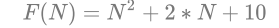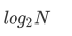数据结构作为比较难学习的学科来说,它也是我们未来作为程序员必须要牢牢掌握的一门学科,我们应该多画图,多写代码,才能有所收获,本篇博客可以作为入门级别的教学,里面会有图解和详细的代码,总结的内容即代表个人观点,还有部分数据结构内容没有总结,但足够作为一名数据结构的初学者学习,还有各种大厂的笔试题详解。本篇博客内容较长,建议收藏。如果你认为本篇博客写的不错的话,求点赞,求收藏,制作不易,废话不多说,让我们学起来吧!!!
一、时间复杂度和空间复杂度
1,算法效率
算法效率分析分为两种:第一种是时间效率,第二种是空间效率。时间效率被称为时间复杂度,而空间效率被 称作空间复杂度。 时间复杂度主要衡量的是一个算法的运行速度,而空间复杂度主要衡量一个算法所需要的额 外空间,在计算机发展的早期,计算机的存储容量很小。所以对空间度很是在乎。但是经过计算机行业的 迅速发展,计算机的存储容量已经达到了很高的程度。所以我们如今已经不需要再特别关注一个算法的空间复杂度。
2,时间复杂度
①时间复杂度的概念
时间复杂度的定义:在计算机科学中,算法的时间复杂度是一个函数,它定量描述了该算法的运行时间。一个算法执行所耗费的时间,从理论上说,是不能算出来的,只有你把你的程序放在机器上跑起来,才能知道。但 是我们需要每个算法都上机测试吗?是可以都上机测试,但是这很麻烦,所以才有了时间复杂度这个分析方 式。一个算法所花费的时间与其中语句的执行次数成正比例,算法中的基本操作的执行次数,为算法的时间复杂度。
②大O的渐进表示法
void func1(int N){
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N ; j++) {
count++;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < 2 * N ; k++) {
count++;
}
int M = 10;
while ((M--) > 0) {
count++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
请计算一下func1基本操作执行了多少次?

Func1 执行的基本操作次数 :
N = 10 F(N) = 130
N = 100 F(N) = 10210
N = 1000 F(N) = 1002010
实际中我们计算时间复杂度时,我们其实并不一定要计算精确的执行次数,而只需要大概执行次数,那么这里 我们使用大O的渐进表示法。
大O符号(Big O notation):是用于描述函数渐进行为的数学符号。
推导大O阶方法:
1、用常数1取代运行时间中的所有加法常数。
2、在修改后的运行次数函数中,只保留最高阶项。
3、如果最高阶项存在且不是1,则去除与这个项目相乘的常数。得到的结果就是大O阶。
使用大O的渐进表示法以后,Func1的时间复杂度为:
O(N^2)
N = 10 F(N) = 100
N = 100 F(N) = 10000
N = 1000 F(N) = 1000000
通过上面我们会发现大O的渐进表示法去掉了那些对结果影响不大的项,简洁明了的表示出了执行次数。 另外有些算法的时间复杂度存在最好、平均和最坏情况:
最坏情况:任意输入规模的最大运行次数(上界)
平均情况:任意输入规模的期望运行次数
最好情况:任意输入规模的最小运行次数(下界)
在实际中一般情况关注的是算法的最坏运行情况,所以数组中搜索数据时间复杂度为O(N)
③常见时间复杂度计算举例
void func2(int N) {
int count = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 2 * N ; k++) {
count++;
}
int M = 10;
while ((M--) > 0) {
count++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}

void func3(int N, int M) {
int count = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < M; k++) {
count++;
}
for (int k = 0; k < N ; k++) {
count++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}

void func4(int N) {
int count = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 100; k++) {
count++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}

void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
for (int end = array.length; end > 0; end--) {
boolean sorted = true;
for (int i = 1; i < end; i++) {
if (array[i -1] > array[i]) {
Swap(array, i - 1, i);
sorted = false;
}
}
if (sorted == true) {
break;
}
}
}

int binarySearch(int[] array, int value) {
int begin = 0;
int end = array.length - 1;
while (begin <= end) {
int mid = begin + ((end-begin) / 2);
if (array[mid] < value)
begin = mid + 1;
else if (array[mid] > value)
end = mid - 1;
else
return mid;
}
return -1;
}

long factorial(int N) {
return N < 2 ? N : factorial(N-1) * N;
}
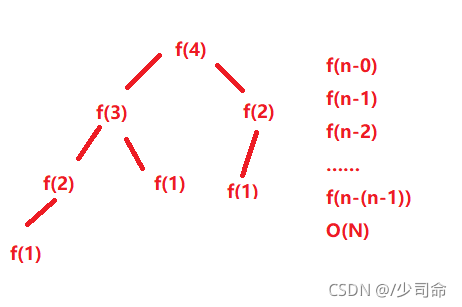

// 计算斐波那契递归fibonacci的时间复杂度?
int fibonacci(int N) {
return N < 2 ? N : fibonacci(N-1)+fibonacci(N-2);
}

3,空间复杂度
空间复杂度是对一个算法在运行过程中临时占用存储空间大小的量度 。空间复杂度不是程序占用了多少bytes 的空间,因为这个也没太大意义,所以空间复杂度算的是变量的个数。空间复杂度计算规则基本跟实践复杂度 类似,也使用大O渐进表示法。
// 计算bubbleSort的空间复杂度?
void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
for (int end = array.length; end > 0; end--) {
boolean sorted = true;
for (int i = 1; i < end; i++) {
if (array[i - 1] > array[i]) {
Swap(array, i - 1, i);
sorted = false;
}
}
if (sorted == true) {
break;
}
}
}
使用了常数个额外空间,所以空间复杂度为 O(1)
// 计算fibonacci的空间复杂度?
int[] fibonacci(int n) {
long[] fibArray = new long[n + 1];
fibArray[0] = 0;
fibArray[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n ; i++) {
fibArray[i] = fibArray[i - 1] + fibArray [i - 2];
}
return fibArray;
}
动态开辟了N个空间,空间复杂度为 O(N)
// 计算阶乘递归Factorial的时间复杂度?
long factorial(int N) {
return N < 2 ? N : factorial(N-1)*N;
}
递归调用了N次,开辟了N个栈帧,每个栈帧使用了常数个空间。空间复杂度为O(N)
二,线性表(单链表和双链表)
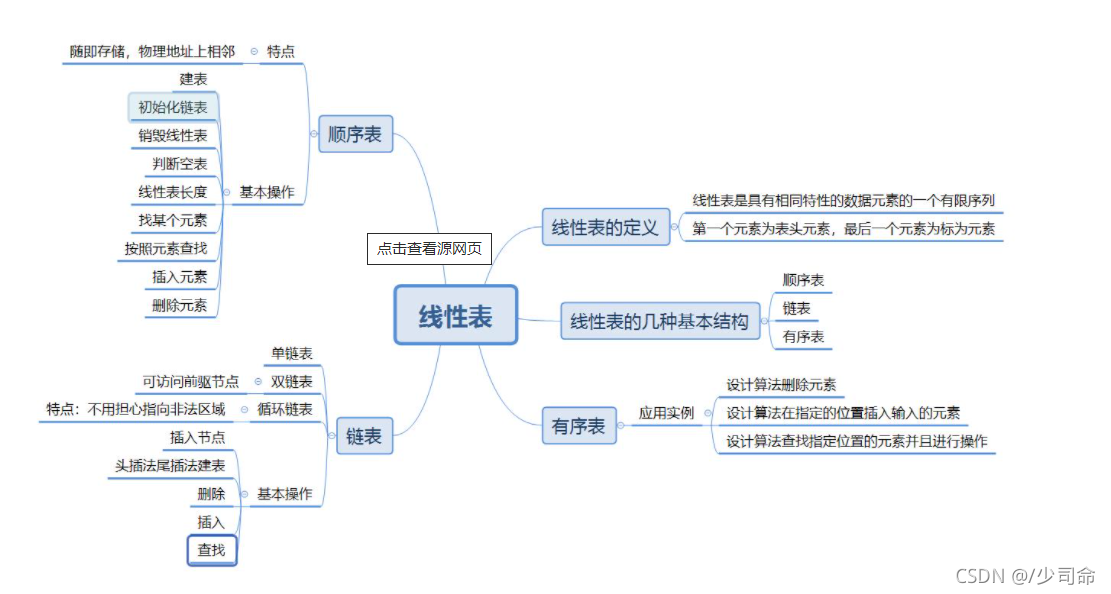
1,概念
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串.
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储 时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
2,顺序表
①概念
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数 据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储。
动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。
静态顺序表适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景
静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空间开多了浪费,开少了不够用
相比之下动态顺序表更灵活, 根据需要动态的分配空间大小。
②接口实现
class SeqList {
// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
}
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
return true;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int search(int toFind) {
return -1;
}
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int getPos(int pos) {
return -1;
}
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
}
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() {
return 0;
}
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
}
}
③创建顺序表

public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;//有效的数据个数
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
④打印顺序表

// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
⑤获取顺序表有效长度
// 获取顺序表的有效数据长度
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
⑥在pos位置增加元素
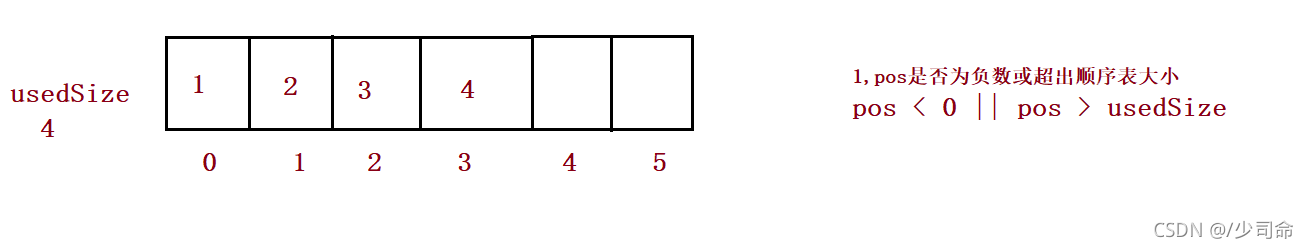

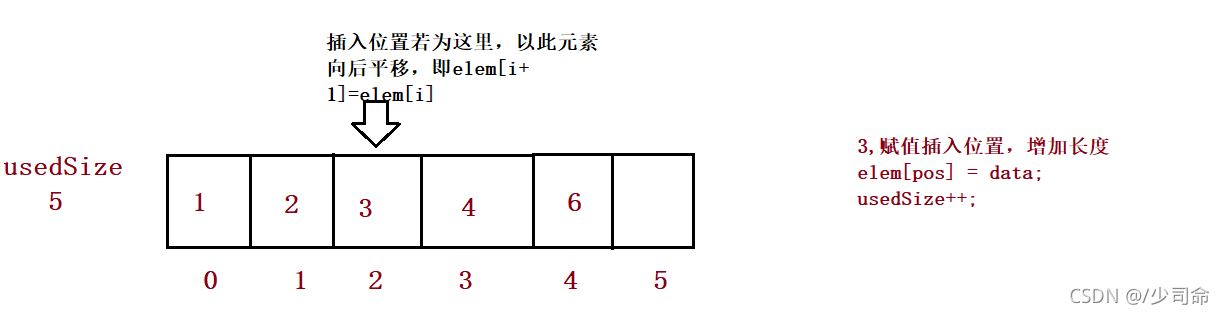


public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
if(pos < 0 || pos > usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//3、
for (int i = this.usedSize-1; i >= pos ; i--) {
this.elem[i+1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(0,1);
myArrayList.add(1,2);
myArrayList.add(2,3);
myArrayList.add(3,4);
myArrayList.display();
}

⑦判断是否由某个元素、查找某个元素对应的位置,找不到返回-1
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public int search(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
⑧获取 pos 位置的元素、给 pos 位置的元素设为/更新 value
public int getPos(int pos) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法");
return -1;//所以 这里说明一下,业务上的处理,这里不考虑 后期可以抛异常
}
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize==0;
}
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return;
}
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
⑨删除第一次出现的关键字key


public void remove(int toRemove) {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return;
}
int index = search(toRemove);
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的数字!");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < this.usedSize-1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
//this.elem[usedSize] = null; 如果数组当中是引用数据类型。
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(0,1);
myArrayList.add(1,2);
myArrayList.add(2,3);
myArrayList.add(3,4);
myArrayList.remove(3);
myArrayList.display();
}

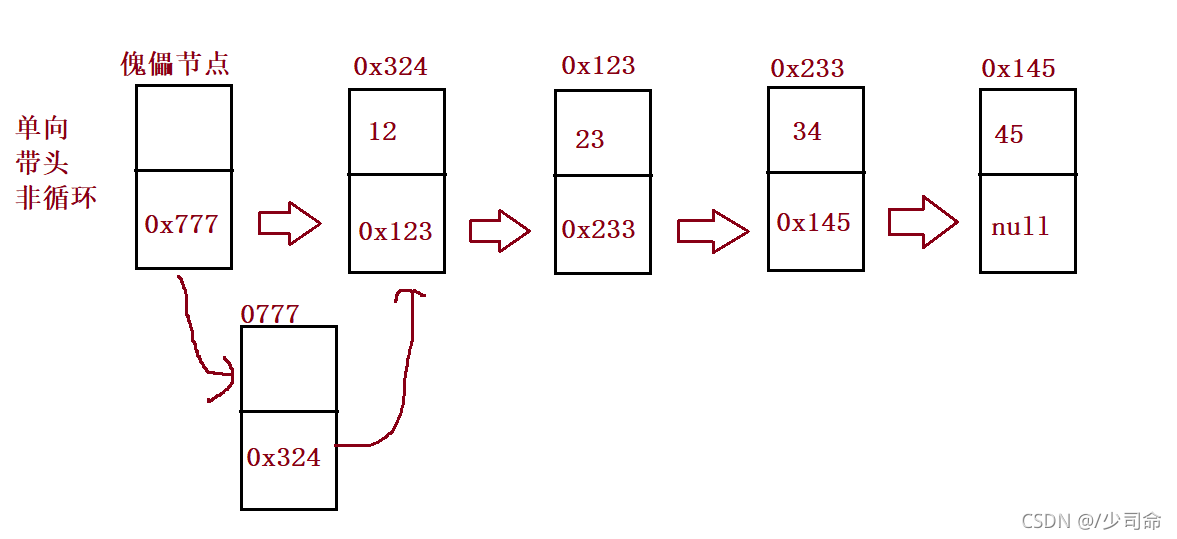
3,链表
①概念
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
链表分类

②链表的实现
// 1、无头单向非循环链表实现
public class SingleLinkedList {
//头插法
}
public void addFirst(int data){
//尾插法
}
public void addLast(int data){
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
}
public boolean addIndex(int index,int data){
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
}
public boolean contains(int key){
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
}
public void remove(int key){
//删除所有值为key的节点
}
public void removeAllKey(int key){
//得到单链表的长度
}
public int size(){
}
public void display(){
}
public void clear(){
}
}
③创建节点

public ListNode head;//链表的头引用
lass ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;//null
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}


④创建链表、打印链表

public void createList() {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(56);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
//listNode5.next = null;
this.head = listNode1;
}
public void display() {
//this.head.next != null
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.display();
}

⑤查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中、得到单链表的长度
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.display();
boolean flg = myLinkedList.contains(56);
}
public int size(){
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
System.out.println(myLinkedList.size());
}

** ⑥头插法、尾插法**

//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
/*if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}*/
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addFirst(10);
myLinkedList.display();
}


//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
//cur.next == null;
cur.next = node;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.display();
}

⑦找到index-1位置的节点的地址、插入元素
public ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (index-1 != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}


//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
if(index < 0 || index > size()) {
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.addIndex(2,20);
myLinkedList.display();
}
⑧找到要删除的关键字的前驱、删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public ListNode searchPerv(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if(cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}

//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
if(this.head == null) {
System.out.println("单链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchPerv(key);
if(cur == null) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的节点!");
return;
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.remove(23);
myLinkedList.display();
}
⑨ 删除所有值为key的节点

//删除所有值为key的节点
public ListNode removeAllKey(int key){
if(this.head == null) return null;
ListNode prev = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//最后处理头
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
return this.head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
//myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.addLast(90);
myLinkedList.removeAllKey(23);
myLinkedList.display();
}

⑩清空链表
public void clear(){
//this.head == null
while (this.head != null) {
ListNode curNext = head.next;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = curNext;
}
}
4,双向链表
①链表的实现
public class DoubleLinkedList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public boolean addIndex(int index,int data){
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
}
public void display(){
}
public void clear(){
}
}
②构造节点和链表
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
}
public ListNode head;//指向双向链表的头节点
//public ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);//指向双向链表的头节点
public ListNode last;//指向的是尾巴节点

③打印链表、求链表长度
public void display() {
//和单链表的打印方式是一样的
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
④查询key
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
⑤头插法

//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addFirst(12);
myLinkedList.addFirst(23);
myLinkedList.addFirst(34);
myLinkedList.addFirst(45);
myLinkedList.addFirst(56);
myLinkedList.display();
}

⑥尾插法


//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
this.last.next = node;
node.prev = this.last;
this.last = node;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.display();
}

⑦寻找插入节点
public ListNode searchIndex (int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
⑧插入元素


//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(index < 0 || index > size()) {
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchIndex(index);
node.next = cur.prev.next;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.addIndex(3,99);
myLinkedList.display();
}

⑨删除元素


//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
if(cur == head) {
head = head.next;
if(head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}else {
last = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if(cur.next != null) {
//中间位置
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
last = last.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(23);
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(45);
myLinkedList.addLast(56);
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.remove(23);
myLinkedList.display();
}

⑩清空链表
public void clear() {
while (head != null) {
ListNode curNext = head.next;
head.next = null;
head.prev = null;
head = curNext;
}
last = null;
}
5,笔试习题
①反转一个单链表

