1.gazebo 仿真环境创建
安装依赖:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-gazebo-ros-control
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-effort-controllers
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-joint-state-controller
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-driver-base
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-ackermann-msgs
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-rtabmap-ros
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-teb-local-planner
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt install tcl-dev tk-dev python3-tk
若在安装依赖的过程中出现以下错误:
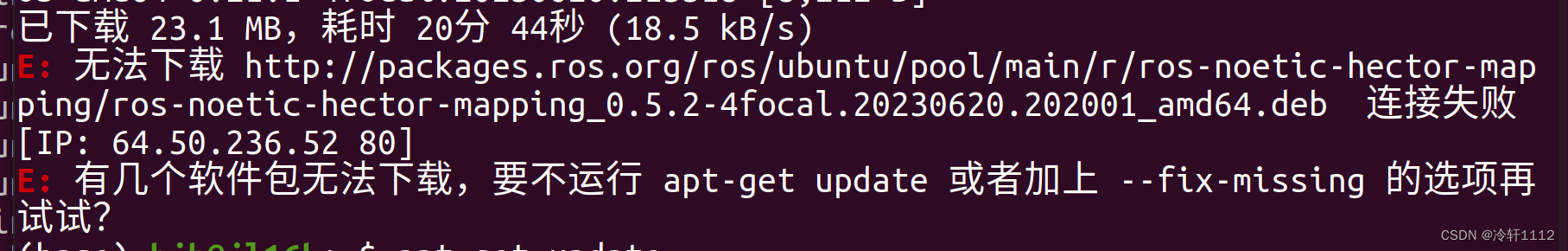
通过输入以下代码尝试解决:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo apt-get update
创建工作空间:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ mkdir -p catkin_gazebo_ws/src
下载git工程:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ cd src
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws/src$ git clone https://github.com/soonuse/racecar.git
编译:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws/src$ cd ..
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ catkin_make
如果编译过程中出现以下错误:
错误1:
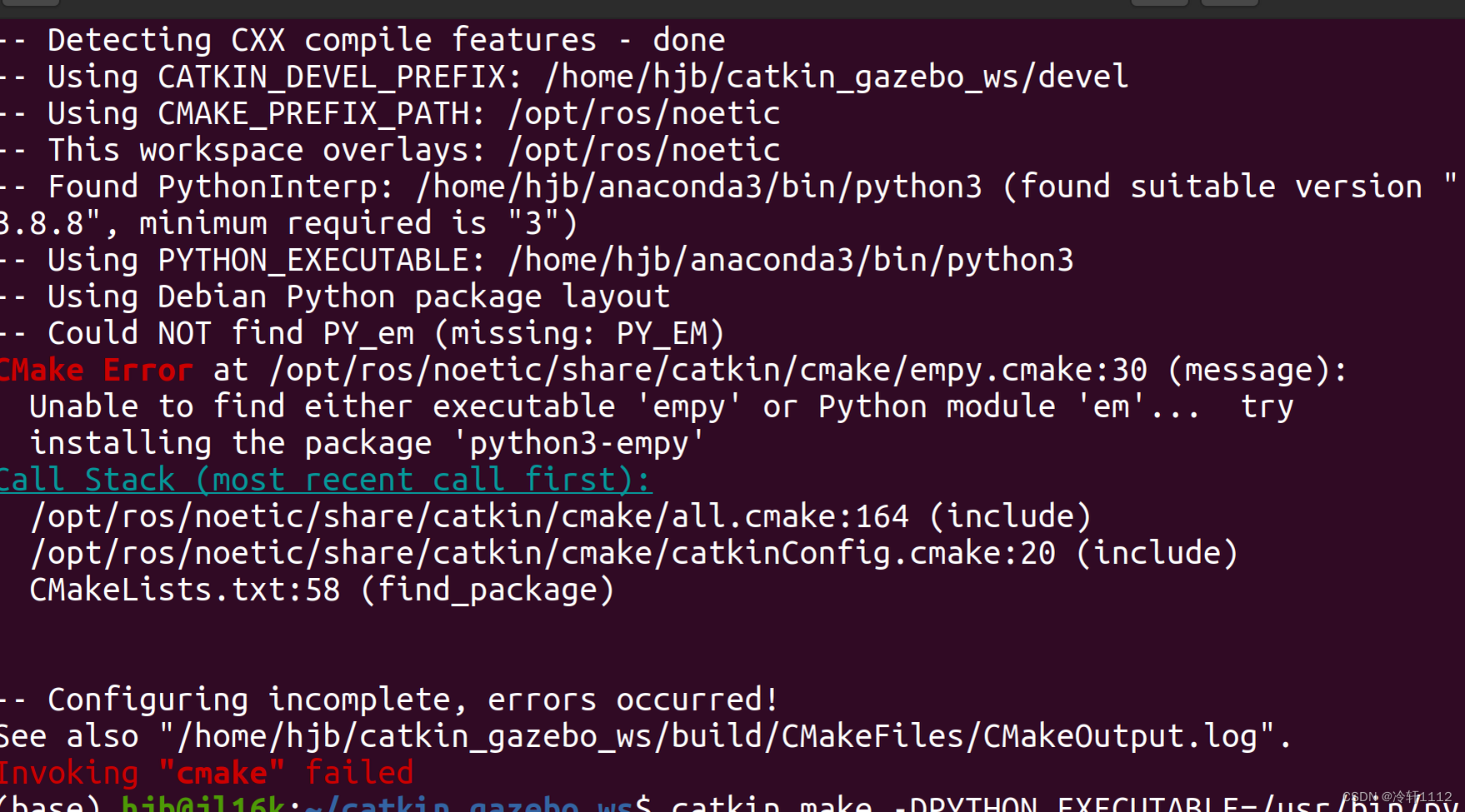
解决办法:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ catkin_make -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=/usr/bin/python3
错误2:

解决办法:
找到自己的opencv安装路径,像我的就是 /usr/local/include/opencv4/opencv2
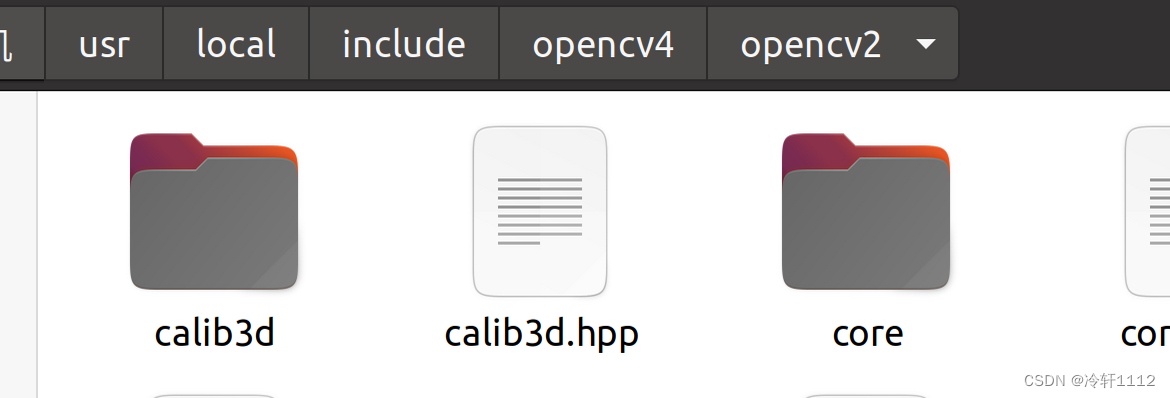
然后打开提示错误的这个文件,当然这个文件只可读,可以使用以下命令打开并修改:

(base) hjb@jl16k:/opt/ros/noetic/share/cv_bridge/cmake$ sudo gedit cv_bridgeConfig.cmake
大概在90多行,将箭头所指修改成上面找到的opencv安装路径,注意修改两个地方
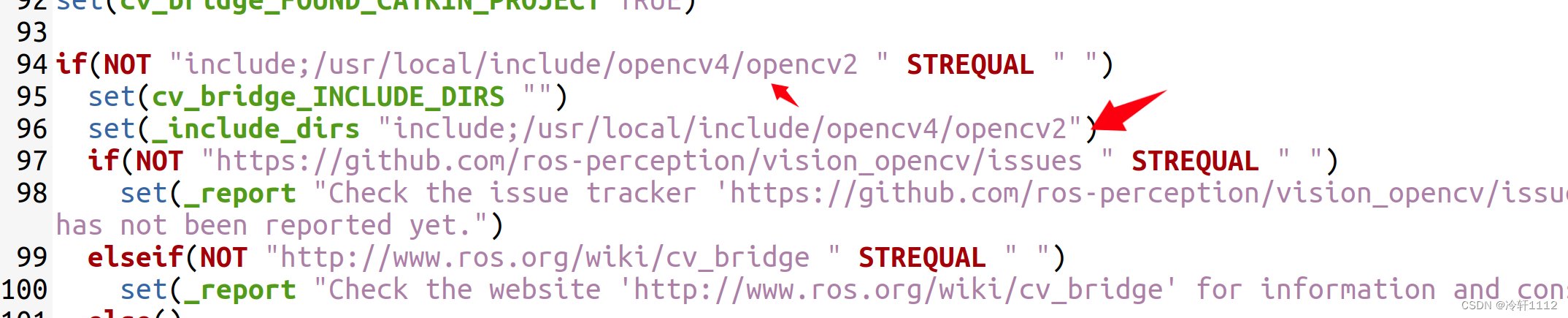
修改完之后,重新编译:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ catkin_make -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=/usr/bin/python3
把工作区的setup.bash文件写入.bashrc文件中,先执行以下命令,然后得到路径/home/hjb/catkin_gazebo_ws/devel
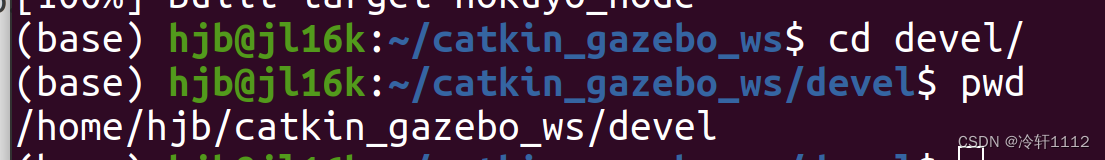 打开新的终端:
打开新的终端:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ sudo gedit .bashrc
添加下图中的两行,路径就是上面所得到的路径并加上setup.bash文件名:

保存文件,为了使用配置,输入:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ . .bashrc
** 需要注意的是,这个仿真环境是从网上下载的,也就是git那一步。需要了解这个工作空间中各个文件的用处:**
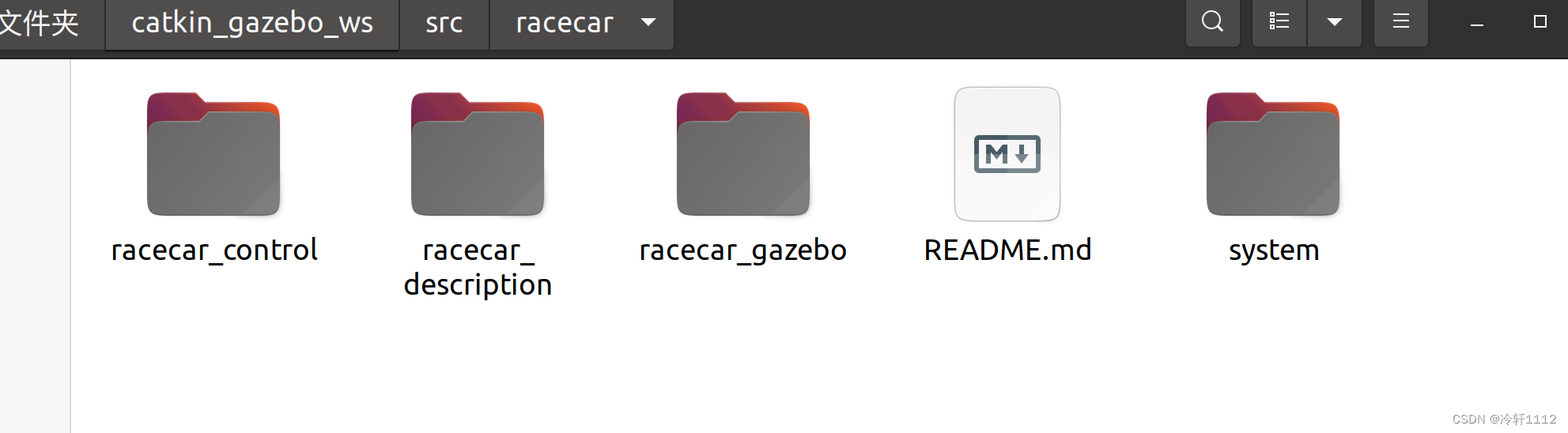
像途中racecar_description里面存的是机器人模型(urdf)等,而racecar_gazebo里面是放与Gazebo有关的启动文件(launch)和世界文件(word)等。这个工作空间完全是可以自己创建的,其中图所示名字也是可以改变的,例如racecar_description完全可以改成myrobot_description,当然这是有能力自己创建的前提下。
2.gazebo的使用
初次使用gazebo的可以参考一下,里面有一些功能建的说明与使用:ROS入门(四)——Gazebo的基本使用 - 古月居
(1)简单创建一个地图模型
首先进入gazebo:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ gazebo
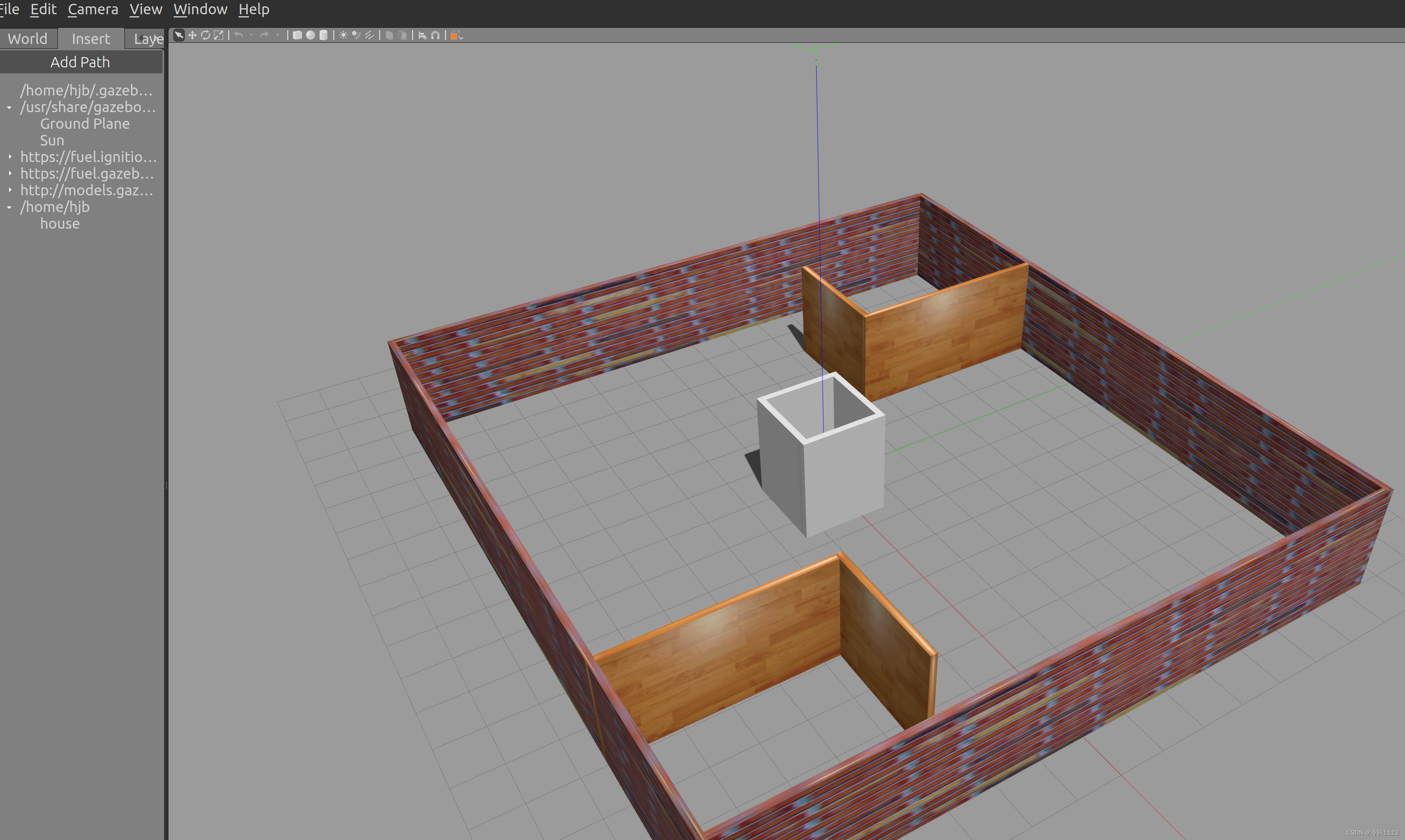
然后左上角点击Edit,选择Buiding Editor,进入下图界面

可以看到左窗口有walls(墙)等,点击wall简单创建一个房子后,点击左上角File,然后选择Save,建议第一次使用保存在主目录(home)下。如下图所示,我保存下来的是house文件,命名是随意的。打开house文件会发现有两个文件。
保存完之后,选择File Exit Building Editor,然后会有弹窗,选择Exit。就会回到原来的界面。如下图所示。
这个就属于world文件了,点击File,选择Save world,名字最好加上world(注意这个文件后缀记得加 .world,保存的时候不会默认是world文件的,需要自己加,图中我是保存错了)以区分这是一个world文件,然后也是先保存在主目录,以后熟练了可以根据需求保存。保存完之后目录下的文件如下图所示:

到此,关掉gazebo。那又该如何打开之前建好的模型呢?
重新打开gazebo,点击左窗口的Insert,然后看到我下图箭头所指,这个就是上面所建的模型,点击即可拉到界面。
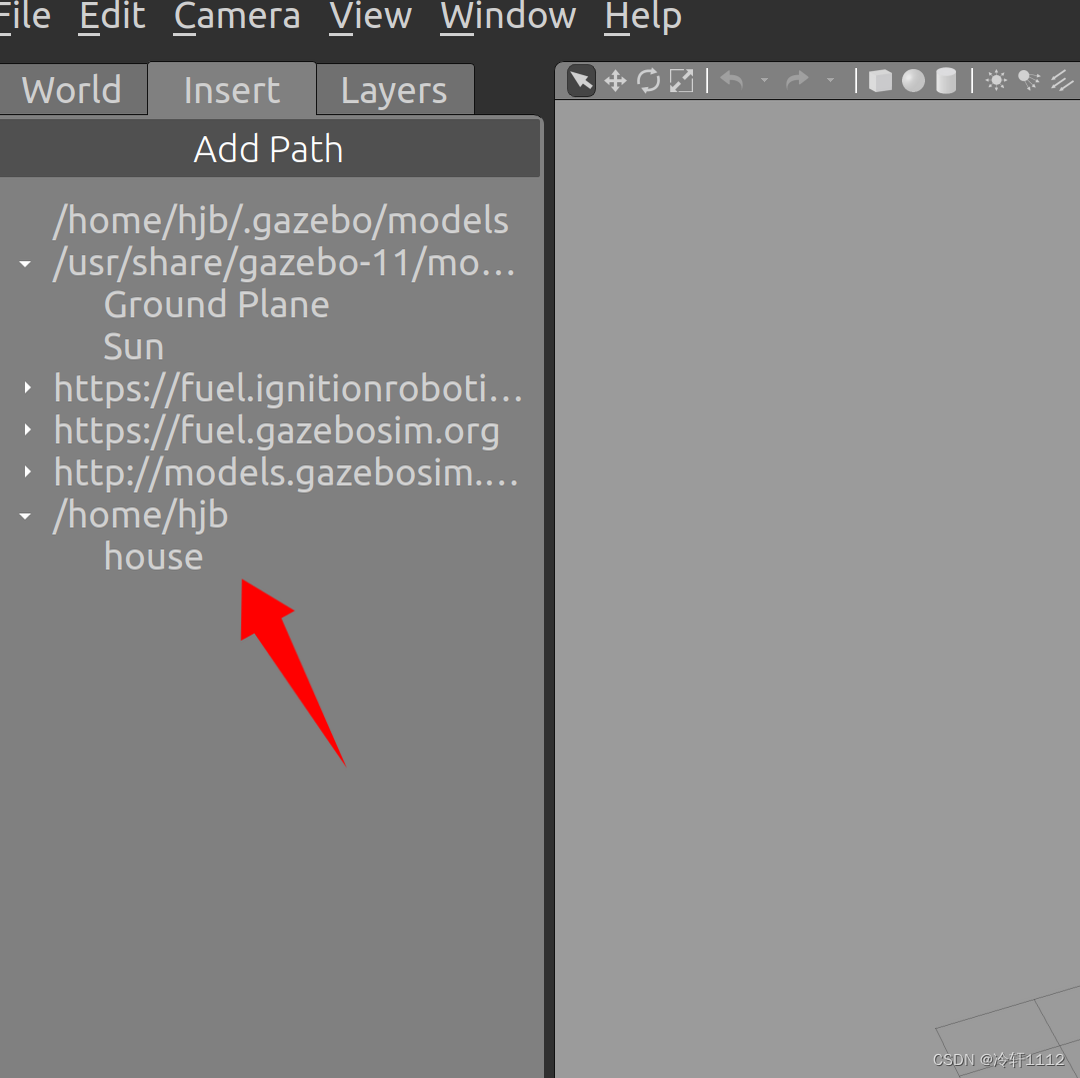
当然值的注意的是,上面的例子是墙体模型,也有其他的模型,这需要慢慢去探索了。
(2)下载模型
一般来说,如果有现成的图形模型的话,那就大大节省了自己的时间,可以使用有的模型来做实验。
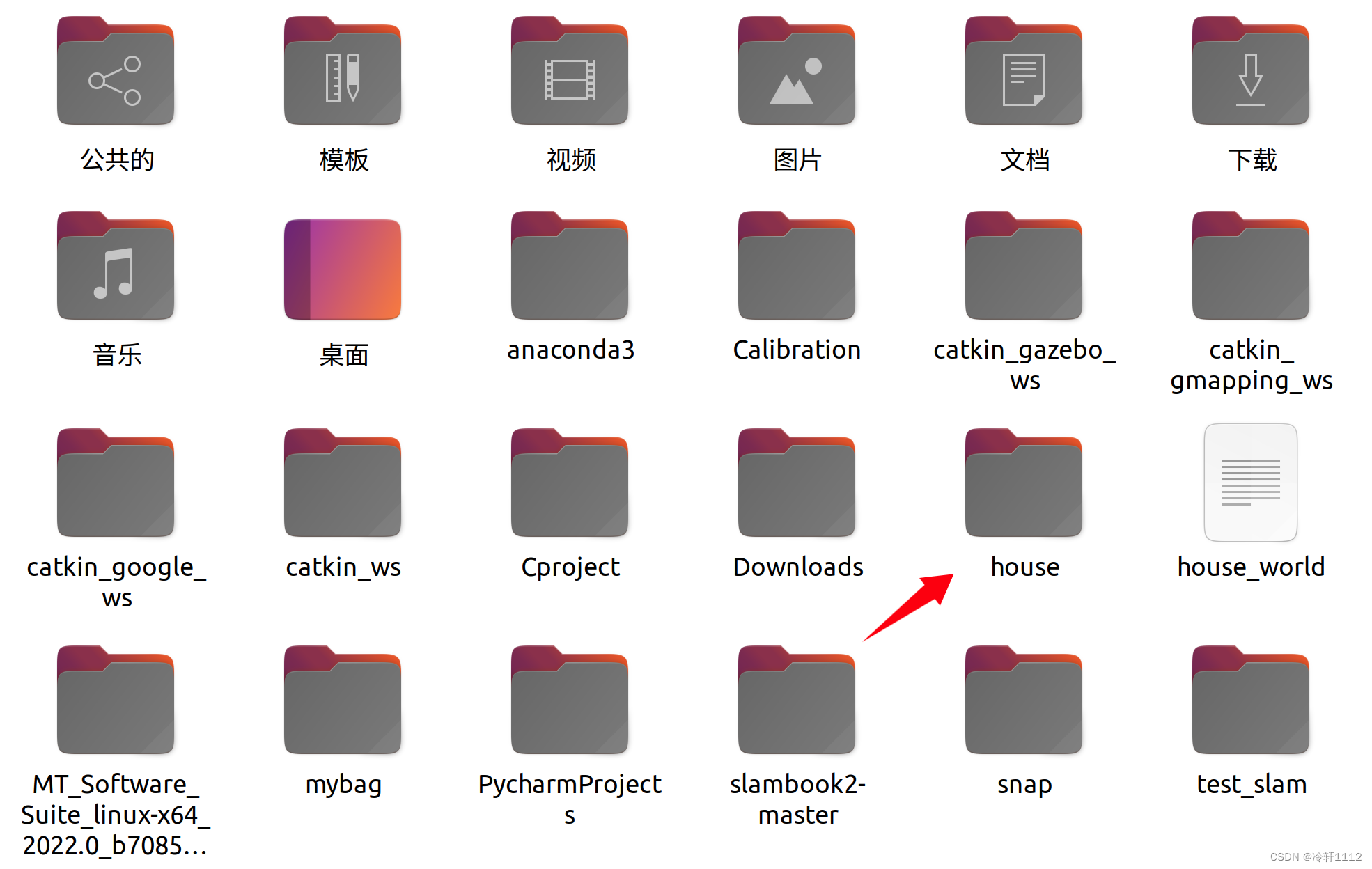
下载模型有两种反法,我用的是第二种方法,因为第一种方法可能是我的网不行下载的非常慢,虽然第二种方法我也下载了3个多小时。
方法1:注意的是.gazebo是隐藏的文件,可以在主目录(home)使用ctrl+H来显示出来,此外使用该方法下载的文件名为gazebo_models,需要将这个文件名改为models
