文章目录
测试使用:【Win10+cuda11.0+cudnn8.2.1+TensorRT8.2.5.1】
关于安装
一、模型转换 onnx2trt
方法1:使用wang-xinyu/tensorrtx部署yolov5方法:https://wangsp.blog.csdn.net/article/details/121718501
方法2:使用tensorRT转成engine
方法3:使用C++ onnx_tensorrt将onnx转为trt 的推理engine 参考 【python 方法参考】
方法4:直接使用TensorRT部署onnx【参考】
- 使用TensorRT部署pytorch模型(c++推理)【参考】
- TensorRT-pytorch权重文件转engine【参考】
- pth->onnx->下载好TensorRT库, 进入~/samples/trtexec, 运行make,生成.engine->python run engine 【参考】 【参考2】
使用 trtexec工具转engine
使用
./trtexec --help
查看命令:
#生成静态batchsize的engine
./trtexec --onnx=<onnx_file>\#指定onnx模型文件--explicitBatch\#在构建引擎时使用显式批大小(默认=隐式)显示批处理--saveEngine=<tensorRT_engine_file>\#输出engine--workspace=<size_in_megabytes>\#设置工作空间大小单位是MB(默认为16MB)--fp16#除了fp32之外,还启用fp16精度(默认=禁用)#生成动态batchsize的engine
./trtexec --onnx=<onnx_file>\#指定onnx模型文件--minShapes=input:<shape_of_min_batch>\#最小的NCHW--optShapes=input:<shape_of_opt_batch>\#最佳输入维度,跟maxShapes一样就好--maxShapes=input:<shape_of_max_batch>\#最大输入维度--workspace=<size_in_megabytes>\#设置工作空间大小单位是MB(默认为16MB)--saveEngine=<engine_file>\#输出engine--fp16#除了fp32之外,还启用fp16精度(默认=禁用)#小尺寸的图片可以多batchsize即8x3x416x416
/home/zxl/TensorRT-7.2.3.4/bin/trtexec --onnx=yolov4_-1_3_416_416_dynamic.onnx \--minShapes=input:1x3x416x416 \--optShapes=input:8x3x416x416 \--maxShapes=input:8x3x416x416 \--workspace=4096\--saveEngine=yolov4_-1_3_416_416_dynamic_b8_fp16.engine \--fp16#由于内存不够了所以改成4x3x608x608
/home/zxl/TensorRT-7.2.3.4/bin/trtexec --onnx=yolov4_-1_3_608_608_dynamic.onnx \--minShapes=input:1x3x608x608 \--optShapes=input:4x3x608x608 \--maxShapes=input:4x3x608x608 \--workspace=4096\--saveEngine=yolov4_-1_3_608_608_dynamic_b4_fp16.engine \--fp16
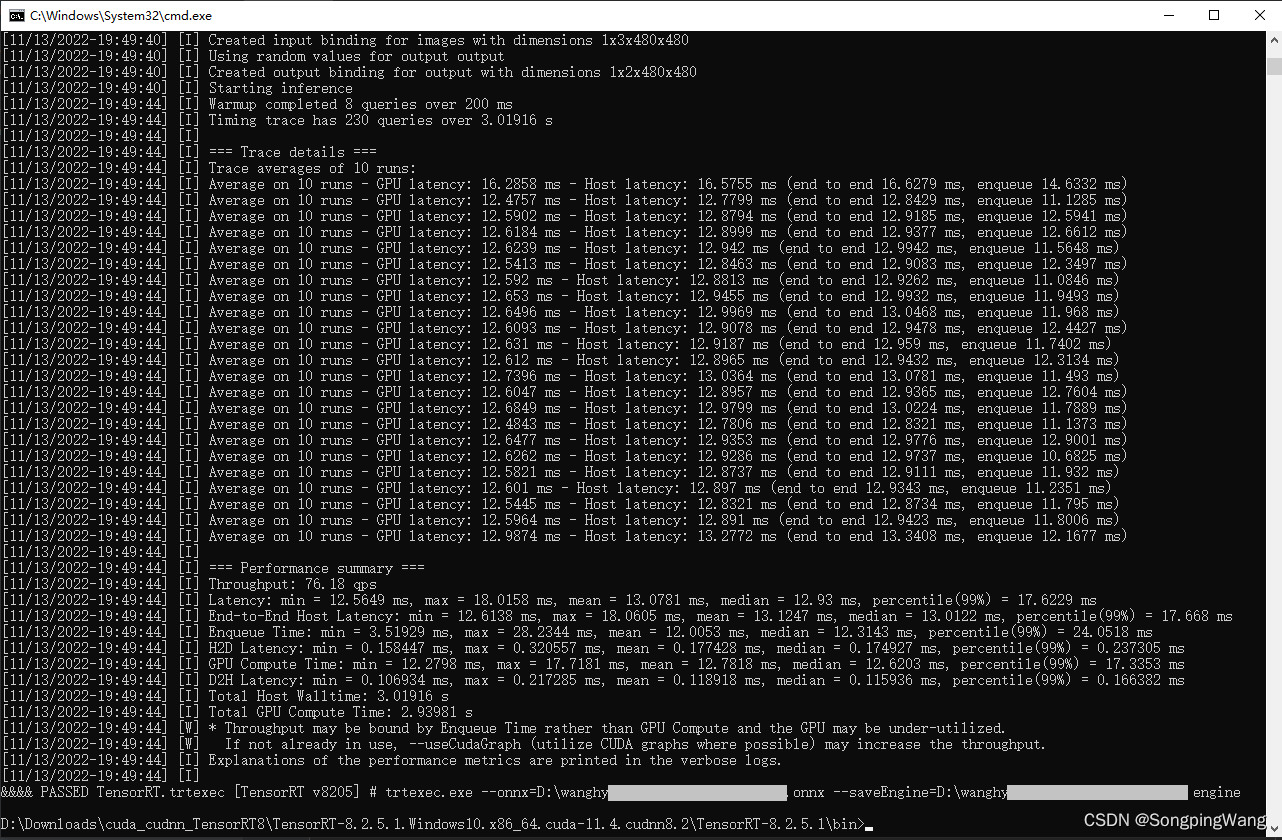
测试,执行: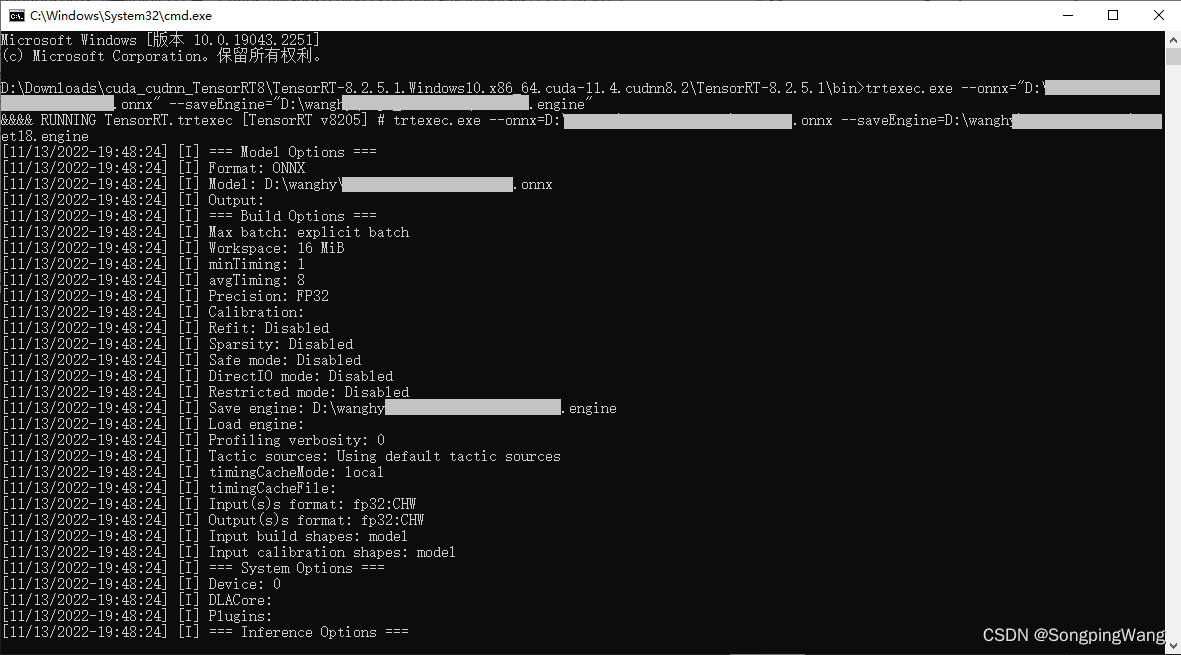
二、配置环境变量
################ TenorRT 包含目录 ######################
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.0\include;
D:\opencv_build\install\include;D:\opencv_build\install\include\opencv2;
D:\Downloads\cuda_cudnn_TensorRT8\TensorRT-8.2.5.1.Windows10.x86_64.cuda-11.4.cudnn8.2\TensorRT-8.2.5.1\samples\common
#################### TenorRT 库目录 ############################
D:\opencv_build\install\x64\vc16\lib\*.lib
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.0\lib\x64\*.lib
三、调用推理
使用pycuda【下载】地址。模型训练代码来自 https://github.com/bubbliiiing
