
T
类型的元素,
get()
方法返回一个
Iterable<T>
。同时,额外定义了 2 个方法:
update(List<T> values):使用values替换到当前状态中的列表addAll(List<T> values):将values添加到当前状态的列表中
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ListState
@PublicEvolvingpublicinterfaceListState<T>extendsMergingState<T,Iterable<T>>{voidupdate(List<T> values)throwsException;voidaddAll(List<T> values)throwsException;}
5.2.4.2
ReducingState
:输入和输出类型一致
ReducingState<T>
接口并没有定义新的方法,但是调整了
MergingState
接口的泛型类型,
add(T value)
接受一个
T
类型的元素,
get()
方法返回一个
T
类型的对象。
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ReducingState
@PublicEvolvingpublicinterfaceReducingState<T>extendsMergingState<T,T>{}
5.2.4.3
AggregatingState
:在每个输入元素后直接聚合
AggregatingState<IN, OUT>
接口并没有定义额外的逻辑,
add(IN value)
接受一个
IN
类型的元素,
get()
方法返回一个
OUT
类型的对象。但是规定在每个元素输入后,都需要直接将该元素聚合到当前的最终结果上。
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.AggregatingState
@PublicEvolvingpublicinterfaceAggregatingState<IN, OUT>extendsMergingState<IN, OUT>{}
5.3 使用键控状态
在使用键控状态时,必须创建一个
StateDescriptor
,并在 UDF 的
open()
方法中,并从
RuntimeContext
中获取该状态的状态句柄(state handle)。在状态句柄中,记录了状态名称、状态所持有值的类型以及用户所指定的函数。根据不同的状态类型,可以创建
ValueStateDescriptor
、
ListStateDescriptor
、
AggregatingStateDescriptor
、
ReducingStateDescriptor
或
MapStateDescriptor
。
StateDescriptor
的详细介绍详见 5.4。
样例|获取
Tuple2<Long, Long>
类型
ValueState
的状态句柄
privatetransientValueState<Tuple2<Long,Long>> sum;// 定义状态句柄@Overridepublicvoidopen(Configuration config){ValueStateDescriptor<Tuple2<Long,Long>> descriptor =newValueStateDescriptor<>("average",// 状态名称TypeInformation.of(newTypeHint<Tuple2<Long,Long>>(){}),// 状态的类型信息Tuple2.of(0L,0L));// 状态的默认值
sum =getRuntimeContext().getState(descriptor);}
在使用状态时,直接使用状态句柄中的方法即可。
样例|使用
Tuple2<Long, Long>
类型的
ValueState
// 访问 ValueState 类型状态的值Tuple2<Long,Long> currentSum = sum.value();
// 更新 ValueState 类型状态的值
sum.update(currentSum);
因为状态句柄需要通过
RuntimeContext
获取,因此只能在富函数中使用。富函数的详细介绍见 “3 UDF 接口与富函数”。
下面来看一个 Flink 官方文档中的状态使用样例。
样例|使用
ValueState
计算每 2 个相邻元素的平均值发往下游的 UDF 函数的样例
publicclassCountWindowAverageextendsRichFlatMapFunction<Tuple2<Long,Long>,Tuple2<Long,Long>>{/**
* The ValueState handle. The first field is the count, the second field a running sum.