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ cd ~/.gazebo
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/.gazebo$ git clone https://github.com/osrf/gazebo_models
方法2:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ cd ~/.gazebo
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/.gazebo$ mkdir -p models
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/.gazebo$ cd models/
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/.gazebo/models$ wget http://file.ncnynl.com/ros/gazebo_models.txt
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/.gazebo/models$ wget -i gazebo_models.txt
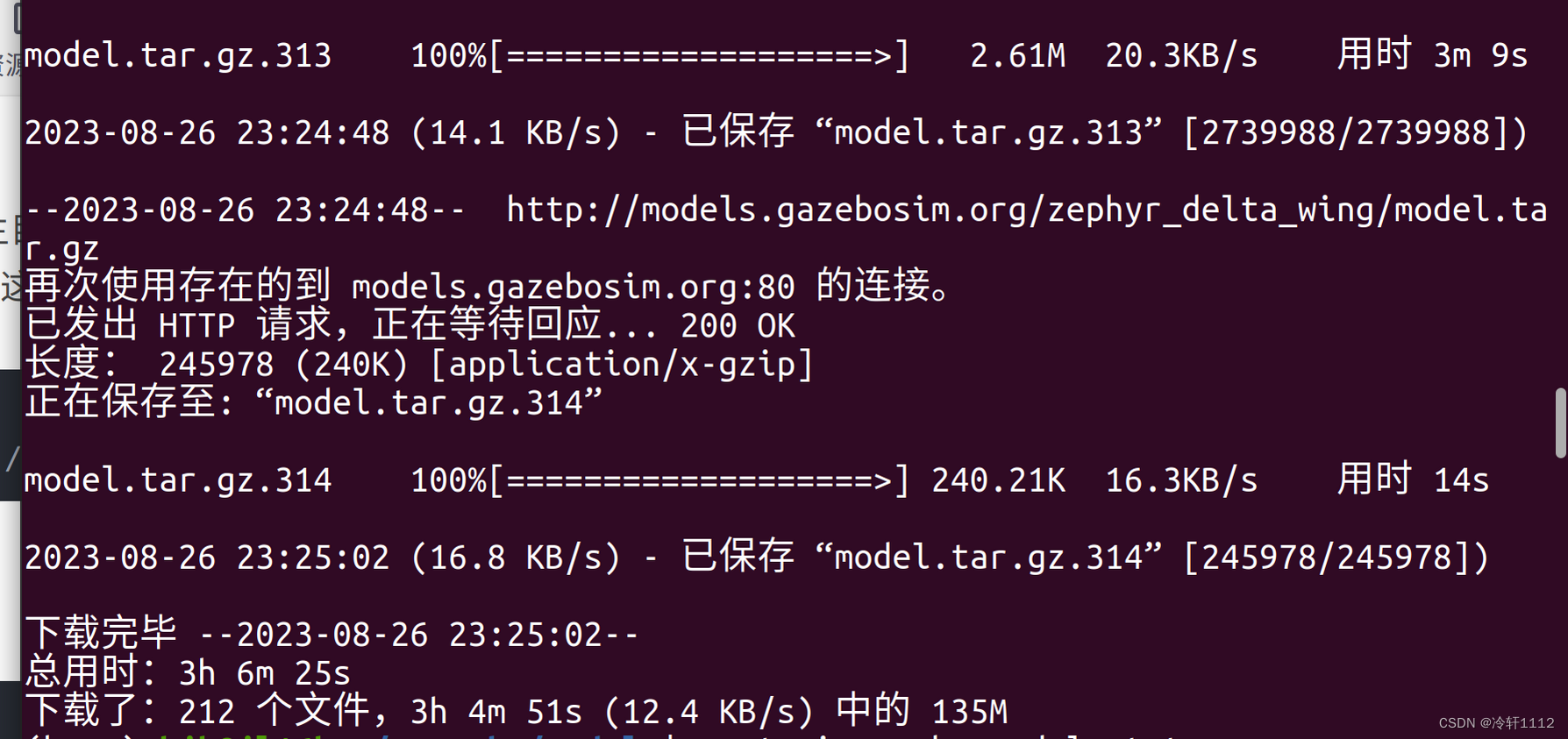
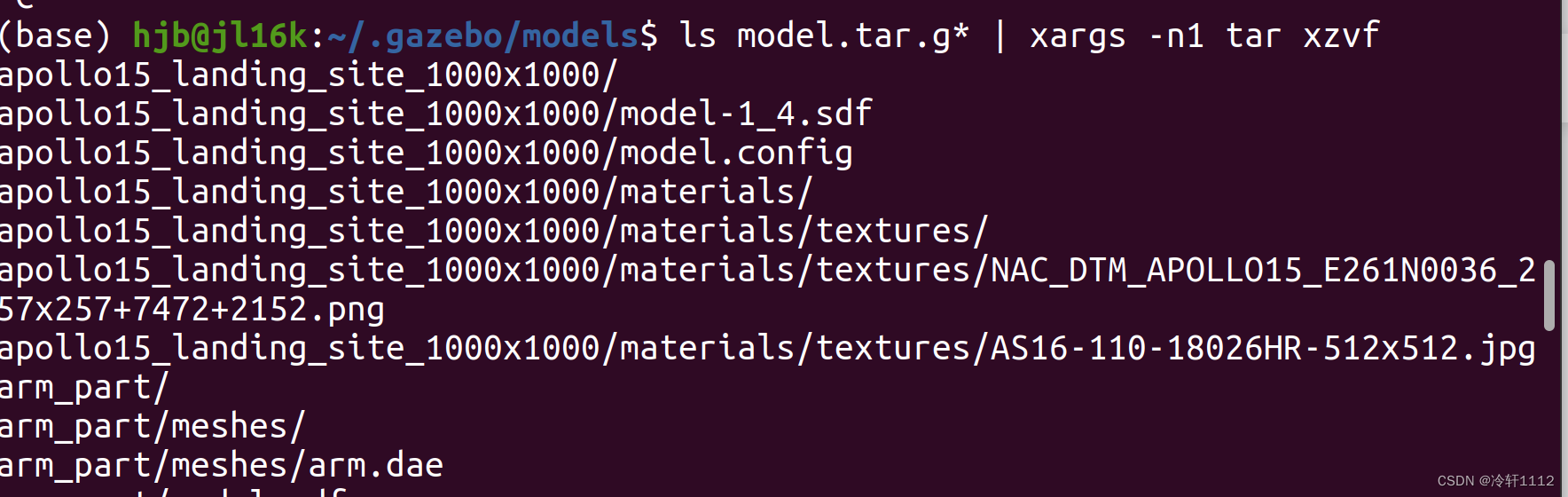
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/.gazebo/models$ ls model.tar.g* | xargs -n1 tar xzvf
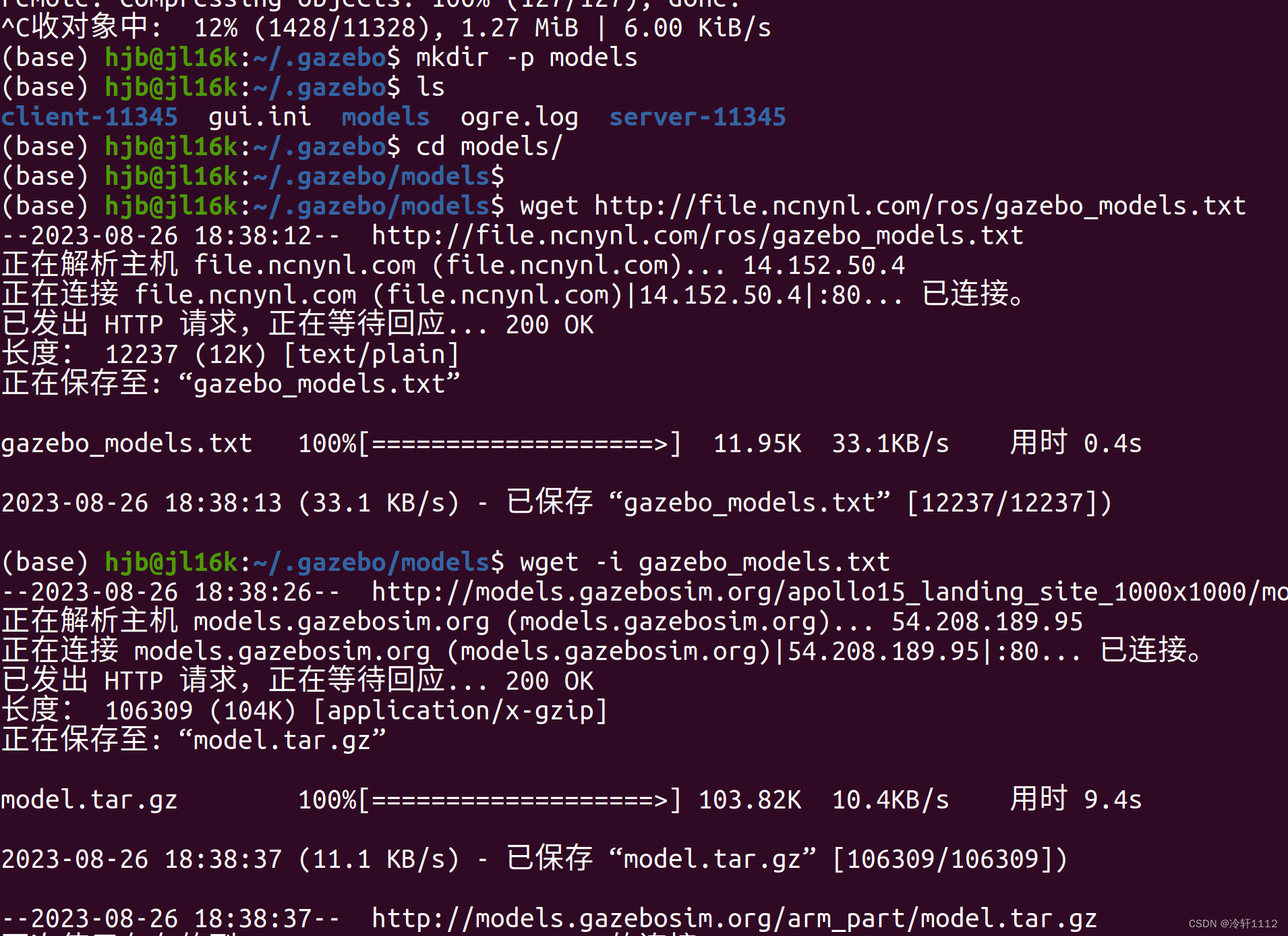
如果到下图这一步,应该算成功了吧。我也是刚入门不太懂,从文字上看下载了135M,应该不止这么小的。重复方法2倒数第二条命令还可以下载,我浅浅试了一下,不过我终止了,以后有需要再尝试一下吧。 最后解压一下就Ok了。
打开gazebo:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ gazebo
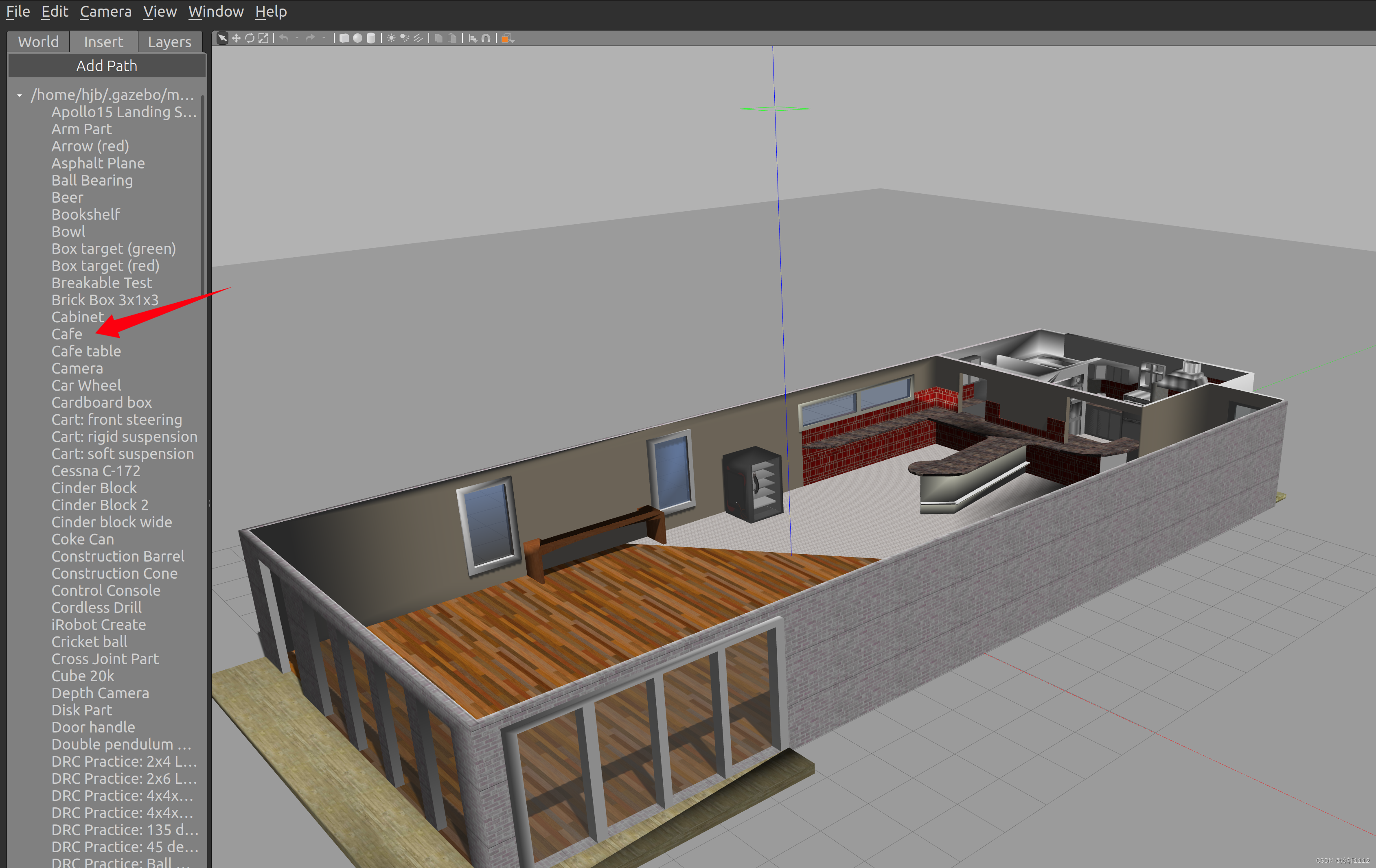
进入下图界面会发现,本地模型有了,随便拉一个进入 ,有显示就成功了。我拉了cafe这个模型进去。
(3)world模型的打开,使用launch文件
此前建了一个模型,有house的地图模型,以及world模型。

上面所示的打开是使用house模型,而建好的world场景又如何打开呢?这就得用launch文件打开了。
如下图所示,一般仿真环境都会有保存launch文件的功能包,像我这个环境存放launch文件的是racecar_gazebo,并且在这个功能包中有worlds文件,所创建的world文件应该拉到这个地方。所以将上面创建的house.world文件拉到worlds文件中,方便写launch文件。

写文件推荐使用vscode,用vscode打开catkin_gazebo_ws这个工作空间,然后在launch文件夹中创建一个launch文件,我创建的文件名为 display_house_world_in_gazebo.launch,这样创建可以知道这个launch文件是干嘛的,从意思上看我这个就是在gazebo中展示house.world。
代码如下,唯一要修改的就是 <arg name="world_name" value="$(find racecar_gazebo)/worlds/house_world_as.world"/>这一行了,自己world文件的路径如果不同根据自己作修改,$(find racecar_gazebo)就是找到racecar_gazebo这个功能包的路径,如果创建的功能包名字不一样修改一下就好了:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<launch>
<!-- We resume the logic in empty_world.launch, changing only the name of the world to be launched -->
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find racecar_gazebo)/worlds/house_world_as.world"/>
<arg name="paused" value="false"/>
<arg name="use_sim_time" value="true"/>
<arg name="gui" value="true"/>
<arg name="headless" value="false"/>
<arg name="debug" value="false"/>
</include>
</launch>
然后执行一下命令即可看到打开的world文件:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ roslaunch racecar_gazebo display_house_world_in_gazebo.launch
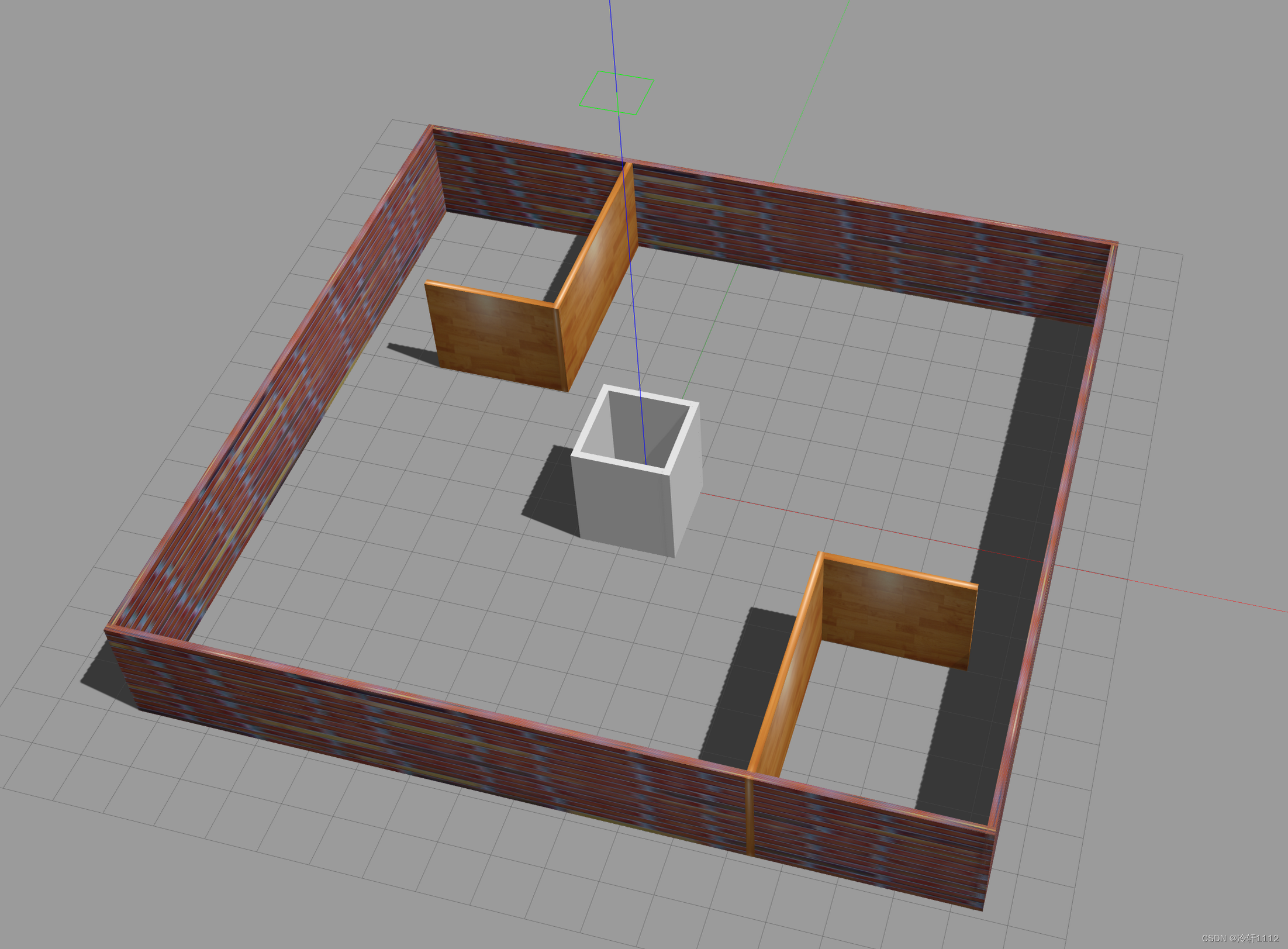
(4)world模型+小车模型的打开,使用launch文件
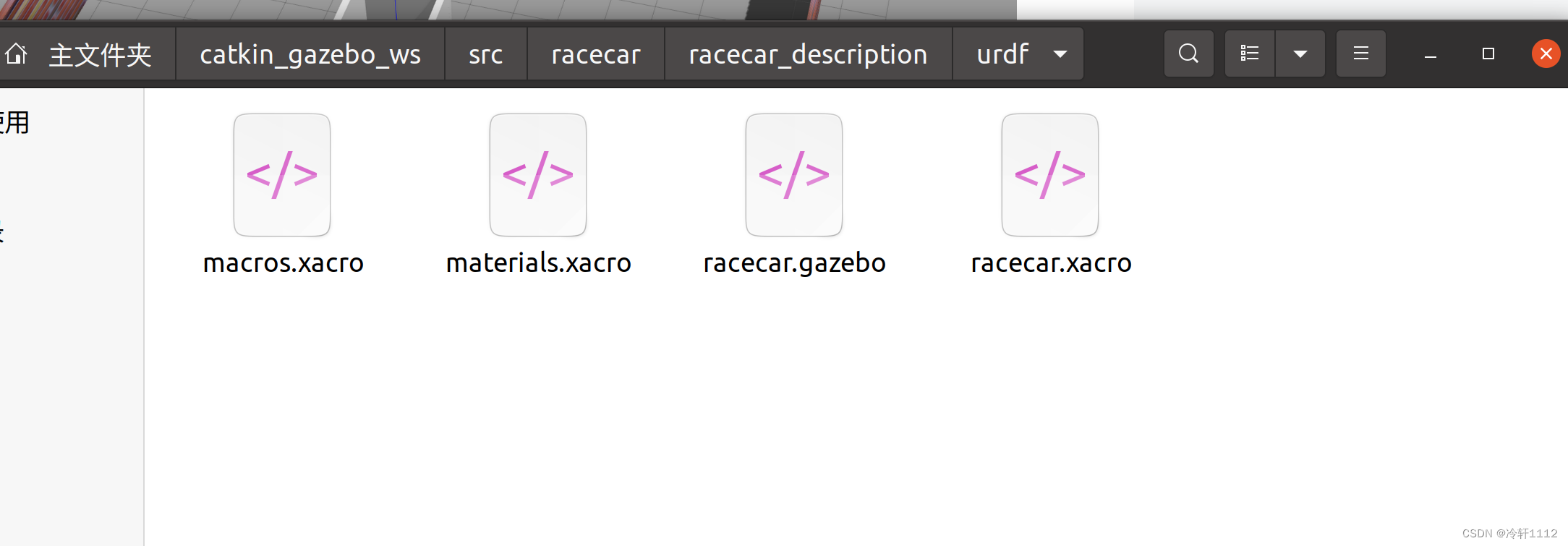
world+小车的打开也就是在world场景下增加了一辆小车,这就需要一个小车模型了。一般来说从网上下载的仿真环境都会有小车模型 。像下图中所示,我的小车模型就是在/catkin_gazebo_ws/src/racecar/racecar_description/urdf,其中我要使用的就是racecar_xacro。
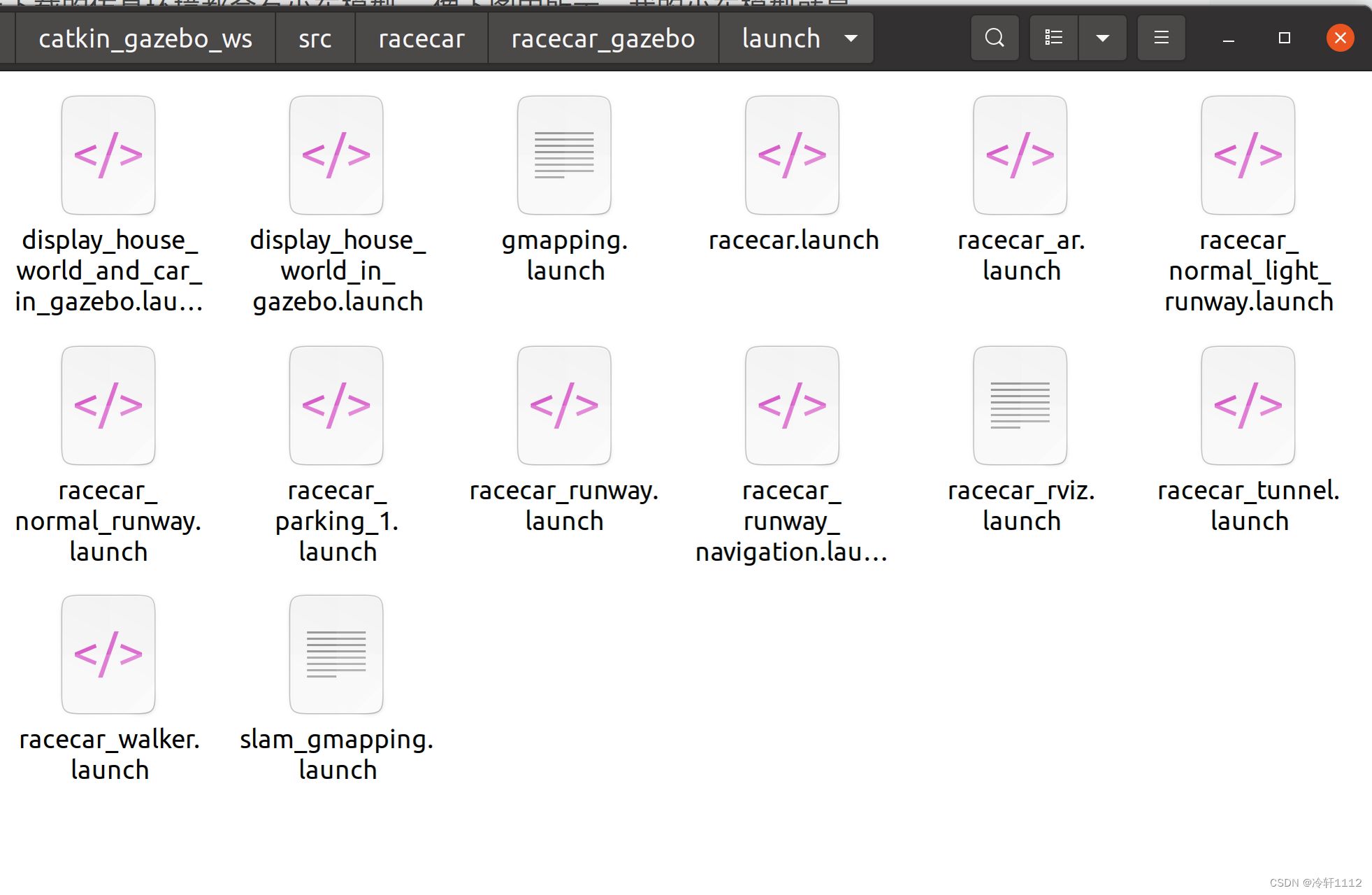
同样需要在launch文件夹中创建一个launch文件,一般来说展示world场景和小车的launch文件较为复杂,我是通过复制所下载的环境中的一个launch文件修改得到的。
如下图所示,我所下载的仿真环境中小车+world展示的launch文件是racecar.launch,但是这个文件所指定的world文件并不是我想要的场景,因此负责该文件的内容创建一个launch文件,然后修改一下world文件的名字。
 代码修改说明:
代码修改说明:
像我这个文件的话,其实以及很友好了,如果想要换world文件,只需要在<arg name="world_name" default="house_world_as" />这一行中修改default的值就可以了,像我的world文件名是house_world_as。注意这个地方不需要加文件名的后缀.world。当然在include的那部分中找world_name的路径也是需要注意的,如果和我的仿真环境不同需要自己改。我的launch文件名是display_house_world_and_car_in_gazebo.launch
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<launch>
<arg name="world_name" default="house_world_as" />
<arg name="gui" default="true" />
<arg name="run_camera" default="false"/>
<arg name="x_pos" default="-5.388334"/>
<arg name="y_pos" default="-4.094883"/>
<arg name="z_pos" default="0.0"/>