安装pycuda 对应python的版本:pycuda-2020.1+cuda101-cp38-cp38-win_amd64.whl
安装tensorrt对应python的版本:tensorrt-8.2.5.1-cp38-none-win_amd64.whl(来自TensorRT-8.2.5.1.Windows10.x86_64.cuda-11.4.cudnn8.2\TensorRT-8.2.5.1\python目录下)
TensorRT调用步骤
- 创建IBuilder的指针builder
- 设置推理的显存大小
- 设置推理的模式,float或者int
- 利用builder创建ICudaEngine的实例engine
- 由engine创建上下文context
- 利用context进行推理,得到结果
- 释放显存空间
python示例代码
# --*-- coding:utf-8 --*--import pycuda.autoinit
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import tensorrt as trt
import torch
import time
from PIL import Image
import cv2, os
import torchvision
import numpy as np
filename ='/home/img.png'
max_batch_size =1
onnx_model_path ="./resnet18.onnx"
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)defget_img_np_nchw(filename):
image = cv2.imread(filename)
image_cv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image_cv = cv2.resize(image_cv,(224,224))
miu = np.array([0.485,0.456,0.406]).reshape(3,1,1)
std = np.array([0.229,0.224,0.225]).reshape(3,1,1)
img_np = np.array(image_cv, dtype=np.float)/255.
img_np = img_np.transpose((2,0,1))
img_np -= miu
img_np /= std
img_np_nchw = img_np[np.newaxis]
img_np_nchw = np.tile(img_np_nchw,(max_batch_size,1,1,1))return img_np_nchw
classHostDeviceMem(object):def__init__(self, host_mem, device_mem):"""
host_mem: cpu memory
device_mem: gpu memory
"""
self.host = host_mem
self.device = device_mem
def__str__(self):return"Host:\n"+str(self.host)+"\nDevice:\n"+str(self.device)def__repr__(self):return self.__str__()defallocate_buffers(engine):
inputs, outputs, bindings =[],[],[]
stream = cuda.Stream()for binding in engine:# print(binding) # 绑定的输入输出# print(engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) # get_binding_shape 是变量的大小
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding))* engine.max_batch_size
# volume 计算可迭代变量的空间,指元素个数# size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) # 如果采用固定bs的onnx,则采用该句
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))# get_binding_dtype 获得binding的数据类型# nptype等价于numpy中的dtype,即数据类型# allocate host and device buffers
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)# 创建锁业内存
device_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)# cuda分配空间# print(int(device_mem)) # binding在计算图中的缓冲地址
bindings.append(int(device_mem))# append to the appropriate listif engine.binding_is_input(binding):
