这里写目录标题
栈的概念与特点
- 栈是一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
- 压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
- 出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
如图所示: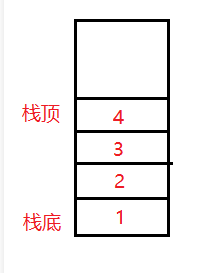
这里的 1 2 3 4 就是压入栈中的元素,新压入的元素放在栈顶,比如说压入新的元素:5 。那么就是这样的: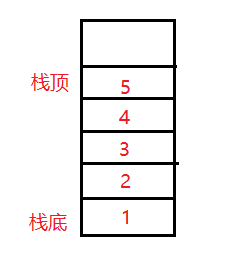
出栈也是从栈顶往外出。
栈的使用
栈的功能有:压栈,出栈,比较栈顶元素,判空,栈的比较等等。
压栈
通过 push 来进行栈的压入:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){java.util.Stack<Integer> stack =newjava.util.Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);System.out.println(stack);}
运行结果如下: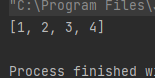
出栈
通过 pop 方法来出栈:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){java.util.Stack<Integer> stack =newjava.util.Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);System.out.println(stack);
stack.pop();
stack.pop();System.out.println(stack);}
运行结果如下: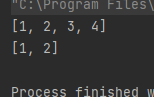
求得栈顶元素
通过 peek 方法来得到:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){java.util.Stack<Integer> stack =newjava.util.Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);System.out.println(stack.peek());System.out.println(stack);}
运行结果如下: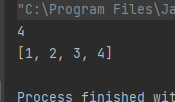
使用 peek 的时候,只是获得栈顶元素。
判断栈是否为空
通过 isEmpty 来判断:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){java.util.Stack<Integer> stack =newjava.util.Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());}
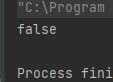
栈的比较
通过 equals 来比较是否相等:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){java.util.Stack<Integer> stack =newjava.util.Stack<>();java.util.Stack<Integer> stack1 =newjava.util.Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack1.push(1);
stack1.push(2);System.out.println(stack.equals(stack1));}
运行结果如下: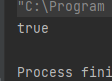
手把手实现栈
因为栈的特点是先进后出,后进先出。而且入栈和出栈的时间复杂度都是 O(1) ,所以我们选用顺序表来实现栈。
写出顺序表
先写出代码的初始部分:
publicint[] elem;publicint usedSize;publicMyStack(){this.elem =newint[5];}
这里实现了顺序表的内容,也就是自己实现的栈。
判断是否满了
通过直接比较使用空间大小和数组大小就可以知道有没有满:
publicbooleanisFull(){returnthis.usedSize ==this.elem.length;}
压栈
压栈也就是直接放入元素,在放入元素的时候要先判断满没满,如果满了就扩容,没满就直接放在 usedSize 位置就可以了:
publicvoidpush(int val){if(isFull()){this.elem =Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);}this.elem[this.usedSize]= val;this.usedSize++;}
判断是否为空
通过判断 usedSize 是否为 0 来完成判断:
publicbooleanisEmpty(){returnthis.usedSize ==0;}
出栈
在出栈的时候,先判断是否为空,如果是空的话,就扔出栈为空的异常,不是的话先保存 usedSize -1 位置的值。然后 usedSize-- ,最后再返回 usedSize -1 位置的值就可以了。
publicintpop(){if((isEmpty())){thrownewRuntimeException("栈为空!");}int oldVal =this.elem[this.usedSize-1];this.usedSize--;return oldVal;}
比较栈顶元素
第一步还是先判断栈是否为空。如果不是的话,就返回 usedSize -1 位置的值就好了。
publicintpeek(){if((isEmpty())){thrownewRuntimeException("栈为空!");}returnthis.elem[this.usedSize-1];}
栈的大小
通过返回 usedSize 的大小就知道栈的大小了。
publicintsize(){returnthis.usedSize;}
测试
测试上述功能:
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){MyStack stack =newMyStack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(6);
stack.push(7);System.out.println(stack.size());
stack.pop();
stack.pop();System.out.println(stack.peek());System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());}
运行结果如下: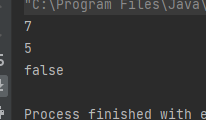
版权归原作者 Lockey-s 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。