提示:本文采用的蒸馏方式为 Distilling Object Detectors with Fine-grained Feature Imitation 这篇文章
文章目录
前言
提示:这里可以添加本文要记录的大概内容:
本文介绍的论文《Distilling Object Detectors with Fine-grained Feature Imitation》即是基于 Fine-grained Feature Imitation 技术的目标检测知识蒸馏方法。该方法将 Fine-grained Feature Imitation 应用于学生模型的中间层,以捕捉更丰富的特征信息。通过在训练过程中引入目标检测任务的监督信号,Fine-grained Feature Imitation 技术可以更好地保留复杂模型中的细节特征,从而提高了轻量级模型的性能。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、Distilling Object Detectors with Fine-grained Feature Imitation 论文介绍
示例:pandas 是基于NumPy 的一种工具,该工具是为了解决数据分析任务而创建的。
1.创新点
Fine-grained Feature Imitation 技术可以概括为以下三个步骤:
- 利用复杂模型的中间层作为特征提取器,并用它提取学生模型的中间层的特征。
- 利用 Fine-grained Feature Imitation 技术对特征进行蒸馏,使学生模型能够学习到更丰富的特征信息。
- 在训练过程中引入目标检测任务的监督信号,以更好地保留复杂模型中的细节特征。
其核心思想是 teacher 网络中需要传递给 student 网络的应该是有效信息,而非无效的 background 信息。
2.内容介绍
1. Fine-Gained区域提取
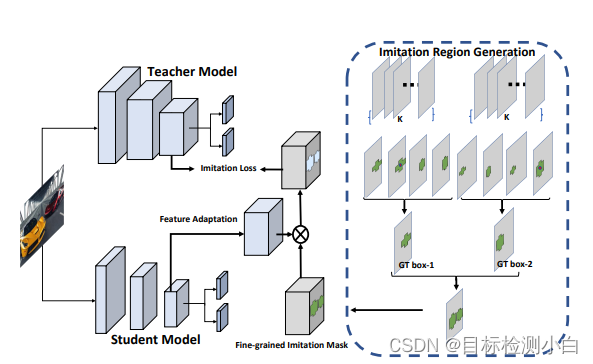
上图中的红色和绿色边界框是在相应位置上的锚框。红色 anchor 表示与 gt 的边界框重叠最大,绿色 anchor 表示附近的物体样本。蒸馏时并不是对所有的anchor蒸馏,而是对gt框附近的anchor进行蒸馏,对于backbone输出的特征图,假设尺度为H X W,
网络中使用的anchor数量为K, 具体执行步骤如下:
- 对于给定的特征图,生成H X W X K 个anchor, 并计算与gt anchor的IOU值m,
- 计算最大的IOU值 M = max(m), 引入参数阈值因子Ψ, 计算过滤阈值F = M x Ψ, 利用F进行IOU过滤,这里只保留大于F的部分,计算之后得到一个mask, 尺度为H X W.
