一.训练数据集准备
YOLOv8的训练数据格式与YOLOv5的训练数据格式一致,这一部分可以进行沿用。之前博文有发布VOC标注格式转YOLO标注格式的脚本,有需要可以查看。
二.项目克隆
YOLOv8项目文件可以直接去github上下载zip文件然后解压,也可以直接Git克隆。项目官方地址
三.训练前准备
这一部分首先保证机子上安装好了深度学习环境(可以跑YOLOv5就行)。
下一步用Pycharm打开YOLOv8项目,打开项目的终端,输入
pip install -r requirements.txt
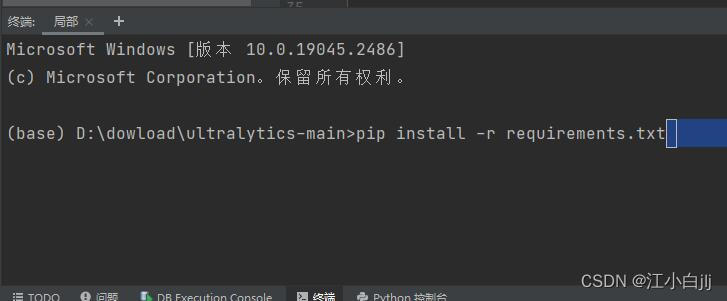
到这里。如果按照官方的操作指南需安装ultralytics这个包(我认为,这也是YOLOv8相较于YOLOv5区别最大的地方),但是如果大家要对YOLOv8做出改进,这里可能会出现问题。因此,我推荐大家不要执行这一步操作(如果不需要对YOLOv8做出改进,可以按照官方的指南进行操作)。
四.模型训练
第一、需要创建数据集的yanl文件

NWPU VHR-10 dataset/split_data
train images 000001.jpg 000002.jpg 000003.jpg ...... labels 000001.txt 000002.txt 000003.txt ...... val images ...... labels ...... test images ...... labels ......
第二、下载YOLOv8的预训练权重文件(这一步也可以不需要)
链接地址