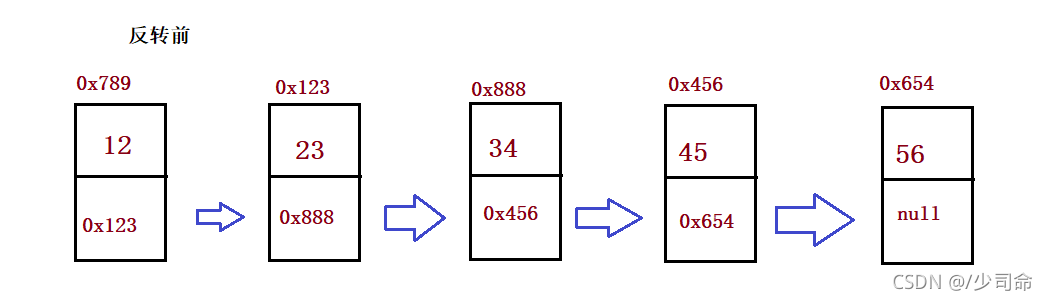

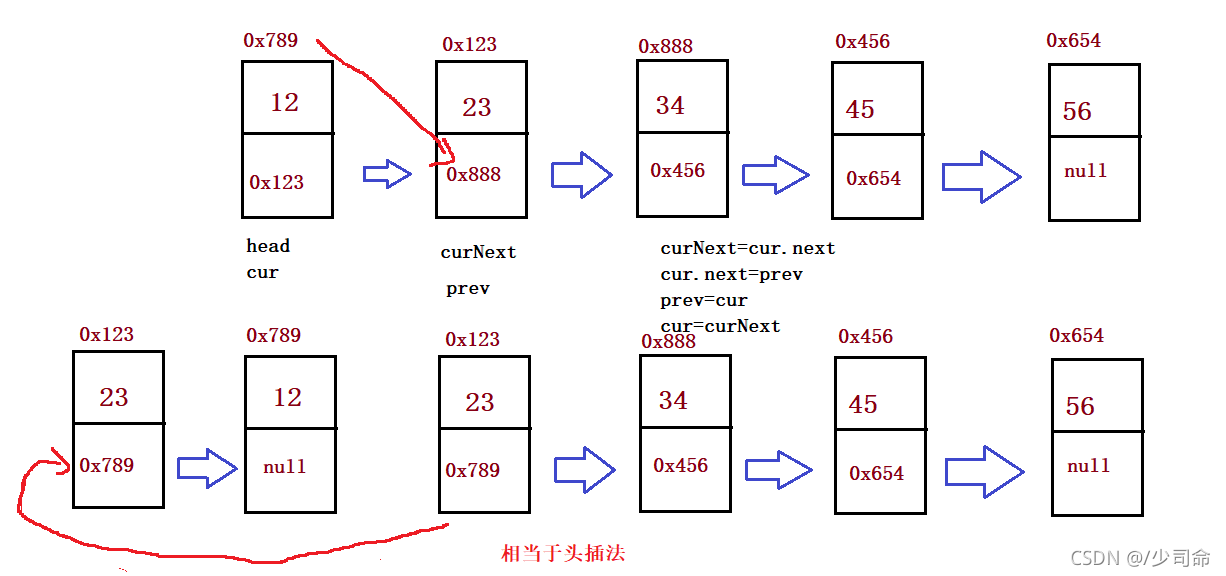
public ListNode reverseList() {
if(this.head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
ListNode prev = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return prev;
}
②给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点

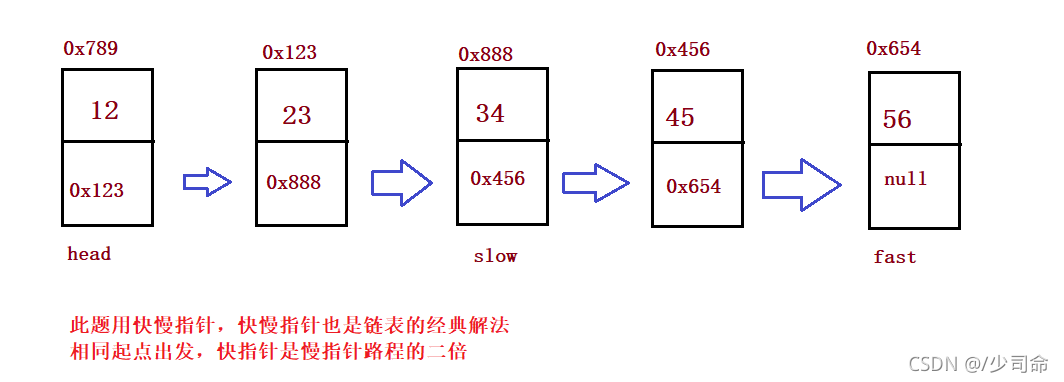

public ListNode middleNode() {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
if(fast == null) {
return slow;
}
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
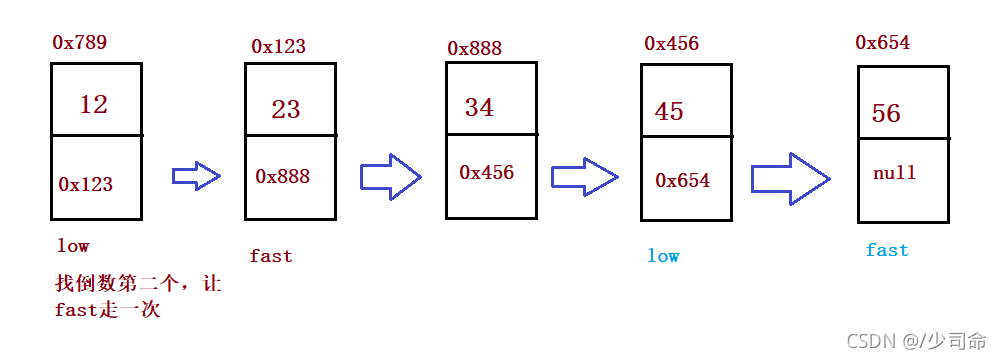
③输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点


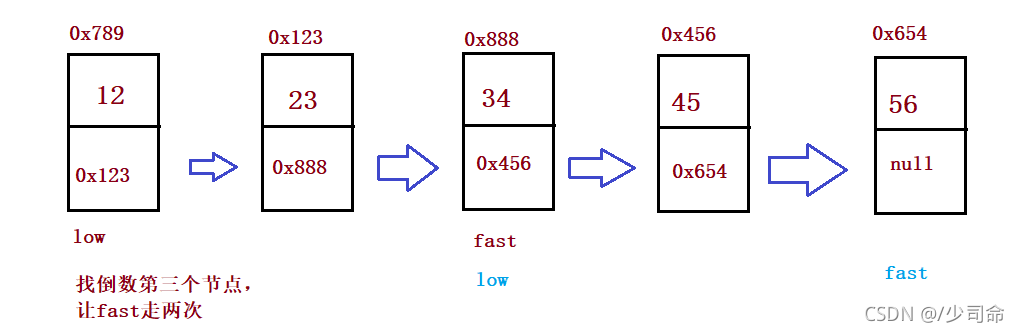
public ListNode findKthToTail(int k) {
if(k <= 0 || head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (k-1 != 0) {
fast = fast.next;
if(fast == null) {
return null;
}
k--;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
④删除链表中的多个重复值

//删除所有值为key的节点
public ListNode removeAllKey(int key){
if(this.head == null) return null;
ListNode prev = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//最后处理头
if(this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
return this.head;
}
⑤链表的回文结构



public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
// write code here
if(head == null) return true;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//slow走到了中间位置-》反转
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
//反转完成
while(head != slow) {
if(head.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
if(head.next == slow) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
⑥合并两个链表
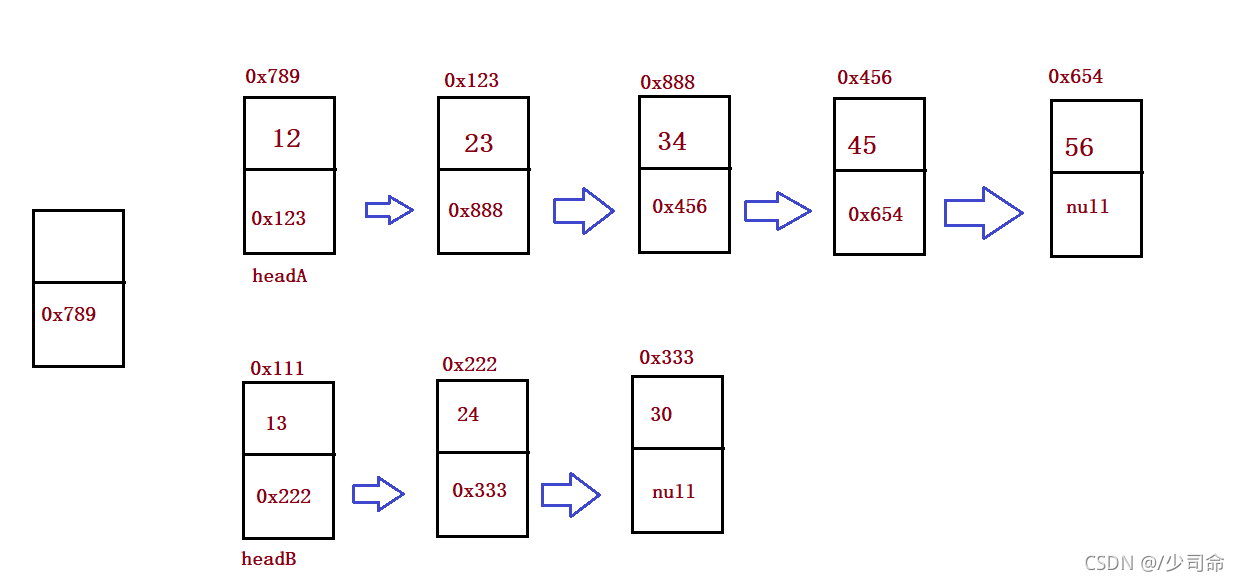

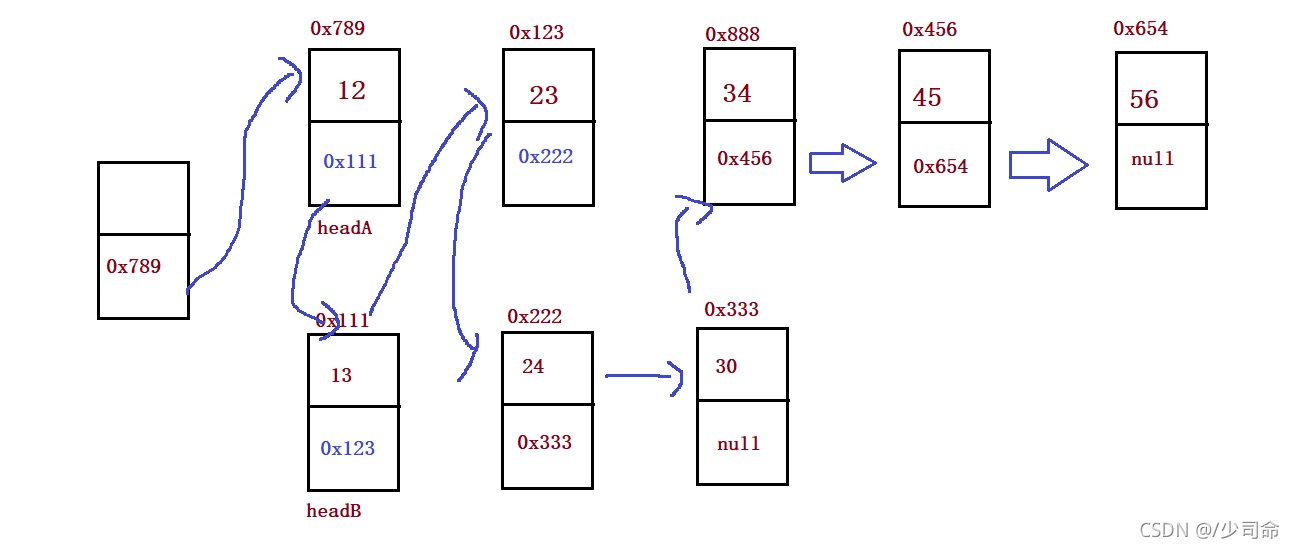
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while (headA != null && headB != null) {
if(headA.val < headB.val) {
tmp.next = headA;
headA = headA.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}else {
tmp.next = headB;
headB = headB.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
if(headA != null) {
tmp.next = headA;
}
if(headB != null) {
tmp.next = headB;
}
return newHead.next;
}
⑦输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
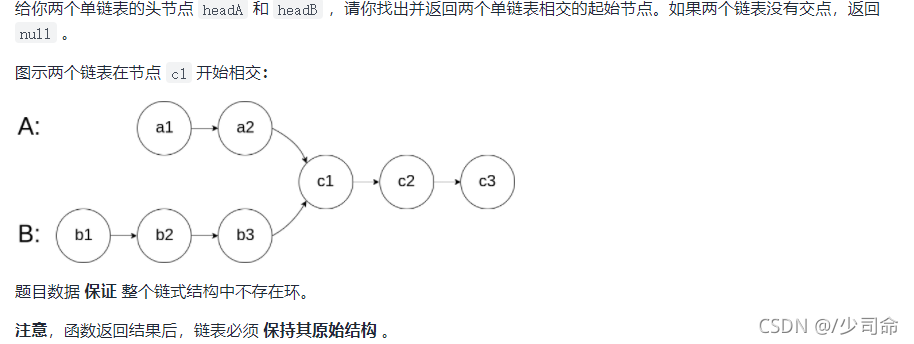

public static ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pl = headA;
ListNode ps = headB;
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
while (pl != null) {
lenA++;
pl = pl.next;
}
//pl==null
pl = headA;
while (ps != null) {
lenB++;
ps = ps.next;
}
//ps==null
ps = headB;
int len = lenA-lenB;//差值步
if(len < 0) {
pl = headB;
ps = headA;
len = lenB-lenA;
}
//1、pl永远指向了最长的链表 ps 永远指向了最短的链表 2、求到了差值len步
//pl走差值len步
while (len != 0) {
pl = pl.next;
len--;
}
//同时走 直到相遇
while (pl != ps) {
pl = pl.next;
ps = ps.next;
}
return pl;
}
⑧判断一个链表是否有环


public boolean hasCycle() {
if(head == null) return false;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
⑨求有环链表的环第一个结点
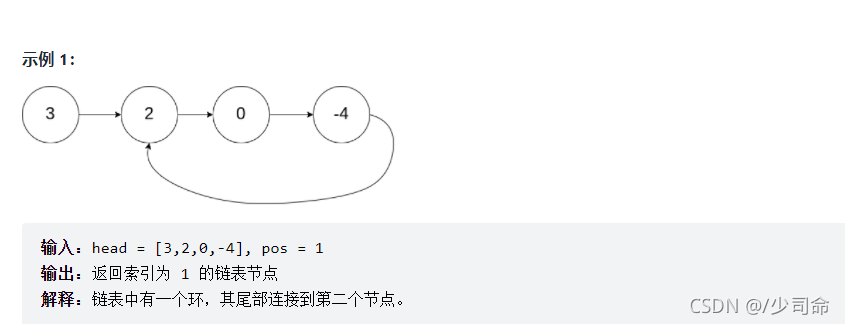


public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow) {
break;
}
}
if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null;
}
fast = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
三,栈和队列

1,栈
①概念
在我们软件应用 ,栈这种后进先出数据结构的应用是非常普遍的。比如你用浏 览器上网时不管什么浏览器都有 个"后退"键,你点击后可以接访问顺序的逆序加载浏览过的网页。
很多类似的软件,比如 Word Photoshop 等文档或图像编 软件中 都有撤销 )的操作,也是用栈这种方式来实现的,当然不同的软件具体实现会有很大差异,不过原理其实都是一样的
栈( stack )是限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除的线性表
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈 顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
②栈的操作
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶。

③栈的实现
入栈

public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
int ret = stack.push(4);
System.out.println(ret);
}

出栈
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
int ret1 = stack.pop();
int ret2 = stack.pop();
System.out.println(ret1);
System.out.println(ret2);
}

获取栈顶元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
int ret1 = stack.pop();
int ret2 = stack.pop();
int ret3 = stack.peek();
System.out.println(ret1);
System.out.println(ret2);
System.out.println(ret3);
}

判断栈是否为空

public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
int ret1 = stack.pop();
int ret2 = stack.pop();
int ret3 = stack.peek();
System.out.println(ret1);
System.out.println(ret2);
System.out.println(ret3);
stack.pop();
boolean flag = stack.empty();
System.out.println(flag);
}

④实现mystack
public class MyStack<T> {
private T[] elem;//数组
private int top;//当前可以存放数据元素的下标-》栈顶指针
public MyStack() {
this.elem = (T[])new Object[10];
}
/**
* 入栈操作
* @param item 入栈的元素
*/
public void push(T item) {
//1、判断当前栈是否是满的
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//2、elem[top] = item top++;
this.elem[this.top++] = item;
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.elem.length == this.top;
}
/**
* 出栈
* @return 出栈的元素
*/
public T pop() {
if(empty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("栈为空!");
}
T ret = this.elem[this.top-1];
this.top--;//真正的改变了top的值
return ret;
}
/**
* 得到栈顶元素,但是不删除
* @return
*/
public T peek() {
if(empty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("栈为空!");
}
//this.top--;//真正的改变了top的值
return this.elem[this.top-1];
}
public boolean empty(){
return this.top == 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack<Integer> myStack = new MyStack<>();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.push(3);
System.out.println(myStack.peek());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.pop());
System.out.println(myStack.empty());
System.out.println("============================");
MyStack<String> myStack2 = new MyStack<>();
myStack2.push("hello");
myStack2.push("word");
myStack2.push("thank");
System.out.println(myStack2.peek());
System.out.println(myStack2.pop());
System.out.println(myStack2.pop());
System.out.println(myStack2.pop());
System.out.println(myStack2.empty());
}