2. loss 损失值
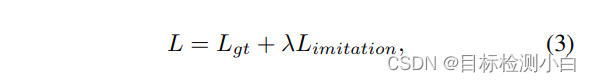
损失函数部分由两块组成,一块为Fine-grained Feature Imitation 损失,另一块为目标检测的分类和回归损失,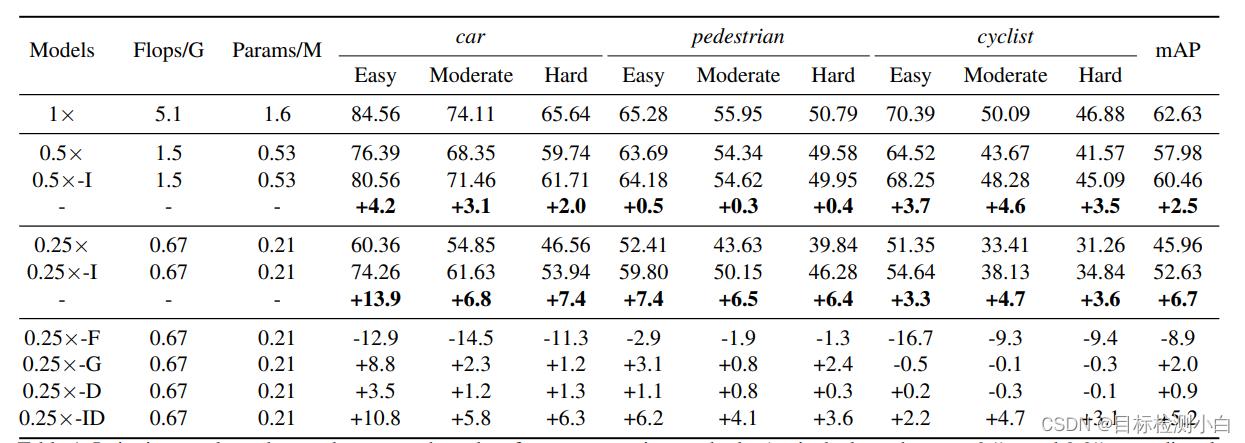
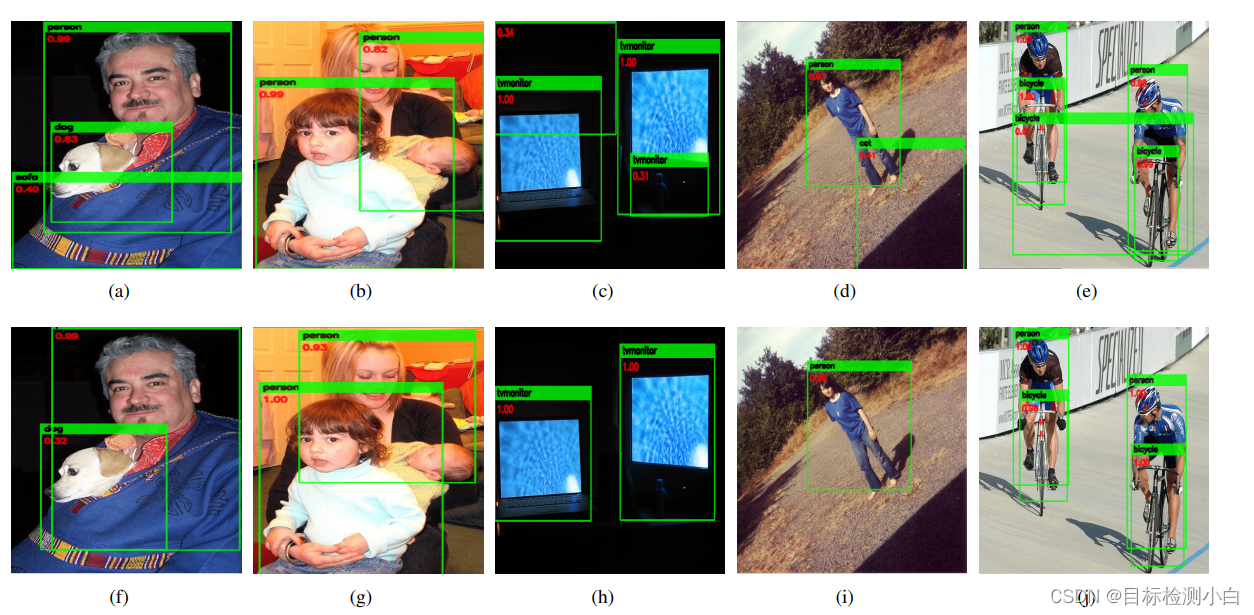
论文中展示了实验的对比结果,原论文是基于Faster Rcnn算法进行蒸馏,因此本文选择基于yolov5算法进行蒸馏。
二、yolov5 添加知识蒸馏
1.部分代码展示
调整gt anchors转换为相对于原图的位置
defmake_gt_boxes(gt_boxes, max_num_box, batch, img_size):
new_gt_boxes =[]for i inrange(batch):# 获取第i个batch的所有真实框
boxes = gt_boxes[gt_boxes[:,0]== i]# 真实框的个数
num_boxes = boxes.size(0)if num_boxes < max_num_box:
gt_boxes_padding = torch.zeros([max_num_box, gt_boxes.size(1)], dtype=torch.float)
gt_boxes_padding[:num_boxes,:]= boxes
else:
gt_boxes_padding = boxes[:max_num_box]
new_gt_boxes.append(gt_boxes_padding.unsqueeze(0))
new_gt_boxes = torch.cat(new_gt_boxes)# transfer [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2]
new_gt_boxes_aim = torch.zeros(size=new_gt_boxes.size())
new_gt_boxes_aim[:,:,2]=(new_gt_boxes[:,:,2]-0.5* new_gt_boxes[:,:,4])* img_size[1]
new_gt_boxes_aim[:,:,3]=(new_gt_boxes[:,:,3]-0.5* new_gt_boxes[:,:,5])* img_size[0]
new_gt_boxes_aim[:,:,4]=(new_gt_boxes[:,:,2]+0.5* new_gt_boxes[:,:,4])* img_size[1]
new_gt_boxes_aim[:,:,5]=(new_gt_boxes[:,:,3]+0.5* new_gt_boxes[:,:,5])* img_size[0]return new_gt_boxes_aim
计算掩码 mask
defgetMask(batch_size, gt_boxes, img_size, feat, anchors, max_num_box, device):# [b, K, 4]
gt_boxes = make_gt_boxes(gt_boxes, max_num_box, batch_size, img_size)# 原图相对于当前特征图的步长
feat_stride = img_size[0]/ feat.size(2)
anchors = torch.from_numpy(generate_anchors(feat_stride, anchors))
feat = feat.cpu()
height, width = feat.size(2), feat.size(3)
feat_height, feat_width = feat.size(2), feat.size(3)
shift_x = np.arange(0, feat_width)* feat_stride
shift_y = np.arange(0, feat_height)* feat_stride
shift_x, shift_y = np.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