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find racecar_gazebo)/worlds/$(arg world_name).world"/>
<arg name="gui" value="$(arg gui)"/>
</include>
<!-- urdf xml robot description loaded on the Parameter Server, converting the xacro into a proper urdf file-->
<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro --inorder '$(find racecar_description)/urdf/racecar.xacro'" />
<!-- push robot_description to factory and spawn robot in gazebo -->
<node name="racecar_spawn" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" output="screen" args="-urdf -param robot_description -model racecar -x $(arg x_pos) -y $(arg y_pos) -z $(arg z_pos)" />
<!-- ros_control racecar launch file -->
<include file="$(find racecar_control)/launch/racecar_control.launch" ns="/"/>
<!-- Spawn the MUXs -->
<arg name="racecar_version" default="racecar-v2" />
<include file="$(find racecar)/launch/mux.launch" ns="vesc" />
<!-- Publish "better odom" topic that is normally generated by the particle filter -->
<node name="better_odom" pkg="topic_tools" type="relay"
args="/vesc/odom /pf/pose/odom" />
<!--Launch the simulation joystick control-->
<rosparam command="load" file="$(find racecar_gazebo)/config/keyboard_teleop.yaml" />
<node pkg="racecar_gazebo" type="keyboard_teleop.py" name="keyboard_teleop" />
</launch>
执行,会发现多了个小车:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ roslaunch racecar_gazebo display_house_world_and_car_in_gazebo.launch

(5)使用这个world模型+小车模型来建一下图(gmapping)
这一步需要gmapping功能包,这个功能包的下载可以网上找教程下载,下载好之后就可以不管了。launch文件还是创在仿真环境中的,在launch文件中指定gmapping的功能包名字会自动寻找并使用。
一般来说网上下载的仿真环境一般都会有gmapping的launch文件,如果没有也没有关系。启动gmapping建图需要创建两个launch文件,这些launch文件全都是放在图中上面所示的路径中,此后不在赘述。并且这两个文件的内容是不需要改就可以直接使用了,当然前提是有gmapping功能包。
slam_gmapping.launch(这个文件的作用是调用gmapping,如果调用的文件名不一样注意修改文件路径):
<launch>
<include file="$(find racecar_gazebo)/launch/gmapping.launch"/>
<!-- 启动rviz -->
<node pkg="rviz" type="rviz" name="rviz" args="-d $(find racecar_gazebo)/config/new_gmapping.rviz"/>
</launch>
gmapping.launch:
<launch>
<node pkg="gmapping" type="slam_gmapping" name="slam_gmapping" output="screen">
<param name="base_frame" value="base_link"/> <!--机器人底盘坐标系基框架,附带在移动底盘的框架,原点-->
<param name="odom_frame" value="odom"/> <!--里程计坐标系里程计框架,附带在里程计的框架-->
<param name="map_frame" value="map"/> <!--地图坐标系地图框架,附带在地图上的框架-->
<param name="map_update_interval" value="0.01"/><!--地图更新速度,秒0.01-->
<param name="maxUrange" value="10.0"/><!--激光最大可用距离-->
<param name="maxRange" value="12.0"/><!--zuida juli-->
<param name="sigma" value="0.05"/>
<param name="kernelSize" value="3"/><!--moren:1-->
<param name="lstep" value="0.05"/>
<param name="astep" value="0.05"/>
<param name="iterations" value="5"/>
<param name="lsigma" value="0.075"/>
<param name="ogain" value="3.0"/>
<param name="lskip" value="0"/>
<param name="srr" value="0.1"/>
<param name="srt" value="0.2"/>
<param name="str" value="0.1"/>
<param name="stt" value="0.2"/>
<param name="minimumScore" value="0"/>
<param name="linearUpdate" value="0.05"/><!--线速度角速度在地图的更新-->
<param name="angularUpdate" value="0.0436"/>
<param name="temporalUpdate" value="-1"/><!--moren:-1-->
<param name="resampleThreshold" value="0.5"/>
<param name="particles" value="8"/><!--moren:30 gaicheng:8-->
<param name="xmin" value="-50.0"/>
<param name="ymin" value="-50.0"/>
<param name="xmax" value="50.0"/>
<param name="ymax" value="50.0"/>
<param name="delta" value="0.05"/>
<param name="llsamplerange" value="0.01"/>
