

💬推荐一款模拟面试、刷题神器 、从基础到大厂笔试题:👉点击跳转刷题网站进行注册学习
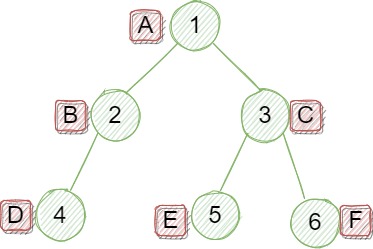
本文以该颗二叉树为例:
一、二叉树的接口
1、二叉树的结构体
typedef int BinaryDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTree
{
BinaryDataType data;
struct BinaryTree* left;
struct BinaryTree* right;
}BTNode;
一个二叉树的节点包含数据、指向左子树、右子树的指针。
2、手动造一颗二叉树
BTNode* BTBuyNode()//动态申请一个二叉树节点
{
BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
return newnode;
}
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate()//创造一颗二叉树
{
BTNode* A = BTBuyNode();BTNode* B = BTBuyNode();BTNode* C = BTBuyNode();
BTNode* D = BTBuyNode();BTNode* E = BTBuyNode();BTNode* F = BTBuyNode();
A->data = 1;B->data = 2;C->data = 3;D->data = 4;E->data = 5;F->data = 6;
A->left = B;A->right = C;
B->left = D;B->right = NULL;
C->left = E;C->right = F;
D->left = NULL;D->right = NULL;
E->left = NULL;E->right = NULL;
F->left = NULL;F->right = NULL;
return A;
}
3、二叉树的销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode** root)//二叉树的销毁
{
if (*root == NULL)
{
return;
}
BinaryTreeDestory(&(*root)->left);
BinaryTreeDestory(&(*root)->right);
free(*root);
*root = NULL;
}
注意二叉树的销毁要销毁每个节点,先销毁左右子树,再销毁根。再将根节点置空。
4、二叉树的前、中、后序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)//前序遍历
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)//中序遍历
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)//后序遍历
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
前序遍历(先根):根 、左子树、右子树
中序遍历(中根):左子树、根、右子树
后序遍历(后根):左子树、右子树 、根
5、二叉树的节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)//二叉树节点个数
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
6、二叉树的叶子节点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)//二叉树的叶子结点
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
7、二叉树第k层节点的个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)//二叉树第k层的节点个数,化简为k-1层问题
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else if (k == 1)//k走到1就是一个节点
return 1;
return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
8、求树的高度
int BinaryTreeHeight(BTNode* root)//求树的高度
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight = BinaryTreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = BinaryTreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
9、查找二叉树节点值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BinaryDataType x)//查找二叉树节点值为x的节点
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* leftRet = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
BTNode* rightRet = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
return leftRet == NULL ? rightRet : leftRet;
}
10、二叉树的层序遍历、判断一颗二叉树是否是完全二叉树
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)//二叉树的层序遍历,广度优先遍历,使用队列
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);//初始化
QueuePush(&q, root);//入队,尾插
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);//访问队头数据
QueuePop(&q);//出队(头删)
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left != NULL)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);//入队,尾插
if (front->right != NULL)
QueuePush(&q, front->right);//入队,尾插
}
QueueDestroy(&q);//销毁
}
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)//判断一颗树是否是完全二叉树,层序判断
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);//初始化
QueuePush(&q, root);//入队,尾插
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);//访问队头数据
if (front == NULL)//当队头为NULL时,后续全是NULL,则为完全二叉树
break;
QueuePop(&q);//出队(头删)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);//入队,尾插
QueuePush(&q, front->right);//入队,尾插
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);//访问队头数据
if (front != NULL)
return false;
QueuePop(&q);//出队(头删)
}
QueueDestroy(&q);//销毁
return true;
}
二叉树的层序遍历可以使用队列来完成,先将根节点入队,根节点出队时将自己的左右节点带入队列中。注意,这里要带入节点而不是节点的值(因为你把节点的值入队列,那节点的值是没有办法找到它的左右子树的)
判断一颗二叉树是不是一颗完全二叉树,同样使用队列来进行判断,先对节点不断入队,出队时遇到NULL,就跳出第一个循环。加入第二个循环如果这是一颗完全二叉树,那么继续出队将全是NULL,如果不是,将会遇到不为空的节点。
二、二叉树相关OJ题
1、二叉树的前序遍历
思路:
这道题的参数只有一个root,还需要知道二叉树的节点个数,用于动态申请空间用于存储节点值。
1、求出二叉树节点个数
2、因为原函数开辟了空件,不能对原函数递归,需要写一个前序遍历函数。
代码:
int BinaryTreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)//节点个数
{
return root==NULL?0:BinaryTreeSize(root->left)+BinaryTreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
void PreOrdre(struct TreeNode* root,int* arr,int* pi)//前序遍历
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return;
}
arr[(*pi)++]=root->val;
PreOrdre(root->left,arr,&pi);
PreOrdre(root->right,arr,&pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
int size=BinaryTreeSize(root);
*returnSize=size;
int* arr=(struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
int i=0;
PreOrdre(root,arr,&i);
return arr;
}
注意这里的i需要传入i的地址,因为i需要改变,所以要传入i的地址,并且i在递归调用时,属于不同的栈帧空间,需要使用i的地址将改变的i带回。
2、单值二叉树

