SeAFusion:首个结合高级视觉任务的图像融合框架
论文:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2021.12.004
代码:https://github.com/Linfeng-Tang/SeAFusion
图像融合系列博客还有:
- 图像融合论文及代码整理最全大合集参见:图像融合论文及代码整理最全大合集
- 图像融合综述论文整理参见:图像融合综述论文整理
- 图像融合评估指标参见:红外和可见光图像融合评估指标
- 图像融合常用数据集整理参见:图像融合常用数据集整理
- 通用图像融合框架论文及代码整理参见:通用图像融合框架论文及代码整理
- 基于深度学习的红外和可见光图像融合论文及代码整理参见:基于深度学习的红外和可见光图像融合论文及代码整理
- 更加详细的红外和可见光图像融合代码参见:红外和可见光图像融合论文及代码整理
- 基于深度学习的多曝光图像融合论文及代码整理参见:基于深度学习的多曝光图像融合论文及代码整理
- 基于深度学习的多聚焦图像融合论文及代码整理参见:基于深度学习的多聚焦图像融合(Multi-focus Image Fusion)论文及代码整理
- 基于深度学习的全色图像锐化论文及代码整理参见:基于深度学习的全色图像锐化(Pansharpening)论文及代码整理
- 基于深度学习的医学图像融合论文及代码整理参见:基于深度学习的医学图像融合(Medical image fusion)论文及代码整理
- 彩色图像融合参见: 彩色图像融合
- DIVFusion:首个耦合互促低光增强&图像融合的框架参见:DIVFusion:首个耦合互促低光增强&图像融合的框架
写在前面
最近Information Fusion 接收了一篇题为《Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network》的文章。在此之前,图像融合领域一直徘徊在魔改网络,设计loss,引入新的范式等。但是却似乎忘记了一个一直被强调,但一直未被重视的点,即图像融合如何才能有效地促进高级视觉任务的性能提升?
接触图像融合已经两年左右了,从一个有一定研究基础的角度来学习这篇文章,可以发现文章的并没有在网络架构或者学习范式上进行很大的创新。但是却以一种新的视角来审视图像融合任务, 即利用高级视觉任务来驱动图像融合。

源图像经过融合网络生成融合图像,而融合网络图像在经过一个分割网络得到分割结果。分割结果与labels构造语义损失,融合图像与源图像之前构造内容损失,其中语义损失只用于约束分割网络,而内容损失与语义损失共同约束融合网络的优化。这样语义损失能够将高级视觉任务(分割)所需的语义信息反传回融合网络从而促使融合网络能够有效地保留源图像中的语义信息。
再回顾一下SeAFusion的highlights:
- We bridge the gap between IR/VIS image fusion and high-level vision tasks.
- We propose a semantic-aware IR/VIS image fusion network, termed SeAFusion.
- We devise GRDB to boost the description ability for fine-grained detail.
- SeAFusion is a light-weight model that can achieve real-time image fusion.
- We evaluate various fusion methods from the perspective of high-level tasks.
以及其Contribution:
- We devise a novel semantic-aware infrared and visible image fusion framework, which effectively achieves superior performance in both image fusion and high-level vision tasks.
- A gradient residual dense block is designed to boost the description ability of the network for fine-grained detail and achieve feature reuse.
- The proposed SeAFusion is a light-weight model that can achieve real-time image fusion. This allows it to be deployed as a pre-processing module for high-level vision tasks.
- We propose a task-driven evaluation manner that evaluates the performance of image fusion from the perspective of high-level vision tasks.
总之,该方法首次提出考虑高级视觉任务与图像融合之前的鸿沟,并提出了一个语义感知的图像融合框架,同时考虑到作为一个预处理的操作对实时性的要求,在网络设计方面设计了一个轻量级的网络。而且为了增强网络对细粒度细节特征的描述,设计了一个Gradient Residual Dense Block(GRDB)。最后,考虑到现有的评估指标仅利用EN,MI,SF等统计指标来衡量图像融合的好坏。作者还提出了一种任务驱动的评估方式,即利用融合结果在高级视觉任务上的表现来衡量融合结果的质量。
方法设计
接下来进一步聚焦到SeAFusion的方法设计。
网络架构

