**1 **主要内容
该程序参考《光热电站促进风电消纳的电力系统优化调度》光热电站模型,主要做的是考虑N-k安全约束的含义风电-光伏-光热电站的电力系统优化调度模型,从而体现光热电站在调度灵活性以及经济性方面的优势。同时代码还考虑了光热电站对风光消纳的作用,对比了含义光热电站和不含光热电站下的弃风弃光问题,同时还对比了考虑N-k约束下的调度策略区别。以14节点和118节点算例为例,对模型进行了系统性的测试,复现效果良好,是学习N-k约束以及光热电站调度的必备程序!程序采用matlab+cplex(mosek/gurobi)进行求解,可以选择已经安装的求解器进行求解。

程序算例

程序对于118节点系统采用了四个算例进行对比,14节点系统有3种算例对比,并增加了弃风量的对比程序。
程序模型

程序亮点
- 采用光热电站模型,也是最近研究比较热的一个方向。
- 采用转移分布因子矩阵处理潮流问题,这也是很多文献中都采用的方法。
**2 **部分程序
clc; clear; close all; % 关闭所有已打开的绘图窗口
%% 参数设定
NT = 24; % 时间范围
CoeffReseve_load = 0.03;
CoeffReserve_VRE = 0.05;
yita_TES = 0.98;
yita_PB = 0.415;
% 文章里Table 2的数据
Capacity_TES_CSP = 0;
initial_TES_t0 = 0.5;
initial_TES_t1 = 0.78;
TES_initial = 0.5;
beta_Load = 3*10e3;
mpc = case14_1; % 载入数据 matpower 数据格式
%% 有功负荷 24h所有节点总的
% mpc.load = [
% 2842.42 3020.2 3296.96 3444.44 3607.07 3891.91 4070.7 4295.95 4476.76 4661.61 4859.59 5077.77 ...
% 4717.17 4519.19 4301.01 3995.95 3703.03 3806.06 4037.37 4063.63 3721.21 3245.45 3097.97 2827.27
% ]/6.3;
mpc.load = [
683.42 792.2 896.96 1044.44 1087.07 1121.91 1200.7 1235.95 1326.76 1461.61 1489.59 1577.77 ...
1417.17 1219.19 1101.01 1075.95 903.03 1186.06 1237.37 1463.63 1221.21 1005.45 827.97 807.27
]/2;
mpc.P_RE = [0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 15.76 43.17 82.35 109.44 122.55 146.10 ...% PV
126.66 86.05 60.05 52.82 25.78 4.28 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
100.26 133.95 147.28 134.11 170.52 159.44 138.55 72.83 58.83 73.37 79.90 80.54 ... % Wind
91.96 101.68 121.49 122.93 133.11 162.44 130.95 133.25 151.26 139.33 120.60 90.33
]*1; % 可再生能源 24小时数据(实际发电量)
%% 电网相关名称
baseMVA = mpc.baseMVA;
bus = mpc.bus;
gen = mpc.gen;
branch = mpc.branch;
gencost = mpc.gencost;
RE = mpc.RE;
CSP = mpc.CSP;
P_RE = mpc.P_RE;
N = length(bus(:,1)); % 网络中所有节点数
N_Br = length(branch(:,1));% 线路数
N_Gen = length(gen(:,1)); % 火电发电机组数
N_RE = length(RE(:,1)); % 可再生能源节点机组数
N_CSP = length(CSP(:,1)); % CSP发电站数
% 常规机组相关数据提取, 取数据矩阵中的列向量 和功率有功的项,均需标幺值化,以便运算和求解
P_Gen_max = gen(:,9)/baseMVA;
P_Gen_min = gen(:,10)/baseMVA;
type_Gen = gen(:,22);
P_Gen_up = gen(:,23) /baseMVA;
P_Gen_down = gen(:,24) /baseMVA;
T_Gen_min_on = gen(:,25);
T_Gen_min_off = gen(:,26);
c_ST_g = gen(:,28);
c_G_g = gen(:,30);
% CSP机组相关数据提取
P_CSP_max = CSP(:,9)/baseMVA;
P_CSP_min = CSP(:,10)/baseMVA;
P_CSP_up = CSP(:,23)/baseMVA;
P_CSP_down = CSP(:,24)/baseMVA;
T_CSP_min_on = CSP(:,25);
T_CSP_min_off = CSP(:,26);
c_CSP_g = CSP(:,30);
PtCSP_fore = [ % 可用的太阳能热功率向量
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 190.57 390.57 790.57 990.57 1390.57 1891.03 ...
