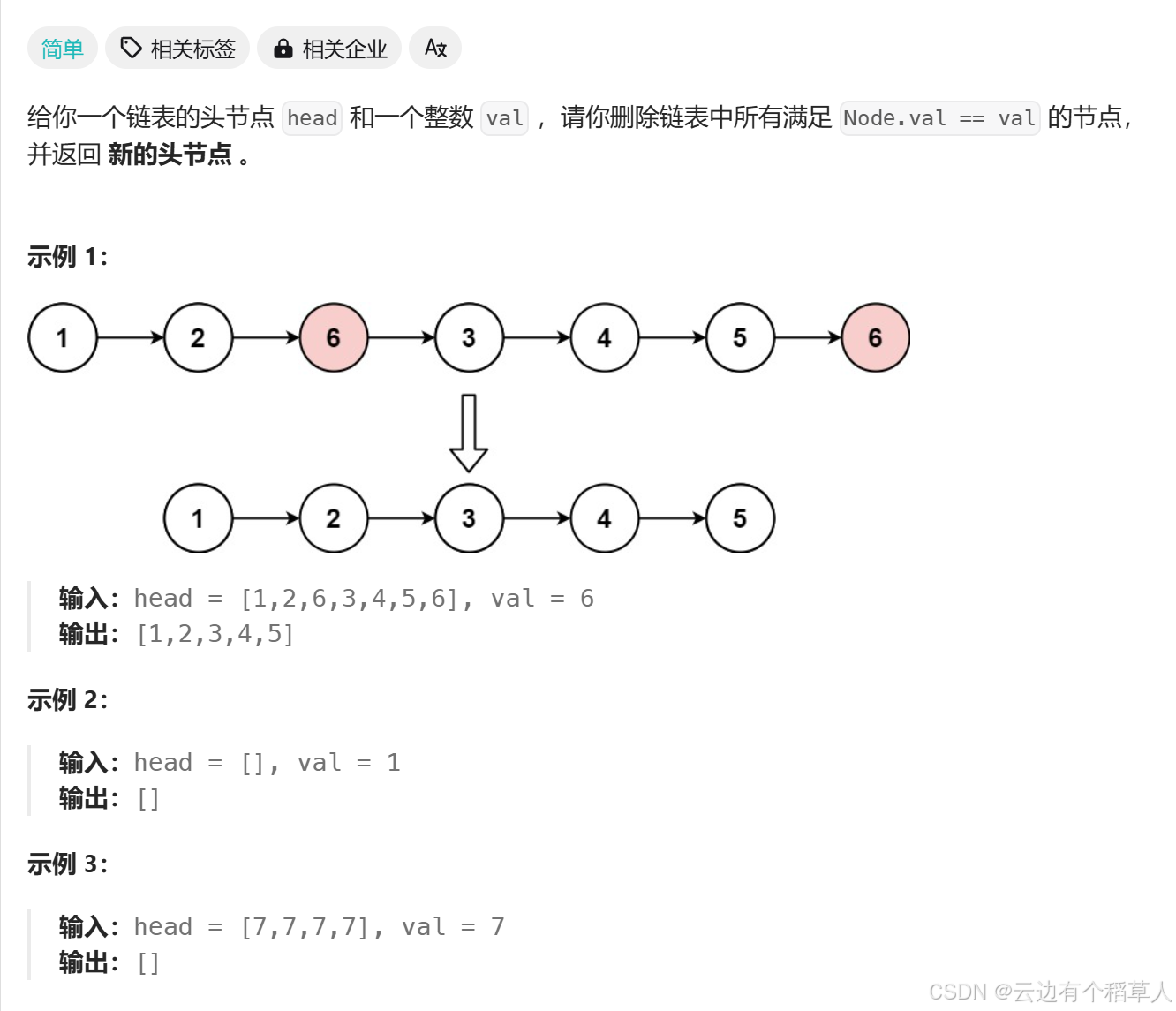
1、移除元素
思路:
创建一个新链表(newhead,newtail),遍历原链表,把不等于 val 的结点尾插到新链表中。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
//创建新链表
ListNode* newhead;ListNode* newtail;
newhead=newtail=NULL;
//遍历数组
ListNode* pcur=head;
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val!=val)
{
//又分两种情况,链表为空,不为空
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newtail=newhead=pcur;
}
else
{
newtail->next=pcur;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
}
pcur=pcur->next;
}
//[7,7,7,7,7],val=7 ,这种情况下,newtail=NULL,newtail->next=NULL,此时newtail不能解引用,所以加上if条件
if(newtail)
newtail->next=NULL;
return newhead;
}
注意:
当原链表为空时,newhead = newtail = pcur;
在实例中,最后一个5结点被尾插到新链表中时,5结点的next指针指向的仍然是后面的6结点,所以最后返回的时候结果里面含有6,所以我们把最后一个等于val结点的next指针指向NULL即可!