<param name="llsamplestep" value="0.01"/>
<param name="lasamplerange" value="0.005"/>
<param name="lasamplestep" value="0.005"/>
<!--param name="transform_publish_period" value="0.01"/-->
</node>
</launch>
有了建图启动文件就可以建图了。
一般来说,我一旦使用ros,都会先roscore一下,建议也roscore一下:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ roscore
首先,先打开之前自己创建的场景,也就是world+小车的场景,打开一个新的终端,使用launch文件启动:
(base) hjb@jl16k:$ cd catkin_gazebo_ws
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ roslaunch racecar_gazebo display_house_world_and_car_in_gazebo.launch
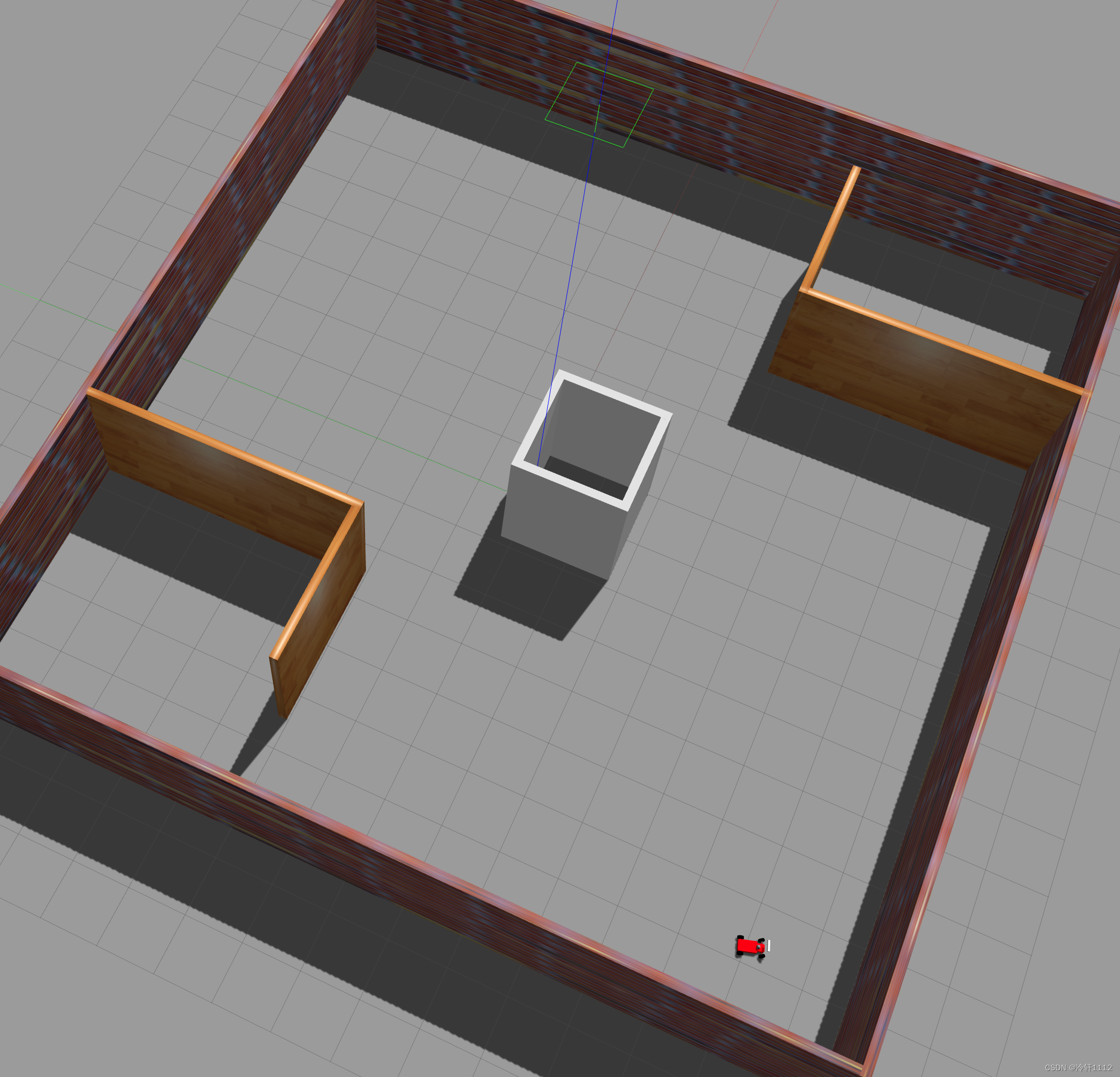
有真实地图和机器人了,就可以控制机器人使用算法建图了,使用launch文件启动建图和键盘控制,这个键盘控制是我这个仿真环境写好的,至于其他仿真环境的话,那我只能说我无能为力:
打开新终端:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ cd catkin_gazebo_ws/
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ roslaunch racecar_gazebo slam_gmapping.launch
键盘控制移动扫描完整个地图完成建图,在建图想要移动必须点击下图所示的这个界面才能移动:
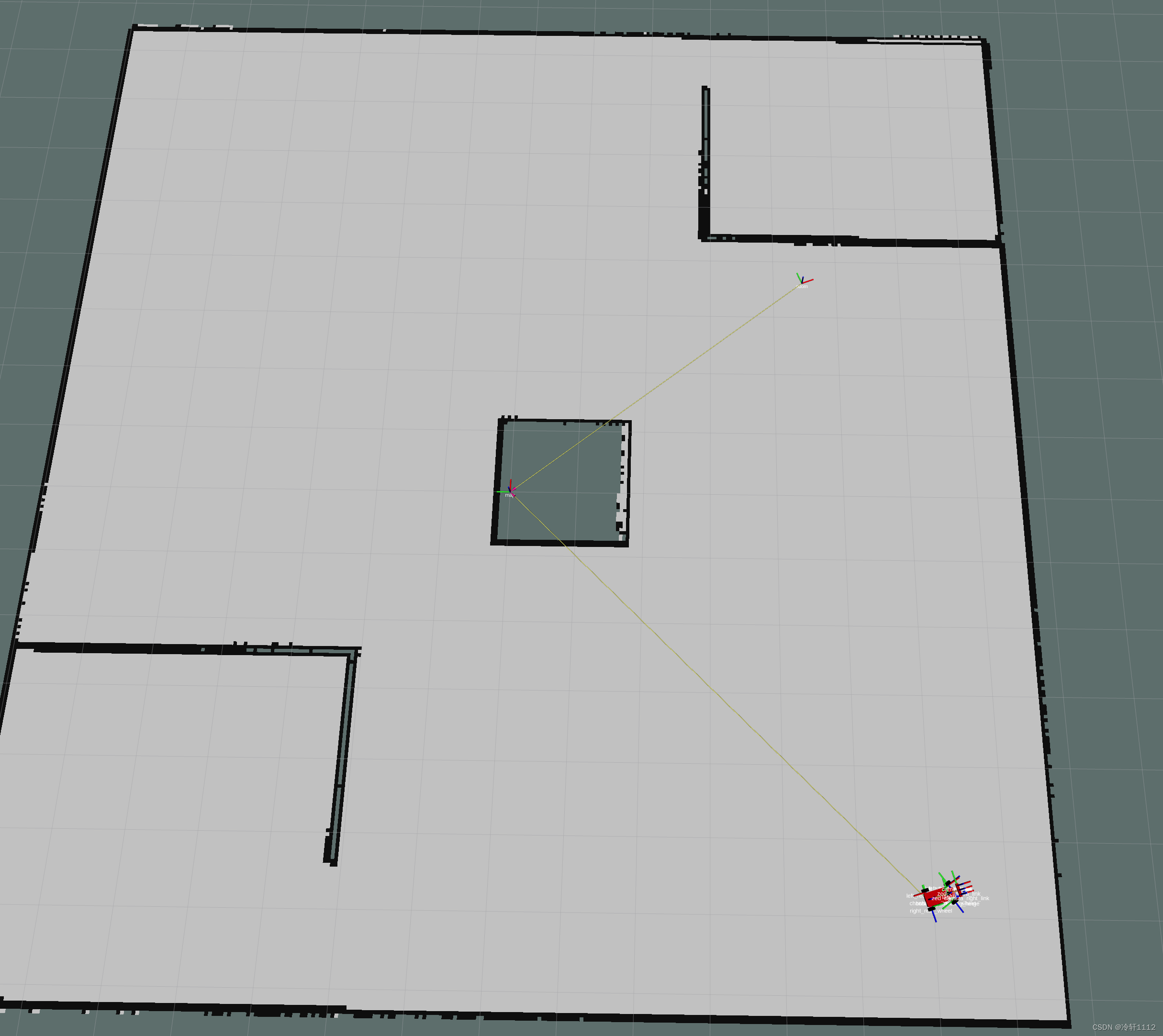
建好图的效果:
打开新终端,保存地图,可以根据自己需求改路径:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ rosrun map_server map_saver -f /home/hjb/catkin_gazebo_ws/src/racecar/racecar_gazebo/map/house
(6)使用上步所保存的图来导航
有了建图自然少不了导航,先说一下导航的前提条件,一般来说导航需要使用move_base功能包,这个包一般在navigation包中。而这个navigation包一般安装gmapping算法的时候会自带,如果没有需要自己下载这个navigation包,这个包网上教程参考下载即可。
到这一步,之前打开的终端可以都关了。实现导航需要两个launch文件,一个rivz配置文件,以及一个路径追踪的脚本。
racecar_house_and_car_world_navigation.launch :
有两处有根据自己修改:
<arg name="world_name" value="house_world_as"/> 的house_world_as要改成自己的文件名。
<node name="map_server" pkg="map_server" type="map_server" args="$(find racecar_gazebo)/map/house .yaml" />要house.yaml文件的路径要根据自己保存的修改,这个文件就是(5)保存地图的文件。
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<launch>
<!-- Launch the racecar -->
<include file="$(find racecar_gazebo)/launch/racecar.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="house_world_as"/>
</include>
<!-- Launch the built-map -->
<node name="map_server" pkg="map_server" type="map_server" args="$(find racecar_gazebo)/map/house .yaml" />
<!--Launch the move base with time elastic band-->
<param name="/use_sim_time" value="true"/>
<node pkg="move_base" type="move_base" respawn="false" name="move_base" output="screen">
<rosparam file="$(find racecar_gazebo)/config/costmap_common_params.yaml" command="load" ns="global_costmap" />
<rosparam file="$(find racecar_gazebo)/config/costmap_common_params.yaml" command="load" ns="local_costmap" />
<rosparam file="$(find racecar_gazebo)/config/local_costmap_params.yaml" command="load" />
<rosparam file="$(find racecar_gazebo)/config/global_costmap_params.yaml" command="load" />
<rosparam file="$(find racecar_gazebo)/config/teb_local_planner_params.yaml" command="load" />
<param name="base_global_planner" value="global_planner/GlobalPlanner" />
<param name="planner_frequency" value="0.01" />
<param name="planner_patience" value="5.0" />
<!--param name="use_dijkstra" value="false" /-->
<param name="base_local_planner" value="teb_local_planner/TebLocalPlannerROS" />
<param name="controller_frequency" value="5.0" />
<param name="controller_patience" value="15.0" />
<param name="clearing_rotation_allowed" value="false" />
</node>
</launch>
racecar_rviz.launch :
<launch>
<!-- 启动rviz -->
<node pkg="rviz" type="rviz" name="rviz" args="-d $(find racecar_gazebo)/config/racecar_rviz.rviz"/>
</launch>
因为这个rviz配置是我所下载的这个仿真环境自带有的,如果使用的不是我这个仿真环境需要自己写一个rviz配置文件,并将上面的racecar_rviz.launch文件的路径改为这个rviz文件的路径。。
racecar_rviz.rviz :
Panels:
- Class: rviz/Displays
