扩散模型代码详细解读
代码地址:denoising-diffusion-pytorch/denoising_diffusion_pytorch.py at main · lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch (github.com)
前向过程和后向过程的代码都在
GaussianDiffusion
这个类中。
有问题可以一起讨论!
常见问题解决
Why self-conditioning? · Issue #94 · lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch (github.com)
"pred_x0" preforms better than "pred_noise" · Issue #58 · lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch (github.com)
What is objective=pred_x0 and how do you use it? · Issue #34 · lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch (github.com)
Conditional generation · Issue #7 · lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch (github.com)
Questions About DDPM · Issue #10 · lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch (github.com)
The difference between pred_x0, pred_v, pred_noise three objectives · Issue #153 · lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch (github.com)
前向训练过程
p_losses
首先是p_losses函数,这个是训练过程的主体部分。
defp_losses(self, x_start, t, noise =None):
b, c, h, w = x_start.shape
# 首先随机生成噪声
noise = default(noise,lambda: torch.randn_like(x_start))# noise sample# 噪声采样,注意这个是一次性完成的
x = self.q_sample(x_start = x_start, t = t, noise = noise)# if doing self-conditioning, 50% of the time, predict x_start from current set of times# and condition with unet with that# this technique will slow down training by 25%, but seems to lower FID significantly# 判断是否进行self-condition,就是利用前面步骤预测出的x0来辅助当前的预测
x_self_cond =Noneif self.self_condition and random()<0.5:with torch.no_grad():
x_self_cond = self.model_predictions(x, t).pred_x_start
x_self_cond.detach_()# predict and take gradient step# 将采样的x和self condition的x一起输入到model当中,这个model是UNet结构
model_out = self.model(x, t, x_self_cond)# 模型预测的目标,分为三种if self.objective =='pred_noise':
target = noise
elif self.objective =='pred_x0':
target = x_start
elif self.objective =='pred_v':
v = self.predict_v(x_start, t, noise)
target = v
else:raise ValueError(f'unknown objective {self.objective}')# 计算损失
loss = self.loss_fn(model_out, target, reduction ='none')
loss =reduce(loss,'b ... -> b (...)','mean')
loss = loss * extract(self.p2_loss_weight, t, loss.shape)return loss.mean()
对其中的extract函数进行分析,extract函数实现如下:
defextract(a, t, x_shape):# Extract some coefficients at specified timesteps,# then reshape to [batch_size, 1, 1, 1, 1, ...] for broadcasting purposes.
b,*_ = t.shape
# 使用了gather函数
out = a.gather(-1, t)return out.reshape(b,*((1,)*(len(x_shape)-1)))
q_sample
然后介绍p_losses函数中使用的其他函数,第一个是q_sample函数,它的作用是加上噪声,对应论文的公式: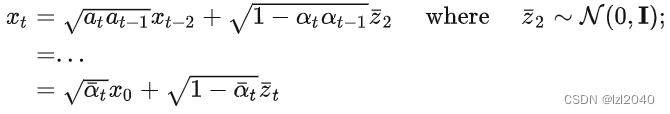
其中
self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod
和
self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod
分别是alpha的累乘值和1-alpha的累乘值,x_start相当于x0,noise相当于z。
defq_sample(self, x_start, t, noise=None):
noise = default(noise,lambda: torch.randn_like(x_start))return(
extract(self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape)* x_start +
extract(self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape)* noise
)
model_predictions
然后是model_predictions函数,它的实现如下:
defmodel_predictions(self, x, t, x_self_cond =None, clip_x_start =False):# 输入到UNet结构中获得输出
model_output = self.model(x, t, x_self_cond)
maybe_clip = partial(torch.clamp,min=-1.,max=1.)if clip_x_start else identity
# 暂不明确它的作用if self.objective =='pred_noise':
pred_noise = model_output