2,队列
①概念
像移动、联通、电信等客服电话,客服人员与客户相比总是少数,在所有的客服人员都占线的情况下,客户会被要求等待,直到有某个客服人员空下来,才能让最先等待的客户接通电话。这里也是将所有当前拨打客服电话的客户进行了排队处理。
操作系统和客服系统中,都是应用了种数据结构来实现刚才提到的先进先出的排队功能,这就是队列。
队列(queue) 是只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear) 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头 (Head/Front)
②队列的实现
入队
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
}
出队
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}

获取队首元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println("-----------------");
System.out.println(queue.peek());
}

③实现myqueue
class Node {
private int val;
private Node next;
public int getVal() {
return val;
}
public void setVal(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class MyQueue {
private Node first;
private Node last;
//入队
public void offer(int val) {
//尾插法 需要判断是不是第一次插入
Node node = new Node(val);
if(this.first == null) {
this.first = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
this.last.setNext(node);//last.next = node;
this.last = node;
}
}
//出队
public int poll() {
//1判断是否为空的
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("队列为空!");
}
//this.first = this.first.next;
int ret = this.first.getVal();
this.first = this.first.getNext();
return ret;
}
//得到队头元素但是不删除
public int peek() {
//不要移动first
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("队列为空!");
}
return this.first.getVal();
}
//队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.first == null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.offer(1);
myQueue.offer(2);
myQueue.offer(3);
System.out.println(myQueue.peek());
System.out.println(myQueue.poll());
System.out.println(myQueue.poll());
System.out.println(myQueue.poll());
System.out.println(myQueue.isEmpty());
}

四,二叉树
1,树
①概念

树是一种非线性的数据结构,它是由n(n>=0)个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。把它叫做树是因为它看 起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。它具有以下的特点:
有一个特殊的节点,称为根节点,根节点没有前驱节点
除根节点外,其余节点被分成M(M > 0)个互不相交的集合T1、T2、......、Tm,其中每一个集合 Ti (1 <= i <= m) 又是一棵与树类似的子树。每棵子树的根节点有且只有一个前驱,可以有0个或多个后继
树是递归定义的。
②树的基础概念
节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度
树的度:一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度
叶子节点或终端节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点
双亲节点或父节点:若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点
孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点
根结点:一棵树中,没有双亲结点的结点
节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推
树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次
2,二叉树
①概念
一棵二叉树是结点的一个有限集合,该集合或者为空,或者是由一个根节点加上两棵别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成。
二叉树的特点:
每个结点最多有两棵子树,即二叉树不存在度大于 2 的结点。
二叉树的子树有左右之分,其子树的次序不能颠倒,因此二叉树是有序树。
②两种特殊的二叉树
- 满二叉树: 一个二叉树,如果每一个层的结点数都达到最大值,则这个二叉树就是满二叉树。也就是说,如果 一个二叉树的层数为K,且结点总数是 ,则它就是满二叉树。

- 完全二叉树: 完全二叉树是效率很高的数据结构,完全二叉树是由满二叉树而引出来的。对于深度为K的,有n 个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为K的满二叉树中编号从1至n的结点一一对应时称之为完全 二叉树。 要注意的是满二叉树是一种特殊的完全二叉树。
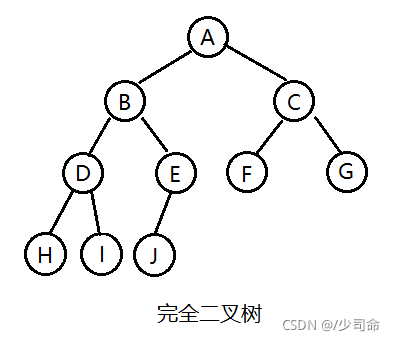
③二叉树的性质
若规定根节点的层数为1,则一棵非空二叉树的第i层上最多有2^(i-1) (i>0)个结点
若规定只有根节点的二叉树的深度为1,则深度为K的二叉树的最大结点数是2^k-1 (k>=0)
对任何一棵二叉树, 如果其叶结点个数为 n0, 度为2的非叶结点个数为 n2,则有n0=n2+1
具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度k为log2(n+1)上取整
3,二叉树遍历
①二叉树的遍历
所谓遍历(Traversal)是指沿着某条搜索路线,依次对树中每个结点均做一次且仅做一次访问。访问结点所做的操作 依赖于具体的应用问题(比如:打印节点内容、节点内容加1)。 遍历是二叉树上最重要的操作之一,是二叉树上进 行其它运算之基础。
在遍历二叉树时,如果没有进行某种约定,每个人都按照自己的方式遍历,得出的结果就比较混乱,如果按照某种 规则进行约定,则每个人对于同一棵树的遍历结果肯定是相同的。如果N代表根节点,L代表根节点的左子树,R代 表根节点的右子树,则根据遍历根节点的先后次序有以下遍历方式:
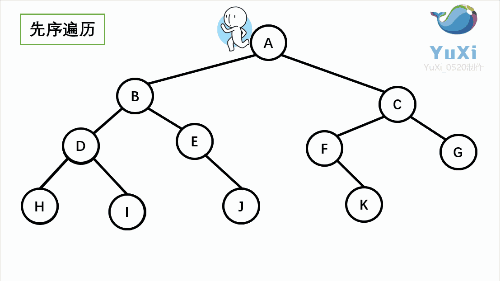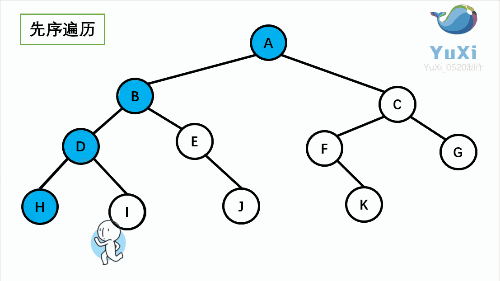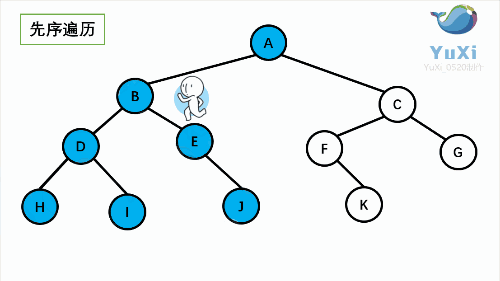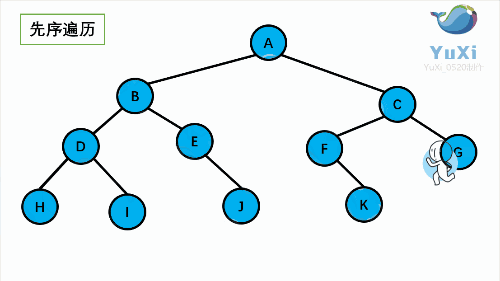
- NLR:**前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历)**——访问根结点--->根的左子树--->根的右子树。
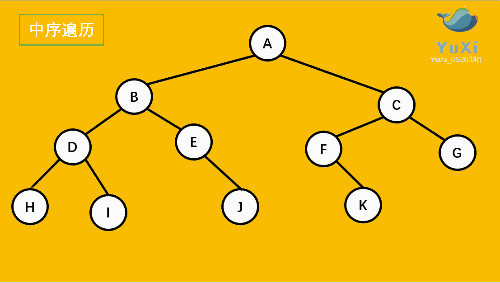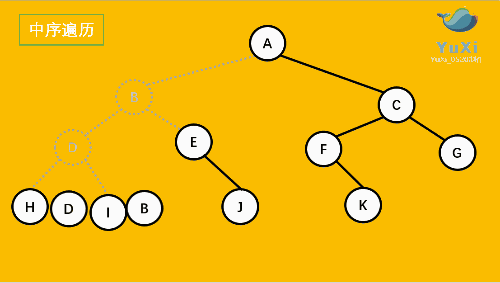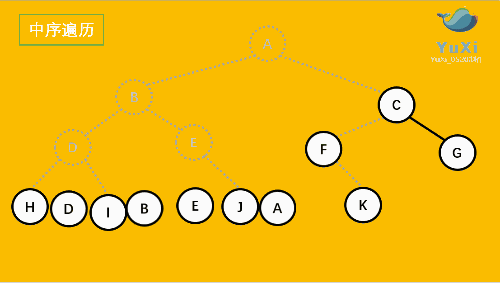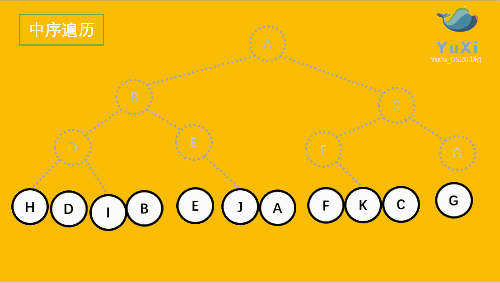
- LNR:**中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)**——根的左子树--->根节点--->根的右子树。
- LRN:**后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)**——根的左子树--->根的右子树--->根节点。
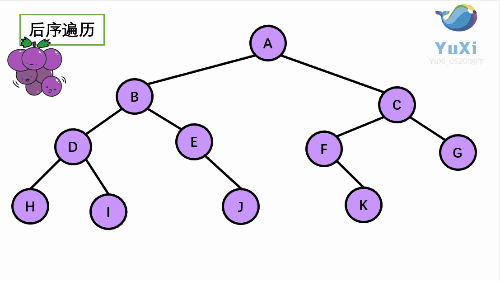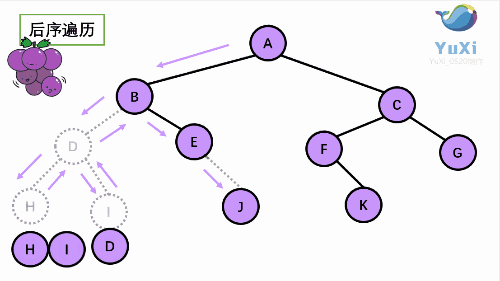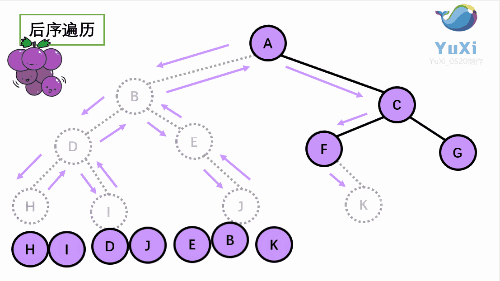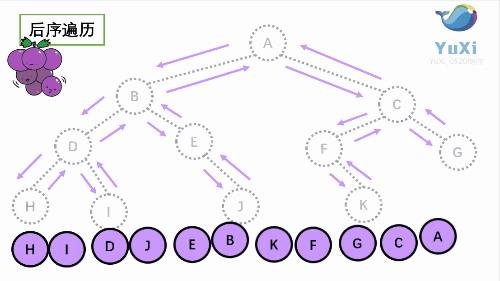
由于被访问的结点必是某子树的根,所以N(Node)、L(Left subtree)和R(Right subtree)又可解释为根、根 的左子树和根的右子树。NLR、LNR和LRN分别又称为先根遍历、中根遍历和后根遍历。
注意:三种遍历中只有访问根节点打印,每一种遍历当访问到每一个节点都要有对应三种不同的遍历方式,直到遍历到null返回到该根节点继续完成遍历!!!比如说前序遍历,我每访问一个节点都要执行问根结点--->根的左子树--->根的右子树这三步,中序后序遍历一样。
以下面这个二叉树为例,接下来就是详解
②前序遍历
图解
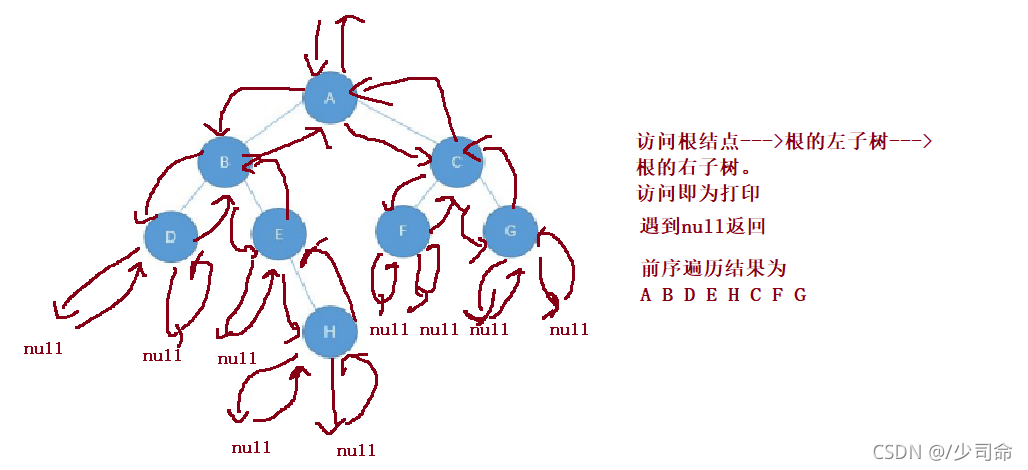
代码分析
我们用枚举法创建这个二叉树
public TreeNode createTree() {
TreeNode A = new TreeNode('A');
TreeNode B = new TreeNode('B');
TreeNode C = new TreeNode('C');
TreeNode D = new TreeNode('D');
TreeNode E = new TreeNode('E');
TreeNode F = new TreeNode('F');
TreeNode G = new TreeNode('G');
TreeNode H = new TreeNode('H');
A.left = B;
A.right = C;
B.left = D;
B.right = E;
C.left = F;
C.right = G;
E.right = H;
return A;
}
// 前序遍历
void preOrderTraversal(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
preOrderTraversal(root.left);
preOrderTraversal(root.right);
}


DeBug分析
 ③中序遍历
③中序遍历
图解
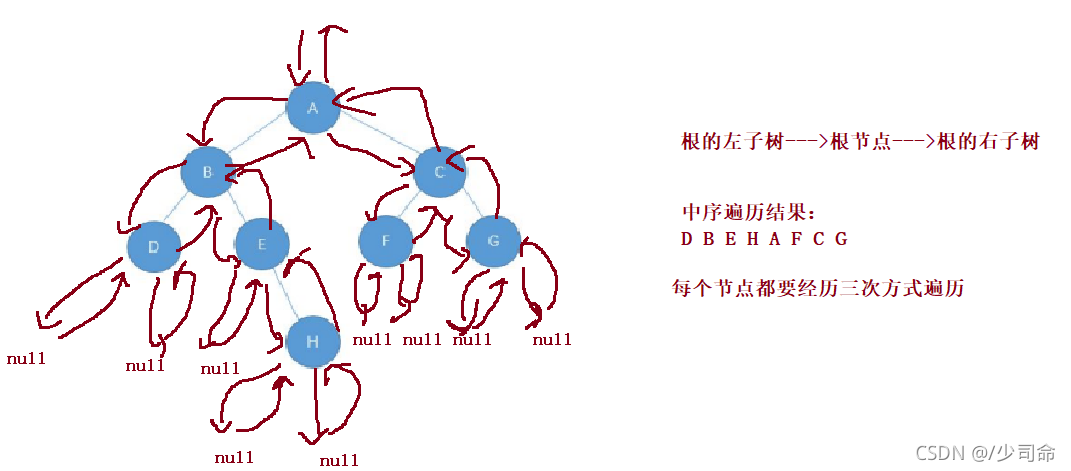
// 中序遍历
void inOrderTraversal(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
inOrderTraversal(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inOrderTraversal(root.right);
}

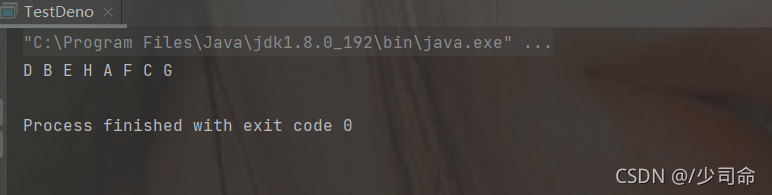
DeBug分析

④后序遍历
图解
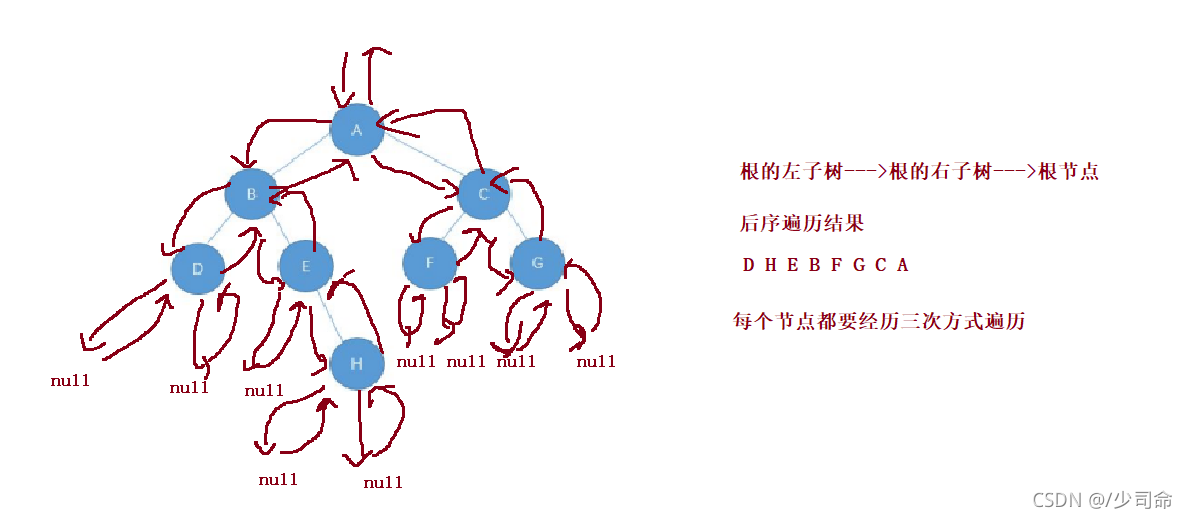
// 后序遍历
void postOrderTraversal(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
postOrderTraversal(root.left);
postOrderTraversal(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
}