Help Height: 78
Name: Displays
Property Tree Widget:
Expanded:
- /Global Options1
- /Status1
- /LaserScan1
- /PoseArray1
Splitter Ratio: 0.5
Tree Height: 775
- Class: rviz/Selection
Name: Selection
- Class: rviz/Tool Properties
Expanded:
- /2D Pose Estimate1
- /2D Nav Goal1
- /Publish Point1
Name: Tool Properties
Splitter Ratio: 0.588679016
- Class: rviz/Views
Expanded:
- /Current View1
Name: Views
Splitter Ratio: 0.5
- Class: rviz/Time
Experimental: false
Name: Time
SyncMode: 0
SyncSource: LaserScan
Toolbars:
toolButtonStyle: 2
Visualization Manager:
Class: ""
Displays:
- Alpha: 0.5
Cell Size: 1
Class: rviz/Grid
Color: 160; 160; 164
Enabled: true
Line Style:
Line Width: 0.0299999993
Value: Lines
Name: Grid
Normal Cell Count: 0
Offset:
X: 0
Y: 0
Z: 0
Plane: XY
Plane Cell Count: 10
Reference Frame: <Fixed Frame>
Value: true
- Alpha: 0.699999988
Class: rviz/Map
Color Scheme: map
Draw Behind: false
Enabled: true
Name: Map
Topic: /map
Unreliable: false
Use Timestamp: false
Value: true
- Alpha: 1
Axes Length: 1
Axes Radius: 0.100000001
Class: rviz/Pose
Color: 255; 25; 0
Enabled: true
Head Length: 0.300000012
Head Radius: 0.100000001
Name: Pose
Shaft Length: 1
Shaft Radius: 0.0500000007
Shape: Arrow
Topic: /move_base_simple/goal
Unreliable: false
Value: true
- Angle Tolerance: 0.100000001
Class: rviz/Odometry
Covariance:
Orientation:
Alpha: 0.5
Color: 255; 255; 127
Color Style: Unique
Frame: Local
Offset: 1
Scale: 1
Value: true
Position:
Alpha: 0.300000012
Color: 204; 51; 204
Scale: 1
Value: true
Value: true
Enabled: true
Keep: 100
Name: Odometry
Position Tolerance: 0.100000001
Shape:
Alpha: 1
Axes Length: 1
Axes Radius: 0.100000001
Color: 255; 25; 0
Head Length: 0.300000012
Head Radius: 0.100000001
Shaft Length: 1
Shaft Radius: 0.0500000007
Value: Arrow
Topic: /vesc/odom
Unreliable: false
Value: true
- Alpha: 1
Autocompute Intensity Bounds: true
Autocompute Value Bounds:
Max Value: 10
Min Value: -10
Value: true
Axis: Z
Channel Name: intensity
Class: rviz/LaserScan
Color: 255; 255; 255
Color Transformer: Intensity
Decay Time: 0
Enabled: true
Invert Rainbow: false
Max Color: 255; 255; 255
Max Intensity: 0
Min Color: 0; 0; 0
Min Intensity: 0
Name: LaserScan
Position Transformer: XYZ
Queue Size: 10
Selectable: true
Size (Pixels): 3
Size (m): 0.100000001
Style: Flat Squares
Topic: /scan
Unreliable: false
Use Fixed Frame: true
Use rainbow: true
Value: true
- Alpha: 1
Buffer Length: 1
Class: rviz/Path
Color: 25; 255; 0
Enabled: true
Head Diameter: 0.300000012
Head Length: 0.200000003
Length: 0.300000012
Line Style: Lines
Line Width: 0.0299999993
Name: Path
Offset:
X: 0
Y: 0
Z: 0
Pose Color: 255; 85; 255
Pose Style: None
Radius: 0.0299999993
Shaft Diameter: 0.100000001
Shaft Length: 0.100000001
Topic: /move_base/TebLocalPlannerROS/global_plan
Unreliable: false
Value: true
- Alpha: 0.699999988
Class: rviz/Map
Color Scheme: map
Draw Behind: false
Enabled: true
Name: Map
Topic: /move_base/local_costmap/costmap
Unreliable: false
Use Timestamp: false
Value: true
- Alpha: 1
Axes Length: 1
Axes Radius: 0.100000001
Class: rviz/Pose
Color: 255; 25; 0
Enabled: true
Head Length: 0.300000012
Head Radius: 0.100000001
Name: Pose
Shaft Length: 1
Shaft Radius: 0.0500000007
Shape: Arrow
Topic: /move_base/current_goal
Unreliable: false
Value: true
- Alpha: 1
Arrow Length: 0.300000012
Axes Length: 0.300000012
Axes Radius: 0.00999999978
Class: rviz/PoseArray
Color: 255; 25; 0
Enabled: true
Head Length: 0.0700000003
