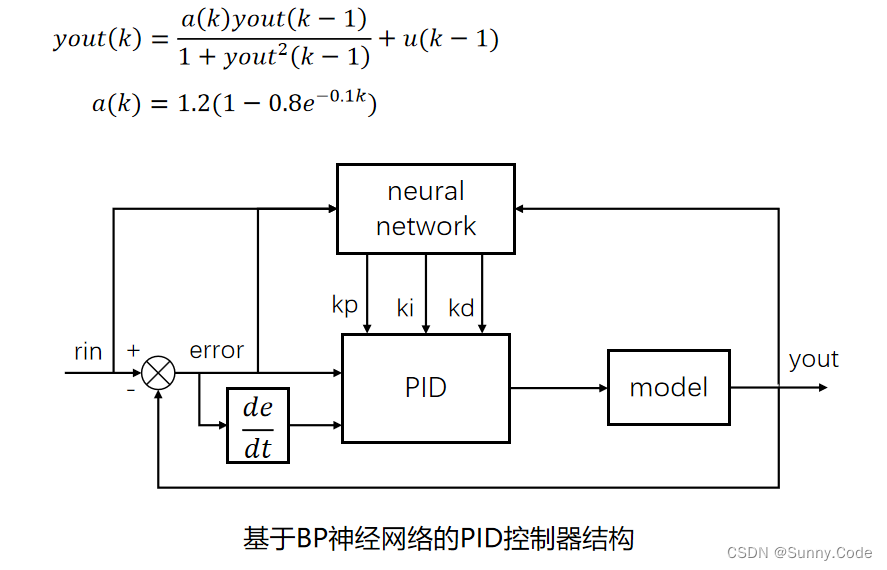
基于BP神经网络的PID智能控制
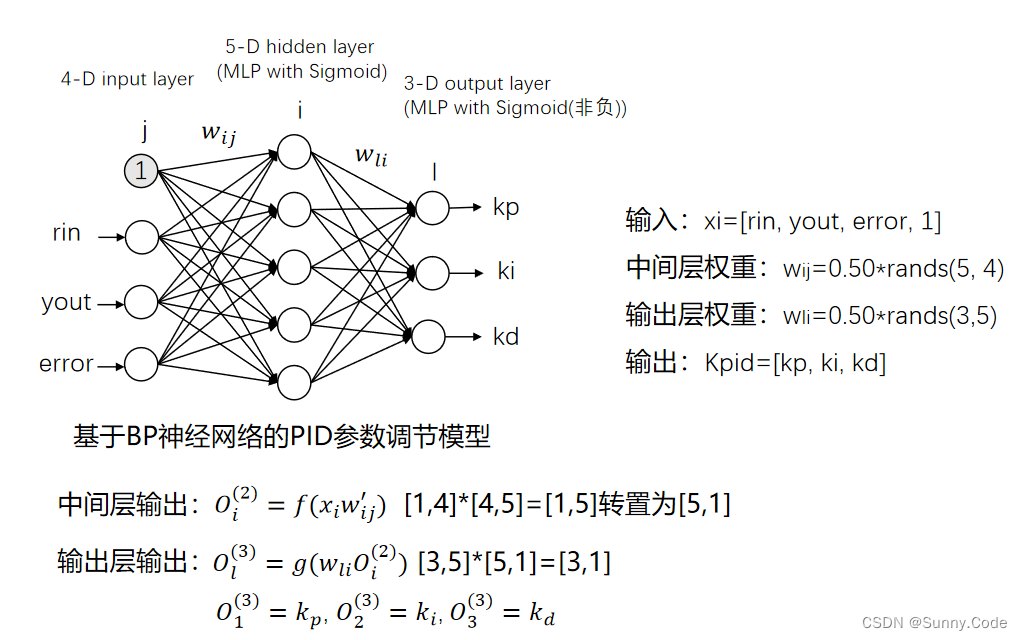
基于BP神经网络的PID整定原理
PID控制要获得较好的控制效果,就必须通过调整好比例、积分和微分三种控制作用,形成控制量中既相互配合又相互制约的关系,这种关系不一定是简单的“线性组合”,从变化无穷的非线性组合中可以找出最佳的。神经网络所具有的任意非线性表达的能力,可以通过对系统性能的学习来实现具有最佳组合的PID控制。采用BP神经网络,可以建立参数Kp、Ki、Kd自学习的PID控制器。
经典的增量式数字PID控制算法为:
u(k)=u(k−1)+∆u(k)
∆u(k)=k_p(error(k)−error(k−1))+k_ierror(k)+k_d(error(k)−2error(k−1)+error(k−2))
BP神经网络结构:
学习算法



仿真模型
Matlab代码
略做优化及解释
%BP based PID Control
clear all;
close all;xite=0.20;alfa=0.05;S=2; %Signal typeIN=4;H=5;Out=3; %NN Structure
ifS==1 %Step Signal
% wi=[-0.6394 -0.2696 -0.3756 -0.7023;
%
% -0.8603 -0.2013 -0.5024 -0.2596;
%
% -1.0749 0.5543 -1.6820 -0.5437;
%
% -0.3625 -0.0724 -0.6463 -0.2859;
%
% 0.14250.0279 -0.5406 -0.7660];wi=0.50*rands(H,IN);wi_1=wi;wi_2=wi;wi_3=wi;
% wo=[0.75760.26160.5820 -0.1416 -0.1325;
%
% -0.1146 0.29490.83520.22050.4508;