shifts = torch.from_numpy(np.vstack((shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel(),
shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel())).transpose())
shifts = shifts.contiguous().type_as(feat).float()# num of anchors [3]
A = anchors.size(0)
K = shifts.size(0)
anchors = anchors.type_as(gt_boxes)# all_anchors [K, A, 4]
all_anchors = anchors.view(1, A,4)+ shifts.view(K,1,4)
all_anchors = all_anchors.view(K * A,4)# compute iou [all_anchors, gt_boxes]
IOU_map = bbox_overlaps_batch(all_anchors, gt_boxes, img_size).view(batch_size, height, width, A, gt_boxes.shape[1])
mask_batch =[]for i inrange(batch_size):
max_iou, _ = torch.max(IOU_map[i].view(height * width * A, gt_boxes.shape[1]), dim=0)
mask_per_im = torch.zeros([height, width], dtype=torch.int64).to(device)for k inrange(gt_boxes.shape[1]):if torch.sum(gt_boxes[i][k])==0:break
max_iou_per_gt = max_iou[k]*0.5
mask_per_gt = torch.sum(IOU_map[i][:,:,:, k]> max_iou_per_gt, dim=2)
mask_per_im += mask_per_gt.to(device)
mask_batch.append(mask_per_im)return mask_batch
计算imitation损失
defcompute_mask_loss(mask_batch, student_feature, teacher_feature, imitation_loss_weight):
mask_list =[]for mask in mask_batch:
mask =(mask >0).float().unsqueeze(0)
mask_list.append(mask)# [batch, height, widt
mask_batch = torch.stack(mask_list, dim=0)
norms = mask_batch.sum()*2
mask_batch_s = mask_batch.unsqueeze(4)
no = student_feature.size(-1)
bs, na, height, width, _ = mask_batch_s.shape
mask_batch_no = mask_batch_s.expand((bs, na, height, width, no))
sup_loss =(torch.pow(teacher_feature - student_feature,2)* mask_batch_no).sum()/ norms
sup_loss = sup_loss * imitation_loss_weight
return sup_loss
总结
完整代码请查看GitHub,麻烦动动小手点亮一下star
https://github.com/xing-bing
版权归原作者 目标检测小白 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。