带环检测的一致代价搜索(Uniform Cost Search, UCS) Python实现
罗马尼亚旅行问题
求从城市Arad到城市Bucharest的最短路径

States:表示当前所处的城市;
Actitons:表示在图中进行移动的动作
Initial state:表示初始位置,也就是起点城市
Goal:表示目标城市

算法思想:
一致代价搜索算法,维护三个线性表,边界表(frontier表),已扩展结点表(close表),前驱结点表(pre表)。考虑当前边界中的最小代价的结点(这部分用优先队列实现)对其进行扩展,将其子结点放入边界中,已经扩展过的结点放入close表,从边界表中取出结点的时候进行目标检测,(这里与BFS不同,BFS是在将结点放入边界时就对目标进行检测);在算法执行过程中进行Cycle checking(环检测), 如果结点已经扩展过,则不能放入边界表中。
算法例题:
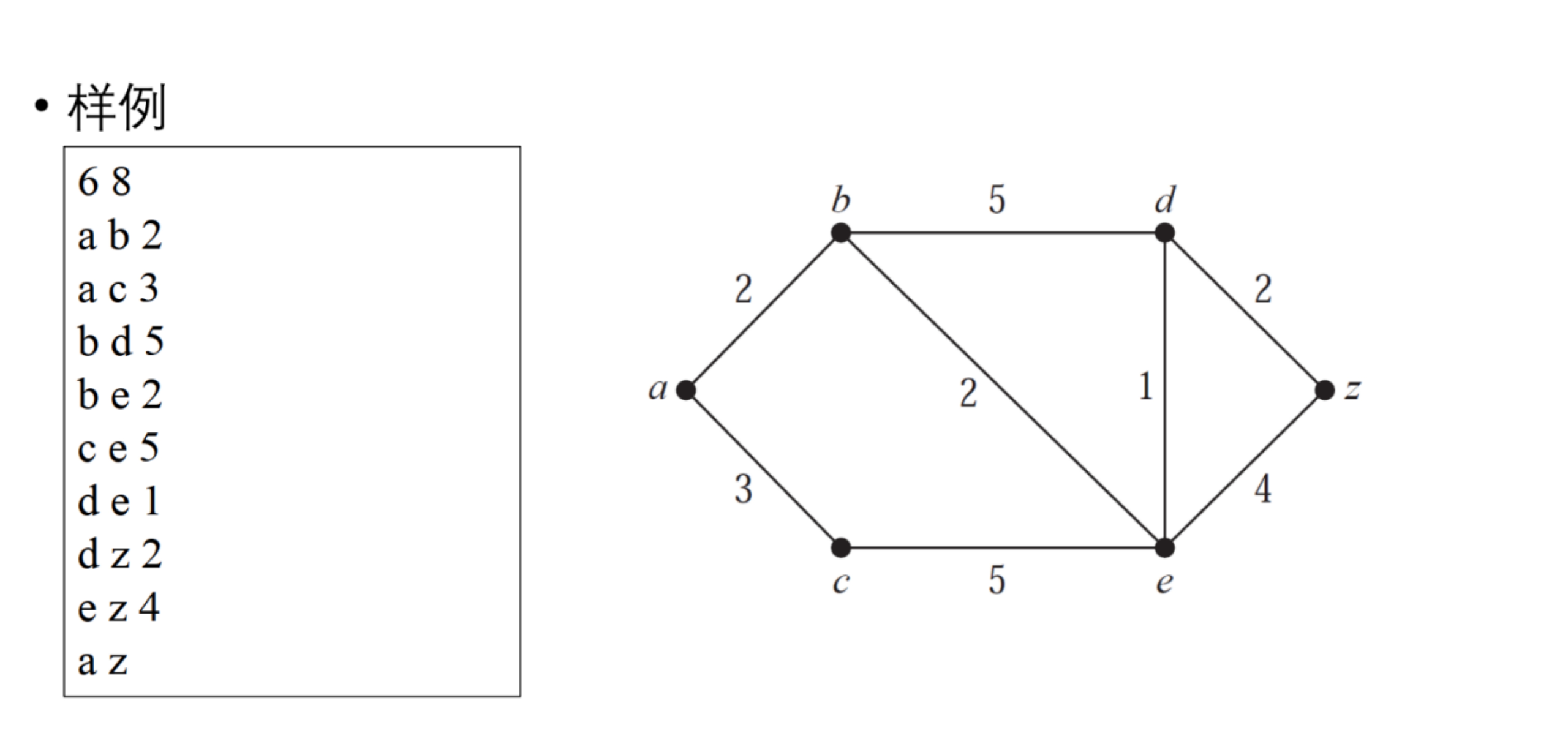
给定无向图,及图上两个节点,求其最短路径及长度
要求:使用Python实现带环检测的一致代价搜索(uniform-cost)算法
输入(统一格式,便于下周的验收)
第1行:节点数m 边数n(中间用空格隔开,下同);
第2行到第n+1行是边的信息,每行是:节点1名称 节点2名称 边权;
第n+2行开始可接受循环输入,每行是:起始节点名称 目标节点名称。
输出(格式不限)
最短路径及其长度。
Python实现代码:
算法实现中采用了优先队列作为frontier表,将代价最小的结点放在表头。具体的细节可以看代码中的注释。
from cmath import cos
from email import header
from importlib.resources import path
from json.tool import main
from os import pread, stat
from re import T
import re
from stat import S_IEXEC
import heapq
classNode:def__init__(self,state,pre,cost)->None:
self.state = state
self.pre = pre
self.cost = cost
edges =[]# 边集
closed =[]# 已经扩展过的结点
frontier =[]#待扩展的结点
path =[]defis_in_frontier(state):for f in frontier:if state == f[1]:returnTruereturnFalsedefprint_path(result):#打印路径whileTrue:
path.append(result[1])if result[2]==None:break
result = result[2]
path.reverse()defmain():