%
% 0.72010.45660.76720.49620.3632];wo=0.50*rands(Out,H);wo_1=wo;wo_2=wo;wo_3=wo;
end
ifS==2 %Sine Signal
% wi=[-0.2846 0.2193 -0.5097 -1.0668;
%
% -0.7484 -0.1210 -0.4708 0.0988;
%
% -0.7176 0.8297 -1.6000 0.2049;
%
% -0.0858 0.1925 -0.6346 0.0347;
%
% 0.43580.2369 -0.4564 -0.1324];
% wi=[0.29090.0504 -0.5608 0.8765;
% -0.4225 0.58900.18400.5660;
% -0.2075 -0.4704 0.1246 -0.3400;
% -0.2277 -0.0930 -0.0809 0.3108;
% 0.3456 -0.1417 -0.5223 0.298]wi=0.50*rands(H,IN)wi_1=wi;wi_2=wi;wi_3=wi;
% wo=[1.04380.54780.86820.14460.1537;
%
% 0.17160.58111.12140.50670.7370;
%
% 1.00630.74281.05340.78240.6494];
% wo=[-0.5582 -0.4503 -0.5845 -0.1433 0.2659;
% -0.3943 -0.3942 0.2685 -0.1449 -0.2649;
% -0.5109 -0.2169 0.3106 -0.2965 -0.5230]wo=0.50*rands(Out,H)wo_1=wo;wo_2=wo;wo_3=wo;
end
x=[0,0,0];du_1=0;u_1=0;u_2=0;u_3=0;u_4=0;u_5=0;y_1=0;y_2=0;y_3=0;Oh=zeros(H,1); %Output from NN middle layer
