在寻找选题的灵感时,通常需要阅读大量论文。由于英语水平所限,阅读英文速度不够快,于是想到了一种辅助整理WoS英文论文题录文档的方法,从WoS导出标题、作者、来源、年份和摘要等信息,然后结合谷歌文档翻译和python-docx整理成Word文档,用于快速浏览论文主题、方法的分布,并快速定位到符合需求的高价值论文,最后再单独下载这些论文仔细阅读。
1. WoS导出Excel题录
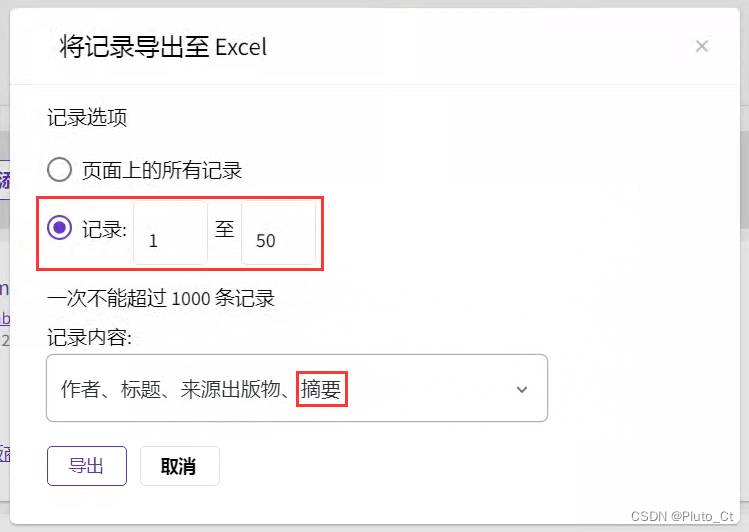
首先在Web of Science中检索文献,然后选择导出Excel格式。
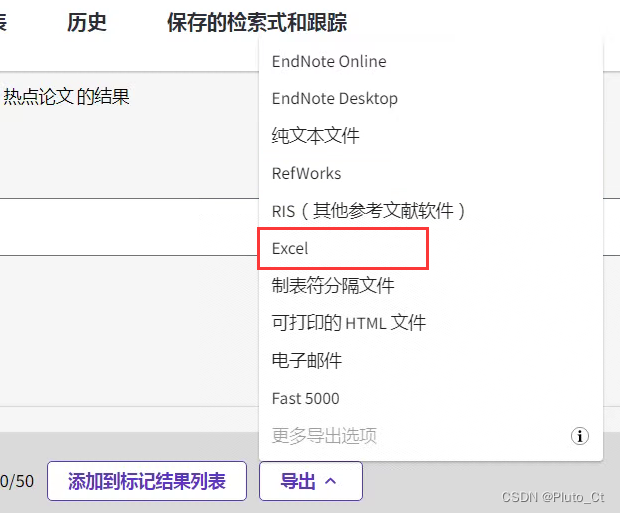
在弹出的框中选择记录x到x,如果少于1000条可以一次性导出;记录内容选择包含摘要的选项。
2. 机器翻译
百度翻译文档需要会员,有道、WPS的文档翻译只支持Word、PPT、PDF等格式,不支持Excel表格。这里使用谷歌翻译Excel文档。
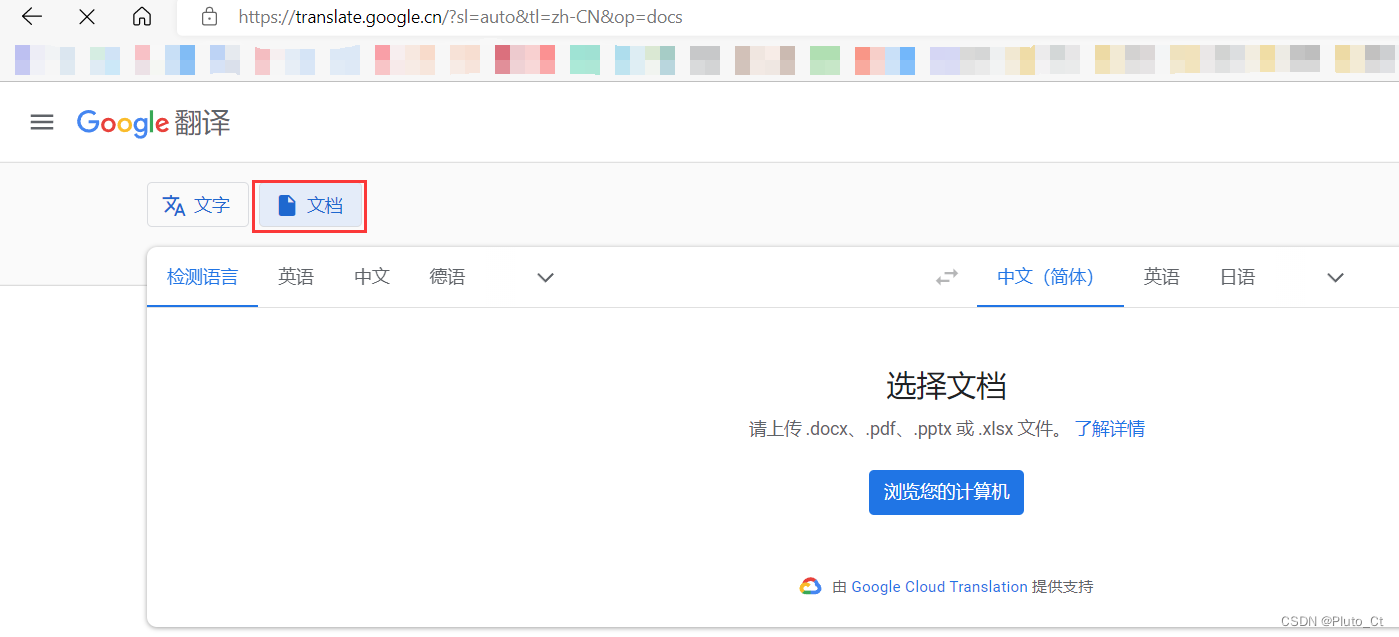
由于谷歌翻译只支持xlsx格式,需要先把xls重新保存成新的格式。

速度非常快,上传后几秒就可以下载译文。

3. 基于python-docx的文档生成与排版
把下载的译文命名为'savedrecs译文.xlsx',与原文件放在同一文件夹,使用Python程序整合两个文件并排版生成Word。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pandas as pd
from docx import Document
from docx.enum.text import WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH
from docx.shared import Pt, RGBColor
from docx.oxml.ns import qn
df = pd.merge(pd.read_excel('savedrecs.xlsx')[['Article Title', 'Authors', 'Source Title', 'Publication Year']], pd.read_excel('savedrecs译文.xlsx')[['文章标题', '来源标题', '抽象的']], left_index=True, right_index=True)[['Article Title', '文章标题', 'Authors', '来源标题', 'Source Title', 'Publication Year', '抽象的']]
df.dropna(inplace=True)
document = Document()