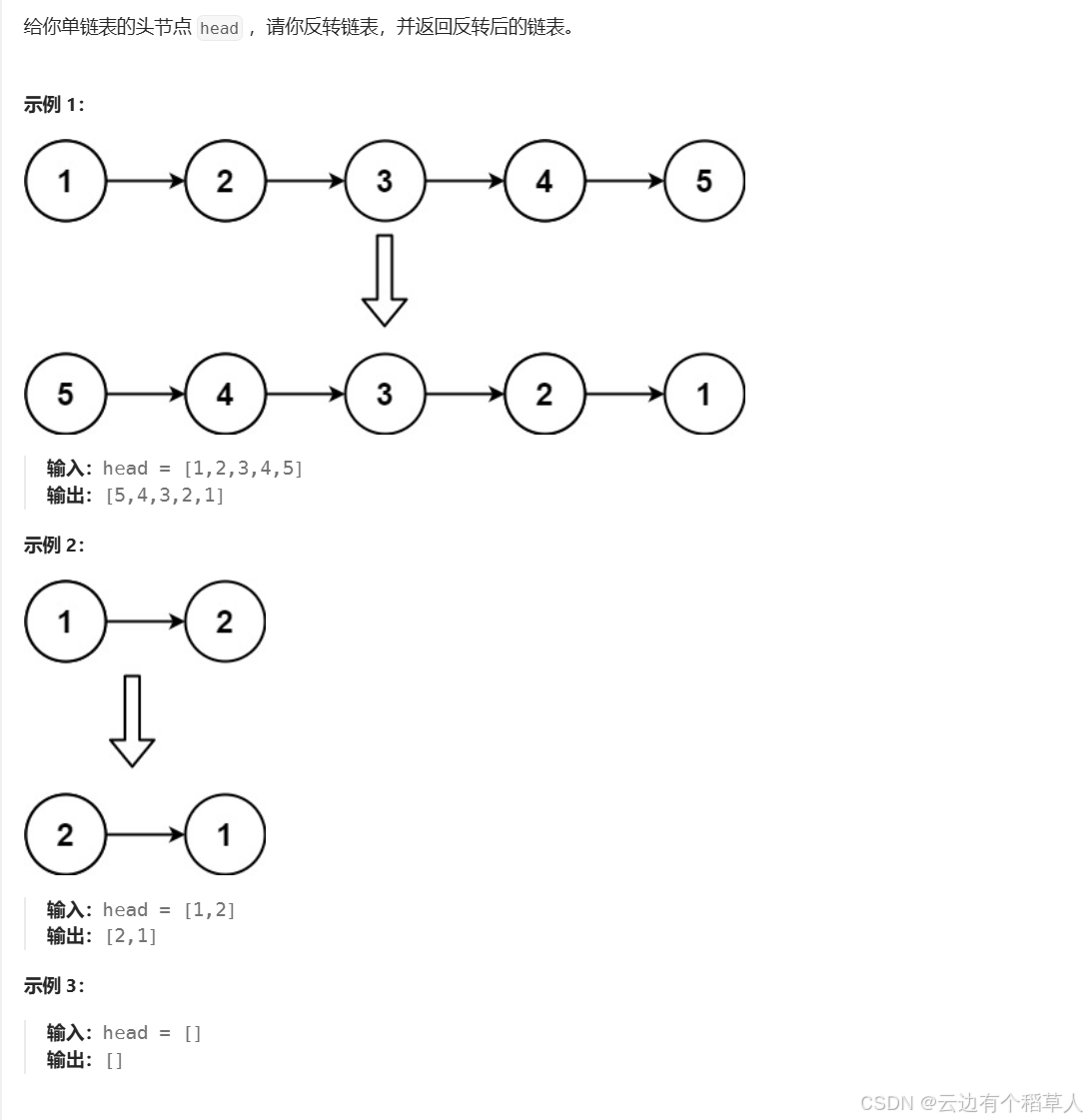
2、反转链表
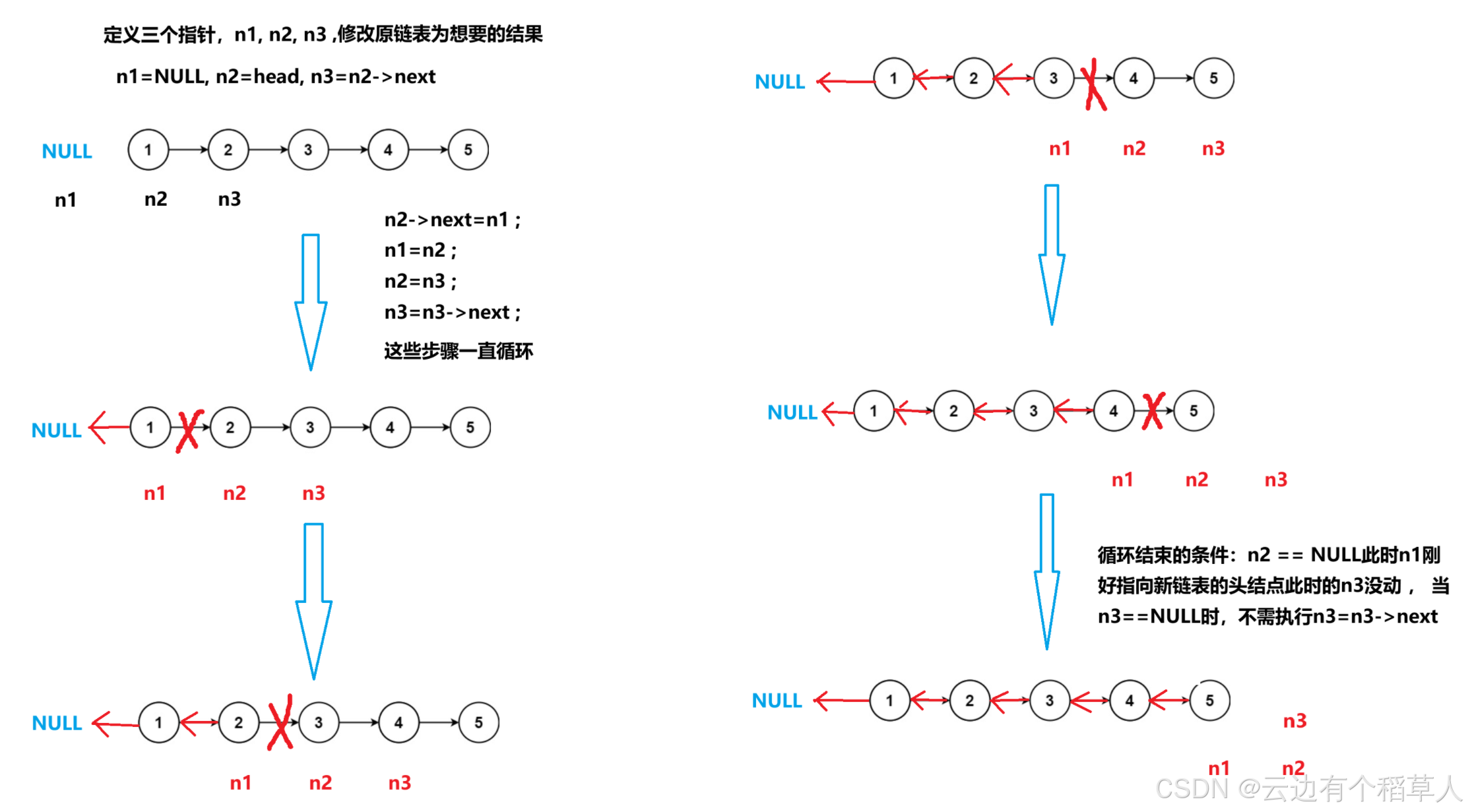
新奇思路:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
//链表也有可能是空链表
if(head==NULL)
{
return head;
}
//定义三个指针变量
ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;
n1=NULL;n2=head;n3=n2->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next=n1;
n1=n2;
n2=n3;
if(n3)
n3=n3->next;
}
return n1;
}
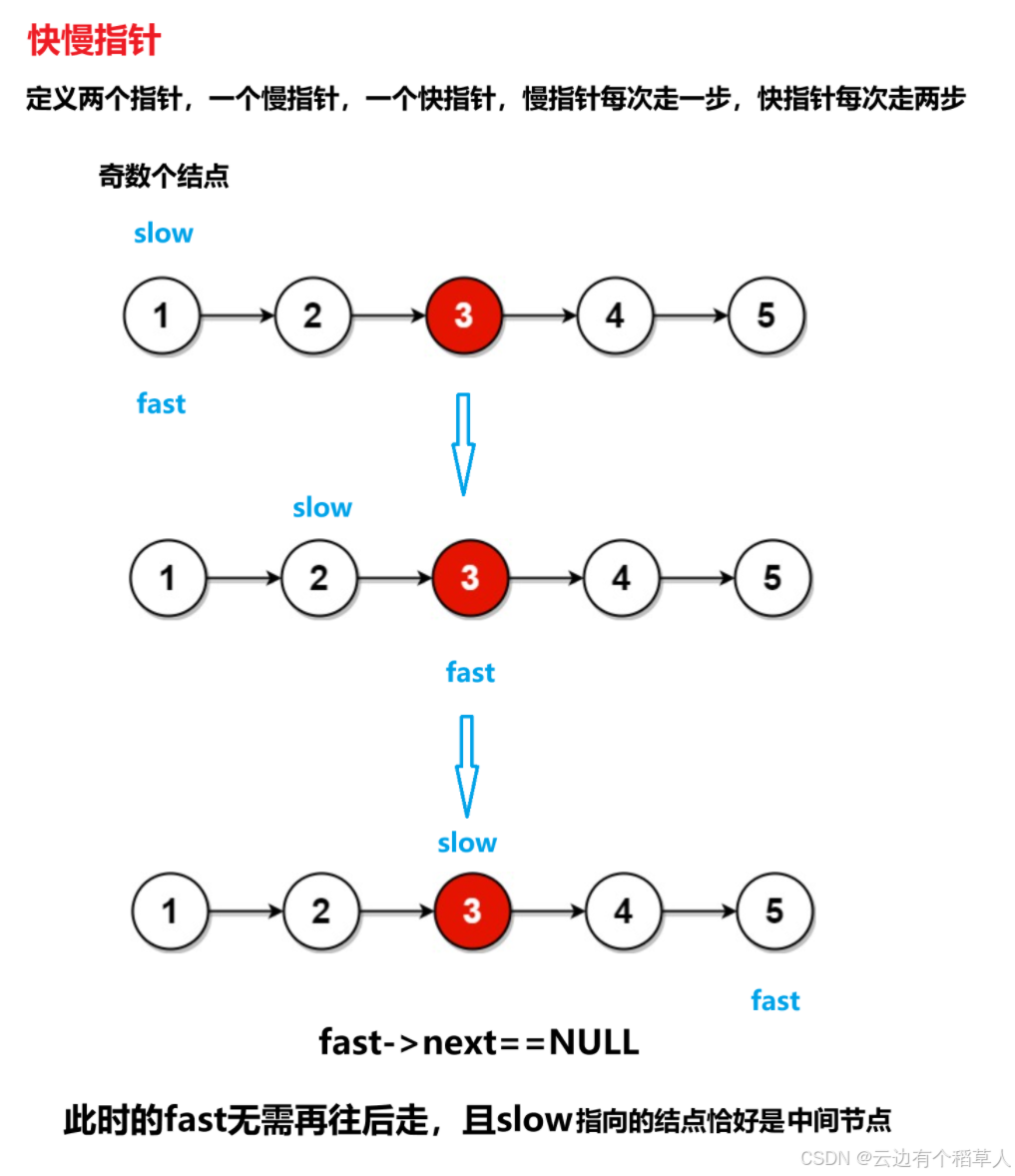
3、链表的中间节点
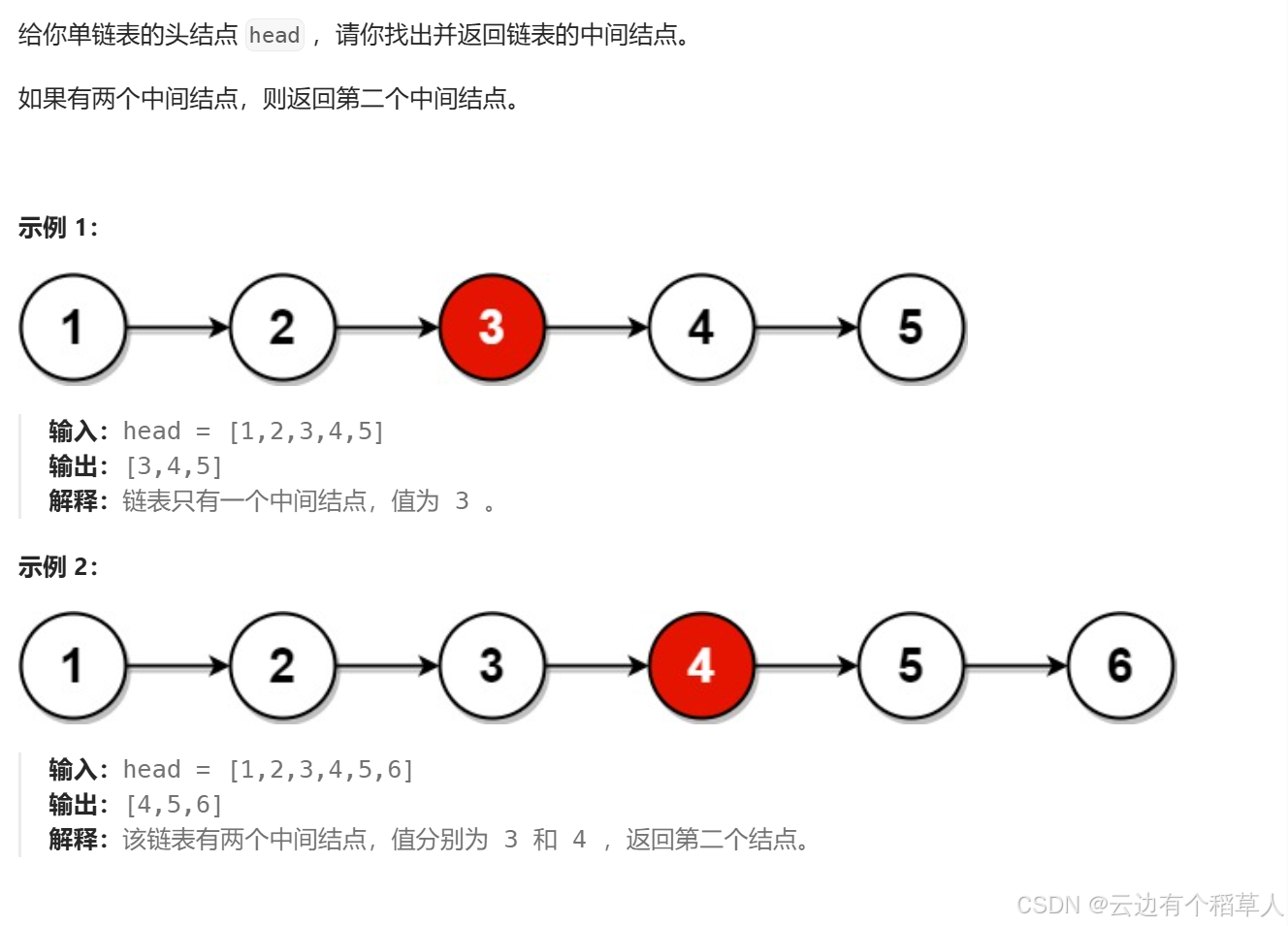
**思路: **
奇数个结点