DeBug分析

3,二叉搜索树
①概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树**,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树

②操作-查找
二叉搜索树的查找类似于二分法查找

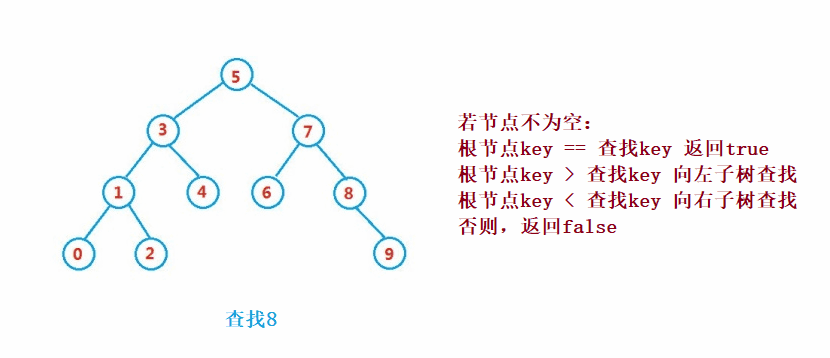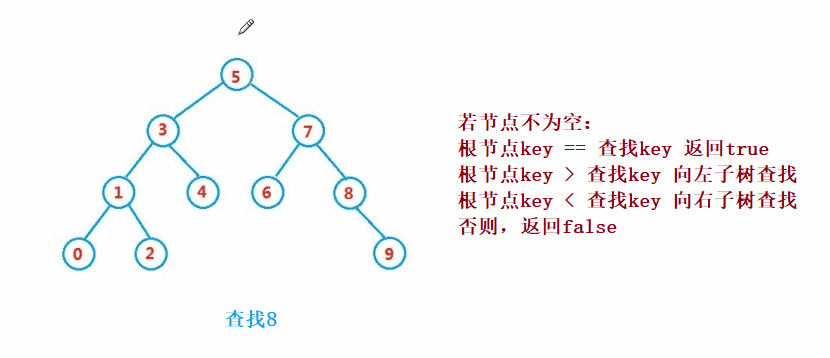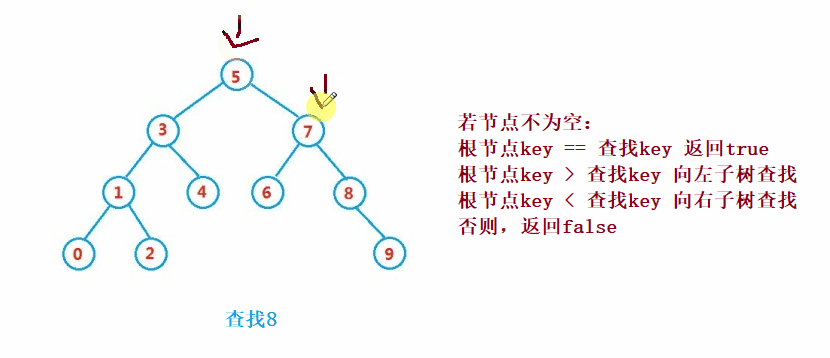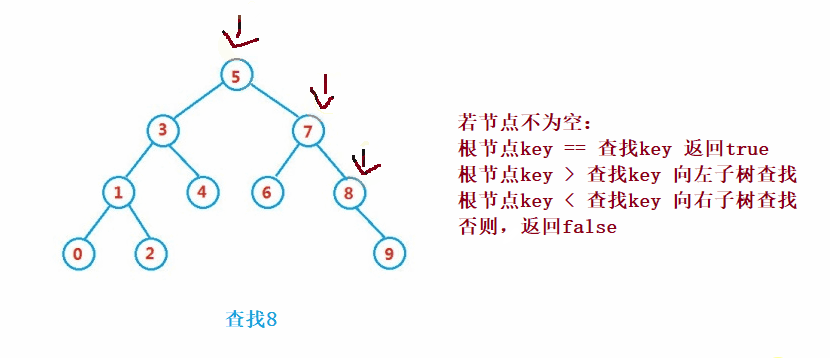

public Node search(int key) {
Node cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return cur;
}else if(cur.val < key) {
cur = cur.right;
}else {
cur = cur.left;
}
}
return null;
}
③操作-插入



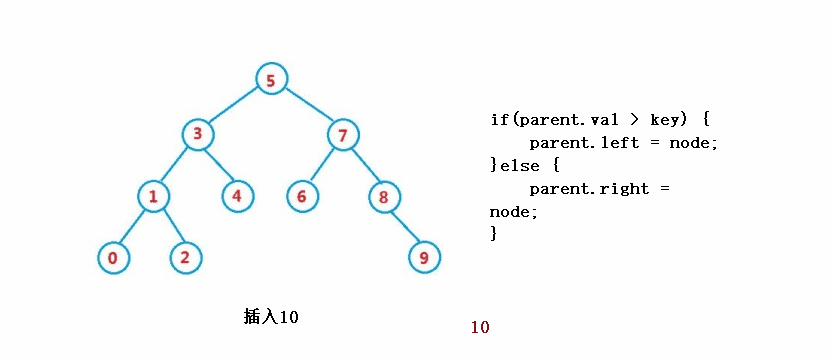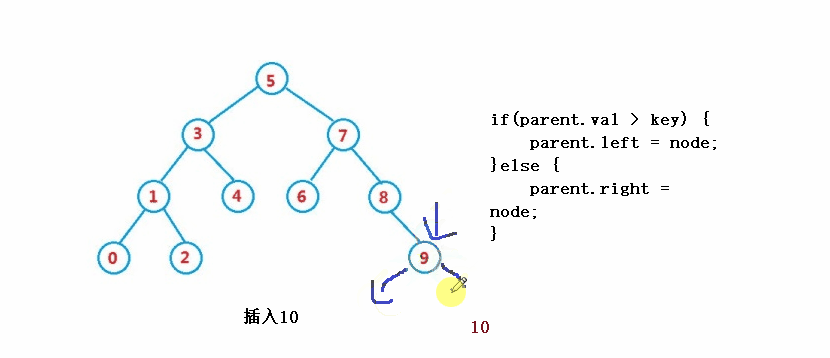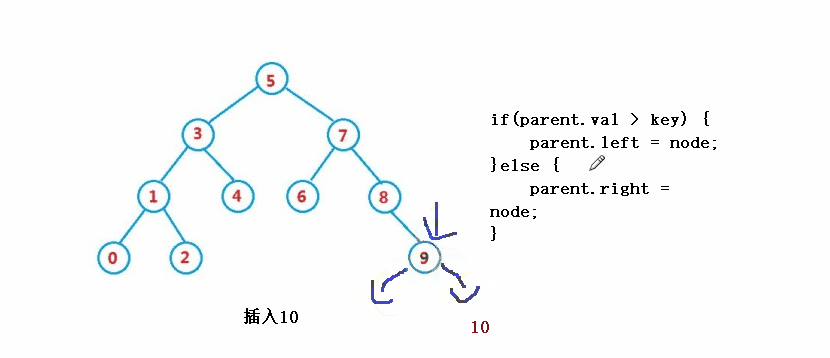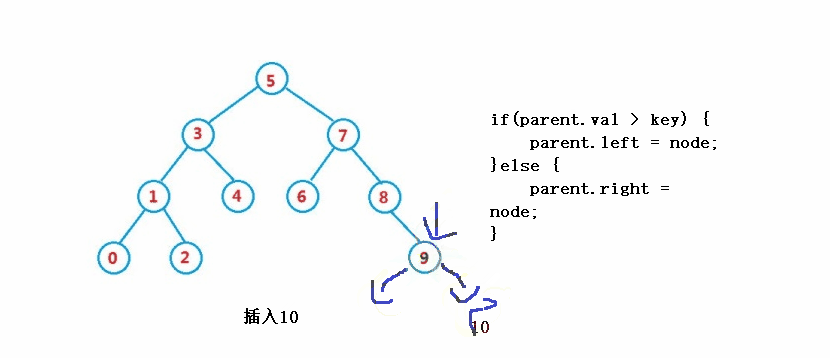
public boolean insert(int key) {
Node node = new Node(key);
if(root == null) {
root = node;
return true;
}
Node cur = root;
Node parent = null;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
return false;
}else if(cur.val < key) {
parent = cur;
cur = cur.right;
}else {
parent = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}
}
//parent
if(parent.val > key) {
parent.left = node;
}else {
parent.right = node;
}
return true;
}
④操作-删除
删除操作较为复杂,但理解了其原理还是比较容易
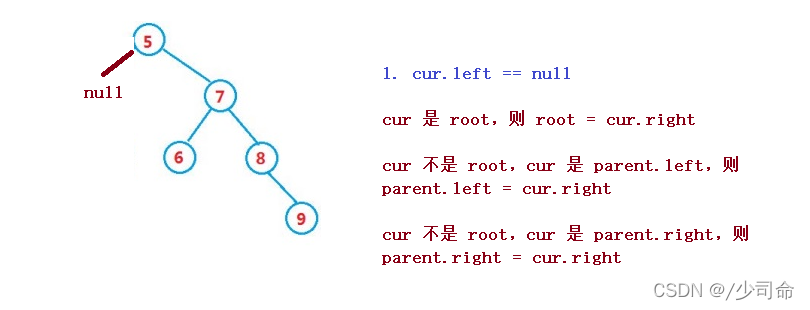
设待删除结点为 cur, 待删除结点的双亲结点为 parent
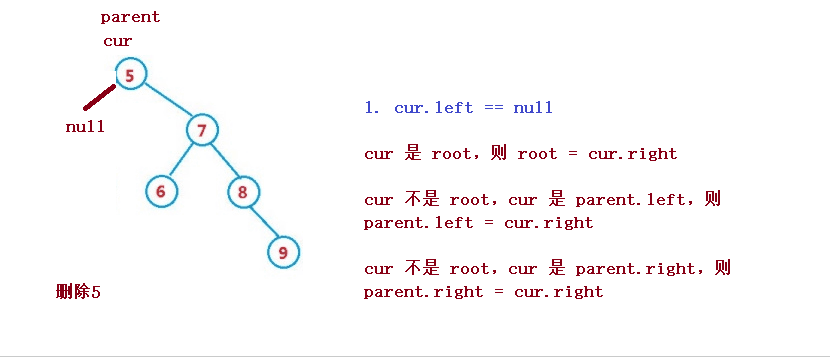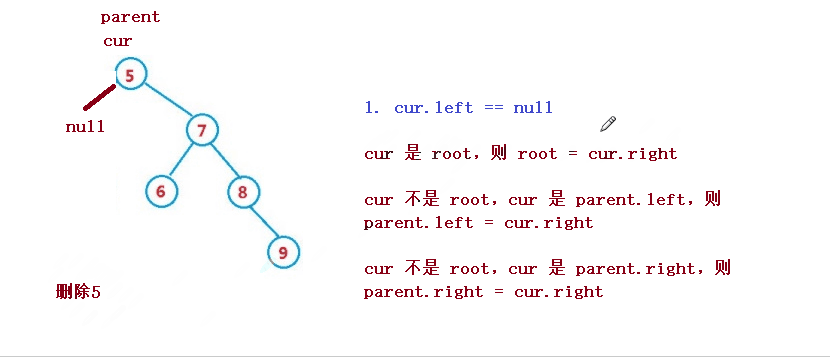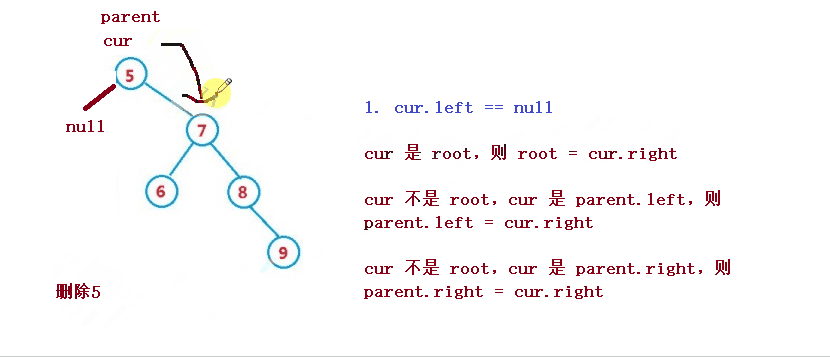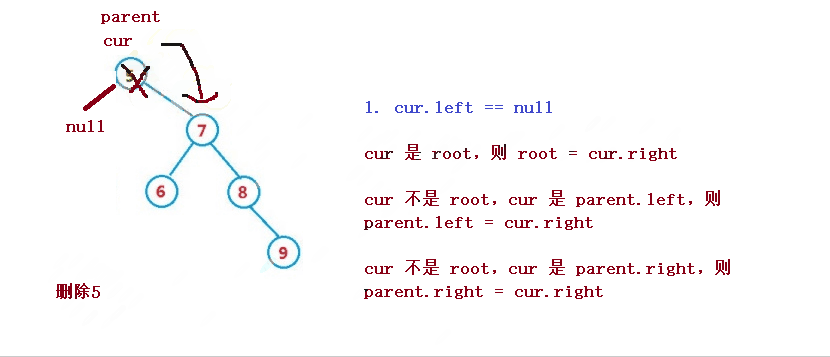
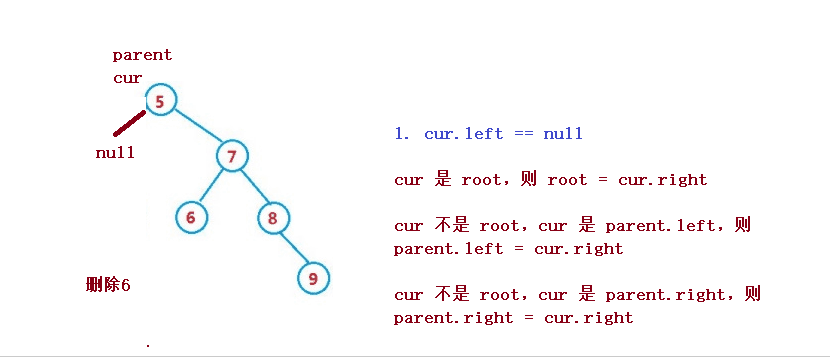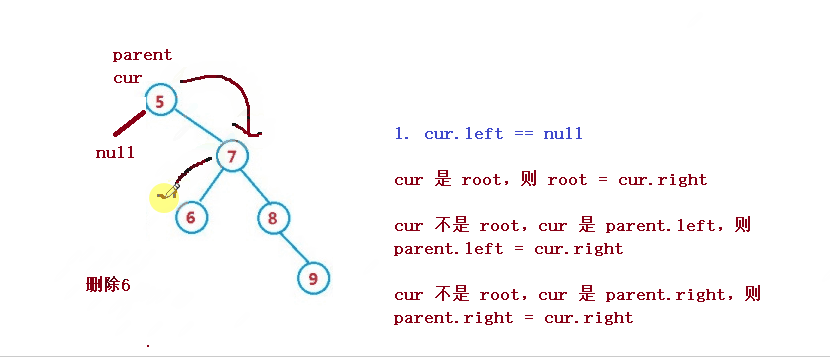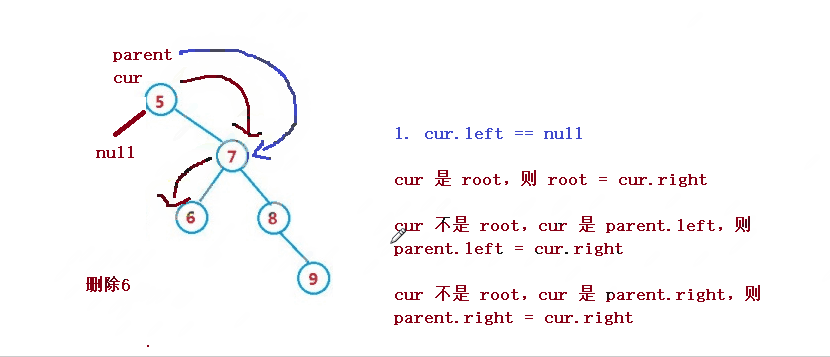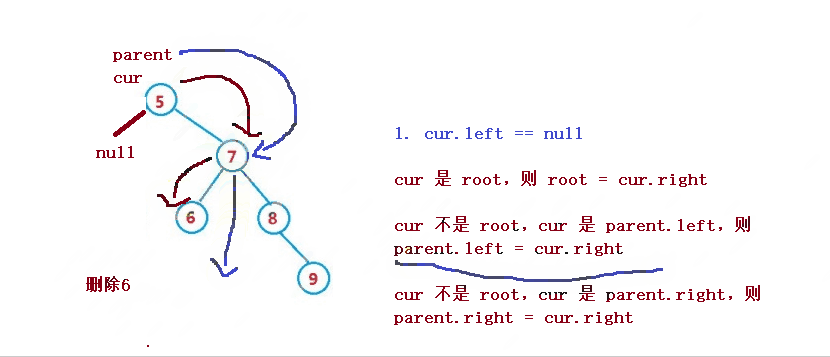
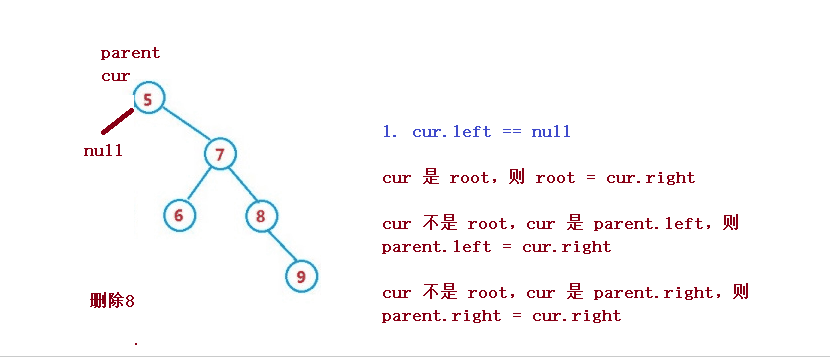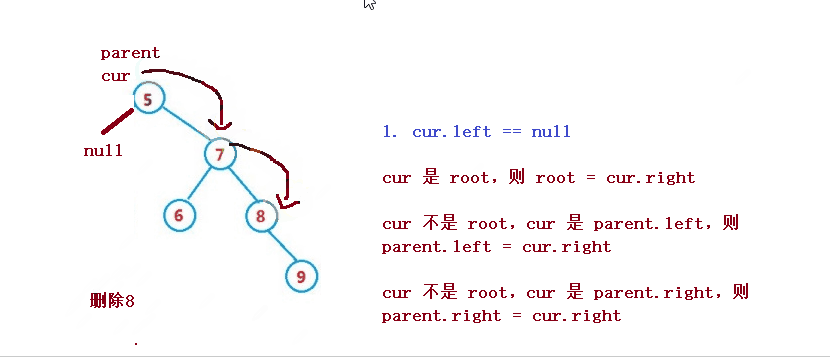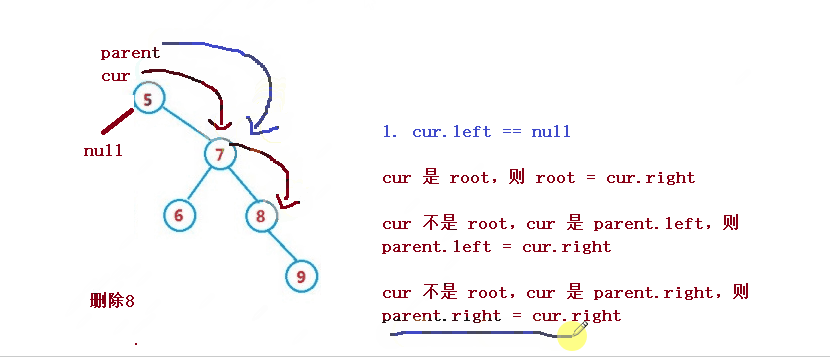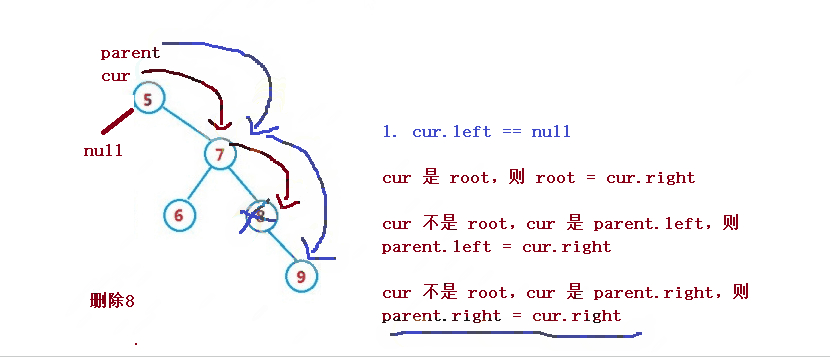
1. cur.left == null
cur 是 root,则 root = cur.right
cur 不是 root,cur 是 parent.left,则 parent.left = cur.right
cur 不是 root,cur 是 parent.right,则 parent.right = cur.right
2. cur.right == null
cur 是 root,则 root = cur.left
cur 不是 root,cur 是 parent.left,则 parent.left = cur.left
cur 不是 root,cur 是 parent.right,则 parent.right = cur.left
第二种情况和第一种情况相同,只是方向相反,这里不再画图
3. cur.left != null && cur.right != null
需要使用替换法进行删除,即在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点中,再来处理该结点的删除问题
当我们在左右子树都不为空的情况下进行删除,删除该节点会破坏树的结构,因此用替罪羊的方法来解决,实际删除的过程还是上面的两种情况,这里还是用到了搜索二叉树的性质