I=Oh; %Input to NN middle layer
error_2=0;error_1=0;ts=0.001;fork=1:1:6000
time(k)=k*ts;ifS==1
rin(k)=1.0;
elseif S==2
rin(k)=sin(1*2*pi*k*ts);
end
%Unlinear model
a(k)=1.2*(1-0.8*exp(-0.1*k));
yout(k)=a(k)*y_1/(1+y_1^2)+u_1;
error(k)=rin(k)-yout(k);xi=[rin(k),yout(k),error(k),1];
x(1)=error(k)-error_1;
x(2)=error(k);
x(3)=error(k)-2*error_1+error_2;epid=[x(1);x(2);x(3)];I=xi*wi'; % [1,4]*[4,5]
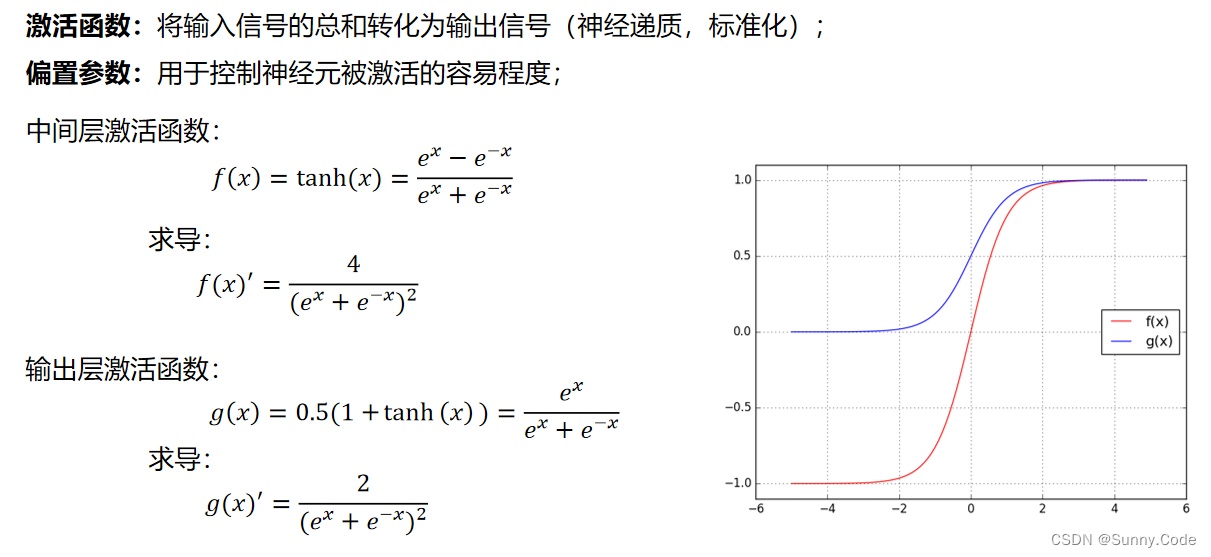
% 中间层激活函数
for j=1:1:H
Oh(j)=(exp(I(j))-exp(-I(j)))/(exp(I(j))+exp(-I(j))); %Middle Layer
end
K=wo*Oh; %Output Layer [3,5]*[5,1]
% 输出层激活函数
for l=1:1:Out
K(l)=exp(K(l))/(exp(K(l))+exp(-K(l))); %Getting kp,ki,kd
end
% 输出层输出结果,PID系数
kp(k)=K(1);ki(k)=K(2);kd(k)=K(3);
Kpid=[kp(k),ki(k),kd(k)];
% 增量PID计算
du(k)=Kpid*epid;
u(k)=u_1+du(k); %PID控制量输出
% 符号函数,模型输出变化量/控制增量的变化量(+0.0001避免出现除0)
