✨hello,进来的小伙伴们,你们好耶!✨
🍅🍅系列专栏:【数据结构与算法】
✈️✈️本篇内容: 栈的认识,栈的使用,栈的模拟实现!
⛵⛵作者简介:一名双非本科大三在读的科班Java编程小白,道阻且长,你我同行!
🍱🍱码云存放仓库gitee:Java数据结构代码存放!
一、栈(Stack)
一、栈的概念
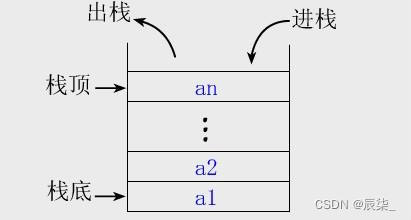
栈,一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶。
二、栈的使用
** 代码演示:**
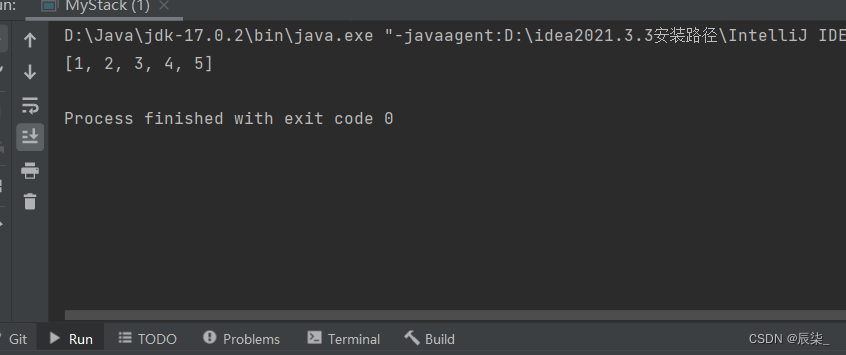
入栈push()
public class MyStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);
s1.push(5);
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
**运行结果: **
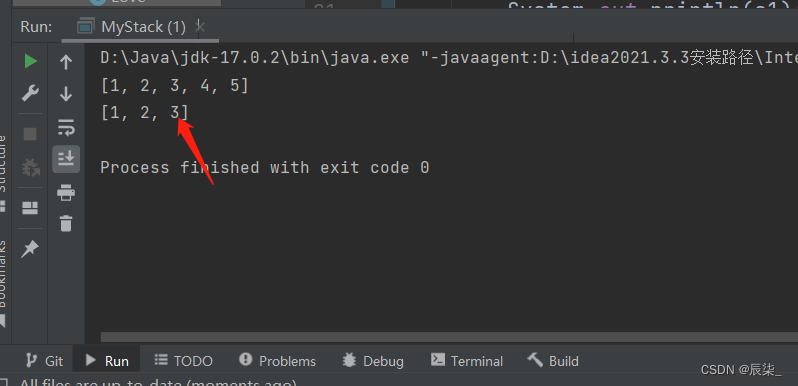
** 出栈pop(),这里我们出栈两个元素,那么剩下的结果应该是1 2 3**
public class MyStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);
s1.push(5);
System.out.println(s1);
s1.pop();
s1.pop();
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
运行结果:
** 获取栈顶元素peek():**
public class MyStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);
s1.push(5);
System.out.println(s1.peek());
}
}
运行结果:
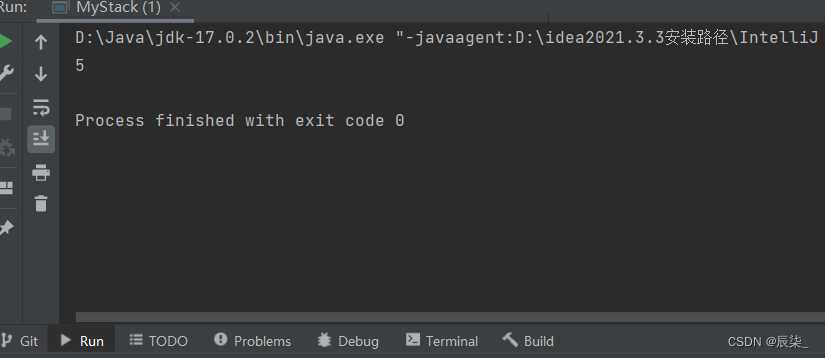
** 获取栈中有效元素的个数**
public class MyStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);
s1.push(5);
System.out.println(s1.size());
}
}
运行结果:
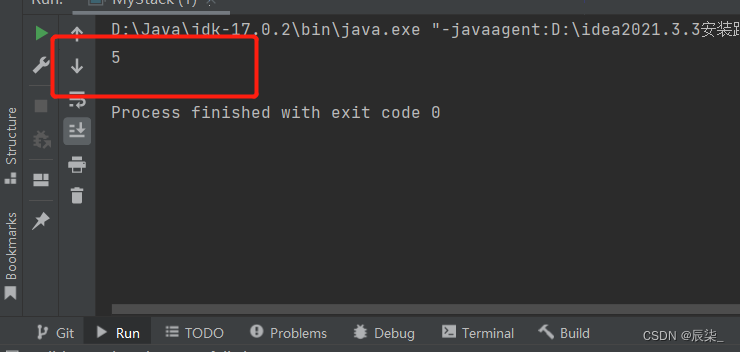
** 判断栈是否为空**
public class MyStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);
s1.push(5);
System.out.println(s1.empty());
}
}
运行结果:
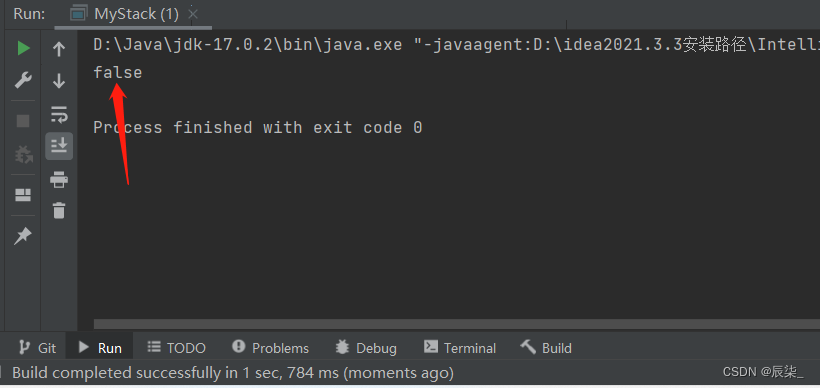
三、栈的应用场景
- 若进栈序列为 1,2,3,4 ,进栈过程中可以出栈,则下列不可能的一个出栈序列是(C)
A: 1,4,3,2 B: 2,3,4,1 C: 3,1,4,2 D: 3,4,2,1
问题分析:类似于这种栈的选择题,如果元素较少,我们直接心算就可以,元素较多的话我们可以画图来解决,本题c选项,先出的是3,那么就是1,2,3进栈,然后3出栈,第二个出栈选项给的是1,我们知道1是第一个进栈的,那么想出1,2必须先出,所以C选项错误!
2.一个栈的初始状态为空。现将元素1、2、3、4、5、A、B、C、D、E依次入栈,然后再依次出栈,则元素出栈的顺序是( B)。
A: 12345ABCDE B: EDCBA54321 C: ABCDE12345 D: 54321EDCBA
问题分析:简单明了,栈的结构先进后出,直接选B。
四、栈的模拟实现
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* 栈的模拟实现
*/
public class MyStack {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;
public MyStack() {
this.elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}
/**
* 压栈
*/
public int push(int val) {
if(isFull()) {
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,2*elem.length);
}
this.elem[usedSize] = val;
usedSize++;
return val;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
throw new MyEmptyStackException("栈为空!");
}
/*int ret = elem[usedSize-1];
usedSize--;
return ret;*/
return elem[--usedSize];
}
public boolean empty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
throw new MyEmptyStackException("栈为空!");
}
return elem[usedSize-1];
}
}
🍎🍎栈的模拟实现我们使用的是数组来实现的,代码也非常的简单明了,易于看懂,博主准备下一篇博客更新栈的几个经典面试题,慢慢干货,期待你的一键三连喔!🤟🤟
版权归原作者 辰柒_ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。