public void remove(Node parent,Node cur) {
if(cur.left == null) {
if(cur == root) {
root = cur.right;
}else if(cur == parent.left) {
parent.left = cur.right;
}else {
parent.right = cur.right;
}
}else if(cur.right == null) {
if(cur == root) {
root = cur.left;
}else if(cur == parent.left) {
parent.left = cur.left;
}else {
parent.right = cur.left;
}
}else {
Node targetParent = cur;
Node target = cur.right;
while (target.left != null) {
targetParent = target;
target = target.left;
}
cur.val = target.val;
if(target == targetParent.left) {
targetParent.left = target.right;
}else {
targetParent.right = target.right;
}
}
}
public void removeKey(int key) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
Node cur = root;
Node parent = null;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.val == key) {
remove(parent,cur);
return;
}else if(cur.val < key){
parent = cur;
cur = cur.right;
}else {
parent = cur;
cur = cur.left;
}
}
}
⑤性能分析
插入和删除操作都必须先查找,查找效率代表了二叉搜索树中各个操作的性能。
对有n个结点的二叉搜索树,若每个元素查找的概率相等,则二叉搜索树平均查找长度是结点在二叉搜索树的深度 的函数,即结点越深,则比较次数越多。
但对于同一个关键码集合,如果各关键码插入的次序不同,可能得到不同结构的二叉搜索树
最优情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树,其平均比较次数为:
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支树,其平均比较次数为:
4,笔试习题
①二叉树前序遍历
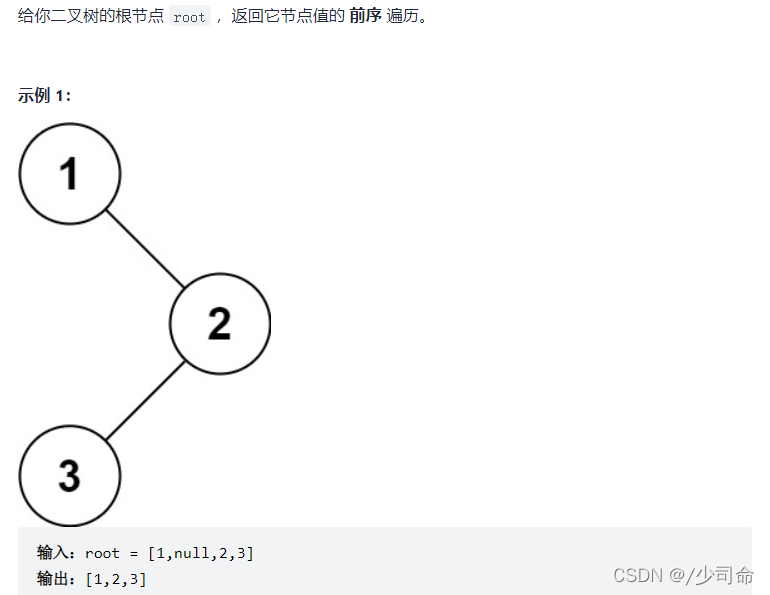

void preOrderTraversal(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
preOrderTraversal(root.left);
preOrderTraversal(root.right);
}
②二叉树中序遍历
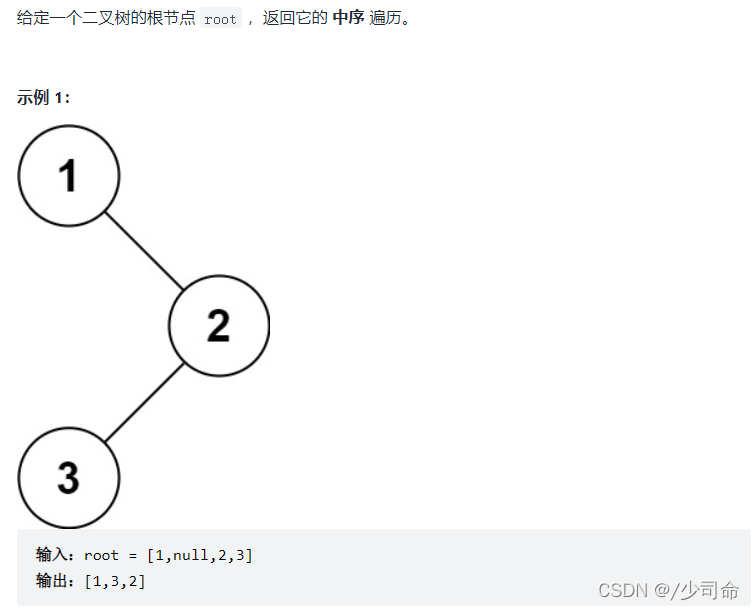

void inOrderTraversal(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
inOrderTraversal(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inOrderTraversal(root.right);
}
③二叉树后序遍历
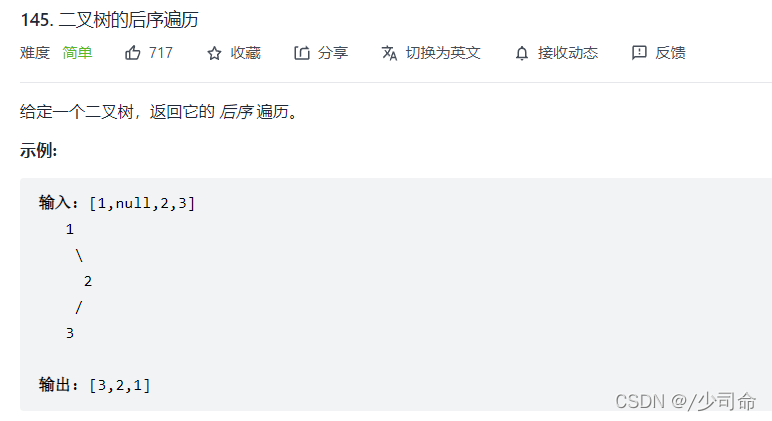

void postOrderTraversal(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
postOrderTraversal(root.left);
postOrderTraversal(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
}
④检查两棵树是否相同
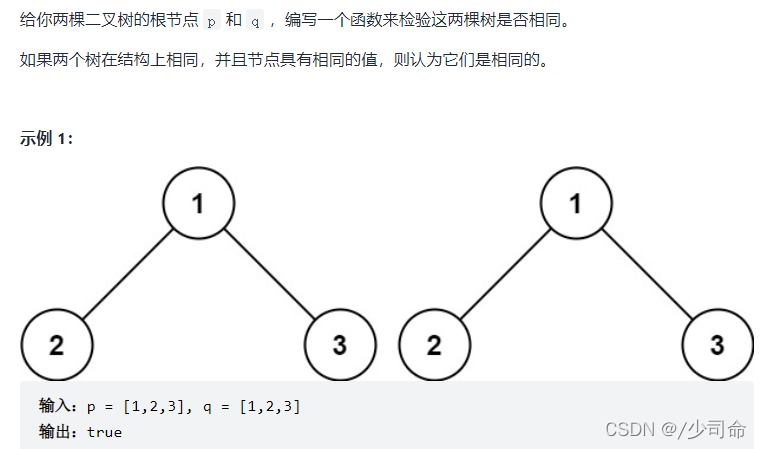
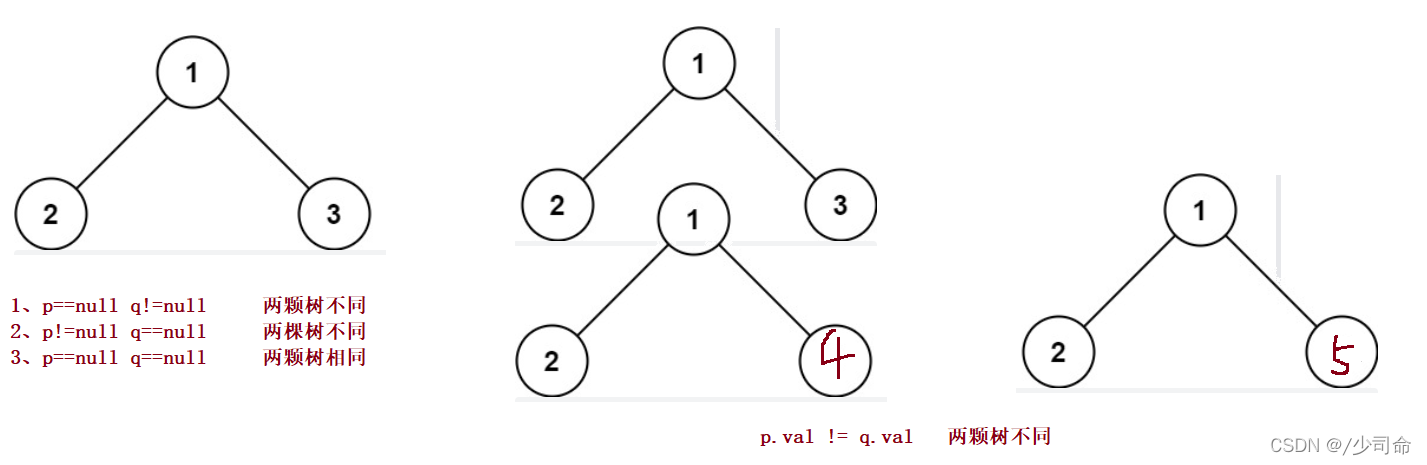

public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p == null && q != null){
return false;
}
if(p != null && q == null){
return false;
}
if(p == null && q ==null){
return true;
}
if(p.val != q.val){
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
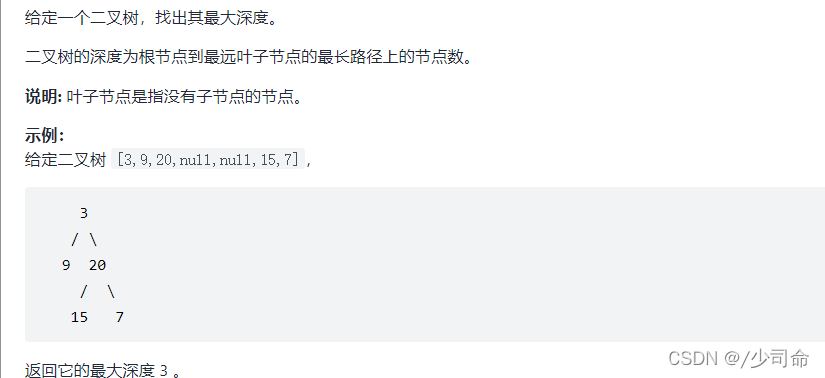
⑤二叉树的最大深度