思路:
判断false的情况,再进行递归,左右子树有一个为false,整体为false
代码:
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if(root->left!=NULL&&root->val!=root->left->val)
return false;
if(root->right!=NULL&&root->val!=root->right->val)
return false;
bool left=isUnivalTree(root->left);
bool right=isUnivalTree(root->right);
return left==false?false:right;
}
3、二叉树的最大深度

思路:
就是求二叉树的高度
代码:
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight=maxDepth(root->left);
int rightHeight=maxDepth(root->right);
return leftHeight>rightHeight?leftHeight+1:rightHeight+1;
}
4、翻转二叉树
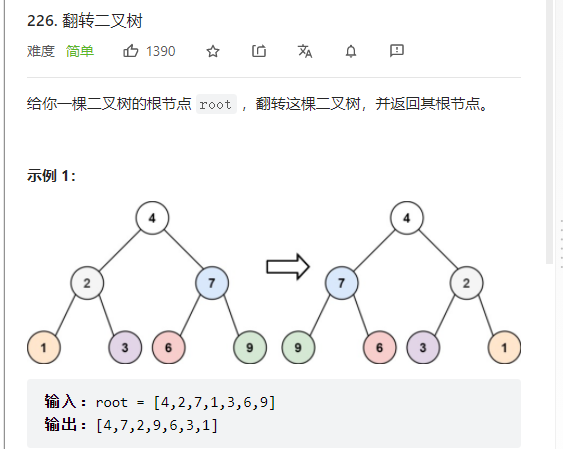
思路:

代码:
void Swap(struct TreeNode** left,struct TreeNode** right)
{
struct TreeNode* tmp=*left;
*left=*right;
*right=tmp;
}
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)
return NULL;
Swap(&(root->left),&(root->right));
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
5、相同的树
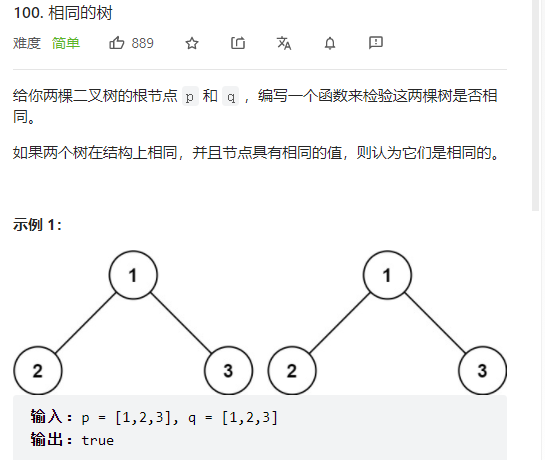
思路:
思路和本文第二题类似,先把一遍的情况全部罗列出来,再执行递归。本题相同的树需要考虑p和q均为空指针、p和q是否均有节点、p和q指向的节点的值是否相等。
代码:
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
return true;
if((p==NULL&&q!=NULL)||(p!=NULL&&q==NULL))
return false;
if(p->val!=q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
6、对称二叉树
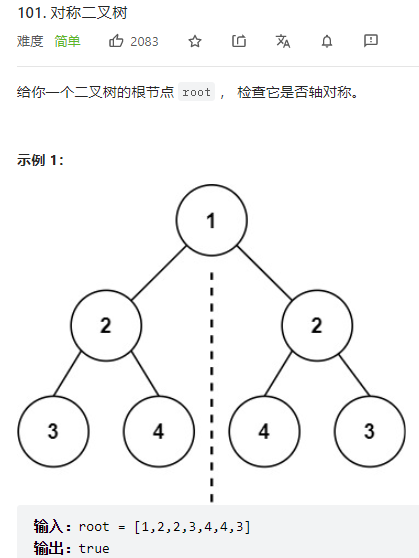
思路:
判断一颗二叉树是不是轴对称,那么只需要判断它的子树是不是轴对称
1、如果左树为空,右树不为空,false
2、如果左树不为空,右树为空,false
3、如果左树右树均为空,true
4、如果左树值等于右树值且左树的左子树和右树的右子树且左树的右子树和右树的左子树,true
代码:
bool A(struct TreeNode* leftTree,struct TreeNode* rightTree)
{
if(leftTree==NULL&&rightTree!=NULL)
return false;
if(leftTree!=NULL&&rightTree==NULL)
return false;
if(leftTree==NULL&&rightTree==NULL)
return true;
if((leftTree->val==rightTree->val)&&A(leftTree->left,rightTree->right)
&&A(leftTree->right,rightTree->left))
return true;
return false;
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)
return true;
return A(root->left,root->right);
}
7、另一颗数的子树