Head Radius: 0.0299999993
Name: PoseArray
Shaft Length: 0.230000004
Shaft Radius: 0.00999999978
Shape: Arrow (Flat)
Topic: /move_base/TebLocalPlannerROS/teb_poses
Unreliable: false
Value: true
Enabled: true
Global Options:
Background Color: 48; 48; 48
Default Light: true
Fixed Frame: map
Frame Rate: 30
Name: root
Tools:
- Class: rviz/Interact
Hide Inactive Objects: true
- Class: rviz/MoveCamera
- Class: rviz/Select
- Class: rviz/FocusCamera
- Class: rviz/Measure
- Class: rviz/SetInitialPose
Topic: /initialpose
- Class: rviz/SetGoal
Topic: /move_base_simple/goal
- Class: rviz/PublishPoint
Single click: true
Topic: /clicked_point
Value: true
Views:
Current:
Class: rviz/Orbit
Distance: 4.41030741
Enable Stereo Rendering:
Stereo Eye Separation: 0.0599999987
Stereo Focal Distance: 1
Swap Stereo Eyes: false
Value: false
Focal Point:
X: -0.749346972
Y: -3.23726511
Z: 2.81896186
Focal Shape Fixed Size: true
Focal Shape Size: 0.0500000007
Invert Z Axis: false
Name: Current View
Near Clip Distance: 0.00999999978
Pitch: 1.13039768
Target Frame: <Fixed Frame>
Value: Orbit (rviz)
Yaw: 6.17858267
Saved: ~
Window Geometry:
Displays:
collapsed: false
Height: 1056
Hide Left Dock: false
Hide Right Dock: false
QMainWindow State: 000000ff00000000fd00000004000000000000016a00000396fc0200000008fb0000001200530065006c0065006300740069006f006e00000001e10000009b0000006100fffffffb0000001e0054006f006f006c002000500072006f007000650072007400690065007302000001ed000001df00000185000000a3fb000000120056006900650077007300200054006f006f02000001df000002110000018500000122fb000000200054006f006f006c002000500072006f0070006500720074006900650073003203000002880000011d000002210000017afb000000100044006900730070006c006100790073010000002800000396000000d700fffffffb0000002000730065006c0065006300740069006f006e00200062007500660066006500720200000138000000aa0000023a00000294fb00000014005700690064006500530074006500720065006f02000000e6000000d2000003ee0000030bfb0000000c004b0069006e0065006300740200000186000001060000030c00000261000000010000010f00000396fc0200000003fb0000001e0054006f006f006c002000500072006f00700065007200740069006500730100000041000000780000000000000000fb0000000a00560069006500770073010000002800000396000000ad00fffffffb0000001200530065006c0065006300740069006f006e010000025a000000b200000000000000000000000200000490000000a9fc0100000001fb0000000a00560069006500770073030000004e00000080000002e100000197000000030000073f0000003efc0100000002fb0000000800540069006d006501000000000000073f0000030000fffffffb0000000800540069006d00650100000000000004500000000000000000000004ba0000039600000004000000040000000800000008fc0000000100000002000000010000000a0054006f006f006c00730100000000ffffffff0000000000000000
Selection:
collapsed: false
Time:
collapsed: false
Tool Properties:
collapsed: false
Views:
collapsed: false
Width: 1855
X: 65
Y: 24
最后的脚本文件,用来让机器人根据规划好的路径移动到终点。
path_pursuit.py :
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
from nav_msgs.msg import Path, Odometry
from ackermann_msgs.msg import AckermannDriveStamped
from geometry_msgs.msg import PoseStamped, PoseArray
import math
import numpy as np
from numpy import linalg as LA
from tf.transformations import euler_from_quaternion, quaternion_from_euler
import csv
import os
class following_path:
def __init__(self):
self.current_pose = rospy.Subscriber('/pf/pose/odom', Odometry, self.callback_read_current_position, queue_size=1)
self.Pose = []
self.path_pose = rospy.Subscriber('/move_base/TebLocalPlannerROS/global_plan', Path, self.callback_read_path, queue_size=1)