在整体框架设计方面SeAFusion采用的是比较经典的双分支特征提取再Concat融合后 重建图像这样的框架,而在GRDB中利用梯度算子提取的特征作为残差连接能够强化网络对于细节特征的提取。

损失函数
在loss设计方面,首先是传统的内容损失设计,主要包括强度损失和纹理损失,强度损失用于约束融合结果的整体表观强度,而纹理损失则约束融合图像尽可能多的包含纹理细节信息。
内容损失:
L
c
o
n
t
e
n
t
=
L
i
n
t
+
α
L
t
e
x
t
u
r
e
\mathcal{L}_{content} = \mathcal{L}_{int} + \alpha \mathcal{L}_{texture}
Lcontent=Lint+αLtexture
强度损失:
L
i
n
t
=
1
H
W
∥
I
f
−
max
(
I
i
r
,
I
v
i
)
∥
1
\mathcal{L}_{int} = \frac{1}{HW}\left\|I_f - \max(I_{ir}, I_{vi})\right\|_1
Lint=HW1∥If−max(Iir,Ivi)∥1
纹理损失:
L
t
e
x
t
u
r
e
=
1
H
W
∥
∣
∇
I
f
∣
−
max
(
∣
∇
I
i
r
∣
,
∣
∇
I
v
i
∣
)
∥
1
\mathcal{L}_{texture} = \frac{1}{HW}\left\| |\nabla I_f| - \max(|\nabla I_{ir}|, |\nabla I_{vi }|)\right\|_1
Ltexture=HW1∥∣∇If∣−max(∣∇Iir∣,∣∇Ivi∣)∥1
更多关于内容损失的描述可以参见原文。
除了内容损失,语义损失是SeAFusion的重要创新之一,值得一提的是作者采用了一个现有的语义分割框架来构造语义损失,因此其语义损失的构造与所采用的分割网络息息相关,关于其采用的分割网络,请参阅SeAFusion以及分割网络原文。
主语义损失:
L
m
a
i
n
=
−
1
H
×
W
∑
h
=
1
H
∑
w
=
1
W
∑
c
=
1
C
L
s
o
(
h
,
w
,
c
)
log
(
I
s
(
h
,
w
,
c
)
)
\mathcal{L}_{main} = \frac{-1}{H \times W} \sum_{h = 1}^{H}\sum_{w = 1}^{W} \sum_{c = 1}^{C} L_{so}^{(h, w, c)}\log(I_s^{(h, w, c)})