inputs.append(HostDeviceMem(host_mem, device_mem))else:
outputs.append(HostDeviceMem(host_mem, device_mem))return inputs, outputs, bindings, stream
defget_engine(max_batch_size=1, onnx_file_path="", engine_file_path="", fp16_mode=False, save_engine=False):"""
params max_batch_size: 预先指定大小好分配显存
params onnx_file_path: onnx文件路径
params engine_file_path: 待保存的序列化的引擎文件路径
params fp16_mode: 是否采用FP16
params save_engine: 是否保存引擎
returns: ICudaEngine
"""# 如果已经存在序列化之后的引擎,则直接反序列化得到cudaEngineif os.path.exists(engine_file_path):print("Reading engine from file: {}".format(engine_file_path))withopen(engine_file_path,'rb')as f, \
trt.Runtime(TRT_LOGGER)as runtime:return runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())# 反序列化else:# 由onnx创建cudaEngine# 使用logger创建一个builder# builder创建一个计算图 INetworkDefinition
explicit_batch =1<<(int)(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH)# In TensorRT 7.0, the ONNX parser only supports full-dimensions mode, meaning that your network definition must be created with the explicitBatch flag set. For more information, see Working With Dynamic Shapes.with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER)as builder, \
builder.create_network(explicit_batch)as network, \
trt.OnnxParser(network, TRT_LOGGER)as parser:# 使用onnx的解析器绑定计算图,后续将通过解析填充计算图
builder.max_workspace_size =1<<30# 预先分配的工作空间大小,即ICudaEngine执行时GPU最大需要的空间
builder.max_batch_size = max_batch_size # 执行时最大可以使用的batchsize
builder.fp16_mode = fp16_mode
# 解析onnx文件,填充计算图ifnot os.path.exists(onnx_file_path):
quit("ONNX file {} not found!".format(onnx_file_path))print('loading onnx file from path {} ...'.format(onnx_file_path))withopen(onnx_file_path,'rb')as model:# 二值化的网络结果和参数print("Begining onnx file parsing")
parser.parse(model.read())# 解析onnx文件# parser.parse_from_file(onnx_file_path) # parser还有一个从文件解析onnx的方法print("Completed parsing of onnx file")# 填充计算图完成后,则使用builder从计算图中创建CudaEngineprint("Building an engine from file{}' this may take a while...".format(onnx_file_path))#################print(network.get_layer(network.num_layers -1).get_output(0).shape)# network.mark_output(network.get_layer(network.num_layers -1).get_output(0))
engine = builder.build_cuda_engine(network)# 注意,这里的network是INetworkDefinition类型,即填充后的计算图print("Completed creating Engine")if save_engine:# 保存engine供以后直接反序列化使用withopen(engine_file_path,'wb')as f:
f.write(engine.serialize())# 序列化return engine
defdo_inference(context, bindings, inputs, outputs, stream, batch_size=1):# Transfer data from CPU to the GPU.[cuda.memcpy_htod_async(inp.device, inp.host, stream)for inp in inputs]# htod: host to device 将数据由cpu复制到gpu device# Run inference.
context.execute_async_v2(bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle)# 当创建network时显式指定了batchsize, 则使用execute_async_v2, 否则使用execute_async# Transfer predictions back from the GPU.[cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(out.host, out.device, stream)for out in outputs]# gpu to cpu# Synchronize the stream
stream.synchronize()# Return only the host outputs.return[out.host for out in outputs]defpostprocess_the_outputs(h_outputs, shape_of_output):
h_outputs = h_outputs.reshape(*shape_of_output)return h_outputs
img_np_nchw = get_img_np_nchw(filename).astype(np.float32)# These two modes are depend on hardwares
fp16_mode =False
trt_engine_path ="./model_fp16_{}.trt".format(fp16_mode)# Build an cudaEngine
engine = get_engine(max_batch_size, onnx_model_path, trt_engine_path, fp16_mode)# 创建CudaEngine之后,需要将该引擎应用到不同的卡上配置执行环境
context = engine.create_execution_context()
inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = allocate_buffers(engine)# input, output: host # bindings# Do inference
shape_of_output =(max_batch_size,1000)# Load data to the buffer
inputs[0].host = img_np_nchw.reshape(-1)# inputs[1].host = ... for multiple input
t1 = time.time()
trt_outputs = do_inference(context, bindings=bindings, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream)# numpy data
t2 = time.time()
feat = postprocess_the_outputs(trt_outputs[0], shape_of_output)print('TensorRT ok')
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True).cuda()
resnet_model = model.eval()
input_for_torch = torch.from_numpy(img_np_nchw).cuda()
t3 = time.time()
feat_2 = resnet_model(input_for_torch)
t4 = time.time()
feat_2 = feat_2.cpu().data.numpy()print('Pytorch ok!')
mse = np.mean((feat - feat_2)**2)print("Inference time with the TensorRT engine: {}".format(t2 - t1))print("Inference time with the PyTorch model: {}".format(t4 - t3))print('MSE Error = {}'.format(mse))print('All completed!')
