新神经网络架构设计的最新进展之一是注意力模块的引入。首次出现在在NLP 上的注意力背后的主要思想是为数据的重要部分添加权重。在卷积神经网络的情况下,第一个注意机制是在卷积块注意模型中提出的。其中注意机制分为两个部分:通道注意模块和空间注意模块。
空间注意模块通过将图像分解为两个通道,即最大池化和跨通道的平均池化来创建特征空间的掩码。这一层是卷积层的输入,卷积层只应用一个保持与输入相同大小的滤波器。然后使用sigmoid激活创建从0到1的激活映射。生成的新的映射会按比例缩放输入,它通过缩放输入增强空间特征。
class SpatialAttention(Layer):
'''
Custom Spatial attention layer
'''
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
self.kwargs = kwargs
def build(self, input_shapes):
self.conv = Conv2D(filters=1, kernel_size=5, strides=1, padding='same')
def call(self, inputs):
pooled_channels = tf.concat(
[tf.math.reduce_max(inputs, axis=3, keepdims=True),
tf.math.reduce_mean(inputs, axis=3, keepdims=True)],
axis=3)
scale = self.conv(pooled_channels)
scale = tf.math.sigmoid(scale)
return inputs * scale
我们可以将其添加到密集卷积块中,创建自编码器模型。还可以通过添加一个选项来检查注意力模块的是否存在
def MakeConvolutionBlock(X, Convolutions,BatchNorm=True,Drop=True,SpAttention=True,Act='relu'):
'''
Parameters
----------
X : keras functional layer
Previous layer in the model.
Convolutions : int
Number of convolutional filters.
BatchNorm : bool, optional
If True a batchnorm layer is added to the convolutional block.
The default is True.
Drop : bool, optional
If true a Droput layer is added to the model. The default is True.
SpAttention : bool, optional
If true a SpatialAttention layer is added to the model. The default is True.
Act : string, optional
Controls the kind of activation to be used. The default is 'relu'.
Returns
-------
X : keras functiona layer
Block of layers added to the model.
'''
X = Conv2D(Convolutions, (3,3), padding='same',use_bias=False)(X)
if SpAttention:
X = SpatialAttention()(X)
if BatchNorm:
X = BatchNormalization()(X)
if Drop:
X = Dropout(0.2)(X)
X=Activation(Act)(X)
return X
随着函数中不同参数的数量增加,直接其添加到下一个函数会有问题。所以可以在 python 中使用 **kwargs 功能,它通过使用字典将关键字参数解包到一个函数中。只需将 **kwargs 添加到使用与主构建块相同的参数的函数中。
def MakeDenseConvolutionalCoder(InputShape,Units,BlockDepth,UpSampling=False,**kwargs):
'''
Parameters
----------
InputShape : tuple
Input shape of the images.
Units : Array-like
Number of convolutional filters to apply per block.
BlockDepth : int
Size of the concatenated convolutional block.
UpSampling : bool, optional
Controls the upsamplig or downsampling behaviour of the network.
