MAE发布以来,各种使用掩码技术的自监督掩码模型在其基础之上有了更进一步的研究。在本文中我们将探索一篇和MAE同期的工作:SimMIM: A Simple Framework for Masked Image Modeling,研究团队是微软亚研院,并在PyTorch中编写它,最后我们也会提供相关的代码。
SimMIM的骨干网络是VIT,熟悉自监督学习的基础知识也非常有帮助,最后我们还要精通PyTorch,因为我们使用它来实现我们的模型。
图像中的掩码技术
在过去的几年中,对比学习和非对比学习方法一直是计算机视觉(CV)的自监督学习(SSL)的主要形式,他们中的最先进的(SOTA)模型与监督学习处于同等地位。从根本上说,对比学习的目的是教会神经网络将相似的数据点(正对)放在一起,并将不同的数据点(负对)分开,这是一项需要学习视觉模式的任务。非对比学习克服了与对比学习相关的障碍(例如,需要大量的标注数据)。
而自然语言处理(NLP)为SSL使用掩码建模,其中输入的一个随机片段被掩码,模型的目标是根据剩余的信息恢复它,这样做的印象是将教会模型语法。像BERT这样的神经网络就属于这一类,这种方式已经取得了惊人的性能。

NLP 和视觉之间存在一定的差异,图像中的局部性非常强,即附近的像素高度相关,因此即使一个像素被屏蔽,通过分析其邻居也可以相对容易地推断出它的值。并且照片是连续的不像 NLP 中的标记是离散的,像素是低级原始特征而单词是人类构建的高级概念。
随着ViT的出现,蒙面建模最近已进入计算机视觉领域,在 ImageNet 分类等下游任务上取得了具有竞争力的分数。但是这些方法很棘手,并且依赖于精细的组件,如像 iGPT 一样像素聚类,以及通过额外的离散变分自动编码器 (dVAE) 进行标记化,这是 BEiT 使用的一种技术。
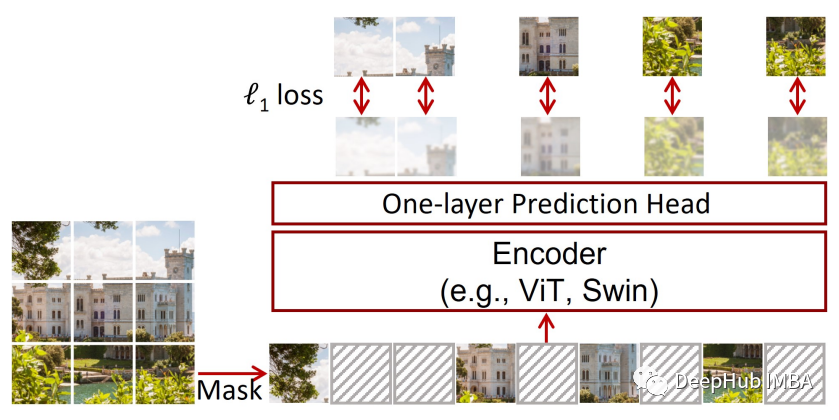
SimMIM 是一个简单的掩码图像建模框架并且超越了以前的 SOTA 基线,在没有复杂的元素的同时保持了效率。具体来说在提取图像的标记后,SimMIM 通过用可学习的掩码标记替换它们来随机屏蔽一些标记,并用 ViT 对数据进行编码。接下来通过将掩码标记的编码表示传递给线性层来重建缺失部分,损失是预测像素和实际像素之间的 L1 损失除以掩码标记的数量。
Pytorch实现
SimMIM 很简单而且没有特别复杂的操作。我们假设从一组维度为 batch_size X n_tokens X token_dim 的令牌开始。
fromtorchimport (
randn,
)
# tokens is currently a dummy tensor.
# Later, it will be replaced by the actual tokens
tokens=randn(batch_size, n_tokens, token_dim)
首先必须确定要屏蔽哪些标记。一种策略是在每个样本的 [0, n_tokens-1] (从零开始的索引)范围内生成一组索引,这些索引将是为该行屏蔽的标记的索引。
fromtorchimport (
randn,
)
tokens=randn(batch_size, n_tokens, token_dim)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