2111.64 2200.92 2202.36 2118.26 1895.37 1408.35 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 ]/20;
PtCSP_fore = PtCSP_fore/baseMVA;
P_RE = P_RE/baseMVA; % 可再生能源PV WT机组出力
beta_Load = beta_Load*baseMVA^2; % $/MWh -> $/p.u.
M_bus_G = zeros(N,N_Gen); % 发电机机组-索引矩阵
for row = 1:N
if abs(find(mpc.gen(:,1) == row)) > 0 % 发电机节点号 与 行号对应
M_bus_G(row,find(mpc.gen(:,1) == row)) = 1; % M_bus_G相应处置1
end
end
M_bus_RE = zeros(N,N_RE); % 可再生能源机组-索引矩阵
for row = 1:N
if abs(find(mpc.RE(:,1) == row))>0
M_bus_RE(row,find(mpc.RE(:,1) == row)) = 1;
end
end
M_bus_CSP = zeros(N,N_CSP); % CSP机组-索引矩阵
for row = 1:N
if abs(find(mpc.CSP(:,1) == row))>0
M_bus_CSP(row,find(mpc.CSP(:,1) == row)) = 1;
end
end
GSDF = makePTDF(mpc); % 发电转移分布因子矩阵,表征节点注入功率在全网络的分布
%% 负荷矩阵数据,按照 算例数据mpc.bus(:,3) 中各节点负荷的比例分配
PD = bus(:,3)/baseMVA;
P_factor = PD/sum(PD);
P_sum = mpc.load/baseMVA;
PD = P_factor*P_sum;
%% 决策变量命名
PG_G = sdpvar(N_Gen,NT,'full');
PG_RE = sdpvar(N_RE,NT,'full'); % (风光并网量)
PG_CSP = sdpvar(N_CSP,NT,'full');
PC_Load = sdpvar(N,NT,'full');
onoff_gen = binvar(N_Gen,NT,'full');
onoff_CSP = binvar(N_CSP,NT,'full');
Branch = sdpvar(N_Br,NT,'full');
Cost_StartUp = sdpvar(N_Gen,NT-1,'full');
Pt_TES_charge = sdpvar(N_CSP,NT,'full');
Pt_TES_discharge= sdpvar(N_CSP,NT,'full');
Et_TES = sdpvar(N_CSP,NT,'full');
%% 约束条件列写
Cons = [];
for t = 1:NT
if t >= 2 % type(1-水电, 2-火电机组)
for i = 1:N_Gen % 火电机组-最小启/停时间约束 式(8-9)
if (type_Gen(i,1)==2) || (type_Gen(i,1)==5)
for tao = t + 1:min(t+T_Gen_min_on(i,1)-1,NT)
Cons = [Cons, onoff_gen(i,t)-onoff_gen(i,t-1) <= onoff_gen(i,tao)];
end
for tao = t + 1:min(t+T_Gen_min_off(i,1)-1,NT)
Cons = [Cons, onoff_gen(i,t-1)-onoff_gen(i,t) <= 1-onoff_gen(i,tao)];
end
end
end
for i = 1:N_CSP
for tao = t+1:min(t+T_CSP_min_on(i,1)-1,NT)
Cons = [Cons, onoff_CSP(i,t)-onoff_CSP(i,t-1) <= onoff_CSP(i,tao)]; % CSP机组最小启/停时间约束
end
for tao = t+1:min(t+T_CSP_min_off(i,1)-1,NT)
Cons = [Cons, onoff_CSP(i,t-1)-onoff_CSP(i,t) <= 1-onoff_CSP(i,tao)];
end
end
end
if t >= 2 % 火电机组 爬坡约束 式(6-7)
Cons = [Cons, PG_G(:,t) - PG_G(:,t-1) <= ...
onoff_gen(:,t-1).* P_Gen_up*60 + ...
