在Pandas 2.0发布以后,我们发布过一些评测的文章,这次我们看看,除了Pandas以外,常用的两个都是为了大数据处理的并行数据框架的对比测试。
本文我们使用两个类似的脚本来执行提取、转换和加载(ETL)过程。
测试内容
这两个脚本主要功能包括:
从两个parquet 文件中提取数据,对于小型数据集,变量path1将为“yellow_tripdata/ yellow_tripdata_2014-01”,对于中等大小的数据集,变量path1将是“yellow_tripdata/yellow_tripdata”。对于大数据集,变量path1将是“yellow_tripdata/yellow_tripdata*.parquet”;
进行数据转换:a)连接两个DF,b)根据PULocationID计算行程距离的平均值,c)只选择某些条件的行,d)将步骤b的值四舍五入为2位小数,e)将列“trip_distance”重命名为“mean_trip_distance”,f)对列“mean_trip_distance”进行排序
将最终的结果保存到新的文件
脚本
1、Polars
数据加载读取
def extraction():
"""
Extract two datasets from parquet files
"""
path1="yellow_tripdata/yellow_tripdata_2014-01.parquet"
df_trips= pl_read_parquet(path1,)
path2 = "taxi+_zone_lookup.parquet"
df_zone = pl_read_parquet(path2,)
return df_trips, df_zone
def pl_read_parquet(path, ):
"""
Converting parquet file into Polars dataframe
"""
df= pl.scan_parquet(path,)
return df
转换函数
def transformation(df_trips, df_zone):
"""
Proceed to several transformations
"""
df_trips= mean_test_speed_pl(df_trips, )
df = df_trips.join(df_zone,how="inner", left_on="PULocationID", right_on="LocationID",)
df = df.select(["Borough","Zone","trip_distance",])
df = get_Queens_test_speed_pd(df)
df = round_column(df, "trip_distance",2)
df = rename_column(df, "trip_distance","mean_trip_distance")
df = sort_by_columns_desc(df, "mean_trip_distance")
return df
def mean_test_speed_pl(df_pl,):
"""
Getting Mean per PULocationID
"""
df_pl = df_pl.groupby('PULocationID').agg(pl.col(["trip_distance",]).mean())
return df_pl
def get_Queens_test_speed_pd(df_pl):
"""
Only getting Borough in Queens
"""
df_pl = df_pl.filter(pl.col("Borough")=='Queens')
return df_pl
def round_column(df, column,to_round):
"""
Round numbers on columns
"""
df = df.with_columns(pl.col(column).round(to_round))
return df
def rename_column(df, column_old, column_new):
"""
Renaming columns
"""
df = df.rename({column_old: column_new})
return df
def sort_by_columns_desc(df, column):
"""
Sort by column
"""
df = df.sort(column, descending=True)
return df
保存
def loading_into_parquet(df_pl):
"""
Save dataframe in parquet
"""
df_pl.collect(streaming=True).write_parquet(f'yellow_tripdata_pl.parquet')
其他代码
import polars as pl
import time
def pl_read_parquet(path, ):
"""
Converting parquet file into Polars dataframe
"""
df= pl.scan_parquet(path,)
return df
def mean_test_speed_pl(df_pl,):
"""
Getting Mean per PULocationID
"""
df_pl = df_pl.groupby('PULocationID').agg(pl.col(["trip_distance",]).mean())
return df_pl
def get_Queens_test_speed_pd(df_pl):
"""
Only getting Borough in Queens
"""
df_pl = df_pl.filter(pl.col("Borough")=='Queens')
return df_pl
def round_column(df, column,to_round):
"""
Round numbers on columns
"""
df = df.with_columns(pl.col(column).round(to_round))
return df
def rename_column(df, column_old, column_new):
"""
Renaming columns
"""
df = df.rename({column_old: column_new})
return df
def sort_by_columns_desc(df, column):
"""
Sort by column
"""
df = df.sort(column, descending=True)
return df
def main():
print(f'Starting ETL for Polars')
start_time = time.perf_counter()
print('Extracting...')
df_trips, df_zone =extraction()
end_extract=time.perf_counter()
time_extract =end_extract- start_time
print(f'Extraction Parquet end in {round(time_extract,5)} seconds')
print('Transforming...')