self.path_info = []
self.Goal = []
self.navigation_input = rospy.Publisher('/vesc/low_level/ackermann_cmd_mux/input/navigation', AckermannDriveStamped, queue_size=1)
self.reach_goal = False
self.MAX_VELOCITY = 0.5
self.MIN_VELOCITY = 0
self.max_angle = 1
self.steering_velocity = 1
self.jerk = 0.0
self.acceleration = 0.0
self.LOOKAHEAD_DISTANCE = 0.4
self.Low_Speed_Mode = False
def callback_read_path(self, data):
# Organize the pose message and only ask for (x,y) and orientation
# Read the Real time pose message and load them into path_info
self.path_info = []
path_array = data.poses
for path_pose in path_array:
path_x = path_pose.pose.position.x
path_y = path_pose.pose.position.y
path_qx = path_pose.pose.orientation.x
path_qy = path_pose.pose.orientation.y
path_qz = path_pose.pose.orientation.z
path_qw = path_pose.pose.orientation.w
path_quaternion = (path_qx, path_qy, path_qz, path_qw)
path_euler = euler_from_quaternion(path_quaternion)
path_yaw = path_euler[2]
self.path_info.append([float(path_x), float(path_y), float(path_yaw)])
self.Goal = list(self.path_info[-1]) # Set the last pose of the global path as goal location
def callback_read_current_position(self, data):
if self.reach_goal: # Stop updating the information.
self.path_info = []
self.Pose = []
ackermann_control = AckermannDriveStamped()
ackermann_control.drive.speed = 0.0
ackermann_control.drive.steering_angle = 0.0
ackermann_control.drive.steering_angle_velocity = 0.0
if not len(self.path_info) == 0:
# Read the path information to path_point list
path_points_x = [float(point[0]) for point in self.path_info]
path_points_y = [float(point[1]) for point in self.path_info]
path_points_w = [float(point[2]) for point in self.path_info]
# Read the current pose of the car from particle filter
x = data.pose.pose.position.x
y = data.pose.pose.position.y
qx = data.pose.pose.orientation.x
qy = data.pose.pose.orientation.y
qz = data.pose.pose.orientation.z
qw = data.pose.pose.orientation.w
# Convert the quaternion angle to eular angle
quaternion = (qx,qy,qz,qw)
euler = euler_from_quaternion(quaternion)
yaw = euler[2]
self.Pose = [float(x), float(y), float(yaw)]
if self.dist(self.Goal, self.Pose) < 1.0:
self.Low_Speed_Mode = True
if self.dist(self.Goal, self.Pose) < 0.3:
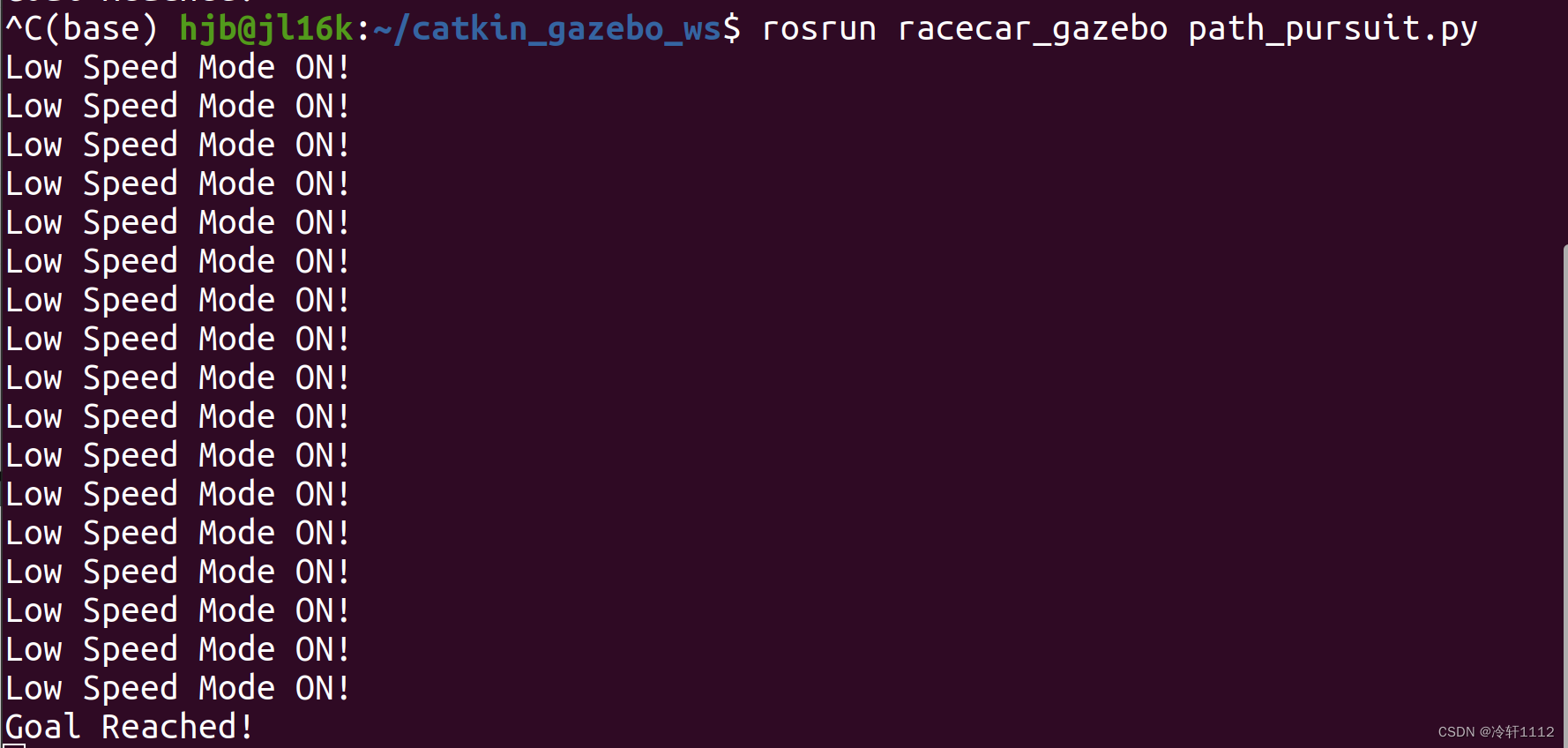
self.reach_goal = True
print('Goal Reached!')
else:
print('Low Speed Mode ON!')
else:
self.Low_Speed_Mode = False
# 2. Find the path point closest to the vehichle tat is >= 1 lookahead distance from vehicle's current location.
dist_array = np.zeros(len(path_points_x))
for i in range(len(path_points_x)):
dist_array[i] = self.dist((path_points_x[i], path_points_y[i]), (x,y))
goal = np.argmin(dist_array) # Assume the closet point as the goal point at first
goal_array = np.where((dist_array < (self.LOOKAHEAD_DISTANCE + 0.3)) & (dist_array > (self.LOOKAHEAD_DISTANCE - 0.3)))[0]
for id in goal_array:
v1 = [path_points_x[id] - x, path_points_y[id] - y]
v2 = [math.cos(yaw), math.sin(yaw)]
diff_angle = self.find_angle(v1,v2)
if abs(diff_angle) < np.pi/4: # Check if the one that is the cloest to the lookahead direction
goal = id
break
L = dist_array[goal]
# 3. Transform the goal point to vehicle coordinates.
glob_x = path_points_x[goal] - x
glob_y = path_points_y[goal] - y
goal_x_veh_coord = glob_x*np.cos(yaw) + glob_y*np.sin(yaw)
goal_y_veh_coord = glob_y*np.cos(yaw) - glob_x*np.sin(yaw)