*/privatetransientValueState<Tuple2<Long,Long>> sum;@OverridepublicvoidflatMap(Tuple2<Long,Long> input,Collector<Tuple2<Long,Long>> out)throwsException{// access the state valueTuple2<Long,Long> currentSum = sum.value();// update the count
currentSum.f0 +=1;// add the second field of the input value
currentSum.f1 += input.f1;// update the state
sum.update(currentSum);// if the count reaches 2, emit the average and clear the stateif(currentSum.f0 >=2){
out.collect(newTuple2<>(input.f0, currentSum.f1 / currentSum.f0));
sum.clear();}}@Overridepublicvoidopen(Configuration config){ValueStateDescriptor<Tuple2<Long,Long>> descriptor =newValueStateDescriptor<>("average",// the state nameTypeInformation.of(newTypeHint<Tuple2<Long,Long>>(){}),// type informationTuple2.of(0L,0L));// default value of the state, if nothing was set
sum =getRuntimeContext().getState(descriptor);}}// this can be used in a streaming program like this (assuming we have a StreamExecutionEnvironment env)
env.fromElements(Tuple2.of(1L,3L),Tuple2.of(1L,5L),Tuple2.of(1L,7L),Tuple2.of(1L,4L),Tuple2.of(1L,2L)).keyBy(value -> value.f0).flatMap(newCountWindowAverage()).print();// the printed output will be (1,4) and (1,5)
定义 UDF 的
ValueState
类型的对象属性
sum
,其值为一个元组,元组中第一个元素用于存储计数结果,第二个元素存储求和结果。
在
open()
方法中,创建
ValueStateDescriptor
并定义了状态名称、状态类型和状态的初始值,在获取到
ValueState
类型的状态句柄后,将其状态存储到实例属性
sum
中。
使用了
ValueState
接口的
value()
、
update()
、
clear()
方法获取、更新、清除当前的值。
5.4
StateDescriptor
及其子类
在从
RuntimeContext
中获取状态时,首先需要创建一个对应类型的
StateDescriptor
,才能获取对应的状态句柄。
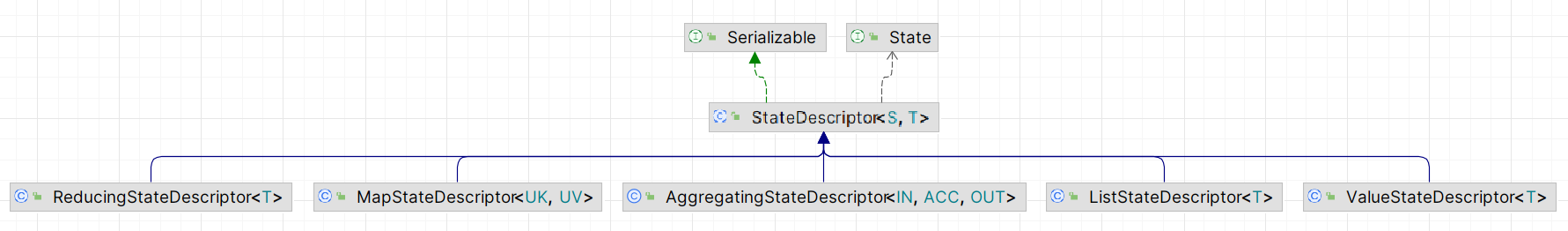
上图为 5 种内置状态类型对应的
StateDescriptor
的 UML 图,可以看到它们均继承了抽象类
StateDescriptor
。
5.4.1
StateDescriptor
下面,具体了解抽象类
StateDescriptor
的核心逻辑。该类有两个泛型,泛型
S extends State
表示状态的类型,泛型
T
表示状态中的值的类型。在
StateDescriptor
类中,主要实现了如下功能(不包括已标注
@Deprecated
的功能):
- 存储状态名称、状态类型信息、状态类型序列化器和状态类型的默认值
- 当使用状态类型信息实例化时,可以根据配置文件自动创建状态类型的序列化器
具体地,在
StateDescriptor
类中,有如下核心实例属性:
name:状态的唯一标识符,即状态名称serializerAtomicReference:类型的序列化器typeInfo:类型信息defaultValue:状态的默认值
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.StateDescriptor
protectedfinalString name;privatefinalAtomicReference<TypeSerializer<T>> serializerAtomicReference =newAtomicReference<>();@NullableprivateTypeInformation<T> typeInfo;@Nullable@DeprecatedprotectedtransientT defaultValue;
5.4.1.1 构造方法
StateDescriptor
有 3 个构造器,它们的访问权限均被修饰为
protected
,即只允许子类访问,要求子类必须重新定义构造方法。
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.StateDescriptor
(部分)
protectedStateDescriptor(String name,TypeSerializer<T> serializer,@NullableT defaultValue){this.name =checkNotNull(name,"name must not be null");this.serializerAtomicReference.set(checkNotNull(serializer,"serializer must not be null"));this.defaultValue = defaultValue;}protectedStateDescriptor(String name,TypeInformation<T> typeInfo,@NullableT defaultValue){this.name =checkNotNull(name,"name must not be null");this.typeInfo =checkNotNull(typeInfo,"type information must not be null");this.defaultValue = defaultValue;}protectedStateDescriptor(String name,Class<T> type,@NullableT defaultValue){this.name =checkNotNull(name,"name must not be null");checkNotNull(type,"type class must not be null");try{this.typeInfo =TypeExtractor.createTypeInfo(type);}catch(Exception e){thrownewRuntimeException("Could not create the type information for '"+ type.getName()+"'. "+"The most common reason is failure to infer the generic type information, due to Java's type erasure. "+"In that case, please pass a 'TypeHint' instead of a class to describe the type. "+"For example, to describe 'Tuple2<String, String>' as a generic type, use "+"'new PravegaDeserializationSchema<>(new TypeHint<Tuple2<String, String>>(){}, serializer);'",