m, n =map(int,input().split(" "))#"Please enter the number of vertex and edge:"for _ inrange(n):
n1, n2, w=input().split(" ")
w =int(w)
edges.append({'c1':n1,'c2':n2,'w':int(w)})whileTrue:
s_city, d_city =input().split(" ")
ans = uniform_cost_search(s_city, d_city)print('Shortest distance from %s to %s is %d'%(s_city,d_city,ans[0]))
print_path(ans)print('Path:',path)defuniform_cost_search(start, dest):
heapq.heapify(frontier)
heapq.heappush(frontier,(0,start,None))# 元组(heapq不支持字典) 分别是 w, state, prewhilelen(frontier):
t = heapq.heappop(frontier)if t[1]== dest:# 目标检测return t
closed.append(t[1])for edge in edges:
des =''if edge['c1']== t[1]:# 由于是无向图,当前的城市可以作为边的起点,也可以作为终点
des = edge['c2']elif edge['c2']== t[1]:
des = edge['c1']if des =='':continue
child ={'state': des,'pre': t,'w': t[0]+edge['w']}# 将子结点封装成一个字典,分别是子结点的状态, 父亲结点, costif child['state']notin closed:# 环检测(如果该结点没有被扩展过)
heapq.heappush(frontier,(child['w'], child['state'], child['pre']))returnNoneif __name__ =='__main__':
main()
运行结果:
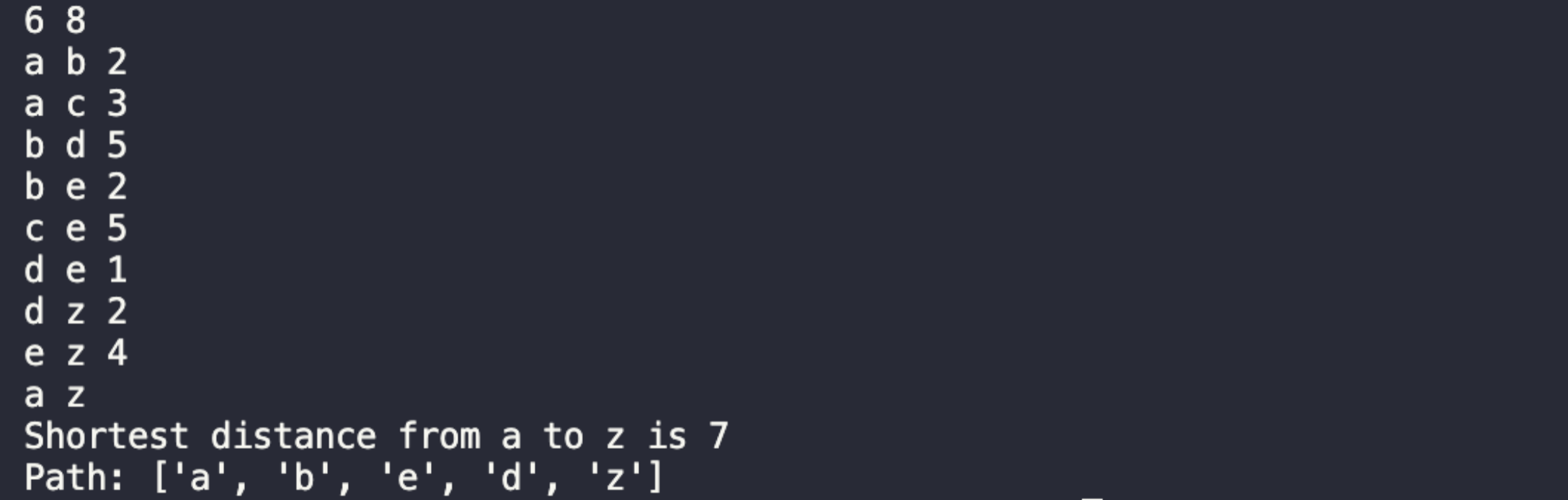
对于题目中给定的图来说,从a城市走到z城市的最短路径为7,对应的路为a->b->e->d->z。
补充:
在开始学习一致代价搜索算法的时候,我隐隐约约地觉得好像在哪见过这个算法,但是又好像没见过。其实这个算法跟Dijkstra算法很像,其核心内容都很相似,但是又不完全相同。
在Dijkstra算法中,我们用图中的所有顶点初始化顶点表。因此,Dijkstra算法只适用于已知所有顶点和边的显式图。
而一致代价搜索算法从源顶点开始,并逐渐遍历必要的图部分。因此,它适用于显式图和隐式图。
版权归原作者 Maxwell-Wong 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。