dyu(k)=sign((yout(k)-y_1)/(du(k)-du_1+0.0001));
%Output layer
% 输出层激活函数求导
for j=1:1:Out
dK(j)=2/(exp(K(j))+exp(-K(j)))^2;
end
for l=1:1:Out
delta3(l)=error(k)*dyu(k)*epid(l)*dK(l);
end
for l=1:1:Out
for i=1:1:H
d_wo(l,i)=xite*delta3(l)*Oh(i)+alfa*(wo_1(l,i)-wo_2(l,i));
end
end
wo=wo_1+d_wo+alfa*(wo_1-wo_2);
%Hidden layer
% 中间层激活函数求导
for i=1:1:H
dO(i)=4/(exp(I(i))+exp(-I(i)))^2;
end
segma=delta3*wo;
for i=1:1:H
delta2(i)=dO(i)*segma(i);
end
d_wi=xite*delta2'*xi;wi=wi_1+d_wi+alfa*(wi_1-wi_2);
%Parameters Update
du_1=du(k);u_5=u_4;u_4=u_3;u_3=u_2;u_2=u_1;u_1=u(k);y_2=y_1;y_1=yout(k);wo_3=wo_2;wo_2=wo_1;wo_1=wo;wi_3=wi_2;wi_2=wi_1;wi_1=wi;error_2=error_1;error_1=error(k);
end
wi
wo
figure(1);
plot(time,rin,'r',time,yout,'b--');
xlabel('time(s)');ylabel('rin,yout');
legend('rin','yout');
grid on
figure(2);
plot(time,error,'r');
xlabel('time(s)');ylabel('error');
grid on
figure(3);