public int maxDepth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.abs(leftHeight-rightHeight > 0? leftHeight + 1: rightHeight + 1);
}
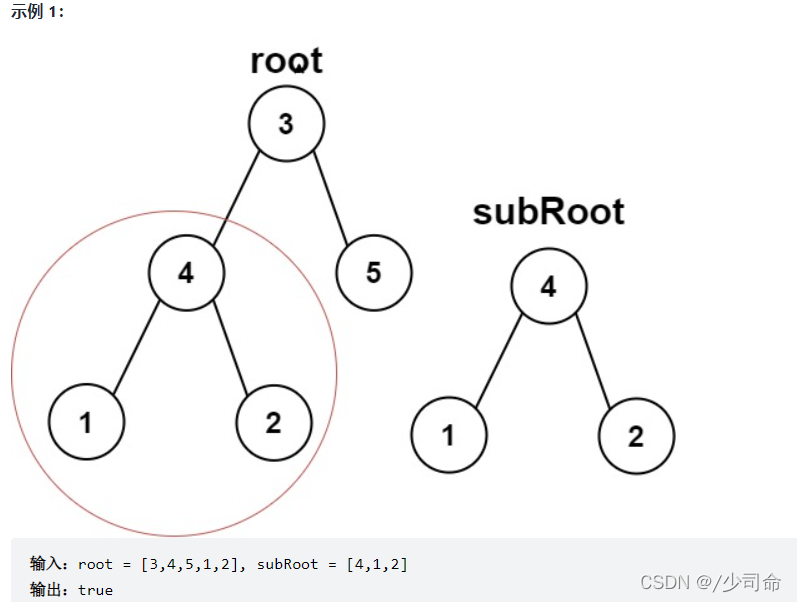
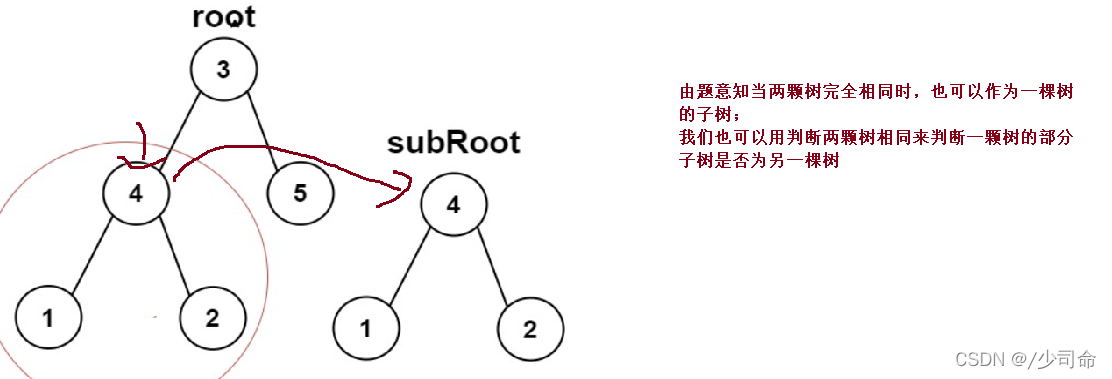
⑥另一颗树的子树
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p == null && q != null){
return false;
}
if(p != null && q == null){
return false;
}
if(p == null && q ==null){
return true;
}
if(p.val != q.val){
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode suBroot){
if(root == null && suBroot == null){
return true;
}
if(isSameTree(root,suBroot)){
return true;
}
if(isSubtree(root.right,suBroot)){
return true;
}
if(isSubtree(root.left,suBroot)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
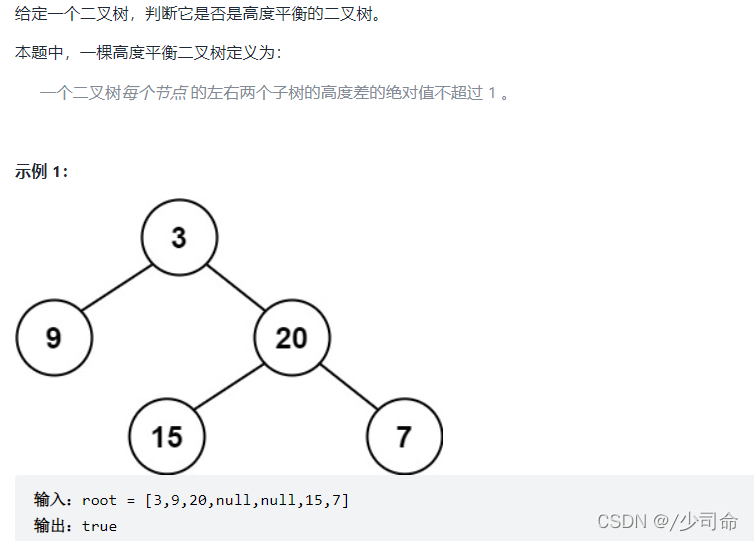
⑦判断一颗树是否为一颗平衡二叉树
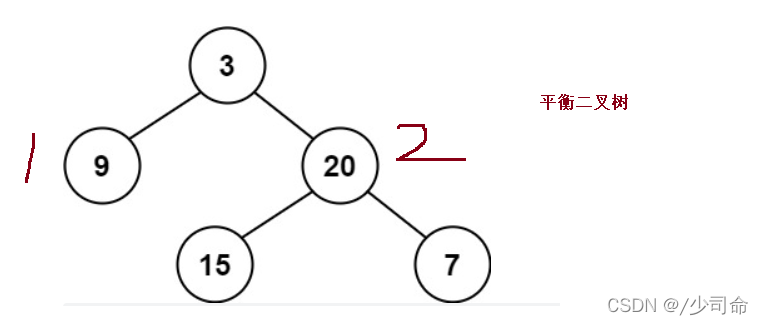
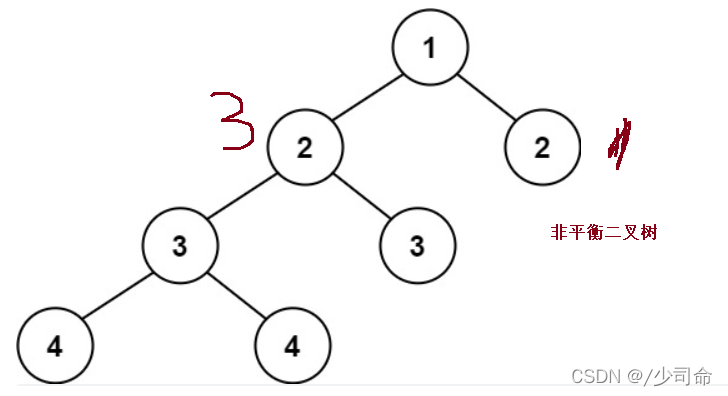
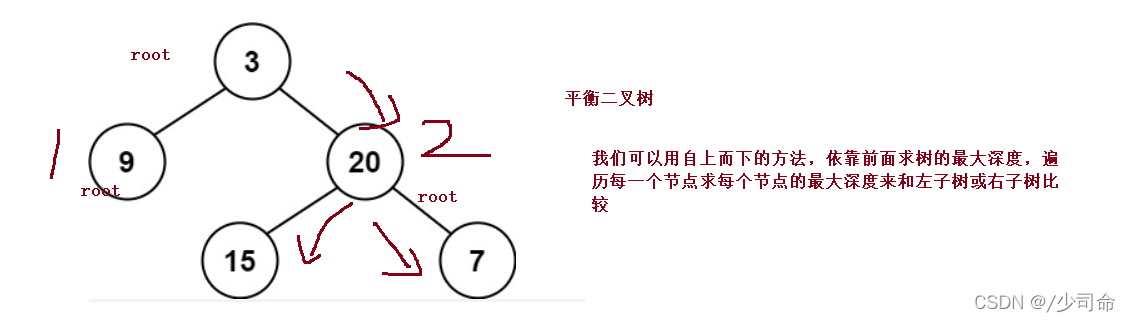
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.abs(leftHeight-rightHeight > 0? leftHeight + 1: rightHeight + 1);
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return
Math.abs(leftHeight-rightHeight) < 2 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}

public int hight(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = hight(root.left);
int rightHeight = hight(root.right);
if(leftHeight >= 0 && rightHeight >= 0 && Math.abs(leftHeight-rightHeight) <= 1){
return Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight)+1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isBalanced2(TreeNode root) {
return hight(root) >= 0;
}
⑧对称二叉树
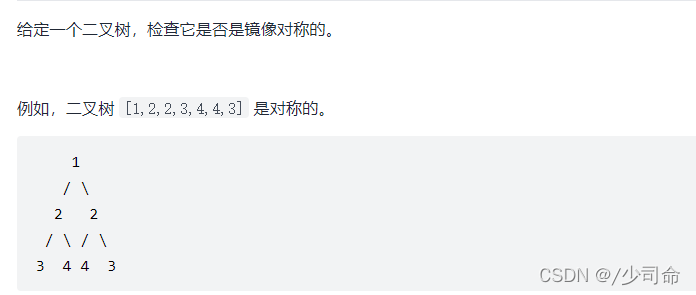


public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode leftTree,TreeNode rightTree){
if(leftTree != null && rightTree == null){
return false;
}
if(leftTree == null && rightTree != null){
return false;
}
if(leftTree == null && rightTree == null){
return true;
}
if(leftTree.val != rightTree.val){
return false;
}
return isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left,rightTree.right) &&
isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left,rightTree.right);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);
}
⑨二叉树镜像
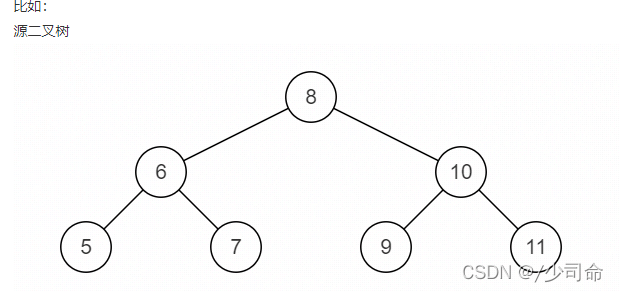
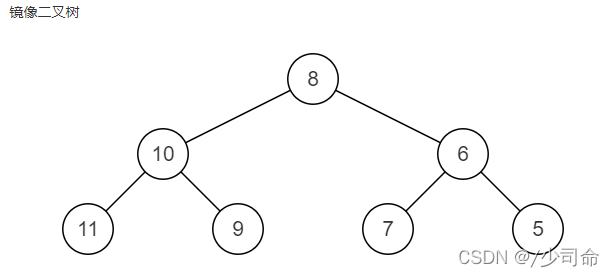