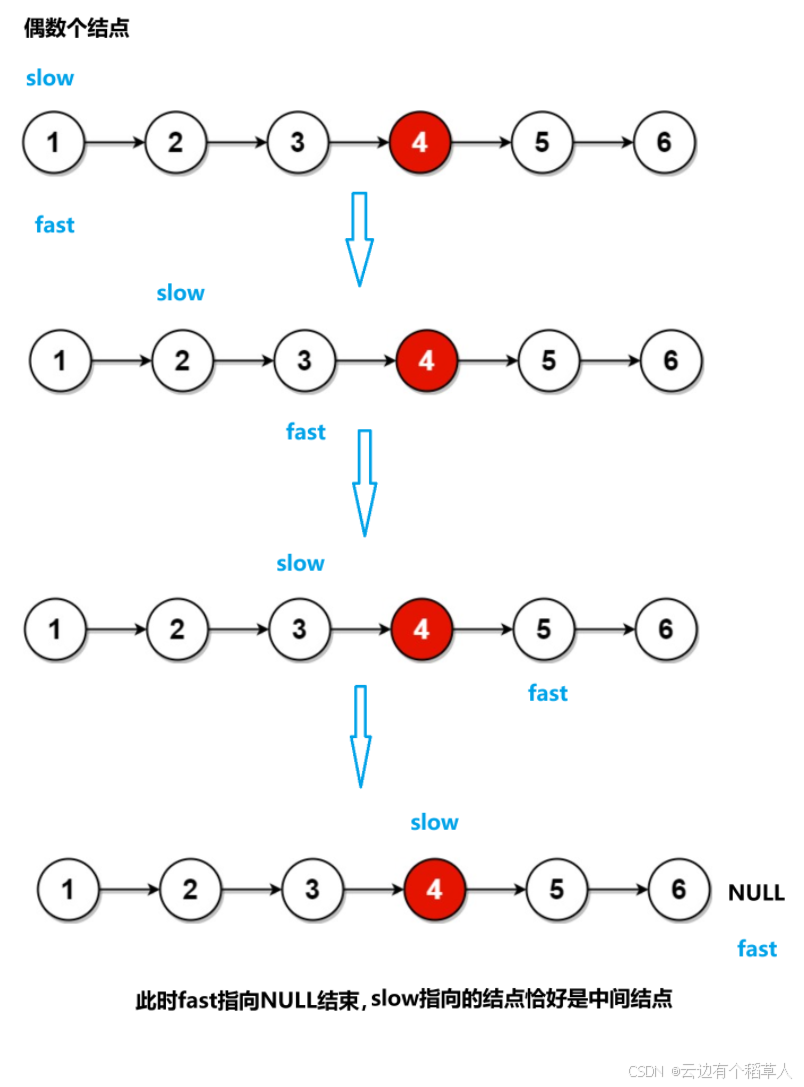
**偶数个结点 **
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
ListNode* slow=head;
ListNode* fast=head;
//while(fast->next&&fast)错误,不可互换顺序,当为偶数个结点时,fast==NULL循环结束,但是while
循环内会先判断fast->next,空指针不能解引用,会报错
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
//慢指针每次走一步
//快指针每次走两步
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
//此时slow指向的结点恰好是中间结点
return slow;
}
快慢指针为什么可以找到中间结点?(快慢指针的原理)
慢指针每次走一步,快指针每次走两步,当快指针走到链表的尾结点时,假设链表的长度为n,快指针走的路程是慢指针的两倍,2*慢=快,即慢指针走的路程是n/2。