plot(time,u,'r');
xlabel('time(s)');ylabel('u');
grid on
figure(4);
subplot(311);
plot(time,kp,'r');
xlabel('time(s)');ylabel('kp');
grid on
subplot(312);
plot(time,ki,'g');
xlabel('time(s)');ylabel('ki');
grid on
subplot(313);
plot(time,kd,'b');
xlabel('time(s)');ylabel('kd');
grid on
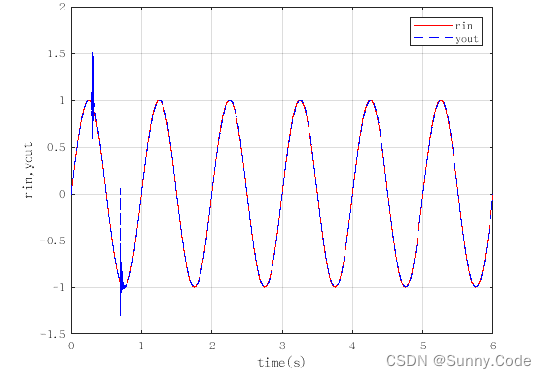
仿真效果图
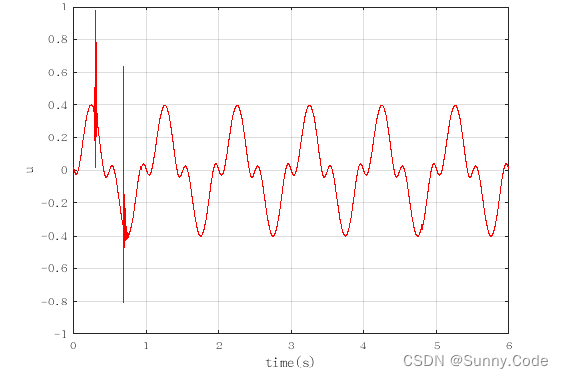
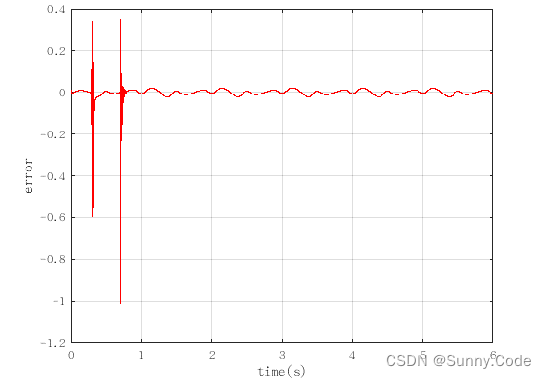
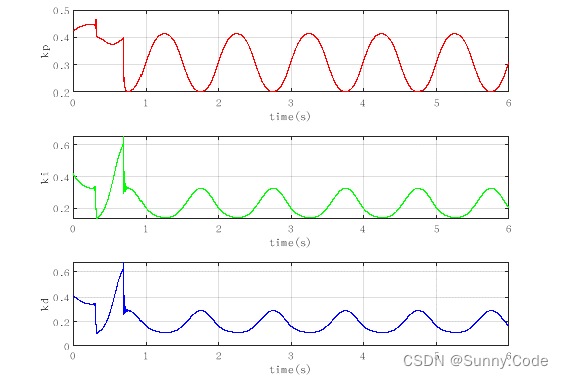
结论
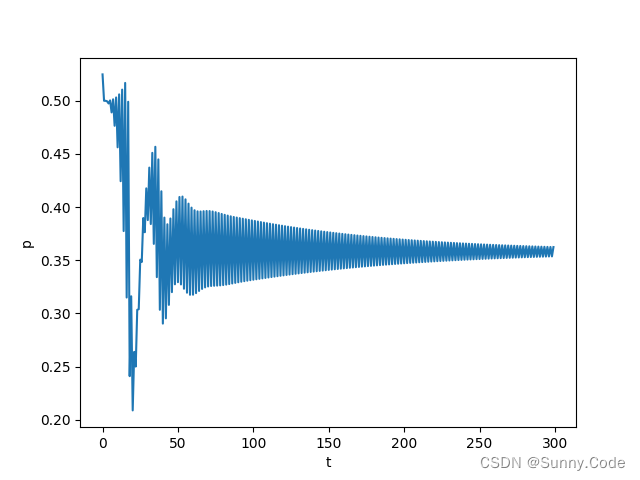
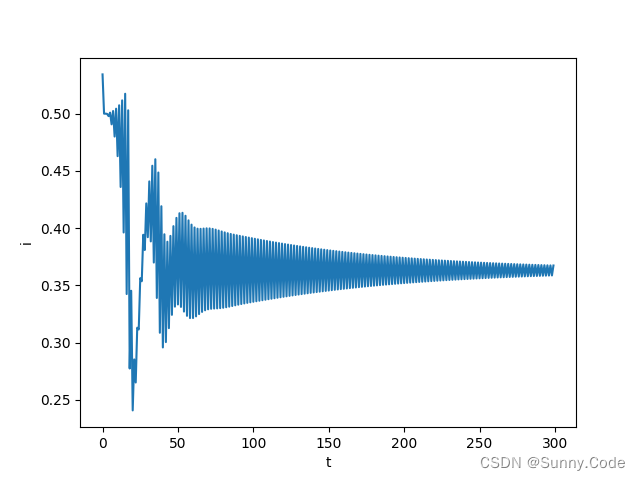
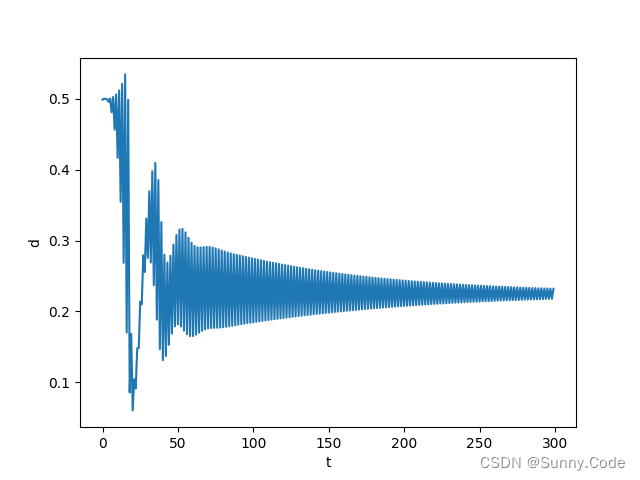
由图可知,该算法经过一段时间的自动调参后误差趋于稳定,PID参数随着误差的变化而变化,证明了算法的有效性。实际使用时可增加一些限制条件,使算法更加鲁棒。
python仿真
单位阶跃信号响应,可根据实际模型使用PID或PI、PD控制,把不用的项系数设为0即可。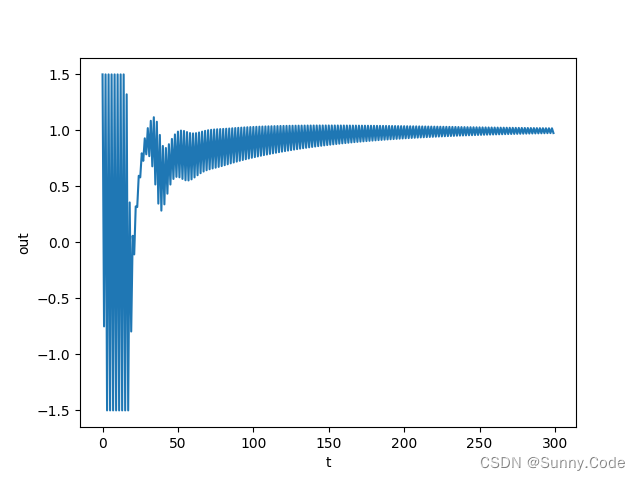
参考文献
[1]: 先进PID控制MATLAB仿真(第二版)刘金琨 第4章 神经PID控制
版权归原作者 Sunny.Code 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。