Lmain=H×W−1h=1∑Hw=1∑Wc=1∑CLso(h,w,c)log(Is(h,w,c))
辅语义损失:
L
a
u
x
=
−
1
H
×
W
∑
h
=
1
H
∑
w
=
1
W
∑
c
=
1
C
L
s
o
(
h
,
w
,
c
)
log
(
I
s
a
(
h
,
w
,
c
)
)
\mathcal{L}_{aux} = \frac{-1}{H \times W} \sum_{h = 1}^{H}\sum_{w = 1}^{W} \sum_{c = 1}^{C} L_{so}^{(h, w, c)}\log(I_{sa}^{(h, w, c)})
Laux=H×W−1h=1∑Hw=1∑Wc=1∑CLso(h,w,c)log(Isa(h,w,c))
语义损失:
L
s
e
m
a
n
t
i
c
=
L
m
a
i
n
+
λ
L
a
u
x
\mathcal{L}_{semantic} =\mathcal{L}_{main} + \lambda \mathcal{L}_{aux}
Lsemantic=Lmain+λLaux
最终用于约束融合网络的loss表达如下:
L
j
o
i
n
t
=
L
c
o
n
t
e
n
t
+
β
L
s
e
m
a
n
t
i
c
\mathcal{L}_{joint} =\mathcal{L}_{content} + \beta \mathcal{L}_{semantic}
Ljoint=Lcontent+βLsemantic
训练策略
由于图像融合的特殊性,无法利用融合结果预训练一个分割模型来指导融合网络的训练,为此作者借鉴生成对抗网络的训练方式提出了Joint low-level and high-level adaptive training strategy,该训练策略能够有效地维持low-level任务(图像融合)以及high-level视觉任务(语义分割)之间的性能平衡,即在保证高级视觉任务性能的同时不降低融合网络的性能。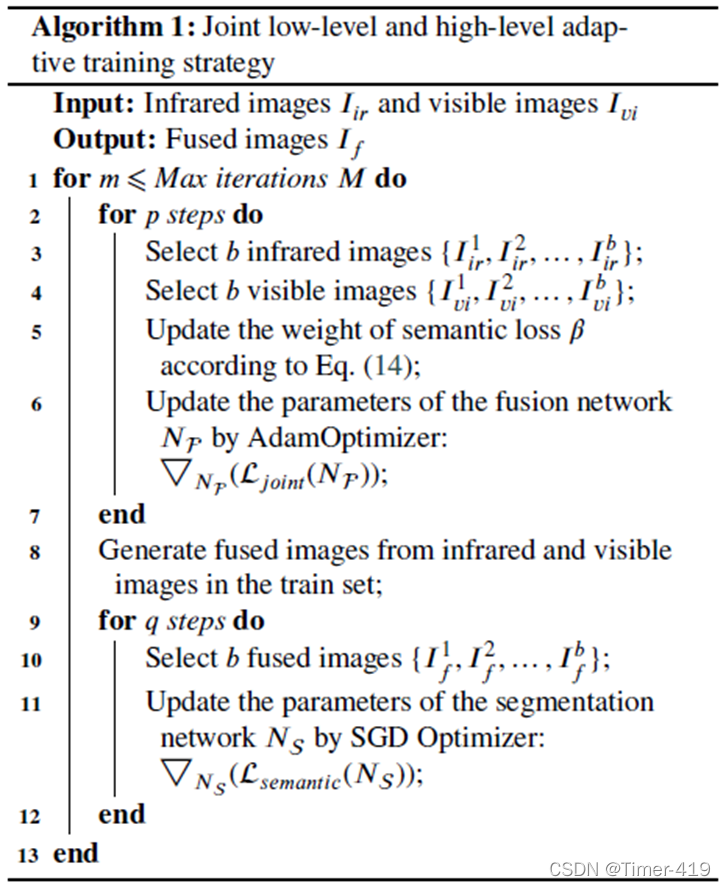
简而言之,通过交替训练融合网络以及分割网络,从而维持图像融合以及语义分割之间的性能,而避免像训练GAN时出现的模式坍塌(Model Collapse)。
实验验证
在实验设计方面,作者首先在MFNet,RoadScene,TNO数据集上进行了定量和定性的对比实验,然后给出了任务驱动的评估结果,以及不同算法运行效率的对比分析和相关的消融实验。
定量&定性实验
MFNet数据集