4、合并两个有序链表
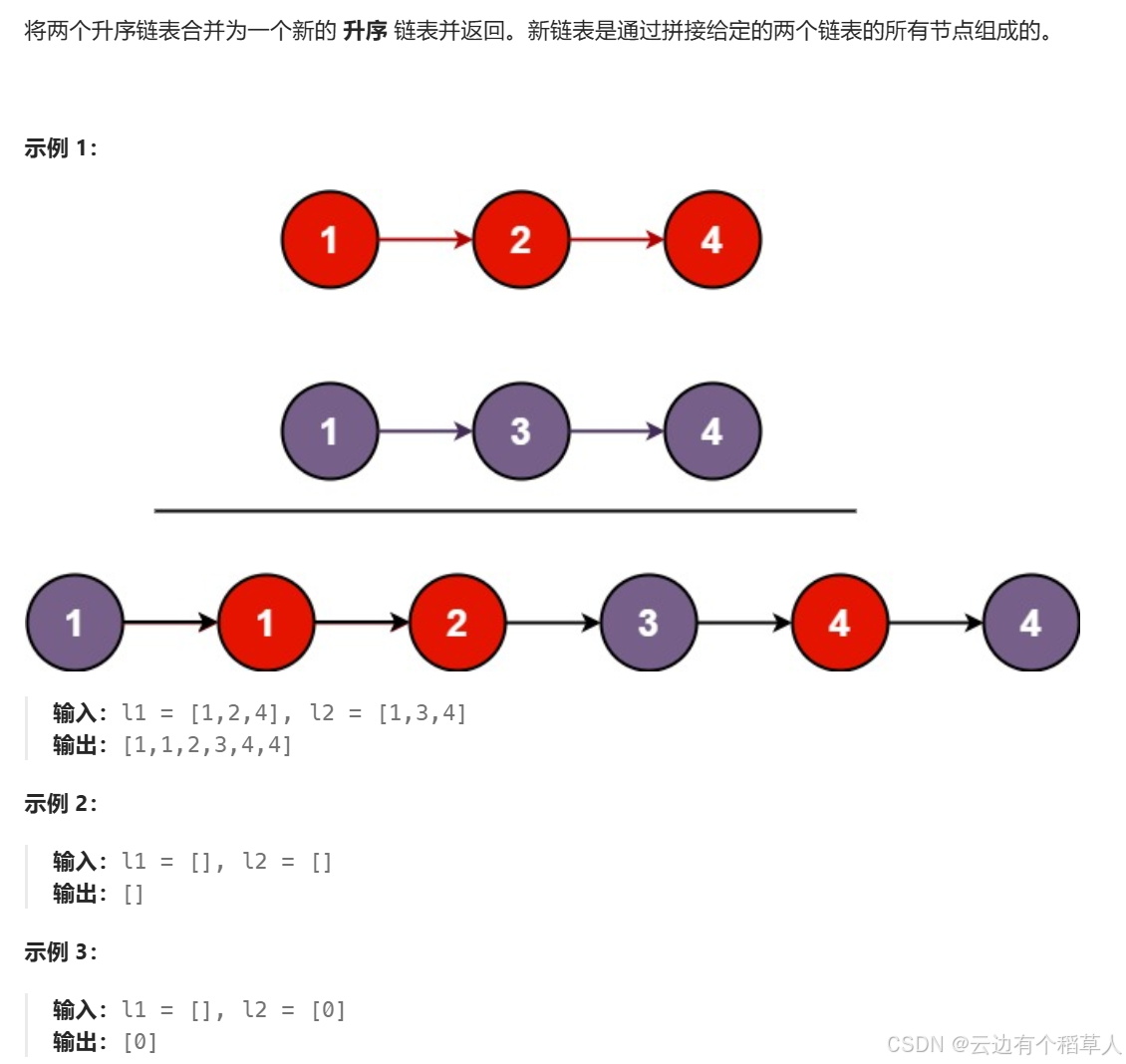
思路:
创建一个新链表,newhead,newtail 指向新链表的头结点,定义两个指针分别指向原链表的头结点,两个指针指向的数据比较大小,谁小谁尾插到新链表里面。思路清晰,不过要注意很多细节,直接上代码:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
//处理原链表为空链表的情况
if(list1==NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2==NULL)
{
return list1;
}
//创建一个新链表
ListNode* newhead=NULL;
ListNode* newtail=NULL;
//创建两个指针分别指向两个链表的头结点来遍历原链表
ListNode* l1=list1;
ListNode* l2=list2;
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