# Number of tokens to mask
# 50% of the total number of tokens performs well on average.
# However, for smaller patch sizes, a higher masking ratio is generally better.
# For example, for a patch size of 32, 0.5 performs well but for
# a patch size of 16, it would be worthwhile to increase it to 0.8.
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
# topk returns the k largest elements as well as their indices
# dim=1 tells it to find the maximum values and their indices
# on a per-row basis
# The indices of the tokens that are to be masked is going
# to be the indices of the n_masked_tokens largest values
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
# The largest values can be accesses via indices_to_mask.values,
# and their indices can be accessed via indices_to_mask.indices
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
indices_to_mask 的形状为 batch_size X n_masked_tokens,每一行都包含要为该特定数据点屏蔽标记的索引。使用 indices_to_mask 索引标记会稍微复杂一些,所以更好的方法是构建大小为 batch_size * n_tokens 的位掩码,其中如果标记[i][j] 被屏蔽,则 bitmask[i][j] 为 True,否则为 False .
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
tokens=randn(batch_size, n_tokens, token_dim)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
# Initially, bitmask is simply full of zeros (i.e., False)
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
# What this line does is as follows:
# For every row i, bitmask[i][j] is replaced
# by the value argument (in this case 1), where j takes every value
# in indices_to_mask[i].
# For example, if indices_to_mask[3] is
# [2, 4, 7], then bitmask[3][2], bitmask[3][4], and bitmask[3][7]
# are all set to 1.
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
要使用位掩码首先要通过VIT从输入产生令牌。我们这里使用的ViT来自timm包,但是它可以很容易地为转换为其他实现。
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
# vit is assumed to be a vision transformer from timm
# To get tokens from a timm ViT, one must call its patch_embed method
# tokens is now of shape batch_size X n_tokens X token_dim
# Keep in mind that input is image data and of size
# batch_size X n_channels X height X width
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
下一步使用掩码令牌替换切片。PyTorch 不允许以Inplace的方式修改变量,不能直接将掩码标记赋值给令牌[bitmask];所以必须用掩码标记填充形状为 batch_size * n_tokens * token_dim 的张量(维度相同),
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
fromtorch.nnimport (
Parameter,
)
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
# The mask token itself is simply a vector of dimension token_dim
mask_token=Parameter(randn(token_dim))
# mask_token is repeated to make it the same shape as tokens
# mask_tokens is now of size batch_size X n_tokens X token_dim
mask_tokens=mask_token.repeat(batch_size, n_tokens, 1)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
这样就完成了掩码的过程
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
fromtorch.nnimport (
Parameter,
)
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
mask_token=Parameter(randn(token_dim))
mask_tokens=mask_token.repeat(batch_size, n_tokens, 1)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
# bitmask must have the same number of axes as tokens and mask_tokens
# Therefore, unsqueeze(2) adds an axis to it and it is now of shape batch_size X n_tokens X 1
bitmask=bitmask.unsqueeze(2)
# ~bitmask turns True to False and False to True
# Here, all that is taking place is (~bitmask) is multiplied by tokens
# to zero out every token that is supposed to be masked, and the result is added
# to bitmask*mask_tokens, in which everything is 0 except the tokens that are
# supposed to mask.
tokens= (~bitmask)*tokens+bitmask*mask_tokens
然后就是位置嵌入
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
fromtorch.nnimport (
Parameter,
)
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
mask_token=Parameter(randn(token_dim))
mask_tokens=mask_token.repeat(batch_size, n_tokens, 1)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
bitmask=bitmask.unsqueeze(2)
tokens= (~bitmask)*tokens+bitmask*mask_tokens
# In timm, a ViT's position embedding is accessible via vit.pos_embed
# The reason for vit.pos_embed[:, 1:] in place of simply vit.pos_embed
# is that the first position embedding vector is for the class token,
# which is not used for self-supervised learning.
tokens=tokens+vit.pos_embed[:, 1:]
令牌可以被输入到 ViT获得它的编码表示。
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
fromtorch.nnimport (
Parameter,
)
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
mask_token=Parameter(randn(token_dim))
mask_tokens=mask_token.repeat(batch_size, n_tokens, 1)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
bitmask=bitmask.unsqueeze(2)
tokens= (~bitmask)*tokens+bitmask*mask_tokens
tokens=tokens+vit.pos_embed[:, 1:]
# The encoded representation of tokens
encoded=vit.blocks(tokens)
被屏蔽的令牌将从编码中获取,然后它们通过线性层来重建像素值。
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
fromtorch.nnimport (
Linear,
Parameter,
)
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
mask_token=Parameter(randn(token_dim))
mask_tokens=mask_token.repeat(batch_size, n_tokens, 1)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
bitmask=bitmask.unsqueeze(2)
tokens= (~bitmask)*tokens+bitmask*mask_tokens
tokens=tokens+vit.pos_embed[:, 1:]
encoded=vit.blocks(tokens)