RoadScene数据集



TNO数据集


任务驱动评估
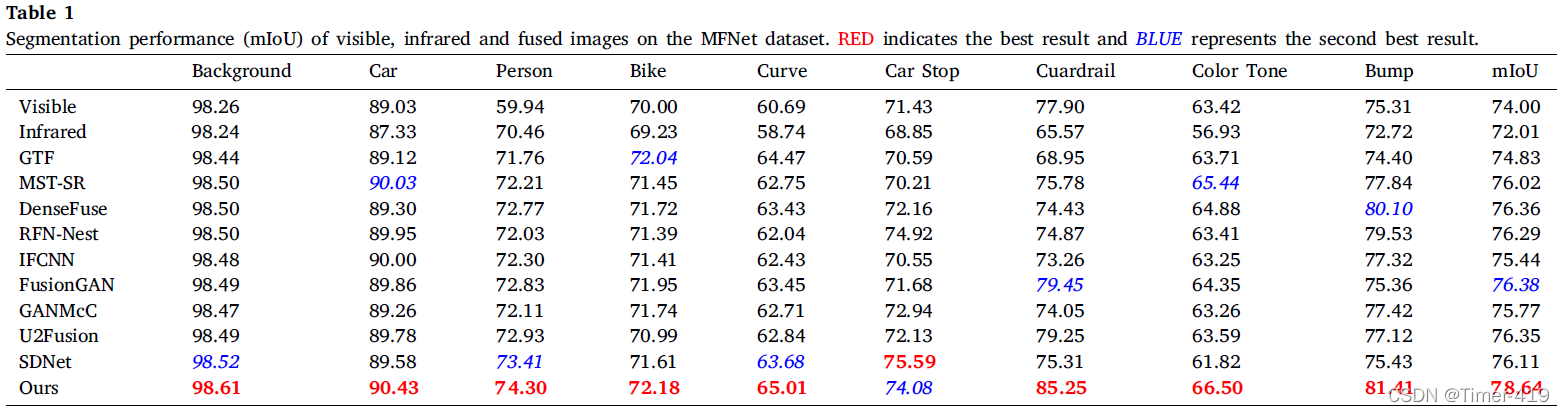
语义分割


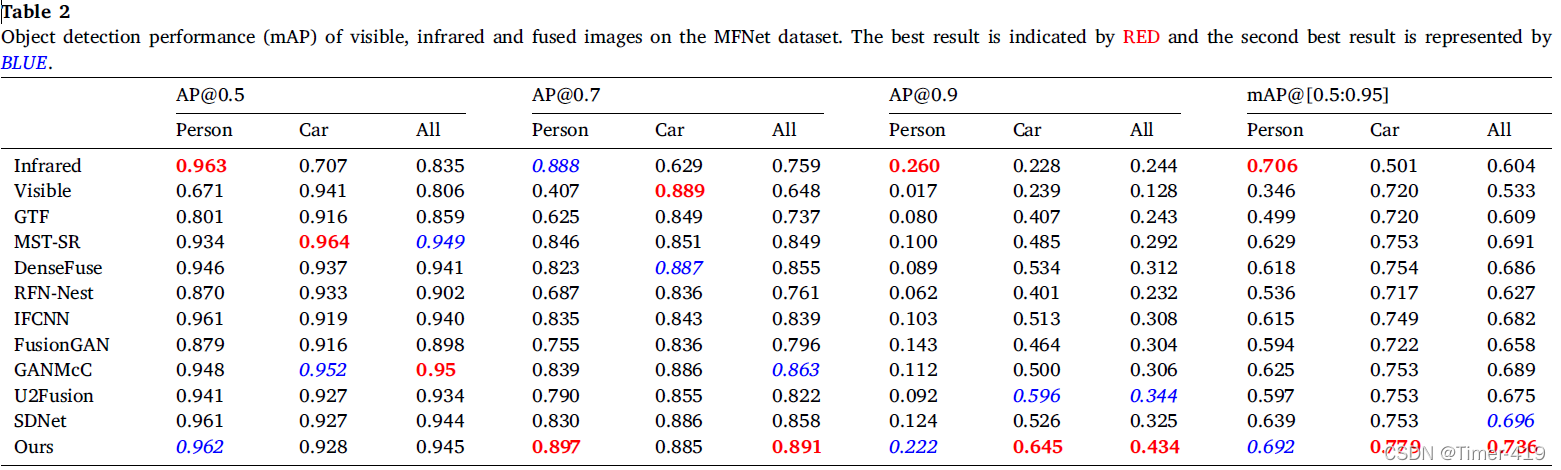
目标检测

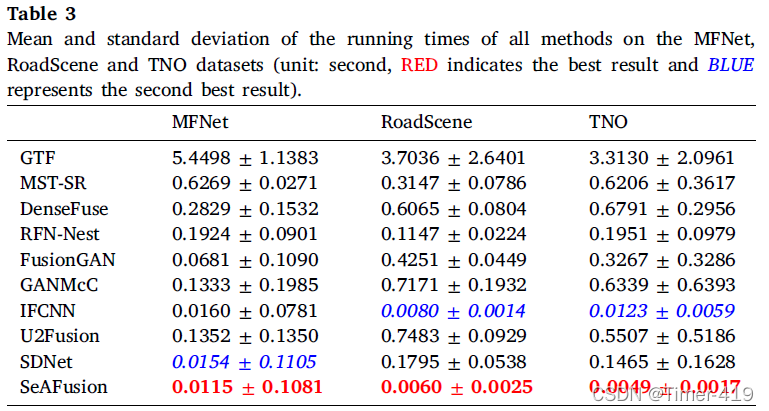
运行效率对比
消融实验

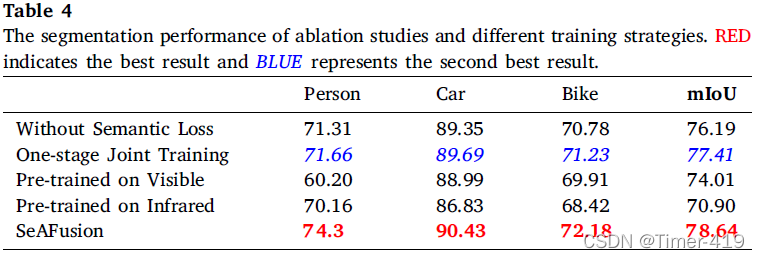
更多的实验设计以及实验分析,请参阅SeAFusion 原论文。
结论
在这项研究中,我们提出了一个语义感知的图像融合框架,即SeAFusion,以实现红外和可见光图像的实时融合。一方面,设计了一个梯度残差密集块来提高融合网络对细粒度细节的描述能力。结合精心设计的内容损失,我们的融合网络有效地实现了突出目标强度的维护和纹理细节的保留。另一方面,我们引入了语义损失,以提高融合结果对高层视觉任务的促进作用。更具体地说,语义损失允许高层语义信息回流到图像融合模块,这有利于高层视觉任务在融合结果上取得优异的表现。此外,我们提出了一种low-level和high-level的联合自适应训练策略,以便在图像融合和各种高层次视觉任务中同时取得优异的表现。充分的比较和泛化实验证明了我们的SeAFusion在主观效果和定量指标上都优于state-of-the-arts。此外,丰富的任务驱动评估实验揭示了我们的框架在促进高层视觉任务方面的天然优势。此外,在运行效率方面的显著优势使我们的算法可以很容易地作为高级视觉任务的预处理模块进行部署。
写在最后
个人感觉SeAFusion的出现很大程度上受益于新发现的数据集即MFNet,其中提供了场景中的语义标签,而且场景特别丰富(包含1600对左右的场景),这为训练性能优异的融合网络提供了可能。此外就是其所使用的分割网络也能够有较强的性能。
在SeAFusion发表之前,关于图像融合的研究一直在魔改网络,设计loss function, 调整学习范式中徘徊,SeAFusion给与了我们新的启发,即联系高级视觉任务来研究图像融合。尽管SeAFusion的方法设计还比较简单,但是这也给了我们更多的优化空间。此外之前感觉大家觉得红外和可见光图像融合都已经没啥可做的,主要是TNO数据集的数据集的局限性,导致不同方法都各有各的优势。但是随着一些新的数据集的发布,图像融合依旧任重而道远。
个人感觉红外和可见光图像融合未来的研究方向可能包括但不限于