(onoff_gen(:,t)-onoff_gen(:,t-1)) .* P_Gen_min + ...
(1-onoff_gen(:,t)) .* P_Gen_max];
Cons = [Cons, -PG_G(:,t) + PG_G(:,t-1) <= ...
onoff_gen(:,t) .* P_Gen_down*60 + ...
(onoff_gen(:,t-1)-onoff_gen(:,t)) .* P_Gen_min + ...
(1-onoff_gen(:,t-1)) .* P_Gen_max];
% CSP 机组 爬坡约束 式(6-7)
Cons = [Cons, PG_CSP(:,t) - PG_CSP(:,t-1) <= ...
onoff_CSP(:,t-1).* P_CSP_up*60 + ... %
(onoff_CSP(:,t)-onoff_CSP(:,t-1)) .* P_CSP_min + ...
(1-onoff_CSP(:,t)) .* P_CSP_max];
Cons = [Cons, -PG_CSP(:,t) + PG_CSP(:,t-1) <= onoff_CSP(:,t) .* P_CSP_down*60 + ...
(onoff_CSP(:,t-1)-onoff_CSP(:,t)) .* P_CSP_min + ...
(1-onoff_CSP(:,t-1)) .* P_CSP_max];
end
end
% 机组出力的上下边界约束-式(3) % t(1-水电,2-火电, 5-燃气发电机组 6-CSP)
Ind_2_5 = union(find(type_Gen(:,1) == 2),find(type_Gen(:,1) == 5));
Cons = [Cons, onoff_gen(Ind_2_5,:) .* (P_Gen_min(Ind_2_5,1) * ones(1,NT)) ...
<= PG_G(Ind_2_5,:) <= ...
onoff_gen(Ind_2_5,:) .* (P_Gen_max(Ind_2_5,1) * ones(1,NT))];
Cons = [Cons, onoff_CSP.*(P_CSP_min*ones(1,NT)) <= PG_CSP <= onoff_CSP.*(P_CSP_max*ones(1,NT))]; % CSP机组出力-边界约束
% Cons = [Cons, onoff_CSP == ones(1,24)]; % CSP机组
Cons = [Cons, sum(PG_G,1) + sum(PG_RE,1) + sum(PG_CSP,1) == sum(PD - PC_Load,1)]; % 式(2)
Cons = [Cons, Branch == GSDF*(M_bus_G*PG_G + M_bus_RE*PG_RE + M_bus_CSP*PG_CSP - (PD-PC_Load))]; %
% Cons = [Cons, -branch(:,6)*ones(1,NT) <= GSDF*(M_bus_G*PG_G+M_bus_RE*PG_RE+M_bus_CSP*PG_CSP-(PD- PC_Load)) <= branch(:,6)*ones(1,NT)]; %
Cons = [Cons, -999*ones(N_Br,NT) <= GSDF*(M_bus_G*PG_G+M_bus_RE*PG_RE+M_bus_CSP*PG_CSP-(PD-PC_Load)) <= 999*ones(N_Br,NT)]; % 118系统有186条线路
Cons = [Cons, 0 <= PG_RE <= P_RE]; % 可再生出力
Cons = [Cons, [60;50;100;80;40]/baseMVA * ones(1,24) <= PG_G ];
Cons = [Cons, 0 <= PC_Load <= PD]; % 式(22)
Cons = [Cons, sum(onoff_gen .* (P_Gen_max*ones(1,NT)) - PG_G,1) + ...
sum(onoff_CSP .* (P_CSP_max*ones(1,NT)) - PG_CSP,1) >= ...