# 4. Calculate the curvature = 1/r = 2x/l^2
# The curvature is transformed into steering wheel angle by the vehicle on board controller.
# Hint: You may need to flip to negative because for the VESC a right steering angle has a negative value.
diff_angle = path_points_w[goal] - yaw # Find the turning angle
r = L/(2*math.sin(diff_angle)) # Calculate the turning radius
angle = 2 * math.atan(0.4/r) # Find the wheel turning radius
angle = np.clip(angle, -self.max_angle, self.max_angle) # 0.4189 radians = 24 degrees because car can only turn 24 degrees max
angle = (0 if abs(angle) < 0.1 else angle)
VELOCITY = self.speed_control(angle, self.MIN_VELOCITY, self.MAX_VELOCITY)
# Write the Velocity and angle data into the ackermann message
ackermann_control = AckermannDriveStamped()
ackermann_control.drive.speed = VELOCITY
ackermann_control.drive.steering_angle = angle
ackermann_control.drive.steering_angle_velocity = self.steering_velocity
else:
ackermann_control = AckermannDriveStamped()
ackermann_control.drive.speed = 0.0
ackermann_control.drive.steering_angle = 0.0
ackermann_control.drive.steering_angle_velocity = 0.0
self.navigation_input.publish(ackermann_control)
# Computes the Euclidean distance between two 2D points p1 and p2
def dist(self, p1, p2):
try:
return np.sqrt((p1[0] - p2[0]) ** 2 + (p1[1] - p2[1]) ** 2)
except:
return 0.5
# Compute the angle between car direction and goal direction
def find_angle(self, v1, v2):
cos_ang = np.dot(v1, v2)
sin_ang = LA.norm(np.cross(v1, v2))
return np.arctan2(sin_ang, cos_ang)
# Control the speed of the car within the speed limit
def speed_control(self, angle, MIN_VELOCITY, MAX_VELOCITY):
# Assume the speed change linearly with respect to yaw angle
if self.Low_Speed_Mode:
Velocity = 0.5
else:
k = (MIN_VELOCITY - MAX_VELOCITY)/self.max_angle + 0.5
Velocity = k * abs(angle) + MAX_VELOCITY
return Velocity
if __name__ == "__main__":
rospy.init_node("pursuit_path")
following_path()
rospy.spin()
都完成后打开新终端,启动导航的launch文件:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ cd catkin_gazebo_ws/
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ roslaunch racecar_gazebo racecar_house_and_car_world_navigation.launch
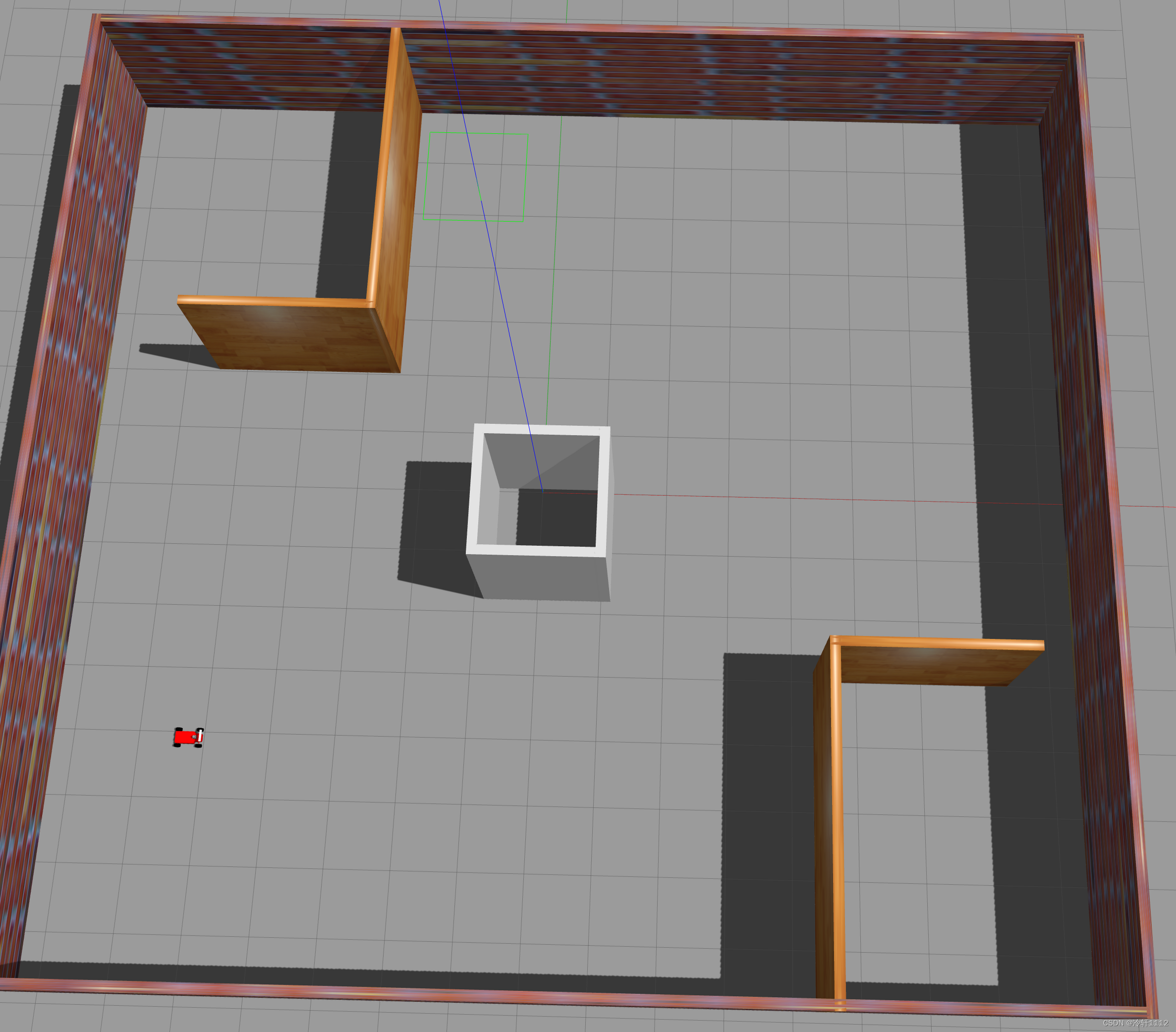
再打开一个终端,启动rivz:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ cd catkin_gazebo_ws/
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ roslaunch racecar_gazebo racecar_rviz.launch
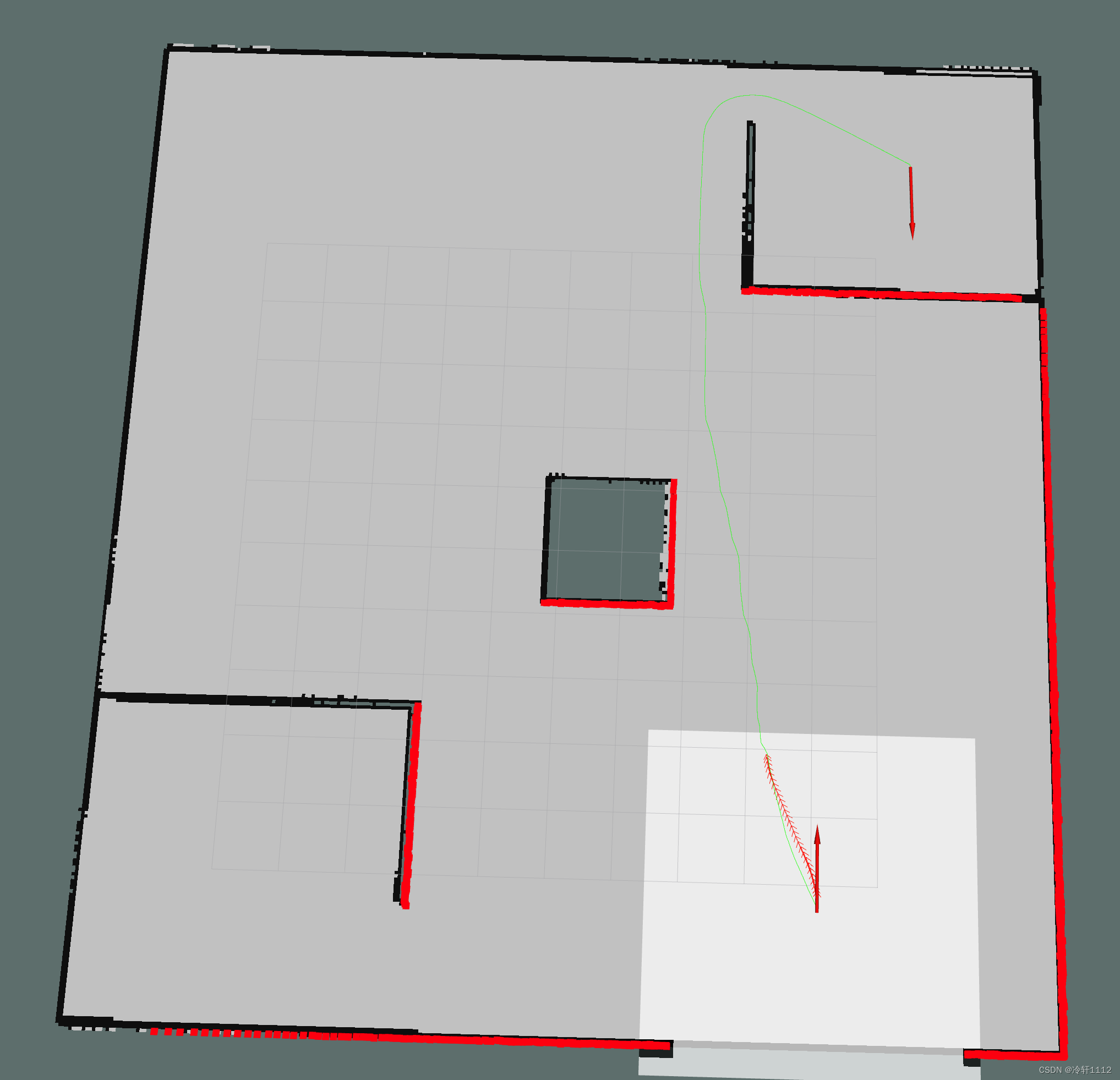
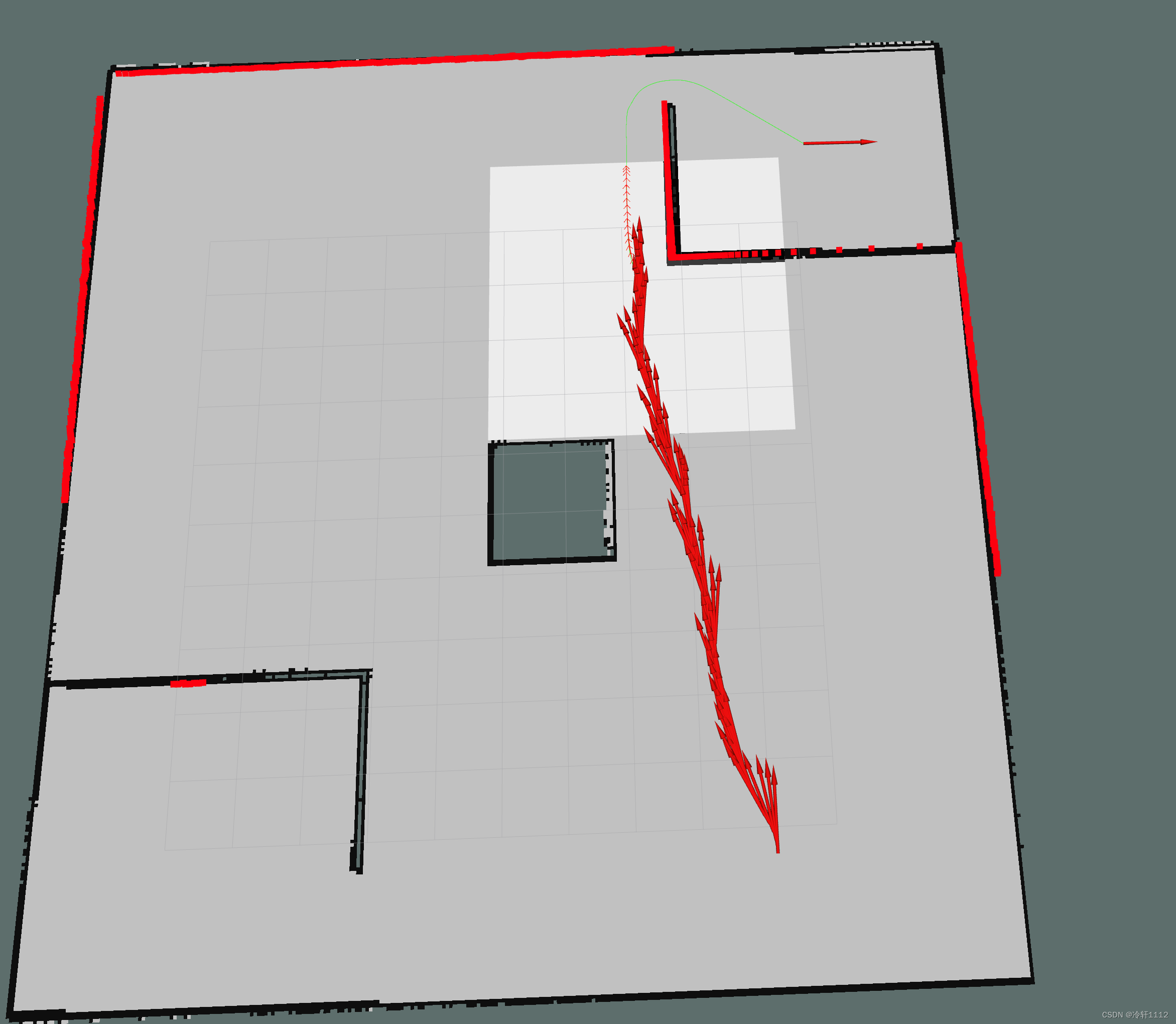
 在rviz中点击下图箭头所指的2D Nav Goal,然后将箭头方向拉成像我一样的 ,当然其他方向也ok的。就会看到算法所得到的路径,绿色那条线。
在rviz中点击下图箭头所指的2D Nav Goal,然后将箭头方向拉成像我一样的 ,当然其他方向也ok的。就会看到算法所得到的路径,绿色那条线。

再打开一个新终端:
(base) hjb@jl16k:~$ cd catkin_gazebo_ws/
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ source devel/setup.bash
(base) hjb@jl16k:~/catkin_gazebo_ws$ rosrun racecar_gazebo path_pursuit.py
3.结束
一次完整的仿真。
版权归原作者 冷轩1112 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。