df = transformation(df_trips, df_zone)
end_transform = time.perf_counter()
time_transformation =time.perf_counter() - end_extract
print(f'Transformation end in {round(time_transformation,5)} seconds')
print('Loading...')
loading_into_parquet(df,)
load_transformation =time.perf_counter() - end_transform
print(f'Loading end in {round(load_transformation,5)} seconds')
print(f"End ETL for Polars in {str(time.perf_counter()-start_time)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2、Dask
函数功能与上面一样,所以我们把代码整合在一起:
import dask.dataframe as dd
from dask.distributed import Client
import time
def extraction():
path1 = "yellow_tripdata/yellow_tripdata_2014-01.parquet"
df_trips = dd.read_parquet(path1)
path2 = "taxi+_zone_lookup.parquet"
df_zone = dd.read_parquet(path2)
return df_trips, df_zone
def transformation(df_trips, df_zone):
df_trips = mean_test_speed_dask(df_trips)
df = df_trips.merge(df_zone, how="inner", left_on="PULocationID", right_on="LocationID")
df = df[["Borough", "Zone", "trip_distance"]]
df = get_Queens_test_speed_dask(df)
df = round_column(df, "trip_distance", 2)
df = rename_column(df, "trip_distance", "mean_trip_distance")
df = sort_by_columns_desc(df, "mean_trip_distance")
return df
def loading_into_parquet(df_dask):
df_dask.to_parquet("yellow_tripdata_dask.parquet", engine="fastparquet")
def mean_test_speed_dask(df_dask):
df_dask = df_dask.groupby("PULocationID").agg({"trip_distance": "mean"})
return df_dask
def get_Queens_test_speed_dask(df_dask):
df_dask = df_dask[df_dask["Borough"] == "Queens"]
return df_dask
def round_column(df, column, to_round):
df[column] = df[column].round(to_round)
return df
def rename_column(df, column_old, column_new):
df = df.rename(columns={column_old: column_new})