C++ 代码示例
TensorRT 傻瓜式部署流程:参考
#include<string>#include<algorithm>#include<assert.h>#include<cmath>#include<cuda_runtime_api.h>#include<fstream>#include<iomanip>#include<iostream>#include<sstream>#include<sys/stat.h>#include<time.h>#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>#include<io.h>#include"NvInfer.h"#include"NvOnnxParser.h"#include"argsParser.h"#include"logger.h"#include"common.h"#ifndefNOMINMAX#ifndefmax_idx#definemax_idx(a,b)(((a)>(b))?(0):(1))#endif#endif/* NOMINMAX */#defineDebugP(x) std::cout <<"Line"<<__LINE__<<" "<< #x <<"="<< x << std::endlusingnamespace nvinfer1;
samplesCommon::Args gArgs;usingnamespace sample;staticconstint INPUT_H =480;staticconstint INPUT_W =480;staticconstint INPUT_C =3;staticconstexprint INPUT_SIZE = INPUT_H * INPUT_W *3;staticconstexprint OUTPUT_SIZE = INPUT_H * INPUT_W *2;staticconst cv::Size newShape = cv::Size(INPUT_W, INPUT_H);const std::string trtModelName ="D:\\xxx.engine";const std::string onnxModeName ="D:\\xxx.onnx";const std::string file_name ="D:\\xxx.jpg";structTensorRT{
IExecutionContext* context;
ICudaEngine* engine;
IRuntime* runtime;};voidimage_to_center(const cv::Mat& image, cv::Mat& outImage, cv::Mat& IM,const cv::Scalar& color){
cv::Size shape = image.size();float scale_xy = std::min((float)newShape.height /(float)shape.height,(float)newShape.width /(float)shape.width);
cv::Mat M =(cv::Mat_<float>(2,3)<<
scale_xy,0,-scale_xy *(float)shape.width *0.5+(float)newShape.width *0.5,0, scale_xy,-scale_xy *(float)shape.height *0.5+(float)newShape.height *0.5);
cv::invertAffineTransform(M, IM);
cv::warpAffine(image, outImage, M, newShape,1,0, color);}voidcenter_to_image(const cv::Mat& image, cv::Mat& outImage, cv::Mat& IM){
cv::warpAffine(image, outImage, IM, newShape);}voidnormal_image2blob(float* blob, cv::Mat& img){for(int c =0; c <3;++c){for(int i =0; i < img.rows;++i){
cv::Vec3b* p1 = img.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(i);for(int j =0; j < img.cols;++j){
blob[c * img.cols * img.rows + i * img.cols + j]= p1[j][c]*0.00392156862745098;}}}}boolonnxToTRTModel(const std::string& modelFile,// name of the onnx modelunsignedint maxBatchSize,// batch size - NB must be at least as large as the batch we want to run with
IHostMemory*& trtModelStream)// output buffer for the TensorRT model{// create the builder
IBuilder* builder =createInferBuilder(gLogger.getTRTLogger());assert(builder !=nullptr);
nvinfer1::INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(maxBatchSize);
nvinfer1::IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig();
config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1<<20);// parserauto parser = nvonnxparser::createParser(*network, gLogger.getTRTLogger());if(!parser->parseFromFile(modelFile.c_str(),static_cast<int>(gLogger.getReportableSeverity()))){
gLogError <<"Failure while parsing ONNX file"<< std::endl;returnfalse;}if(builder->platformHasFastFp16()){
config->setFlag(nvinfer1::BuilderFlag::kFP16);}else{
std::cout <<"This platform does not support fp16"<< std::endl;}// Build the engine
ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network,*config);assert(engine);// serialize the engine, then close everything down
trtModelStream = engine->serialize();
parser->destroy();
engine->destroy();
network->destroy();
builder->destroy();
std::ofstream ofs(trtModelName.c_str(), std::ios::out | std::ios::binary);
ofs.write((char*)(trtModelStream->data()), trtModelStream->size());
ofs.close();DebugP("Trt model save success!");returntrue;}
TensorRT*LoadNet(constchar* trtFileName){
std::ifstream t(trtFileName, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
std::stringstream tempStream;
tempStream << t.rdbuf();
t.close();DebugP("TRT File Loaded successfully!");
tempStream.seekg(0, std::ios::end);constint modelSize = tempStream.tellg();
tempStream.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);void* modelMem =malloc(modelSize);
tempStream.read((char*)modelMem, modelSize);
IRuntime* runtime =createInferRuntime(gLogger);if(runtime ==nullptr){DebugP("Build Runtime Failure");return0;}if(gArgs.useDLACore >=0){
runtime->setDLACore(gArgs.useDLACore);}
ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(modelMem, modelSize,nullptr);if(engine ==nullptr){DebugP("Build Engine Failure");return0;}
IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext();if(context ==nullptr){DebugP("Build Context Failure");return0;}
TensorRT* trt =newTensorRT();