sum(CoeffReseve_load*PD,1) + sum(CoeffReserve_VRE*PG_RE,1) ];
Cons = [Cons, Cost_StartUp >= (onoff_gen(:,2:NT) - onoff_gen(:,1:NT-1)) .* (c_ST_g*ones(1,NT-1))]; % 传统机组启动成本
Cons = [Cons, Cost_StartUp >= 0];
%%%%%% CSP电站运转内部约束 %%%%%%
E_TES_max = Capacity_TES_CSP * P_CSP_max;
Cons = [Cons, PG_CSP/yita_PB + Pt_TES_charge - Pt_TES_discharge <= PtCSP_fore]; % CSP输出电功率与TES充/放热功率,预测光热功率关系
Cons = [Cons, Et_TES(:,2:NT) == Et_TES(:,1:NT-1) + Pt_TES_charge(:,1:NT-1)*yita_TES - Pt_TES_discharge(:,1:NT-1)/yita_TES];
Cons = [Cons, Et_TES(:,1) == TES_initial * E_TES_max];
Cons = [Cons, Et_TES(:,1) == Et_TES(:,NT)];
Cons = [Cons, 0 <= Pt_TES_charge <= Capacity_TES_CSP*ones(N_CSP,NT)];
Cons = [Cons, 0 <= Pt_TES_discharge <= Capacity_TES_CSP*ones(N_CSP,NT)];
Cons = [Cons, 0 <= Et_TES <= E_TES_max * ones(1,NT)];
%% 目标函数
obj = sum(c_G_g'*PG_G) + sum(c_CSP_g'*PG_CSP) + sum(sum(Cost_StartUp) + beta_Load*sum(sum(PC_Load)) );
% 机组的边际发电成本 + 启动成本 + 负荷削减成本
% 运行调度
ops = sdpsettings('solver','cplex'); % gurobi
ans = optimize(Cons,obj,ops)
%% 求解成功后取值
PG_G = value(PG_G) ;
PG_RE = value(PG_RE) ;
PG_CSP = value(PG_CSP) ;
PC_Load = value(PC_Load) ;
onoff_gen = value(onoff_gen) ;