return df
def sort_by_columns_desc(df, column):
df = df.sort_values(column, ascending=False)
return df
def main():
print("Starting ETL for Dask")
start_time = time.perf_counter()
client = Client() # Start Dask Client
df_trips, df_zone = extraction()
end_extract = time.perf_counter()
time_extract = end_extract - start_time
print(f"Extraction Parquet end in {round(time_extract, 5)} seconds")
print("Transforming...")
df = transformation(df_trips, df_zone)
end_transform = time.perf_counter()
time_transformation = time.perf_counter() - end_extract
print(f"Transformation end in {round(time_transformation, 5)} seconds")
print("Loading...")
loading_into_parquet(df)
load_transformation = time.perf_counter() - end_transform
print(f"Loading end in {round(load_transformation, 5)} seconds")
print(f"End ETL for Dask in {str(time.perf_counter() - start_time)}")
client.close() # Close Dask Client
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
测试结果对比
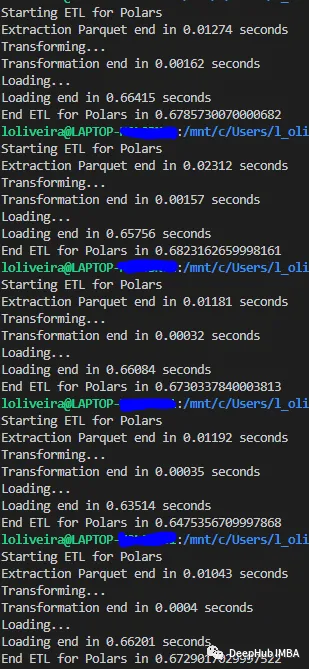
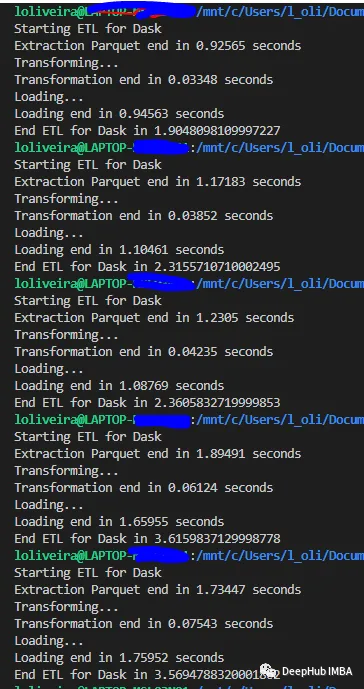
1、小数据集
我们使用164 Mb的数据集,这样大小的数据集对我们来说比较小,在日常中也时非常常见的。
下面是每个库运行五次的结果:
Polars
Dask
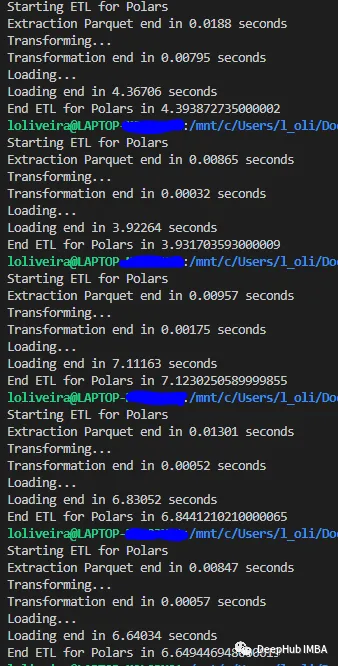
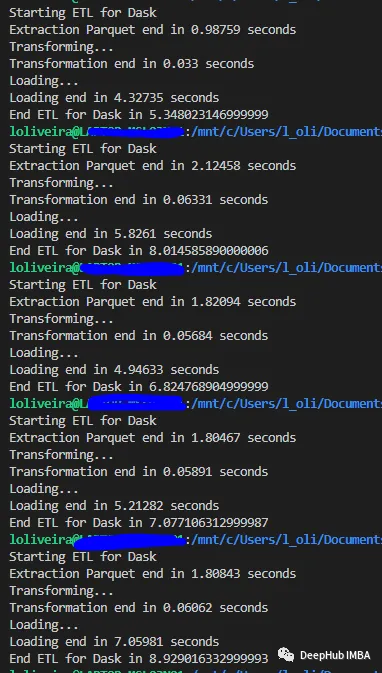
2、中等数据集
我们使用1.1 Gb的数据集,这种类型的数据集是GB级别,虽然可以完整的加载到内存中,但是数据体量要比小数据集大很多。
Polars
Dask
3、大数据集
我们使用一个8gb的数据集,这样大的数据集可能一次性加载不到内存中,需要框架的处理。
Polars
Dask
总结
从结果中可以看出,Polars和Dask都可以使用惰性求值。所以读取和转换非常快,执行它们的时间几乎不随数据集大小而变化;
可以看到这两个库都非常擅长处理中等规模的数据集。
由于polar和Dask都是使用惰性运行的,所以下面展示了完整ETL的结果(平均运行5次)。
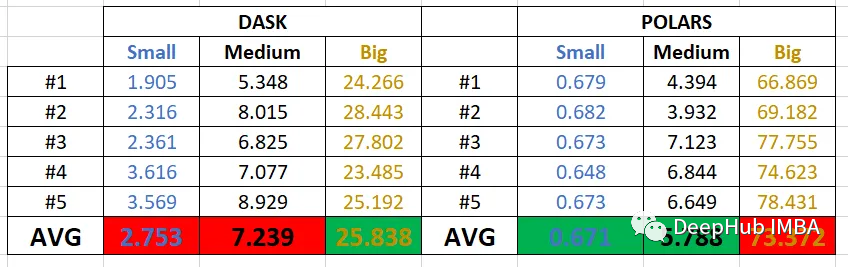
Polars在小型数据集和中型数据集的测试中都取得了胜利。但是,Dask在大型数据集上的平均时间性能为26秒。
这可能和Dask的并行计算优化有关,因为官方的文档说“Dask任务的运行速度比Spark ETL查询快三倍,并且使用更少的CPU资源”。
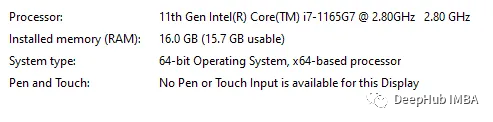
上面是测试使用的电脑配置,Dask在计算时占用的CPU更多,可以说并行性能更好。
作者:Luís Oliveira