document.styles['Normal'].font.size = Pt(12) # 字体大小
document.styles['Normal'].font.name = 'Times New Roman' # 西文字体
document.styles['Normal']._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn('w:eastAsia'), '宋体') # 中文字体
document.styles['Normal'].paragraph_format.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.JUSTIFY # 两端对齐
document.styles['Normal'].paragraph_format.line_spacing = 1.15 # 行距
document.styles['Normal'].paragraph_format.space_before = Pt(3) # 段前
document.styles['Normal'].paragraph_format.space_after = Pt(3) # 断后
document.styles['Normal'].paragraph_format.first_line_indent = document.styles['Normal'].font.size * 2 # 首行缩进
# 增加标题,可能由于版本问题直接改样式不起作用,这里使用h、r2个变量来调整标题格式,分别是paragraph和run格式
def add_heading_func(text, level, font_size, font_color=RGBColor(0, 0, 0), font_bold=True, line_spacing=1.15, first_line_indent=0, space_before=6, space_after=6, en_font='Times New Roman', cn_font='宋体'):
h = document.add_heading(level=level)
r = h.add_run(text)
r.font.size = Pt(font_size) # 字体大小
r.font.color.rgb = font_color # 字体颜色
r.font.bold = font_bold # 加粗
r.font.name = en_font # 西文字体
r._element.rPr.rFonts.set(qn('w:eastAsia'), cn_font) # 中文字体
if level == 0: # 如果为大标题,居中,西文字体同中文字体