第三、添加自定义模块(这里如果不对YOLOv8进行改进可以直接看第五步)
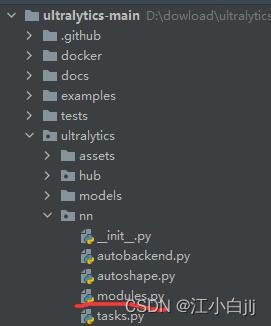
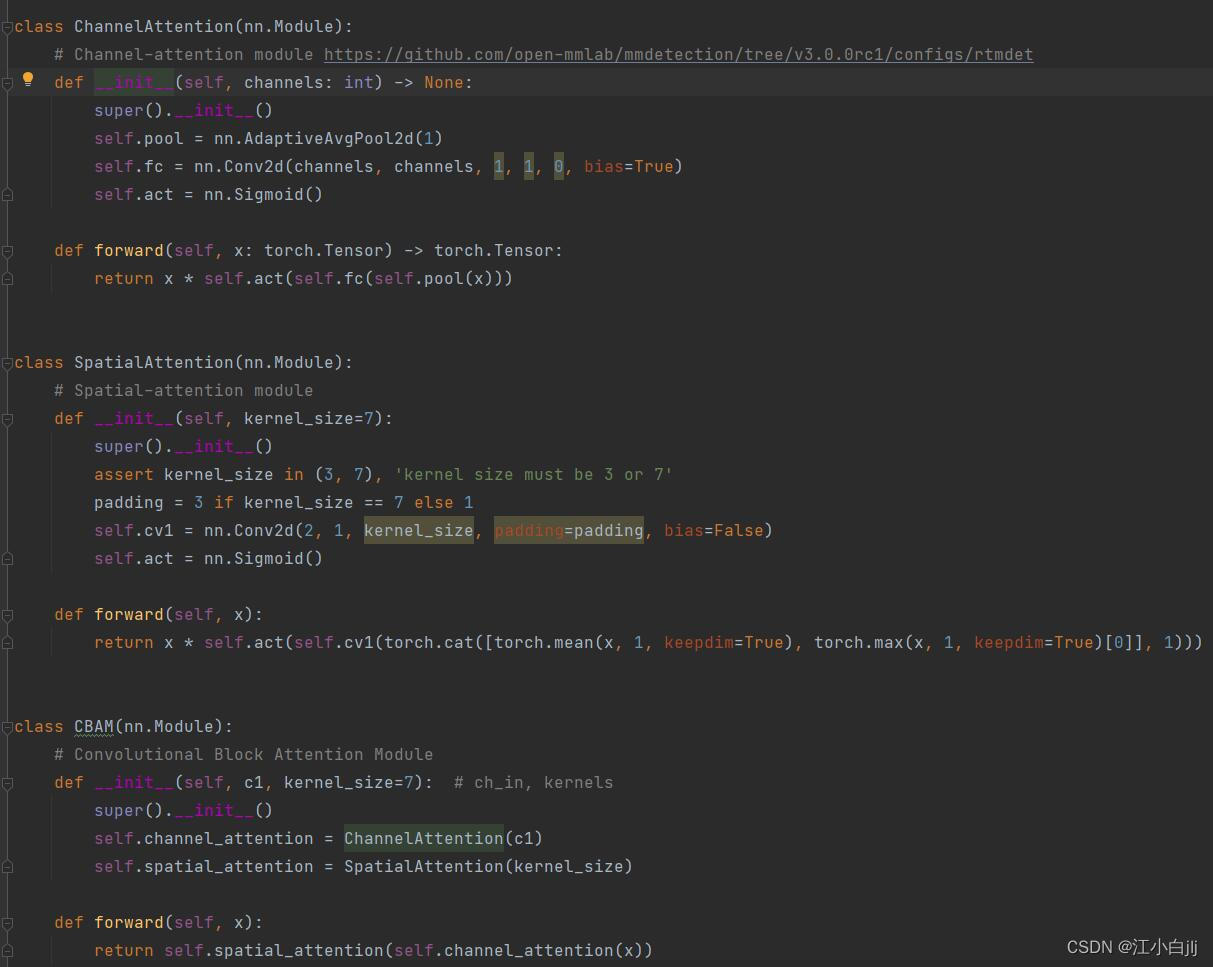
比如这里我要在YOLOv8的基础上添加CBAM注意力模块,首先打开modules.py,在下方添加CBAM注意力模块的代码实现。
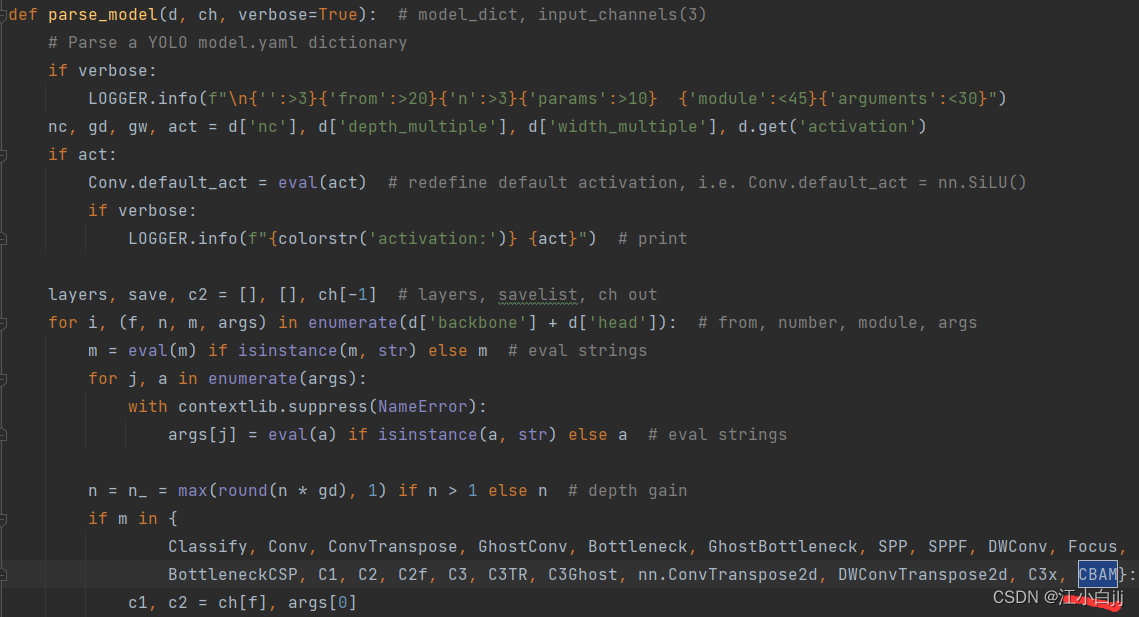
再打开task.py,在对应位置添加CBAM模块的声明