trt->context = context;
trt->engine = engine;
trt->runtime = runtime;DebugP("Build trt Model Success!");return trt;}voiddoInference(IExecutionContext& context,float* input,float* output,int batchSize){const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine();assert(engine.getNbBindings()==2);void* buffers[2];int inputIndex, outputIndex;for(int b =0; b < engine.getNbBindings();++b){if(engine.bindingIsInput(b))
inputIndex = b;else
outputIndex = b;}
std::cout <<"inputIndex="<< inputIndex <<"\n";
std::cout <<"outputIndex="<< outputIndex <<"\n";// create GPU buffers and a streamCHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * INPUT_C * INPUT_H * INPUT_W *sizeof(float)));CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE *sizeof(float)));
cudaStream_t stream;CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream));// DMA the input to the GPU, execute the batch asynchronously, and DMA it back:CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * INPUT_C * INPUT_H * INPUT_W *sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream));
context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream,nullptr);CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE *sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream));cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);// release the stream and the bufferscudaStreamDestroy(stream);CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex]));CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex]));}voidPostProcessing(float* out, cv::Mat& image_clone, cv::Mat& IM, cv::Size& rawShape){
uchar colors[2][3]={{0,0,0},{128,0,0}};constexprint single_len = INPUT_W * INPUT_H;
cv::Mat mask_mat = cv::Mat::zeros(INPUT_W, INPUT_H, CV_8UC3);float src[2]={0};
uchar color_idx =0;for(size_t i =0; i < INPUT_H; i++){
uchar* mask_ptr = mask_mat.ptr<uchar>(i);for(size_t j =0; j < INPUT_W; j++){
color_idx =max_idx(out[i * INPUT_W + j], out[single_len + i * INPUT_W + j]);*mask_ptr++= colors[color_idx][2];*mask_ptr++= colors[color_idx][1];*mask_ptr++= colors[color_idx][0];}}//cv::imwrite("../mask_mat.png", mask_mat);//cv::warpAffine(mask_mat, mask_mat, IM, rawShape);//cv::addWeighted(image_clone, 0.6, mask_mat, 0.4, 0, image_clone);//cv::imwrite("../image_clone.png", image_clone);}intmain(int argc,char** argv){
IHostMemory* trtModelStream{nullptr};
TensorRT* ptensor_rt;
IExecutionContext* context =nullptr;
IRuntime* runtime =nullptr;
ICudaEngine* engine =nullptr;if(_access(trtModelName.c_str(),0)!=1){
ptensor_rt =LoadNet(trtModelName.c_str());
context = ptensor_rt->context;
runtime = ptensor_rt->runtime;
engine = ptensor_rt->engine;}else{if(!onnxToTRTModel(onnxModeName,1, trtModelStream))return1;assert(trtModelStream !=nullptr);
std::cout <<"Successfully parsed ONNX file!!!!"<< std::endl;// deserialize the engine
runtime =createInferRuntime(gLogger);assert(runtime !=nullptr);if(gArgs.useDLACore >=0){
runtime->setDLACore(gArgs.useDLACore);}
engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream->data(), trtModelStream->size(),nullptr);assert(engine !=nullptr);
trtModelStream->destroy();
context = engine->createExecutionContext();assert(context !=nullptr);}// 输入预处理
std::cout <<"Start reading the input image!!!!"<< std::endl;
cv::Mat image = cv::imread(file_name, cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
cv::cvtColor(image, image, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
cv::Mat image_clone = image.clone();
cv::Size rawShape = image.size();// 图像转成blob
cv::Mat outImage, IM;image_to_center(image, outImage, IM, cv::Scalar(128,128,128));float* blob =newfloat[INPUT_SIZE]{0};normal_image2blob(blob, outImage);float* out =newfloat[OUTPUT_SIZE]{0};// 推理计时typedef std::chrono::high_resolution_clock Time;typedef std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1,1000>> ms;typedef std::chrono::duration<float> fsec;double total =0.0;auto t0 =Time::now();doInference(*context, blob, out,1);auto t1 =Time::now();
fsec fs = t1 - t0;
ms d = std::chrono::duration_cast<ms>(fs);
total += d.count();// 网络输出的后处理PostProcessing(out, image_clone,IM, rawShape);// 释放缓存
context->destroy();
engine->destroy();
runtime->destroy();if(blob){delete[] blob;}if(out){delete[] out;}
std::cout << std::endl <<"Running time of one image is:"<< total <<"ms"<< std::endl;return0;}
编译添加预处理:
_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
版权归原作者 SongpingWang 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。