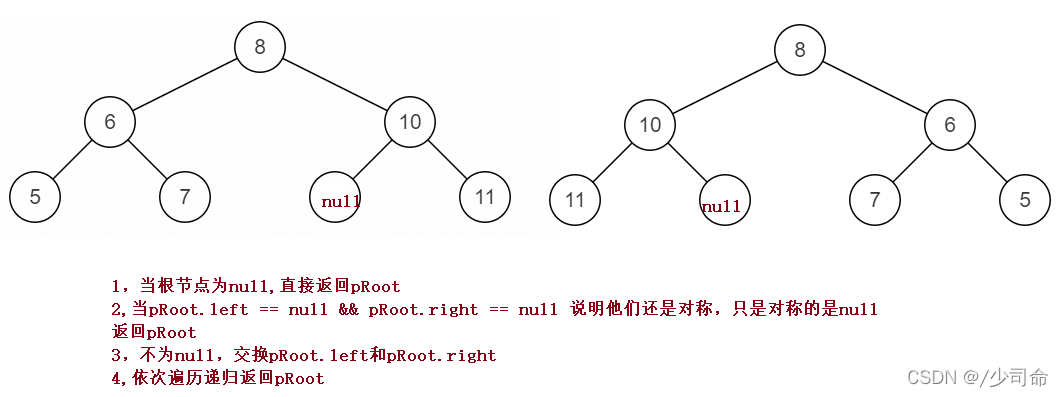
public TreeNode Mirror(TreeNode pRoot){
if(pRoot == null){
return pRoot;
}
if(pRoot.left == null && pRoot.right == null){
return pRoot;
}
TreeNode tmp = pRoot.left;
pRoot.left = pRoot.right;
pRoot.right = tmp;
if(pRoot.left != null){
Mirror(pRoot.left);
return pRoot;
}
if(pRoot.right != null){
Mirror(pRoot.right);
return pRoot;
}
return pRoot;
}
五,优先级队列(堆)
1,二叉树的顺序存储
①存储方式
使用数组保存二叉树结构,方式即将二叉树用层序遍历方式放入数组中。 一般只适合表示完全二叉树,因为非完全二叉树会有空间的浪费。 这种方式的主要用法就是堆的表示。
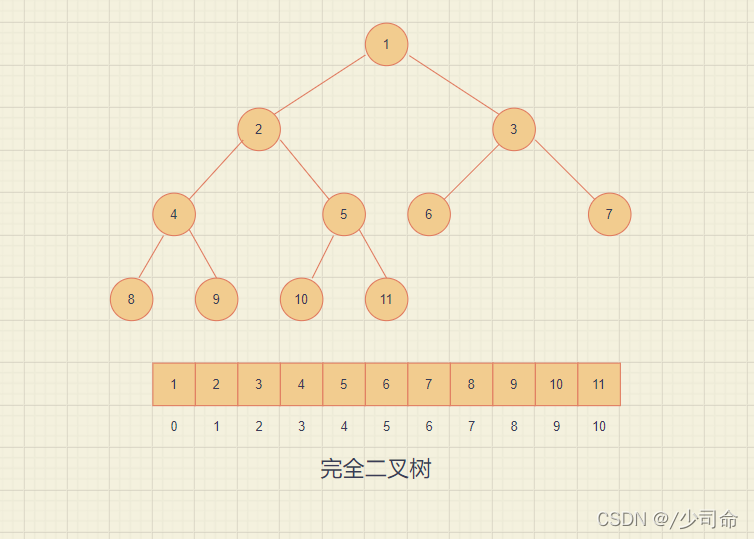
②下标关系
已知双亲(parent)的下标,则:
左孩子(left)下标 = 2 * parent + 1;
右孩子(right)下标 = 2 * parent + 2;
已知孩子(不区分左右)(child)下标,则:
双亲(parent)下标 = (child - 1) / 2;
③二叉树顺序遍历
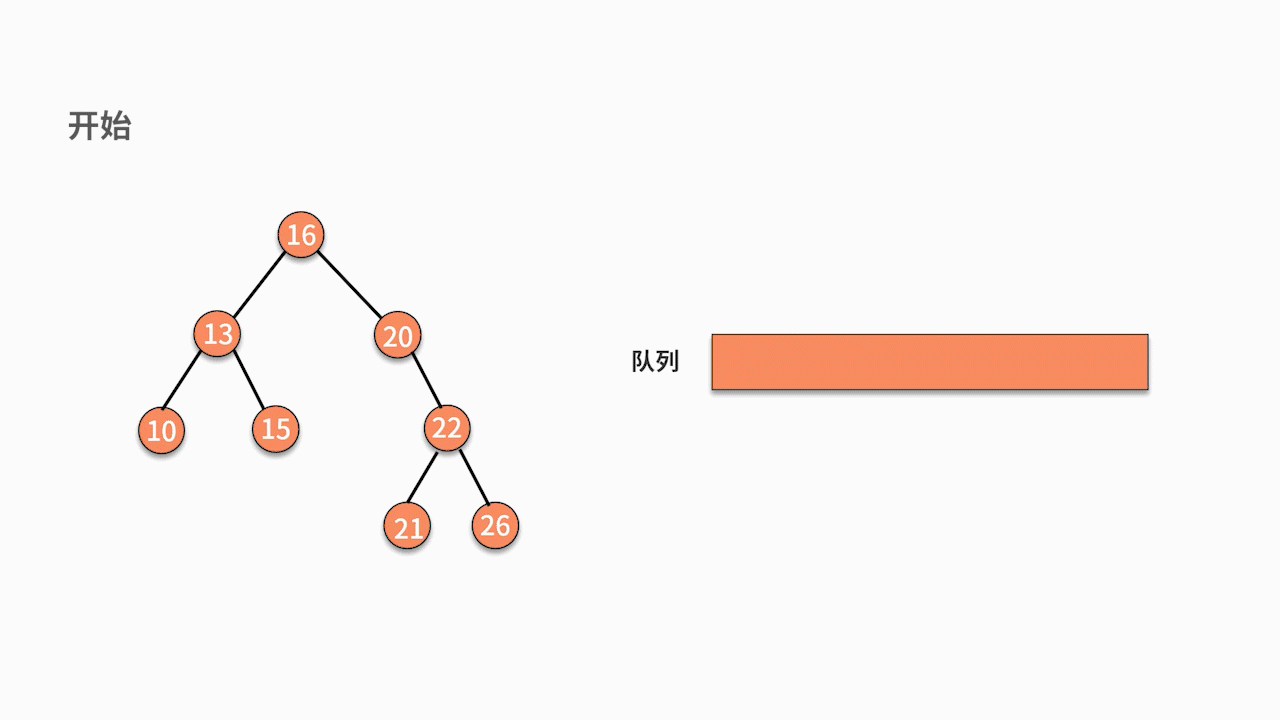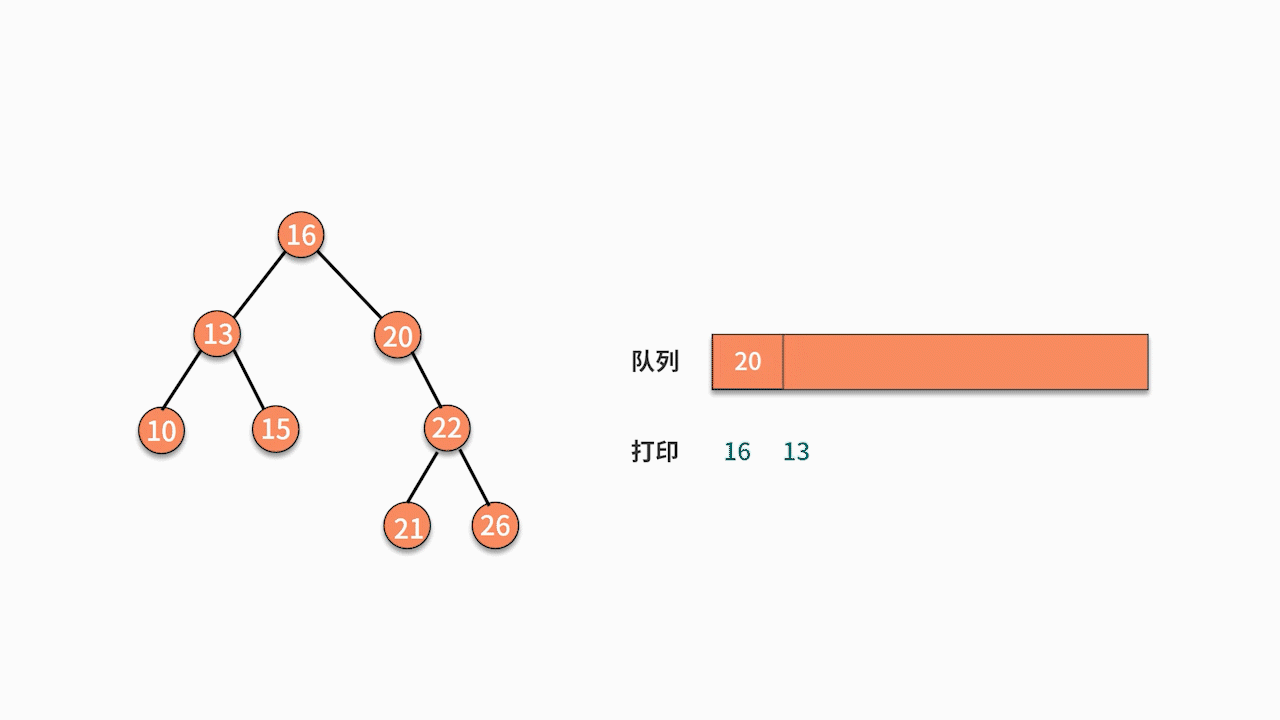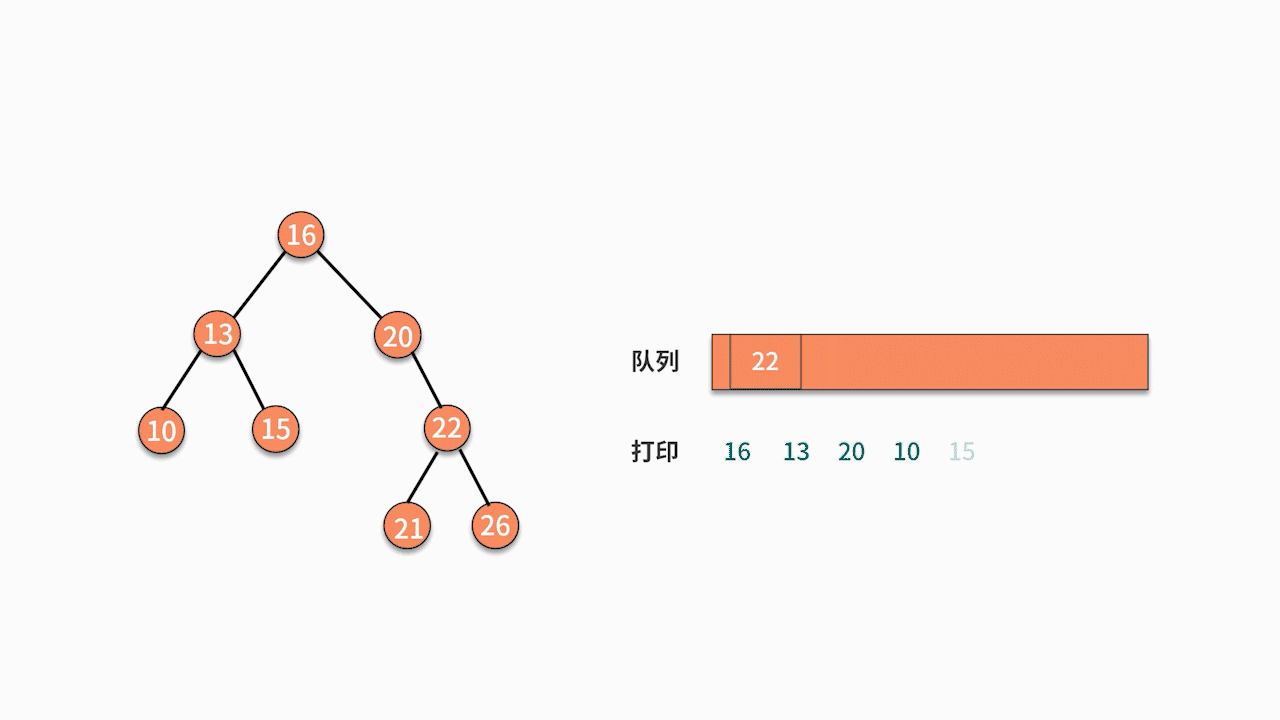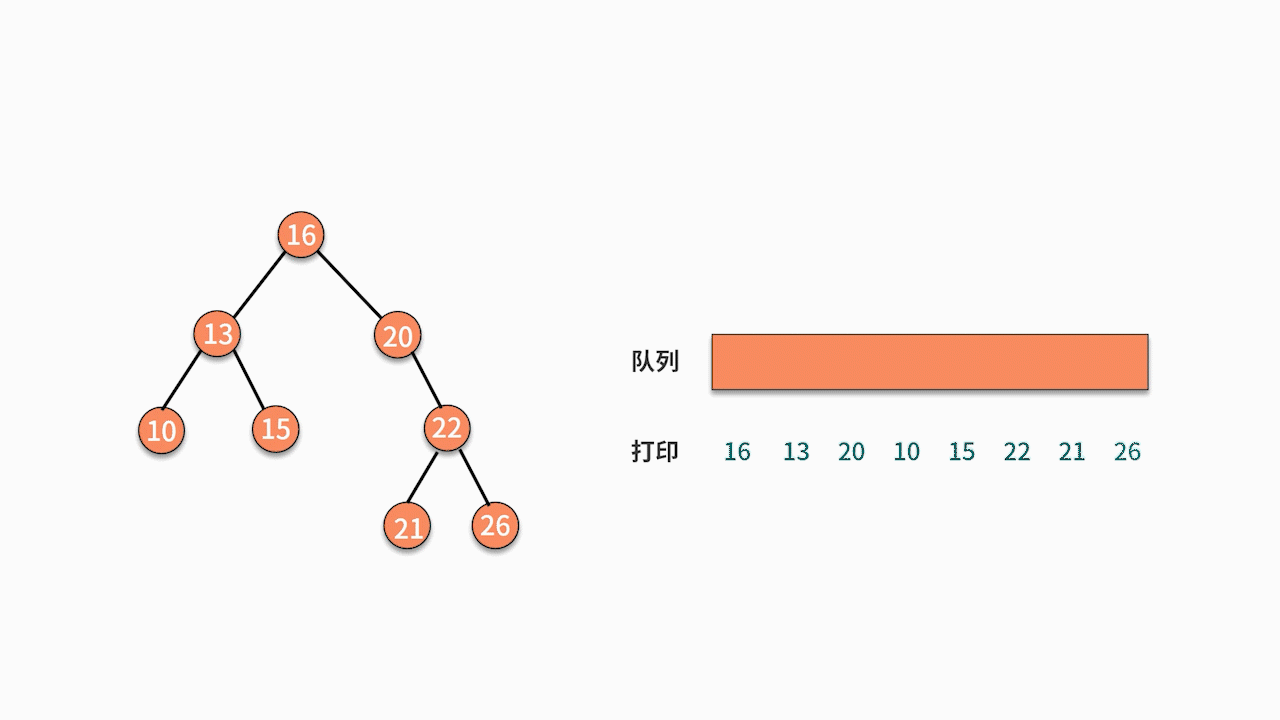
// 层序遍历
void levelOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
System.out.print(top.val+" ");
if(top.left != null) {
queue.offer(top.left);
}
if(top.right!=null) {
queue.offer(top.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
2,堆
①概念
堆逻辑上是一棵完全二叉树
堆物理上是保存在数组中
满足任意结点的值都大于其子树中结点的值,叫做大堆,或者大根堆,或者最大堆
反之,则是小堆,或者小根堆,或者最小堆
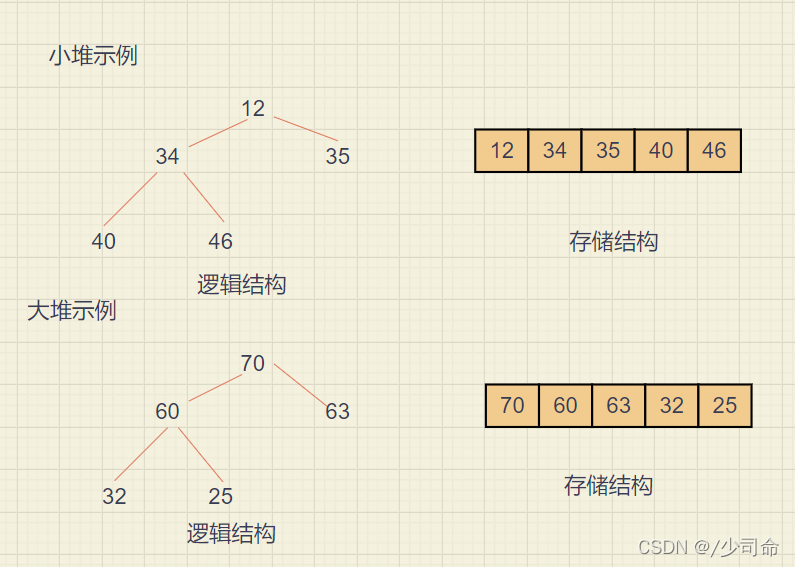
②操作-向下调整
前提:
左右子树必须已经是一个堆,才能调整。
说明:
array 代表存储堆的数组
size 代表数组中被视为堆数据的个数
index 代表要调整位置的下标
left 代表 index 左孩子下标
right 代表 index 右孩子下标
min 代表 index 的最小值孩子的下标
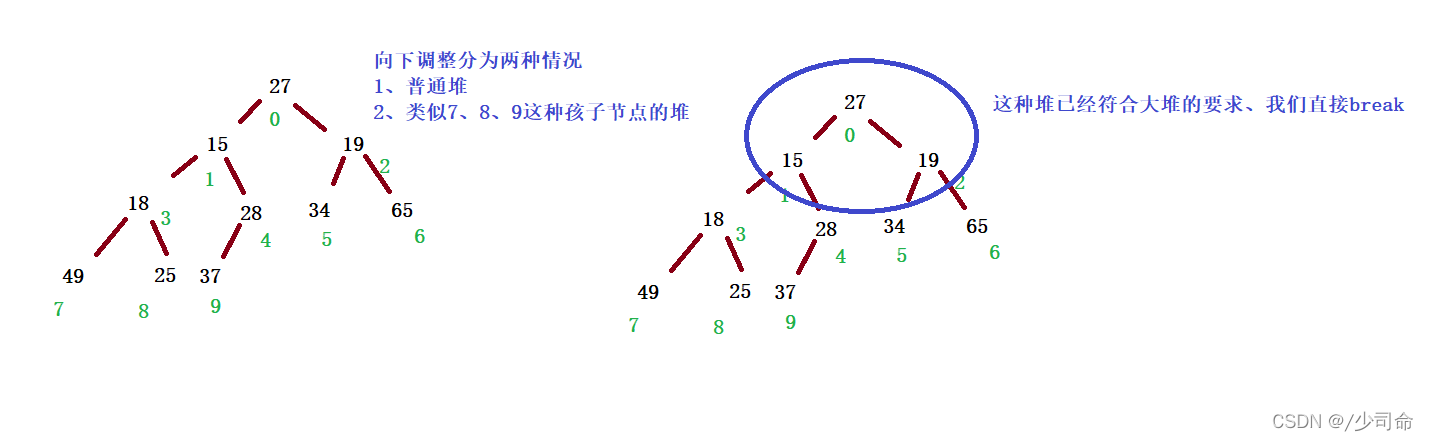
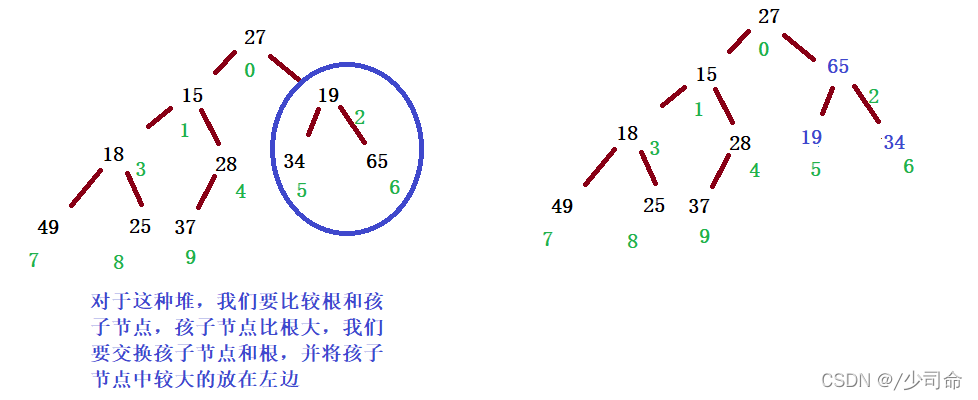
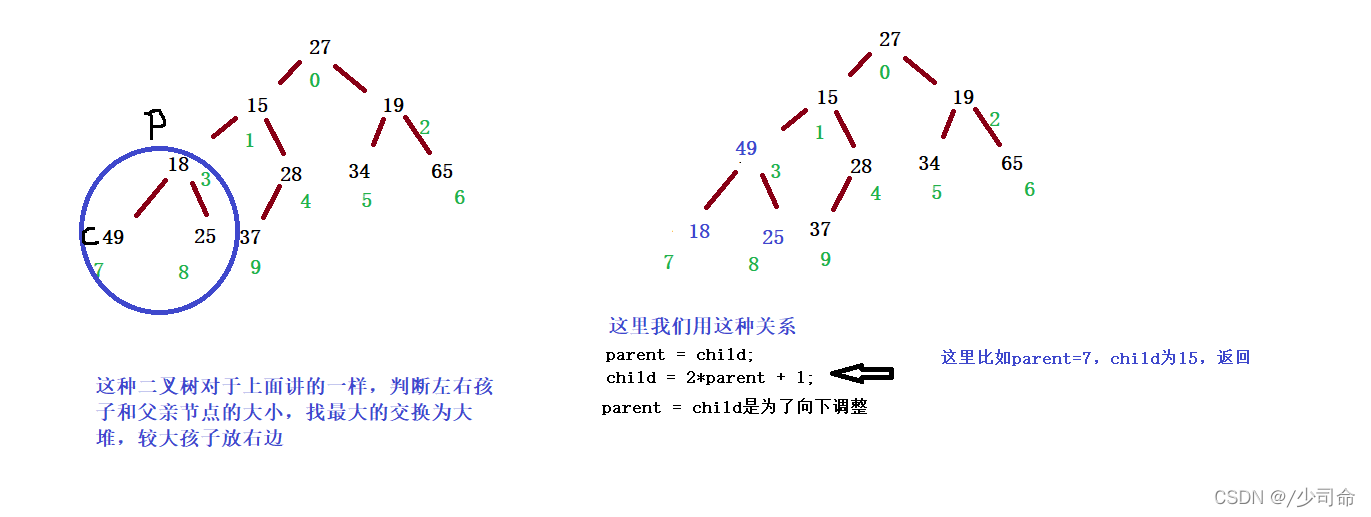
过程(以小堆为例):
Ⅰ index 如果已经是叶子结点,则整个调整过程结束
判断 index 位置有没有孩子
因为堆是完全二叉树,没有左孩子就一定没有右孩子,所以判断是否有左孩子
因为堆的存储结构是数组,所以判断是否有左孩子即判断左孩子下标是否越界,即 left >= size 越界
Ⅱ 确定 left 或 right,谁是 index 的最小孩子 min
如果右孩子不存在,则 min = left
否则,比较 array[left] 和 array[right] 值得大小,选择小的为 min
Ⅲ比较 array[index] 的值 和 array[min] 的值,如果 array[index] <= array[min],则满足堆的性质,调整结束
Ⅳ否则,交换 array[index] 和 array[min] 的值
Ⅴ然后因为 min 位置的堆的性质可能被破坏,所以把 min 视作 index,向下重复以上过程
向下调整是以层序遍历的二叉树为例来遍历
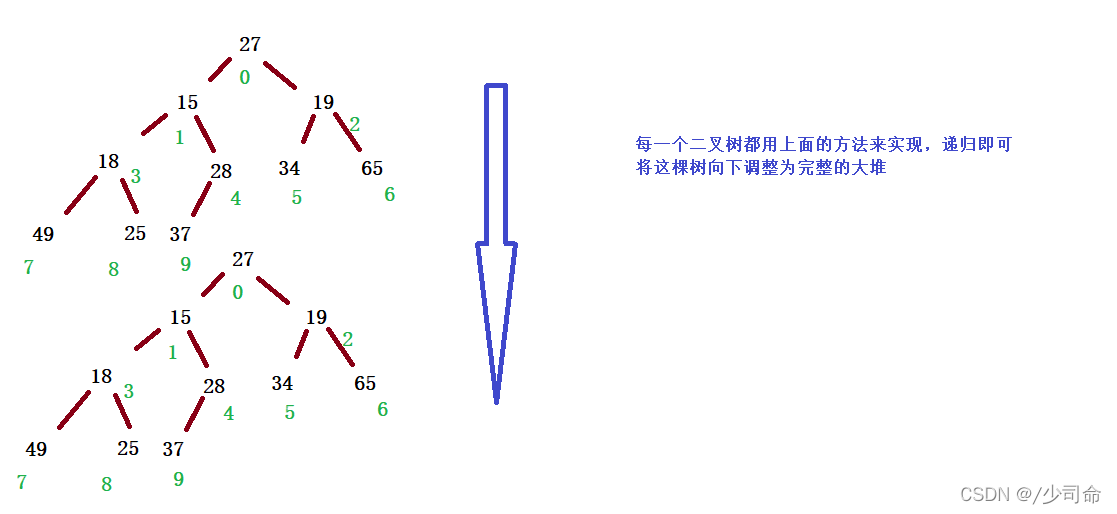
public void adjustDown(int root,int len){
int parent = root;
int child = 2*parent + 1;
while(child < len){
if (child + 1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child + 1] ){
child++;
}
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent + 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
③建堆(建大堆为例)
下面我们给出一个数组,这个数组逻辑上可以看做一颗完全二叉树,但是还不是一个堆,现在我们通过算法,把它构 建成一个堆。根节点左右子树不是堆,我们怎么调整呢?这里我们从倒数的第一个非叶子节点的子树开始调整,一直 调整到根节点的树,就可以调整成堆。
//建大堆
public void creatHeap(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length;i++){
this.elem[i] = array[i];
suedSize++;
}
for (int parent = (array.length - 1 - 1) / 2;parent >= 0;parent--){
adjustDown(parent,this.suedSize);
}
3,堆的应用-优先级队列
①概念
在很多应用中,我们通常需要按照优先级情况对待处理对象进行处理,比如首先处理优先级最高的对象,然后处理次 高的对象。最简单的一个例子就是,在手机上玩游戏的时候,如果有来电,那么系统应该优先处理打进来的电话。 在这种情况下,我们的数据结构应该提供两个最基本的操作,一个是返回最高优先级对象,一个是添加新的对象。这 种数据结构就是优先级队列(Priority Queue)
②内部原理
优先级队列的实现方式有很多,但最常见的是使用堆来构建。
③入队列
过程(以大堆为例):
首先按尾插方式放入数组
比较其和其双亲的值的大小,如果双亲的值大,则满足堆的性质,插入结束
否则,交换其和双亲位置的值,重新进行 2、3 步骤 4. 直到根结点
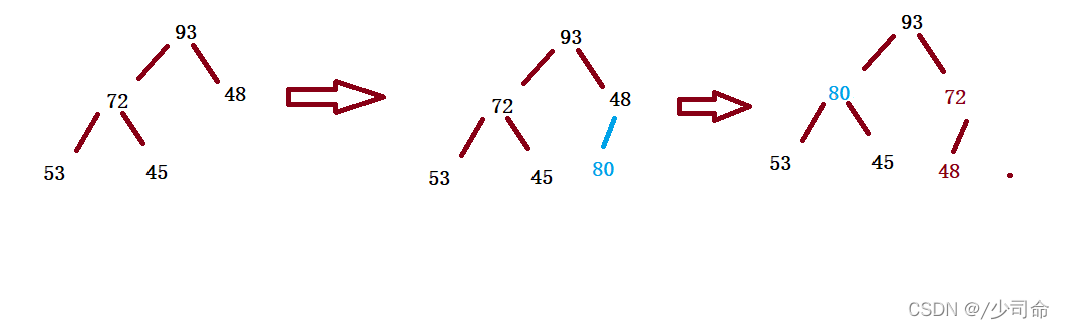
public void adjustUp(int child){
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while(child>0){
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public void push(int val) {
if (isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2 * this.elem.length);
this.elem[this.suedSize] = val;
this.suedSize++;
adjustUp(this.suedSize - 1);
}
}
④出队列(优先级最高)
为了防止破坏堆的结构,删除时并不是直接将堆顶元素删除,而是用数组的最后一个元素替换堆顶元素,然后通过向下调整方式重新调整成堆
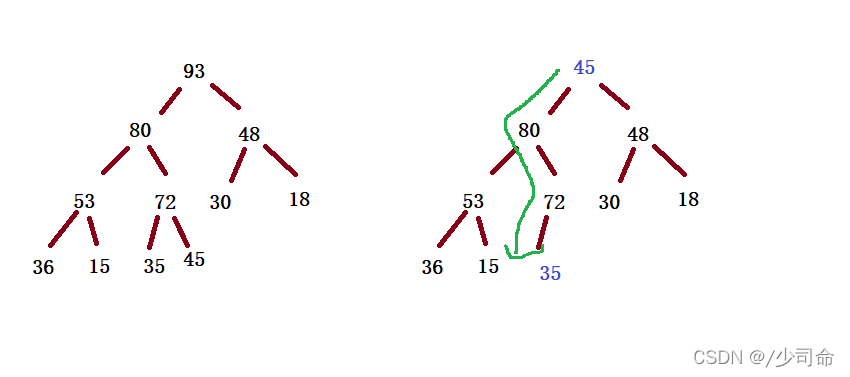
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.suedSize == 0;
}
public void pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
return;
}
int tmp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[this.suedSize-1];
this.elem[this.suedSize-1] = tmp;
this.suedSize--;
adjustDown(0,this.suedSize);
}
⑤返回队首元素(优先级最高)
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return this.elem[0];
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.suedSize == this.elem.length;
}
4,堆排序
/**
* 一定是先创建大堆
* 调整每棵树
* 开始堆排序:
* 先交换 后调整 直到 0下标
*/
public void heapSort(){
int end = this.suedSize-1;
while (end > 0){
int tmp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[end];
this.elem[end] = tmp;
adjustDown(0,end);
end--;
}
}
六,排序
1,概念
①排序
排序,就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或某些关键字的大小,递增或递减的排列起来的操作。 平时的上下文中,如果提到排序,通常指的是排升序(非降序)。 通常意义上的排序,都是指的原地排序(in place sort)。
②稳定性
两个相等的数据,如果经过排序后,排序算法能保证其相对位置不发生变化,则我们称该算法是具备稳定性的排序算法