The default is False.
**kwargs
keyword arguments from MakeConvolutionBlock.
Returns
-------
InputFunction : Keras functional model input
input of the network.
localCoder : Keras functional model
Coder model, main body of the autoencoder.
'''
if UpSampling:
denseUnits=Units[::-1]
Name="Decoder"
else:
denseUnits=Units
Name="Encoder"
nUnits = len(denseUnits)
InputFunction=Input(shape=InputShape)
X = Conv2D(denseUnits[0], (3, 3), padding='same',use_bias=False)(InputFunction)
X=Activation('relu')(X)
for k in range(1,nUnits-1):
X=MakeDenseBlock(X,denseUnits[k],BlockDepth,**kwargs)
if UpSampling:
X=Conv2DTranspose(denseUnits[k], (3, 3), padding='same',use_bias=False,strides=(2,2))(X)
else:
X=Conv2D(denseUnits[k], (3, 3), padding='same',use_bias=False,strides=(2,2))(X)
if UpSampling:
X=Conv2D(1, (3, 3), padding='same',use_bias=False)(X)
X=BatchNormalization()(X)
Output=Activation('sigmoid')(X)
else:
X=Conv2D(denseUnits[-1], (3, 3), padding='same',use_bias=False)(X)
X=BatchNormalization()(X)
Output=Activation('relu')(X)
localCoder=Model(inputs=InputFunction,outputs=Output,name=Name)
return InputFunction,localCoder
上面代码创建了自编码器的主体,并通过在其间添加采样层,我们就可以定义变分自编码器。使用 MNIST 数据集训练模型样本可以得到下面类似的结果。
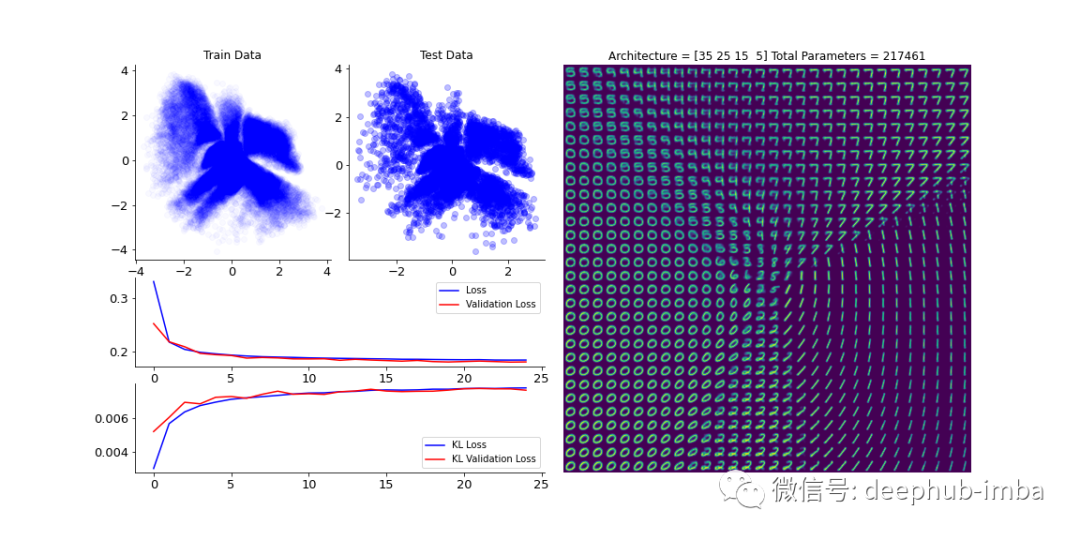
已经定义了神经网络的架构,下面就是评估其他超参数。随着超参数数量的增加,搜索空间的复杂性也随之增加。如果没有明显的差异,许多不同类型的参数组合可能会使解释变得困难。为了规避所有这些问题的一种简单方法是将简单的线性模型应用于在不同设置下训练的模型的性能数据。
names = ['BatchNorm','Dropout','SpatialAttention','Activation_elu','Activation_relu','Activation_selu','Activation_sigmoid']
container = []
for conf in configs:
initial = [int(conf[ky]) for ky in ['BatchNorm', 'Drop', 'SpAttention']]
for k,val in enumerate(activationNames):
current=[0,0,0,0]
if conf['Act']==val:
current[k]=1
break
initial.extend(current)
container.append(initial)
linearModel = sm.OLS(performanceA,np.array(container))
results = linearModel.fit()
results.summary(xname=names)
从这个线性模型中,系数的解释非常简单。正系数表示性能值增加,而负值表示性能值降低。当使用重建损失时,负系数将表示性能提高。
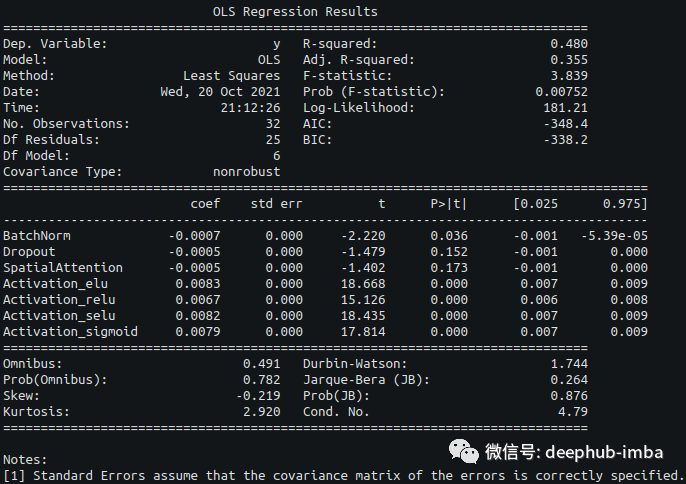
从这个简单的线性模型中,可以看到选择添加到主构建块中的三种不同类型的层提高了模型的性能。在改变激活函数的同时,模型性能向相反的方向移动。即使适合线性模型的样本量很小,它也可以将优化工作导向特定方向。
本文的完整代码在这里:https://github.com/TavoGLC/DataAnalysisByExample/blob/master/NeuralNetworks/MNISTAttention.py
作者:Octavio Gonzalez-Lugo