x_start = self.predict_start_from_noise(x, t, pred_noise)
x_start = maybe_clip(x_start)elif self.objective =='pred_x0':
x_start = model_output
x_start = maybe_clip(x_start)
pred_noise = self.predict_noise_from_start(x, t, x_start)elif self.objective =='pred_v':
v = model_output
x_start = self.predict_start_from_v(x, t, v)
x_start = maybe_clip(x_start)
pred_noise = self.predict_noise_from_start(x, t, x_start)# 返回得到的噪声和return ModelPrediction(pred_noise, x_start)
几种objective
model_predictions函数中有一个难点,就是其中的self.objective,它有三种形式:
- pred_noise:这个相当于是预测噪声,此时UNet模型的输出是噪声
- pred_x0:这个相当于是预测最开始的x,此时UNet模型的输出是去噪的图像
- pred_v:这个相当于是预测速度v,它在这篇文章中提出。然后根据速度求出最开始的x,最后预测出噪声。
如图所示:
在上面的三种objective中,还涉及到了几种预测方法的实现,具体如下:
(1)predict_start_from_noise:这个函数的作用是根据噪声noise预测最开始的x,也就是去噪的图像。
其中
self.sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod
和
self.sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod
来自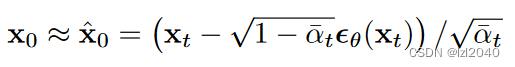
公式,它们分别为:
和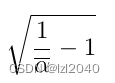
。
公式来源文章:DDPM
defpredict_start_from_noise(self, x_t, t, noise):return(
extract(self.sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape)* x_t -
extract(self.sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape)* noise
)
它对应论文中的公式如下: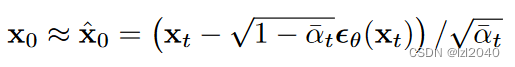
(2)predict_noise_from_start:这个函数的作用是根据图像预测噪声,也就是加噪声。
defpredict_noise_from_start(self, x_t, t, x0):return((extract(self.sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape)* x_t - x0)/ \
extract(self.sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape))
它对应论文中的公式如下: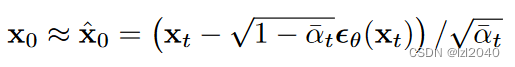
需要注意它是反推过来的,过程如下:
(3)predict_v:预测速度v
defpredict_v(self, x_start, t, noise):return(
extract(self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape)* noise -
extract(self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape)* x_start
)
它对应论文中的公式: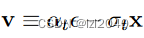
(4)predict_start_from_v:根据速度v预测最初的x,也就是图像
defpredict_start_from_v(self, x_t, t, v):return(
extract(self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape)* x_t -
extract(self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape)* v
)
它对应论文中的公式如下: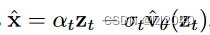 其中zt相当于xt。
其中zt相当于xt。
后向采样过程
sample函数
@torch.no_grad()defsample(self, batch_size =16, return_all_timesteps =False):
image_size, channels = self.image_size, self.channels
# 采样的函数
sample_fn = self.p_sample_loop ifnot self.is_ddim_sampling else self.ddim_sample
# 调用该函数return sample_fn((batch_size, channels, image_size, image_size), return_all_timesteps = return_all_timesteps)
该函数的作用是获取采样的函数然后进行调用,采样函数分成两种:p_sample_loop和ddim_sample。
p_sample_loop函数
@torch.no_grad()defp_sample_loop(self, shape, return_all_timesteps =False):
batch, device = shape[0], self.betas.device
# 随机生成噪声图像
img = torch.randn(shape, device = device)
imgs =[img]
x_start =None# 遍历所有的tfor t in tqdm(reversed(range(0, self.num_timesteps)), desc ='sampling loop time step', total = self.num_timesteps):# 判断是否使用self-condition
self_cond = x_start if self.self_condition elseNone# 进行采样,得到去噪的图像
img, x_start = self.p_sample(img, t, self_cond)
imgs.append(img)# 判断是否返回每个步骤的img还是最后一步的img
ret = img ifnot return_all_timesteps else torch.stack(imgs, dim =1)# 归一化
ret = self.unnormalize(ret)return ret
其中涉及到归一化函数
self.unnormalize
,含有两种