//l1尾插到新链表
if(newtail==NULL)
{
newtail=newhead=l1;
}
else
{
newtail->next=l1;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
l1=l1->next;
}
else
{
//l2尾插到新链表
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newtail=newhead=l2;
}
else
{
newtail->next=l2;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
l2=l2->next;
}
}
//出循环,要么l1==NULL,要么l2==NULL
if(l1)
newtail->next=l1; 想想这里为啥不用while循环?
if(l2)
newtail->next=l2;
return newhead;
}
//优化过后,申请一个不为空的链表,就无需再判断新链表是否为空,最后不要忘记free
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
//链表为空的情况
if(list1==NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2==NULL)
{
return list1;
}
//创建一个新链表
ListNode* newhead,*newtail;
newhead=newtail=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
//定义两个指针来遍历数组
ListNode* l1=list1;
ListNode* l2=list2;
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
newtail->next=l1;
l1=l1->next;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
else
{
newtail->next=l2;
l2=l2->next;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
}
if(l1)
newtail->next=l1;
if(l2)
newtail->next=l2;
ListNode* ret=newhead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead=NULL;
return ret;
}
完—
Relaxing Time!!!
———————————————— 天气之子·幻 ————————————————
天气之子·幻_TypeD_高音质在线试听_天气之子·幻歌词|歌曲下载_酷狗音乐酷狗音乐为您提供由TypeD演唱的高清音质无损天气之子·幻mp3在线听,听天气之子·幻,只来酷狗音乐!https://t4.kugou.com/song.html?id=b43Kh7aCPV2

至此结束——
再见——
版权归原作者 云边有个稻草人 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。