onoff_CSP = value(onoff_CSP) ;
Branch = value(Branch) ;
Cost_StartUp = value(Cost_StartUp);
obj = value(obj); % 总成本
Pt_TES_charge = value(Pt_TES_charge);
Pt_TES_discharge = value(Pt_TES_discharge);
Et_TES = value(Et_TES);
disp(['IEEE14 不考虑N-k的和无CSP的经济调度情况,运行成本为 ', num2str(obj)])
%% 绘图
% 已知的相关输入数据
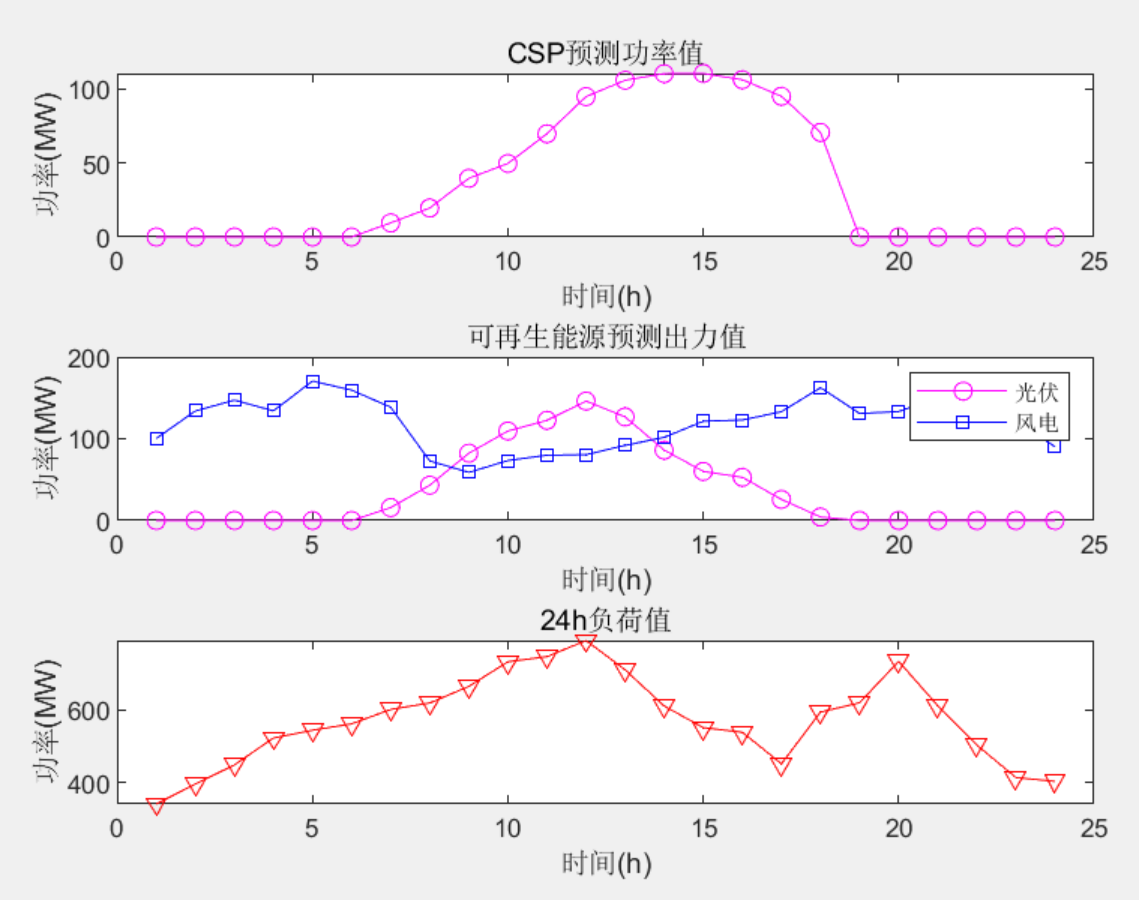
figure
subplot(3,1,1)
plot(PtCSP_fore * baseMVA,'m-o');
title('CSP预测功率值')
xlabel('时间(h)');
ylabel('功率(MW)');
subplot(3,1,2)
plot(P_RE(1,:) * baseMVA,'m-o'); hold on
plot(P_RE(2,:) * baseMVA,'b-s');
title('可再生能源预测出力值')
xlabel('时间(h)');
ylabel('功率(MW)');