# To index input and encoded with bitmask,
# the axis that was added must be removed.
# This reverts bit_mask to a size of batch_size X n_tokens
bitmask=bitmask.squeeze(2)
# The encoded mask tokens, of shape batch_size X n_masked_tokens X token_dim
masked_tokens_encoded=encoded[bitmask]
# In timm, A ViT's patch height and width are vit.patch_embed.patch_size
patch_height=patch_width=vit.patch_embed.patch_size
# The input is the tokens,
# the output is the reconstructed raw pixel values.
# Therefore, the output shape is 3 (for 3 channels)
# multiplied by patch_height*patch_width, which is the original shape
# of the patches before they were tokenized
decoder_out_dim=3*patch_height*patch_width
decoder=Linear(
in_features=token_dim,
out_features=decoder_out_dim,
)
# The reconstructed pixels, of shape batch_size X n_masked_tokens X 3*patch_height*patch_width
masked_patches_reconstructed=decoder(masked_tokens_encoded)
最后masked_patchesde的重构与初始数据中的原始像素进行比较。因为输入的patches不可用,因此必须对输入进行patche处理。PyTorch的reshap函数有一些限制,用torch进行拼接。重塑将产生不正确的输出。所以一个简单的解决方案是einops(它是一个方便用于操作张量的库,并且与框架无关)。
需要注意的是,patches和令牌(Token)是不同的。patches是从 batch_size * 3 * height * width 重塑为 batch_size * n_tokens * 3 * patch_height * patch_width 的数据,而令牌是通过沿最终轴线性变换patches创建的。
fromeinopsimport (
rearrange,
)
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
fromtorch.nnimport (
Linear,
Parameter,
)
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
mask_token=torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(token_dim))
mask_tokens=self.mask_token.repeat(batch_size, n_tokens, 1)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
bitmask=bitmask.unsqueeze(2)
tokens= (~bitmask)*tokens+bitmask*mask_tokens
tokens=tokens+vit.pos_embed[:, 1:]
encoded=vit.blocks(tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.squeeze(2)
masked_tokens_encoded=encoded[bitmask]
patch_height=patch_width=vit.patch_embed.patch_size
decoder_out_dim=3*patch_height*patch_width
decoder=Linear(
in_features=token_dim,
out_features=decoder_out_dim,
)
masked_patches_reconstructed=decoder(masked_tokens_encoded)