思路:
复用本文第5题,相同的树接口,就很简单了
代码:
bool isSametree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot)
{
if(root==NULL&&subRoot==NULL)
return true;
if(root==NULL||subRoot==NULL)
return false;
if(root->val!=subRoot->val)
return false;
return isSametree(root->left,subRoot->left)
&&isSametree(root->right,subRoot->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot){
if(isSametree(root,subRoot))
return true;
if(root==NULL)
return false;
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
8、平衡二叉树
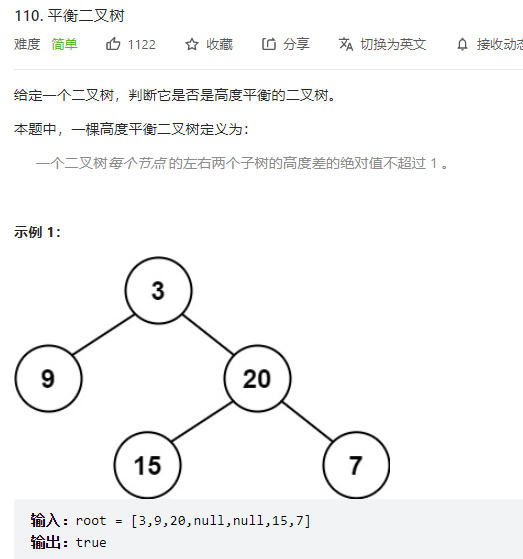
思路:
1、根节点为空,true
2、计算左树的高度、计算右树的高度
3、绝对值是否大于1
4、返回根节点左子树并且右子树的情况
代码:
int BinaryTreeHeight(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight=BinaryTreeHeight(root->left)+1;
int rightHeight=BinaryTreeHeight(root->right)+1;
return leftHeight>rightHeight?leftHeight:rightHeight;
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)
return true;
int leftHeight=BinaryTreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight=BinaryTreeHeight(root->right);
if(abs(leftHeight-rightHeight)>1)
return false;
return isBalanced(root->left)&&isBalanced(root->right);
}
9、二叉树遍历

思路:
1、如果arr[*i]是'#',那么返回NULL
2、如果arr[*i]不是'#',创建一个节点并将对应数组的值赋给这个节点
3、递归左树,递归右树,返回根节点
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct BinaryTree
{
char data;
struct BinaryTree* left;
struct BinaryTree* right;
}BTNode;
void InOrder(BTNode* root)//中序遍历
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
BTNode* create(char* arr,int* i)
{
if(arr[*i]=='#')
{
++(*i);
return NULL;
}
BTNode* root=(BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
root->data=arr[(*i)++];//如果能到这一步,说明arr[*i]不是#
root->left=create(arr,i);
root->right=create(arr,i);
return root;
}
int main()
{
char arr[101];
scanf("%s",arr);
int i=0;//数组下标
BTNode* root=create(arr,&i);
InOrder(root);//中序遍历
return 0;
}
版权归原作者 蒋灵瑜的笔记本 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。