或者我们说没有跳跃的排序也是稳定的排序

2,排序详解

①直接插入排序
整个区间被分为
1. 有序区间 2. 无序区间每次选择无序区间的第一个元素,在有序区间内选择合适的位置插入
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
insertSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
/**
* 时间复杂度:
* 最好:O(N) -> 数据是有序的
* 最坏:O(N^2) -> 无序的数据
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:稳定排序
* @param array
*/
public static void insertSort(int[] array) {
for(int i = 1;i < array.length;i++) {//n-1
int tmp = array[i];
int j = i-1;
for(; j >= 0;j--) {//n-1
if(array[j] > tmp) {
array[j+1] = array[j];
}else{
//array[j+1] = tmp;
break;
}
}
array[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
②希尔排序
希尔排序法又称缩小增量法。希尔排序法的基本思想是:先选定一个整数,把待排序文件中所有记录分成个组,所有 距离为的记录分在同一组内,并对每一组内的记录进行排序。然后,取,重复上述分组和排序的工作。当到达=1时, 所有记录在统一组内排好序。
希尔排序是对直接插入排序的优化。
当gap > 1时都是预排序,目的是让数组更接近于有序。当gap == 1时,数组已经接近有序的了,这样就会很 快。这样整体而言,可以达到优化的效果。我们实现后可以进行性能测试的对比。


/**
* 时间复杂度:不好算 n^1.3 - n^1.5 之间
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定的排序
* 技巧:如果在比较的过程当中 没有发生跳跃式的交换 那么就是稳定的
* @param array
*
*
* @param array 排序的数组
* @param gap 每组的间隔 -》 组数
*/
public static void shell(int[] array,int gap) {
for (int i = gap; i < array.length; i++) {
int tmp = array[i];
int j = i-gap;
for (; j >= 0; j -= gap) {
if(array[j] > tmp) {
array[j+gap] = array[j];
}else {
break;
}
}
array[j+gap] = tmp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
shell(array,5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}

③直接选择排序
每一次从无序区间选出最大(或最小)的一个元素,存放在无序区间的最后(或最前),直到全部待排序的数据元素排完 。

public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
selectSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
/**
* 时间复杂度:
* 最好:O(N^2)
* 最坏:O(N^2)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定的
* @param array
*/
public static void selectSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < array.length; j++) {
if(array[j] < array[i]) {
int tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}

④堆排序
基本原理也是选择排序,只是不在使用遍历的方式查找无序区间的最大的数,而是通过堆来选择无序区间的最大的数。
注意: 排升序要建大堆;排降序要建小堆。

public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
heapSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static void siftDown(int[] array,int root,int len) {
int parent = root;
int child = 2*parent+1;
while (child < len) {
if(child+1 < len && array[child] < array[child+1]) {
child++;
}
//child的下标就是左右孩子的最大值下标
if(array[child] > array[parent]) {
int tmp = array[child];
array[child] = array[parent];
array[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2*parent+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
public static void createHeap(int[] array) {
//从小到大排序 -》 大根堆
for (int i = (array.length-1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0 ; i--) {
siftDown(array,i,array.length);
}
}
/**
* 时间复杂度:O(N*logN) 都是这个时间复杂度
* 复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定的排序
* @param array
*/
public static void heapSort(int[] array) {
createHeap(array);//O(n)
int end = array.length-1;
while (end > 0) {//O(N*logN)
int tmp = array[end];
array[end] = array[0];
array[0] = tmp;
siftDown(array,0,end);
end--;
}
}

⑤冒泡排序
在无序区间,通过相邻数的比较,将最大的数冒泡到无序区间的最后,持续这个过程,直到数组整体有序

public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
/**
* 时间复杂度:
* 最好最坏都是O(n^2)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:稳定的排序
* 冒泡 直接插入
* @param array
*/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++) {
if(array[j] > array[j+1]) {
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}

⑥快速排序
从待排序区间选择一个数,作为基准值(pivot);
Partition: 遍历整个待排序区间,将比基准值小的(可以包含相等的)放到基准值的左边,将比基准值大的(可 以包含相等的)放到基准值的右边;
采用分治思想,对左右两个小区间按照同样的方式处理,直到小区间的长度 == 1,代表已经有序,或者小区间 的长度 == 0,代表没有数据

public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
quickSort1(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static int partition(int[] array,int low,int high) {
int tmp = array[low];
while (low < high) {
while (low < high && array[high] >= tmp) {
high--;
}
array[low] = array[high];
while (low < high && array[low] <= tmp) {
low++;
}
array[high] = array[low];
}
array[low] = tmp;
return low;
}
public static void quick(int[] array,int start,int end) {
if(start >= end) {
return;
}
int mid = (start+end)/2;
int pivot = partition(array,start,end);
quick(array,start,pivot-1);
quick(array,pivot+1,end);
}
/**
* 时间复杂度:
* 最好:O(n*logn) 均匀的分割下
* 最坏:o(n^2) 数据有序的时候
* 空间复杂度:
* 最好:logn
* 最坏:O(n)
* 稳定性:不稳定的排序
*
* k*n*logn
* 2
* 1.2
* @param array
*/
public static void quickSort1(int[] array) {
quick(array,0,array.length-1);
}

⑦归并排序
归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子 序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
mergeSort1(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
public static void merge(int[] array,int low,int mid,int high) {
int s1 = low;
int e1 = mid;
int s2 = mid+1;
int e2 = high;
int[] tmp = new int[high-low+1];
int k = 0;//代表tmp数组的下标
while (s1 <= e1 && s2 <= e2) {
if(array[s1] <= array[s2]) {
tmp[k++] = array[s1++];
}else {
tmp[k++] = array[s2++];
}
}
//有2种情况
while (s1 <= e1){
//说明第2个归并段没有了数据 把第1个归并段剩下的数据 全部拷贝过来
tmp[k++] = array[s1++];
}
while (s2 <= e2) {
//说明第1个归并段没有了数据 把第2个归并段剩下的数据 全部拷贝过来
tmp[k++] = array[s2++];
}
//tmp数组当中 存储的就是当前归并好的数据
for (int i = 0; i < tmp.length; i++) {
array[i+low] = tmp[i];
}
}
public static void mergeSortInternal(int[] array,int low,int high) {
if(low >= high) {
return;
}
int mid = (low+high) / 2;
mergeSortInternal(array,low,mid);
mergeSortInternal(array,mid+1,high);
//合并的过程
merge(array,low,mid,high);
}
/**
* 时间复杂度: O(N*log n)
* 空间复杂度:O(N)
* 稳定性:稳定的
* @param array
*/
public static void mergeSort1(int[] array) {
mergeSortInternal(array, 0,array.length-1);
}

七,List
1,ArrayList简介
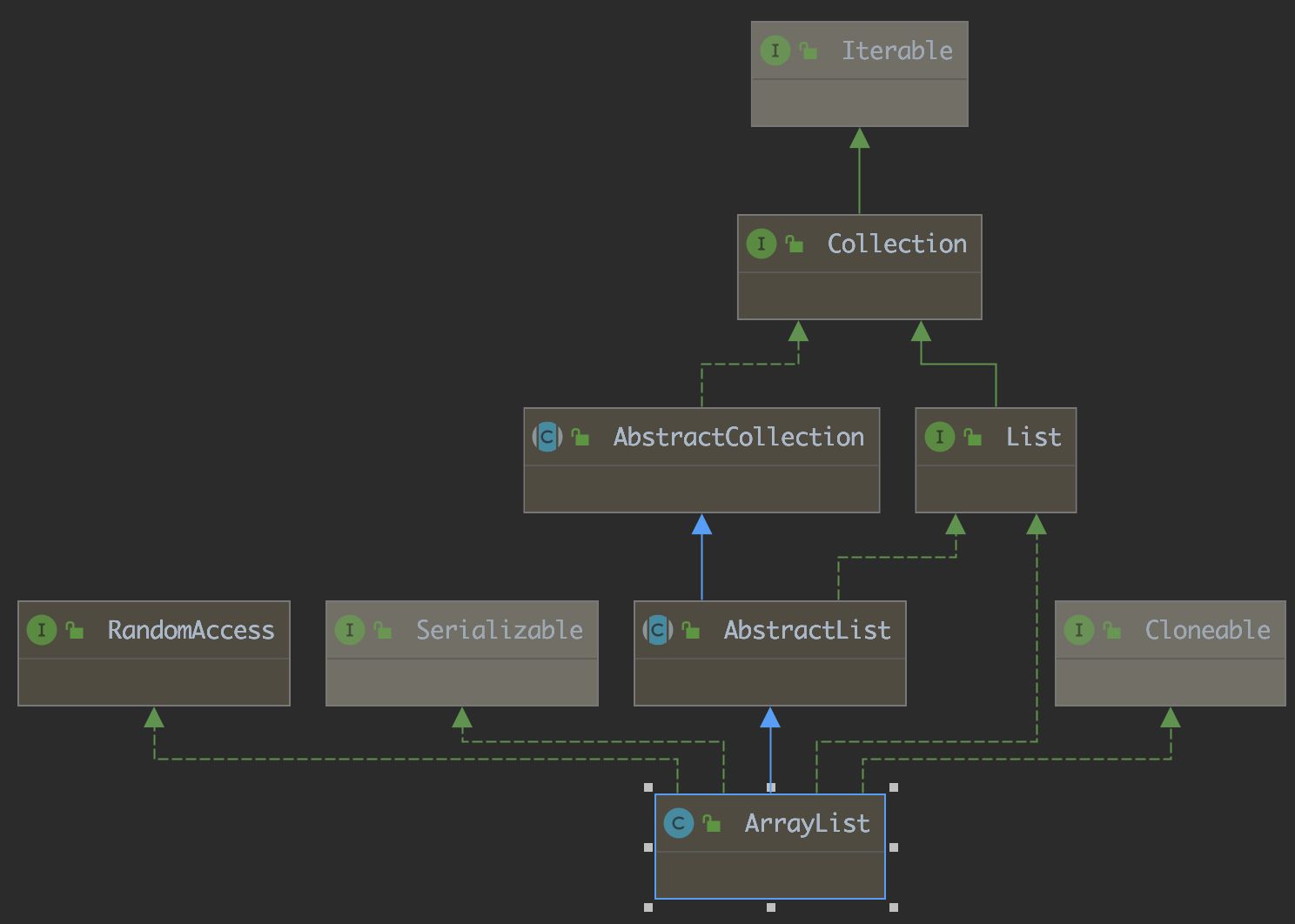
【说明】
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者 CopyOnWriteArrayList
ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表
ArrayList使用
①ArrayList的构造

public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList创建,推荐写法
// 构造一个空的列表
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
// 构造一个具有10个容量的列表
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(10);
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
list2.add(3);
// list2.add("hello"); // 编译失败,List<Integer>已经限定了,list2中只能存储整形元素
// list3构造好之后,与list中的元素一致
ArrayList<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>(list2);
// 避免省略类型,否则:任意类型的元素都可以存放,使用时将是一场灾难
List list4 = new ArrayList();
list4.add("111");
list4.add(100);
}
②ArrayList常见操作

public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1234");
list.add("zhongguo");
list.add("aaaaa");
list.add("gao");
System.out.println(list);
}

//add源码
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1234");
list.add("zhongguo");
list.add("aaaaa");
list.add("gao");
list.add(2,"ssss");
System.out.println(list);
}

//add插入源码
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1234");
list.add("zhongguo");
list.add("aaaaa");
list.add("gao");
ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add("111");
list2.add("44554");
list.addAll(list2);
System.out.println(list);
}

//addAll源码
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1234");
list.add("zhongguo");
list.add("aaaaa");
list.add("gao");
list.remove(2);
System.out.println(list);
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1234");
list.add("zhongguo");
list.add("aaaaa");
list.add("gao");
String a = list.get(1);
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(list);
}

③ ArrayList的遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("123");
list.add("jsss");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("===================");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=====================");
for (String s : list) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=========迭代器打印=======");
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("==========迭代器list打印=======");
ListIterator<String> it2 = list.listIterator();
while (it2.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it2.next() + " ");
}
}

八,Map和Set

1,搜索
①概念及场景
Map和set是一种专门用来进行搜索的容器或者数据结构,其搜索的效率与其具体的实例化子类有关。
搜索方式有:
直接遍历,时间复杂度为O(N),元素如果比较多效率会非常慢
二分查找,时间复杂度为 ,但搜索前必须要求序列是有序的 上述排序比较适合静态类型的查找,即一般不会对区间进行插入和删除操作了,而现实中的查找比如:
根据姓名查询考试成绩
通讯录,即根据姓名查询联系方式
不重复集合,即需要先搜索关键字是否已经在集合中
②模型
一般把搜索的数据称为关键字(Key),和关键字对应的称为值(Value),将其称之为Key-value的键值对,所以 模型会有两种:
- 纯 key 模型,比如:
有一个英文词典,快速查找一个单词是否在词典中 快速查找某个名字在不在通讯录中
- Key-Value 模型,比如:
统计文件中每个单词出现的次数,统计结果是每个单词都有与其对应的次数: 梁山好汉的江湖绰号:每个好汉都有自己的江湖绰号
2,Map的使用
①关于Map的说明
Map是一个接口类,该类没有继承自Collection,该类中存储的是结构的键值对,并且K一定是唯一的,不能重复。
②关于Map.Entry的说明
Map.Entry 是Map内部实现的用来存放键值对映射关系的内部类,该内部类中主要提供了 的获取,value的设置以及Key的比较方式。
方法解释K getKey()返回entry中key的值V getValue()返回entry中的valueV setValue(V value)将键值对中的value替换为指定value
③Map 的常用方法说明

public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("123","李白");
map.put("124","杜甫");
map.put("125","王昌龄");
map.put("126", "文天祥");
System.out.println(map);
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("123","李白");
map.put("124","杜甫");
map.put("125","王昌龄");
map.put("126", "文天祥");
String val = map.get("123");
System.out.println(val);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("123","李白");
map.put("124","杜甫");
map.put("125","王昌龄");
map.put("126", "文天祥");
String val;
val = map.getOrDefault("123","李白");
System.out.println(val);
}

3,Set的使用
①常见方法说明

②TreeSet的使用案例
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("123");
set.add("124");
set.add("125");
System.out.println(set);
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("123");
set.add("124");
set.add("125");
boolean fla = set.contains("123");
System.out.println(fla);
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("123");
set.add("124");
set.add("125");
Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}

版权归原作者 /少司命 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。