# patterns tells einops how to rearrange the tensor
# Its layout is as follows: 'shape_before -> shape_after'
# In this case, the shape before would be batch_size X n_channels X height X width,
# and the shape after would be batch_size X n_tokens X n_channels*patch_height*patch_width
# However, in einops, variables that are in shape_before must be in shape_after as well and vice versa
# For example, in this case, height is in shape_before but not shape_after.
# Therefore, shape_before and shape_after must be restructured.
# Particularly, two new variables can be introduced, n_patches_height and n_patches_width,
# that say how many patches are along the height and width axes respectively.
# Thus, height = n_patches_height * patch_height,
# width = n_patches_width * patch_width, and
# n_tokens = n_patches_height * n_patches width
# Multiplying two variables in einops is denoted by (x y).
pattern= (
'batch_size n_channels (n_patches_height patch_height) (n_patches_width patch_width) -> '
'batch_size (n_patches_height n_patches_width) (n_channels patch_height patch_width)'
)
# einops.rearrange is like torch.reshape
# einops cannot infer patch_height and patch_width,
# so they must be passed manually
# patches is now of shape batch_size X n_tokens X 3*patch_height*patch_width
patches=rearrange(
tensor=input,
pattern=pattern,
patch_height=patch_height,
patch_width=patch_width,
)
得对应于 masked_patches_reconstructed 的patche部分,
fromeinopsimport (
rearrange,
)
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
fromtorch.nnimport (
Linear,
Parameter,
)
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
mask_token=torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(token_dim))
mask_tokens=self.mask_token.repeat(batch_size, n_tokens, 1)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
bitmask=bitmask.unsqueeze(2)
tokens= (~bitmask)*tokens+bitmask*mask_tokens
tokens=tokens+vit.pos_embed[:, 1:]
encoded=vit.blocks(tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.squeeze(2)
masked_tokens_encoded=encoded[bitmask]
patch_height=patch_width=vit.patch_embed.patch_size
decoder_out_dim=3*patch_height*patch_width
decoder=Linear(
in_features=token_dim,
out_features=decoder_out_dim,
)
masked_patches_reconstructed=decoder(masked_tokens_encoded)
pattern= (
'batch_size n_channels (n_patches_height patch_height) (n_patches_width patch_width) -> '
'batch_size (n_patches_height n_patches_width) (n_channels patch_height patch_width)'
)
patches=einops.rearrange(
tensor=input,
pattern=pattern,
patch_height=patch_height,
patch_width=patch_width,
)
# Similar to how masked_tokens_encoded was computed
maskes_patches_original=patches[bitmask]
评估损失。
fromeinopsimport (
rearrange,
)
fromtorchimport (
randn,
zeros,
)
fromtorch.nnimport (
Linear,
Parameter,
)
fromtorch.nn.functionalimport (
l1_loss,
)
tokens=vit.patch_embed(input)
mask_token=torch.nn.Parameter(torch.randn(token_dim))
mask_tokens=self.mask_token.repeat(batch_size, n_tokens, 1)
indices_to_mask=randn(batch_size, n_tokens)
n_masked_tokens=int(0.5*n_tokens)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.topk(
k=n_masked_tokens,
dim=1,
)
indices_to_mask=indices_to_mask.indices
bitmask=zeros(batch_size, n_tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.scatter(
dim=1,
index=indices_to_mask,
value=1,
)
bitmask=bitmask.bool()
bitmask=bitmask.unsqueeze(2)
tokens= (~bitmask)*tokens+bitmask*mask_tokens
tokens=tokens+vit.pos_embed[:, 1:]
encoded=vit.blocks(tokens)
bitmask=bitmask.squeeze(2)
masked_tokens_encoded=encoded[bitmask]
patch_height=patch_width=vit.patch_embed.patch_size
decoder_out_dim=3*patch_height*patch_width
decoder=Linear(
in_features=token_dim,
out_features=decoder_out_dim,
)
masked_patches_reconstructed=decoder(masked_tokens_encoded)
pattern= (
'batch_size n_channels (n_patches_height patch_height) (n_patches_width patch_width) -> '
'batch_size (n_patches_height n_patches_width) (n_channels patch_height patch_width)'
)
patches=einops.rearrange(
tensor=input,
pattern=pattern,
patch_height=patch_height,
patch_width=patch_width,
)
maskes_patches_original=patches[bitmask]
# The loss is the L1 difference between
# the predicted pixel values and the ground truth,
# divided by the number of masked patches
loss=l1_loss(
input=masked_patches_reconstructed,
target=maskes_patches_original,
)/n_masked_tokens
把上面的代码封装成类并增加一些辅助函数,这里就不贴了有兴趣的看下最后的源代码。然后使用的时候如下:
fromtimmimport (
create_model,
)
fromtorch.nn.functionalimport (
l1_loss,
)
fromtorch.optimimport (
AdamW,
)
vit=create_model(
'vit_small_patch32_224',
num_classes=0,
)
simmim=SimMIM(
vit=vit,
masking_ratio=0.5,
)
optimizer=AdamW(
params=simmim.parameters(),
lr=1e-4,
weight_decay=5e-2,
)
forepochinrange(n_epochs):
forinputindataloader:
n_masked_tokens, masked_patches_reconstructed, masked_patches_original=simmim(input)
loss=l1_loss(
input=masked_patches_reconstructed,
target=maskes_patches_original,
)
loss/=n_masked_tokens
loss.backward()
optimizer.backward()
optimizer.zero_grad()
上面的代码可以配置各种超参数(例如学习率,使用余弦退火,但为简单起见,此处省略)。我们的dataloader仅返回随机调整大小的裁剪、随机水平翻转和标准化的图像。
使用上面的代码,任何VIT都可以在大量未注释的数据上进行训练,并且可以很好地学习下游任务。看起来很简单吧,这也就是论文的名字sample的来源。
总结
在本文中,我们介绍 SimMIM,这是一种受掩码建模启发的强大 SSL 算法,其中一部分输入数据被掩码,模型的目标是最小化重建损失。为了更熟悉模型的运行方式我们还是用Pytorch对其进行了实现 ,这样可以帮助我们了解模型的细节。
引用:
A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations
https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.05709
Exploring Simple Siamese Representation Learning
https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.10566
SimMIM: A Simple Framework for Masked Image Modeling
https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09886
本文代码:
https://github.com/BobMcDear/PyTorch-SimMIM
作者:Borna Ahmadzadeh