legend('光伏','风电')
subplot(3,1,3)
plot(sum(PD) * baseMVA,'r-v');
title('24h负荷值')
xlabel('时间(h)');
ylabel('功率(MW)');
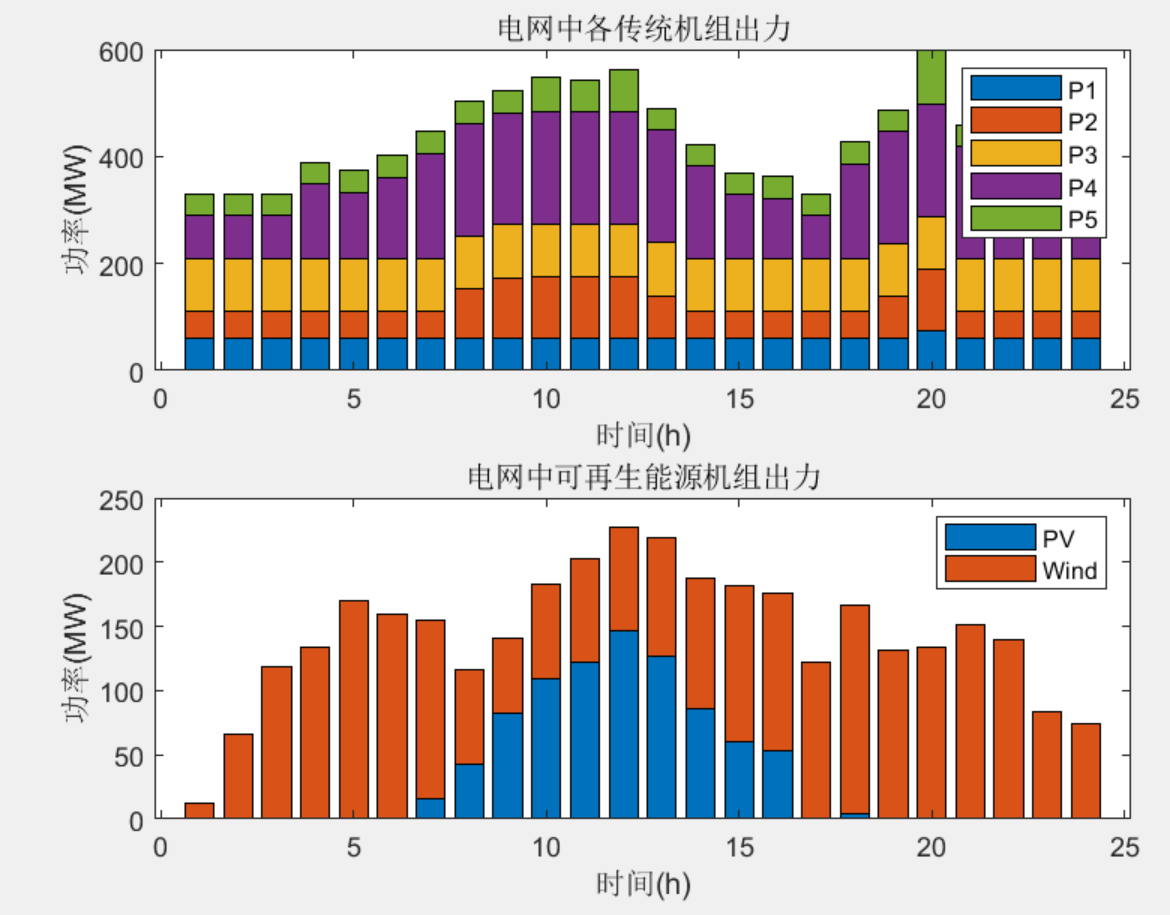
% subplot(2,1,2)
% bar(baseMVA*PG_RE',0.75,'stack'); hold on; % 各PV、Wind机组出力
% legend('PV','Wind')
% title('电网中可再生能源机组出力')
% xlabel('时间(h)');
% ylabel('功率(MW)');
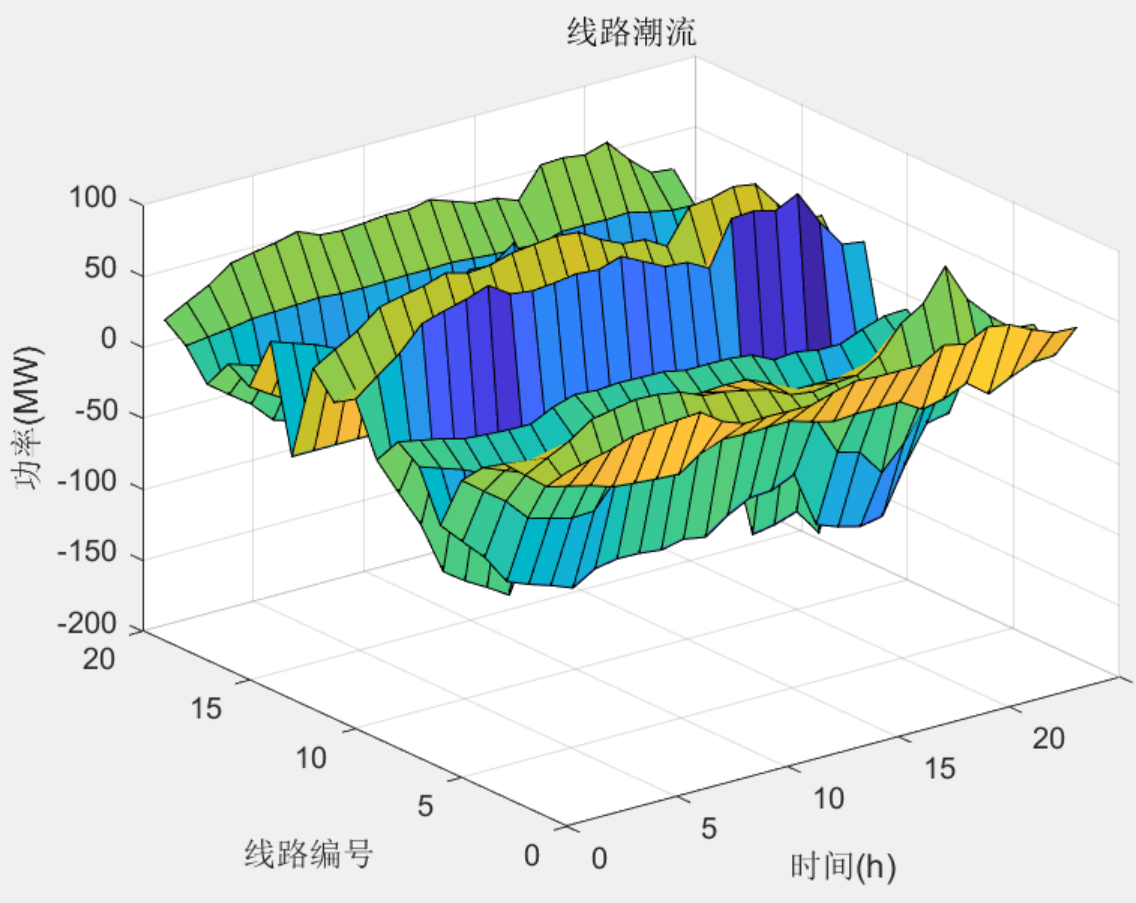
% figure
% surf(baseMVA*PC_Load);
% title('负荷削减量')
% xlabel('时间(h)');
% ylabel('功率(MW)');
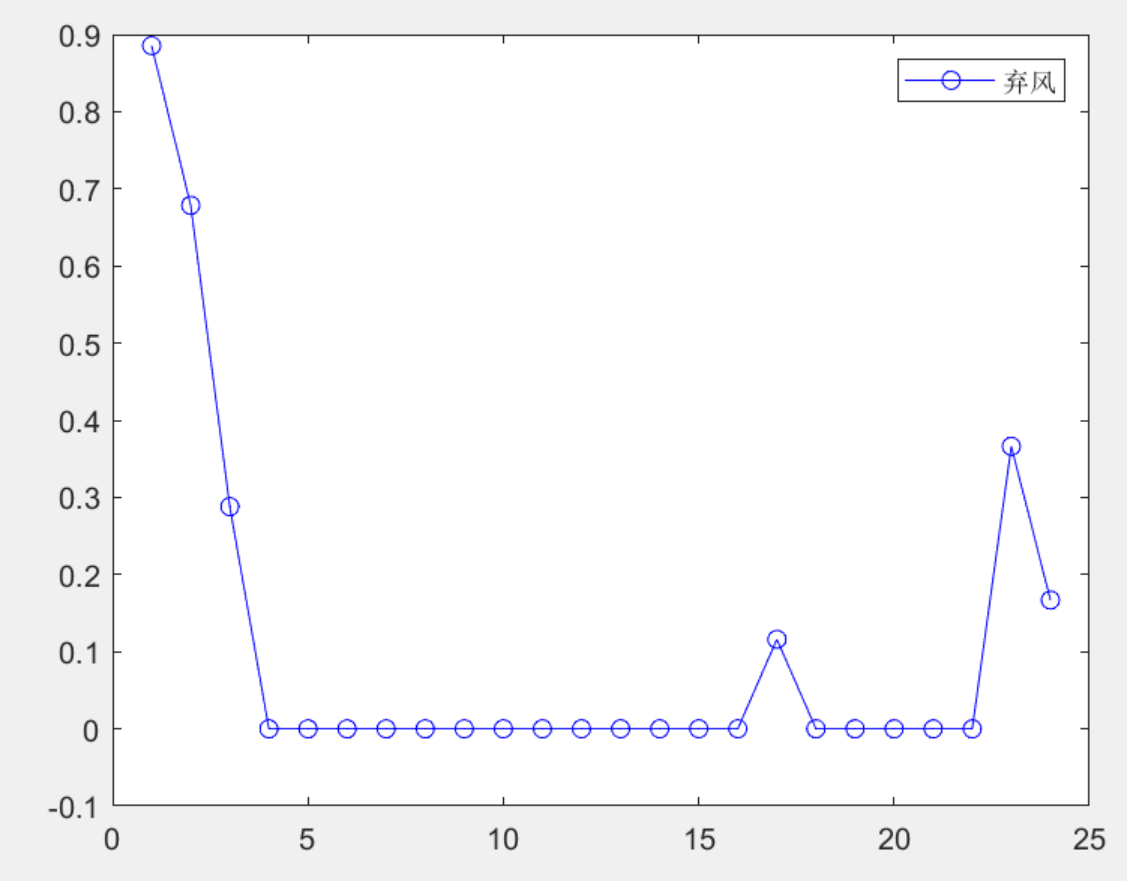
**3 **部分结果
4 下载链接
版权归原作者 科研工作站 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。