- 未配准图像融合
- 高级视觉任务驱动的图像融合
- 跨分辨率的图像融合
- 实时图像融合
- 极端条件下的图像融合(过曝或欠曝)
- 全面的评估准则
MFNet数据集下载地址:https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/18BQFWRfhXzSuMloUmtiBRFrr6NSrf8Fw
(百度云下载地址:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1CVRoUdiCydTQtnNcGIl5nQ 提取码:0223)
作者也对MFNet数据集进行了删选、增强 并发布了MSRS数据集, MSRS数据集地址:https://github.com/Linfeng-Tang/MSRS
MFNet project 地址:https://www.mi.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/static/projects/mil_multispectral/
SeAFusion原论文: Tang, Linfeng, Jiteng Yuan, and Jiayi Ma. “Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network.” Information Fusion 82 (2022): 28-42.
MFNet数据集:Ha, Q., Watanabe, K., Karasawa, T., Ushiku, Y., Harada, T., 2017. Mfnet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp.5108–5115.
分割网络:Peng, C., Tian, T., Chen, C., Guo, X., Ma, J., 2021. Bilateral attention decoder: A lightweight decoder for real-time semantic segmentation. Neural Networks 137, 188–199.
如有疑问可联系:2458707789@qq.com; 备注 姓名+学校
版权归原作者 Timer-419 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。