h.paragraph_format.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.CENTER
r.font.name = cn_font
else: # 其他标题两端对齐
h.paragraph_format.alignment = WD_ALIGN_PARAGRAPH.JUSTIFY
h.paragraph_format.first_line_indent = r.font.size * first_line_indent # 首行缩进
h.paragraph_format.line_spacing = line_spacing # 行距
h.paragraph_format.space_before = Pt(space_before) # 段前
h.paragraph_format.space_after = Pt(space_after) # 段后
add_heading_func('论文题录整理', 0, 16, cn_font='微软雅黑')
add_heading_func('一、分类标题1', 1, 12, cn_font='微软雅黑', en_font='微软雅黑', font_bold=False)
add_heading_func('(一)分类标题2', 2, 12)
for i in df.values: # 循环遍历题录表格
add_heading_func(i[1] + '('+ i[0] + ')(' + str(i[5]) + ')', 3, 12, font_color=RGBColor(0x4f, 0x81, 0xbd))
document.add_paragraph('来源:' + i[4] + '('+ i[3] + ')')
document.add_paragraph('作者:' + i[2])
document.add_paragraph(i[6])
document.add_paragraph()
document.save('论文题录整理.docx') # 保存文件
4. 文档输出与整理
Python生成的Word文档如下。
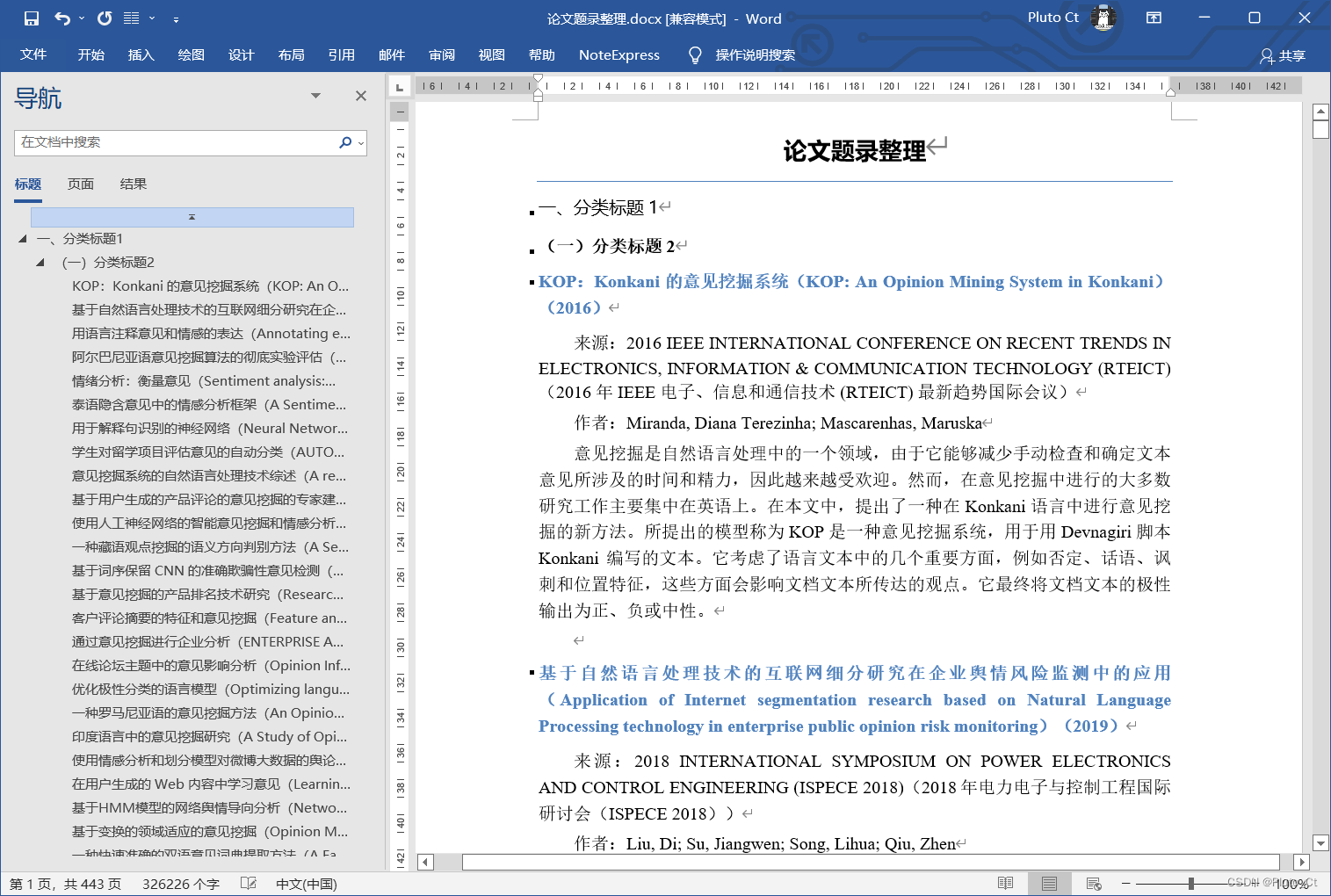
可将标题格式替换到样式中,方便后续进一步分类整理与排版。

5. 不足之处与未来展望
谷歌翻译文档存在少量单元格没有被翻译的情况,原因未知,还需要手动对译文的文件进行一定的检查和修正;未来考虑自动识别未被翻译的内容,补充进行翻译;
可能由于版本原因标题样式没法直接设置,修改到styles['Heading 1']中的样式不起作用,仍需少量的手工操作;
分类整理目前全为手动,未来可考虑结合TextRank、LDA等算法辅助归类。
版权归原作者 Pluto_Ct 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。