《数据结构(C语言版)》实战项目之双向链表(增删查改)功能实现
——By 作者:新晓·故知
完整源码如下,欢迎复制测试指正!
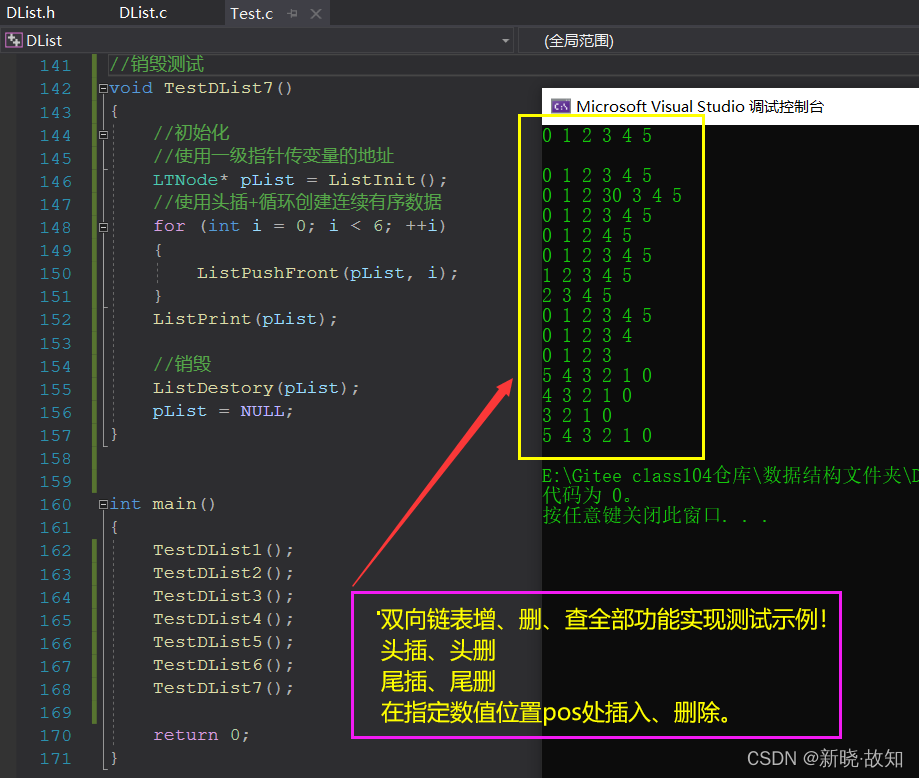
双向链表(增删查改)功能实现测试示例:
完整源码:
Test.c:
#include "DList.h" //双向链表测试 //尾插+尾删测试 void TestDList1() { //使用二级指针需传一级指针的地址 //LTNode* pList = NULL; //ListInit(&pList); //使用一级指针传变量的地址 LTNode* pList = ListInit(); //1.一个一个创建数据 //ListPushBack(pList, 1); //ListPushBack(pList, 2); //ListPushBack(pList, 3); //ListPushBack(pList, 4); //ListPushBack(pList, 5); //ListPushBack(pList, 6); //ListPrint(pList); //2.使用尾插+循环创建连续有序数据 for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { ListPushBack(pList,i); } ListPrint(pList); //1.一个一个删除数据 ListPopBack(pList); ListPopBack(pList); ListPopBack(pList); ListPopBack(pList); ListPopBack(pList); ListPopBack(pList); //ListPopBack(pList); ListPrint(pList); } //在指定数值(pos)位置处插入测试 void TestDList2() { //初始化 //使用一级指针传变量的地址 LTNode* pList = ListInit(); //使用尾插+循环创建连续有序数据 for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { ListPushBack(pList, i); } ListPrint(pList); //查找+在指定数值(pos)位置处插入 LTNode* pos = ListFind(pList, 3); if (pos) { ListInsert(pos, 30); } ListPrint(pList); } //在指定数值(pos)位置处删除测试 void TestDList3() { //初始化 //使用一级指针传变量的地址 LTNode* pList = ListInit(); //使用尾插+循环创建连续有序数据 for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { ListPushBack(pList, i); } ListPrint(pList); //查找+在指定数值(pos)位置处删除 LTNode* pos = ListFind(pList, 3); if (pos) { ListErase(pos); } ListPrint(pList); } //头删——附用ListErase版测试 void TestDList4() { //初始化 //使用一级指针传变量的地址 LTNode* pList = ListInit(); //使用尾插+循环创建连续有序数据 for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { ListPushBack(pList, i); } ListPrint(pList); //头删 ListPopFront(pList); ListPrint(pList); ListPopFront(pList); ListPrint(pList); } //尾删——附用ListErase版测试 void TestDList5() { //初始化 //使用一级指针传变量的地址 LTNode* pList = ListInit(); //使用尾插+循环创建连续有序数据 for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { ListPushBack(pList, i); } ListPrint(pList); //尾删 ListPopBack(pList); ListPrint(pList); ListPopBack(pList); ListPrint(pList); } //头插——附用ListInsert版 void TestDList6() { //初始化 //使用一级指针传变量的地址 LTNode* pList = ListInit(); //使用头插+循环创建连续有序数据 for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { ListPushFront(pList, i); } ListPrint(pList); //头删 ListPopFront(pList); ListPrint(pList); ListPopFront(pList); ListPrint(pList); } //销毁测试 void TestDList7() { //初始化 //使用一级指针传变量的地址 LTNode* pList = ListInit(); //使用头插+循环创建连续有序数据 for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { ListPushFront(pList, i); } ListPrint(pList); //销毁 ListDestory(pList); pList = NULL; } int main() { TestDList1(); TestDList2(); TestDList3(); TestDList4(); TestDList5(); TestDList6(); TestDList7(); return 0; }DList.c:
#include "DList.h" //双向链表功能函数 //打印 void ListPrint(LTNode* phead) { assert(phead); LTNode* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { printf("%d ", cur->data); cur = cur->next; } printf("\n"); } //动态开辟新结点 LTNode* BuyLTNode(LTDataType x) { LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { printf("malloc fail\n"); exit(-1); } newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; newnode->prev = NULL; return newnode; } //初始化——写法1 //优化此处--减少二级指针的使用 //void ListInit(LTNode** pphead) //{ // assert(pphead); // *pphead = BuyLTNode(0); // (*pphead)->next = *pphead; // (*pphead)->prev = *pphead; // //} // 初始化——写法2 //使用一级指针 LTNode* ListInit() { LTNode* phead = BuyLTNode(0); phead->next = phead; phead->prev = phead; return phead; } 尾插 //void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) //{ // assert(phead); // // LTNode* tail = phead->prev; // LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x); // // tail->next = newnode; // newnode->prev = tail; // // newnode->next = phead; // phead->prev = newnode; //} //尾插——附用Insert版 void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) { assert(phead); ListInsert(phead, x); } 尾删 //void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead) //{ // assert(phead); // //判断链表为空 // assert(phead->next != phead); // LTNode* tail = phead->prev; // LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev; // // free(tail); // tail = NULL; // // tailPrev->next = phead; // phead->prev = tailPrev; //} //尾删——附用ListErase版 void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead) { assert(phead); //判断链表为空 assert(phead->next != phead); ListErase(phead->prev); } //查找 LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) { assert(phead); LTNode* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { if (cur->data == x) { return cur; } cur = cur->next; } return NULL; } //在指定数值(pos)位置处插入 写法1:要求注意顺序 //void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x) //{ // assert(pos); // LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x); // pos->prev->next = newnode; // newnode->prev = pos->prev; // // pos->prev = newnode; // newnode->next = pos; //} //写法2:不要求顺序 void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x) { assert(pos); LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x); LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev; newnode->next = pos; pos->prev = newnode; posPrev->next = newnode; newnode->prev = posPrev; } //头插——附用ListInsert版 void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) { assert(phead); ListInsert(phead->next, x); } //头删——附用ListErase版 void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead) { assert(phead); //判断链表为空 assert(phead->next != phead); ListErase(phead->next); } //在指定数值(pos)位置处删除 void ListErase(LTNode* pos) { assert(pos); LTNode* prev = pos->prev; LTNode* next = pos->next; free(pos); pos = NULL; prev->next = next; next->prev = prev; } //销毁双向链表 //保持接口的一致性,传一级指针 void ListDestory(LTNode* phead) { assert(phead); LTNode* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { LTNode* next = cur->next; //附用——ListErase版 没必要,即将销毁,何必再去链接Erase函数 //ListErase(cur); //自己free free(cur); cur = next; } free(phead); //phead = NULL; 效果不大,一级传参的形参不改变实参 }DList.h:
#include "DList.h" //双向链表头函数 //打印 void ListPrint(LTNode* phead) { assert(phead); LTNode* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { printf("%d ", cur->data); cur = cur->next; } printf("\n"); } //动态开辟新结点 LTNode* BuyLTNode(LTDataType x) { LTNode* newnode = (LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { printf("malloc fail\n"); exit(-1); } newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; newnode->prev = NULL; return newnode; } //初始化——写法1 //优化此处--减少二级指针的使用 //void ListInit(LTNode** pphead) //{ // assert(pphead); // *pphead = BuyLTNode(0); // (*pphead)->next = *pphead; // (*pphead)->prev = *pphead; // //} // 初始化——写法2 //使用一级指针 LTNode* ListInit() { LTNode* phead = BuyLTNode(0); phead->next = phead; phead->prev = phead; return phead; } 尾插 //void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) //{ // assert(phead); // // LTNode* tail = phead->prev; // LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x); // // tail->next = newnode; // newnode->prev = tail; // // newnode->next = phead; // phead->prev = newnode; //} //尾插——附用Insert版 void ListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) { assert(phead); ListInsert(phead, x); } 尾删 //void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead) //{ // assert(phead); // //判断链表为空 // assert(phead->next != phead); // LTNode* tail = phead->prev; // LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev; // // free(tail); // tail = NULL; // // tailPrev->next = phead; // phead->prev = tailPrev; //} //尾删——附用ListErase版 void ListPopBack(LTNode* phead) { assert(phead); //判断链表为空 assert(phead->next != phead); ListErase(phead->prev); } //查找 LTNode* ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) { assert(phead); LTNode* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { if (cur->data == x) { return cur; } cur = cur->next; } return NULL; } //在指定数值(pos)位置处插入 写法1:要求注意顺序 //void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x) //{ // assert(pos); // LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x); // pos->prev->next = newnode; // newnode->prev = pos->prev; // // pos->prev = newnode; // newnode->next = pos; //} //写法2:不要求顺序 void ListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x) { assert(pos); LTNode* newnode = BuyLTNode(x); LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev; newnode->next = pos; pos->prev = newnode; posPrev->next = newnode; newnode->prev = posPrev; } //头插——附用ListInsert版 void ListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x) { assert(phead); ListInsert(phead->next, x); } //头删——附用ListErase版 void ListPopFront(LTNode* phead) { assert(phead); //判断链表为空 assert(phead->next != phead); ListErase(phead->next); } //在指定数值(pos)位置处删除 void ListErase(LTNode* pos) { assert(pos); LTNode* prev = pos->prev; LTNode* next = pos->next; free(pos); pos = NULL; prev->next = next; next->prev = prev; } //销毁双向链表 //保持接口的一致性,传一级指针 void ListDestory(LTNode* phead) { assert(phead); LTNode* cur = phead->next; while (cur != phead) { LTNode* next = cur->next; //附用——ListErase版 没必要,即将销毁,何必再去链接Erase函数 //ListErase(cur); //自己free free(cur); cur = next; } free(phead); //phead = NULL; 效果不大,一级传参的形参不改变实参 }
二、双向链表的实现分析:
双向链表的功能函数:
1.双向链表打印+初始化:
打印:
初始化:
2.双向链表动态开辟新结点:
3.双向链表尾插:
(1)尾插法1
(2)尾插法2——附用ListInsert函数版
4.双向链表尾删:
(1)尾删法1
(2)尾删法2——附用ListErase版
5.双向链表头插:(附用ListInsert函数版)
6.双向链表头删:(附用ListErase函数版)
7.双向链表在指定数据位置(pos)处插入数据:
8.双向链表在指定数据位置(pos) 处删除数据:
9.双向链表的销毁:
双向链表调试测试:
删除过多数据测试:
注意事项:
1.删除哨兵位置的头结点,会形成野指针
2.Find是按照顺序查找,有局限性。若需要查找有重复的数据,则需要自己另写算法!
三、顺序表和链表的区别总结:
后记:
●由于作者水平有限,文章难免存在谬误之处,敬请读者斧正,俚语成篇,恳望指教!
——By 作者:新晓·故知
本文转载自: https://blog.csdn.net/m0_57859086/article/details/123717507
版权归原作者 新晓·故知 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
版权归原作者 新晓·故知 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。