e);}this.defaultValue = defaultValue;}
以上 3 个构造器均接受
name
、
type
、
defaultValue
这 3 个参数,其中
name
为状态名称、
type
为状态类型,
defaultValue
为状态的默认值。它们的区别在于状态类型的参数分别为
TypeSerializer<T>
类型、
TypeInformation<T>
类型和
Class<T> type
类型。
5.4.1.2 序列化器相关方法
除
StateDescriptor(String name, TypeSerializer<T> serializer, @Nullable T defaultValue)
构造方法外,另外两个方法均没有初始化状态类型的序列化器
serializerAtomicReference
。因此,在
StateDescriptor
中还定义了如下与序列化器有关的方法:
isSerializerInitialized():检查序列化器是否已经初始化initializeSerializerUnlessSet(ExecutionConfig executionConfig):根据配置信息初始化序列化器initializeSerializerUnlessSet(SerializerFactory serializerFactory):根据SerializerFactory初始化序列化器
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.StateDescriptor
(部分)
publicbooleanisSerializerInitialized(){return serializerAtomicReference.get()!=null;}publicvoidinitializeSerializerUnlessSet(ExecutionConfig executionConfig){initializeSerializerUnlessSet(newSerializerFactory(){@Overridepublic<T>TypeSerializer<T>createSerializer(TypeInformation<T> typeInformation){return typeInformation.createSerializer(executionConfig);}});}@InternalpublicvoidinitializeSerializerUnlessSet(SerializerFactory serializerFactory){if(serializerAtomicReference.get()==null){checkState(typeInfo !=null,"no serializer and no type info");// try to instantiate and set the serializerTypeSerializer<T> serializer = serializerFactory.createSerializer(typeInfo);// use cas to assure the singletonif(!serializerAtomicReference.compareAndSet(null, serializer)){LOG.debug("Someone else beat us at initializing the serializer.");}}}
5.4.2
StateDescriptor
的子类
在
StateDescriptor
的 5 个子类中,主要包含如下逻辑:
- 使用特定状态类型,替换掉将
StateDescriptor类中的泛型 - 所有方法均继承父类,或适配后调用父类的同名方法实现
- 补充存储特定状态类型所必须的信息
- 定义
getType()方法返回自己的状态类型
以
AggregatingStateDescriptor
为例:
源码|Github|
org.apache.flink.api.common.state.AggregatingStateDescriptor
@PublicEvolvingpublicclassAggregatingStateDescriptor<IN, ACC, OUT>extendsStateDescriptor<AggregatingState<IN, OUT>, ACC>{privatestaticfinallong serialVersionUID =1L;privatefinalAggregateFunction<IN, ACC, OUT> aggFunction;publicAggregatingStateDescriptor(String name,AggregateFunction<IN, ACC, OUT> aggFunction,Class<ACC> stateType){super(name, stateType,null);this.aggFunction =checkNotNull(aggFunction);}publicAggregatingStateDescriptor(String name,AggregateFunction<IN, ACC, OUT> aggFunction,TypeInformation<ACC> stateType){super(name, stateType,null);this.aggFunction =checkNotNull(aggFunction);}publicAggregatingStateDescriptor(String name,AggregateFunction<IN, ACC, OUT> aggFunction,TypeSerializer<ACC> typeSerializer){super(name, typeSerializer,null);this.aggFunction =checkNotNull(aggFunction);}publicAggregateFunction<IN, ACC, OUT>getAggregateFunction(){return aggFunction;}@OverridepublicTypegetType(){returnType.AGGREGATING;}}
在父类的基础上,增加了实例属性
aggFunction
用于存储聚合方法,在构造方法中增加聚合方法非空的检查,并额外提供了获取聚合方法的方法。
版权归原作者 长行 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。