第四、根据自己设计的网络结构修改yaml文件
比如这里我将YOLOv8中部分的C2f模块替换为C3模块。

第五、开始训练
这里也是和YOLOv5有着较大的差别,在YOLOv8中train、val和test的参数设置都是依赖于default.yaml这个文件,因此在对参数设置进行修改前,建议先对该文件进行备份。
这里进行切换任务与模式。

这里需要注意,在YOLOv5中是同时包含--weights预训练权重文件和--cfg模型文件,预训练权重(.pt)是由官方提供,模型文件(.yaml)是自己修改的文件,并在训练中导入相同层的权重信息。而在YOLOv8中,只有--model这一个参数设置,且同时允许.pt文件与.yaml文件的接受处理。因此,这里的话,我建议用yaml文件,因为这样我们才能载入我们自己设计的网络结构(注:从目前的实验来看,只导入yaml文件也能进行迁移学习,载入预训练权重文件)。--data存放我们数据集的yaml文件。其他参数可以根据自己的需求自己设定(注:这里发现YOLOv8在训练时GPU的内存占用比YOLOv5的大许多,有bug。部分博主说可通过减少workers来缓解此类现象)。
# Train settings -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
model: # path to model file, i.e. yolov8n.pt, yolov8n.yaml
data: # path to data file, i.e. i.e. coco128.yaml
epochs: 100 # number of epochs to train for
patience: 50 # epochs to wait for no observable improvement for early stopping of training
batch: 16 # number of images per batch (-1 for AutoBatch)
imgsz: 640 # size of input images as integer or w,h
save: True # save train checkpoints and predict results
cache: False # True/ram, disk or False. Use cache for data loading
device: # device to run on, i.e. cuda device=0 or device=0,1,2,3 or device=cpu
workers: 8 # number of worker threads for data loading (per RANK if DDP)
project: # project name
name: # experiment name
exist_ok: False # whether to overwrite existing experiment
pretrained: False # whether to use a pretrained model
optimizer: SGD # optimizer to use, choices=['SGD', 'Adam', 'AdamW', 'RMSProp']
verbose: True # whether to print verbose output
seed: 0 # random seed for reproducibility
deterministic: True # whether to enable deterministic mode
single_cls: False # train multi-class data as single-class
image_weights: False # use weighted image selection for training
rect: False # support rectangular training if mode='train', support rectangular evaluation if mode='val'
cos_lr: False # use cosine learning rate scheduler
close_mosaic: 10 # disable mosaic augmentation for final 10 epochs
resume: False # resume training from last checkpoint
min_memory: False # minimize memory footprint loss function, choices=[False, True, <roll_out_thr>]
最后,运行train.py即可。
python train.py
五.模型验证与测试
模型的验证与测试步骤基本和训练一样,先修改验证/测试的设置,也是在default.yaml中,然后执行val.py和predict.py即可
本文转载自: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42182534/article/details/129040961
版权归原作者 江小白jlj 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
版权归原作者 江小白jlj 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