# normalization functionsdefnormalize_to_neg_one_to_one(img):return img *2-1defunnormalize_to_zero_to_one(t):return(t +1)*0.5
p_sample函数
@torch.no_grad()defp_sample(self, x, t:int, x_self_cond =None):
b,*_, device =*x.shape, x.device
batched_times = torch.full((b,), t, device = x.device, dtype = torch.long)# 获得平均值,方差和x0
model_mean, _, model_log_variance, x_start = self.p_mean_variance(x = x, t = batched_times, x_self_cond = x_self_cond, clip_denoised =True)# 随机生成一个噪声
noise = torch.randn_like(x)if t >0else0.# no noise if t == 0# 得到预测的图像,img = 平均值 + exp(0.5 * 方差) * noise
pred_img = model_mean +(0.5* model_log_variance).exp()* noise
return pred_img, x_start
p_mean_variance函数
其中含有
p_mean_variance
函数,代码实现如下:
defp_mean_variance(self, x, t, x_self_cond =None, clip_denoised =True):# 输入到UNet网络进行预测
preds = self.model_predictions(x, t, x_self_cond)# 得到预测的x0
x_start = preds.pred_x_start
# 压缩x0中值的范围至[-1,1]if clip_denoised:
x_start.clamp_(-1.,1.)# 得到x0后根据xt和t得到分布的平均值和方差
model_mean, posterior_variance, posterior_log_variance = self.q_posterior(x_start = x_start, x_t = x, t = t)return model_mean, posterior_variance, posterior_log_variance, x_start
q_posterior函数
其中
q_posterior
函数的实现如下:
defq_posterior(self, x_start, x_t, t):# 计算平均值
posterior_mean =(
extract(self.posterior_mean_coef1, t, x_t.shape)* x_start +
extract(self.posterior_mean_coef2, t, x_t.shape)* x_t
)# 计算方差
posterior_variance = extract(self.posterior_variance, t, x_t.shape)# 获得一个压缩范围的方差,且取对数
posterior_log_variance_clipped = extract(self.posterior_log_variance_clipped, t, x_t.shape)return posterior_mean, posterior_variance, posterior_log_variance_clipped
平均值和方差对应的公式如下:
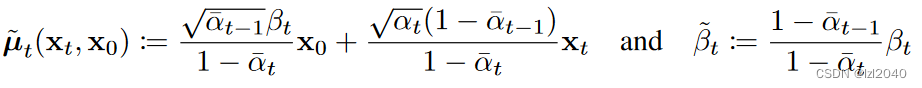
其中
self.posterior_mean_coef1
对应的是x0前面的系数,
self.posterior_mean_coef2
对应的是xt前面的系数。
self.posterior_variance
对应的beta那部分的系数。
ddim_sample函数
@torch.no_grad()defddim_sample(self, shape, return_all_timesteps =False):
batch, device, total_timesteps, sampling_timesteps, eta, objective = shape[0], self.betas.device, self.num_timesteps, self.sampling_timesteps, self.ddim_sampling_eta, self.objective
times = torch.linspace(-1, total_timesteps -1, steps = sampling_timesteps +1)# [-1, 0, 1, 2, ..., T-1] when sampling_timesteps == total_timesteps
times =list(reversed(times.int().tolist()))
time_pairs =list(zip(times[:-1], times[1:]))# [(T-1, T-2), (T-2, T-3), ..., (1, 0), (0, -1)]
img = torch.randn(shape, device = device)
imgs =[img]
x_start =Nonefor time, time_next in tqdm(time_pairs, desc ='sampling loop time step'):
time_cond = torch.full((batch,), time, device = device, dtype = torch.long)
self_cond = x_start if self.self_condition elseNone
pred_noise, x_start,*_ = self.model_predictions(img, time_cond, self_cond, clip_x_start =True)
imgs.append(img)if time_next <0:
img = x_start
continue
alpha = self.alphas_cumprod[time]
alpha_next = self.alphas_cumprod[time_next]
sigma = eta *((1- alpha / alpha_next)*(1- alpha_next)/(1- alpha)).sqrt()
c =(1- alpha_next - sigma **2).sqrt()
noise = torch.randn_like(img)
img = x_start * alpha_next.sqrt()+ \
c * pred_noise + \
sigma * noise
ret = img ifnot return_all_timesteps else torch.stack(imgs, dim =1)
ret = self.unnormalize(ret)return ret
上面部分依据的公式为:(文章)
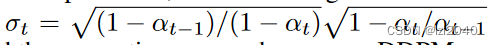
训练的模型(UNet)
后续会继续更新!
对您有帮助请点赞收藏哦!
版权归原作者 lzl2040 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。