目录
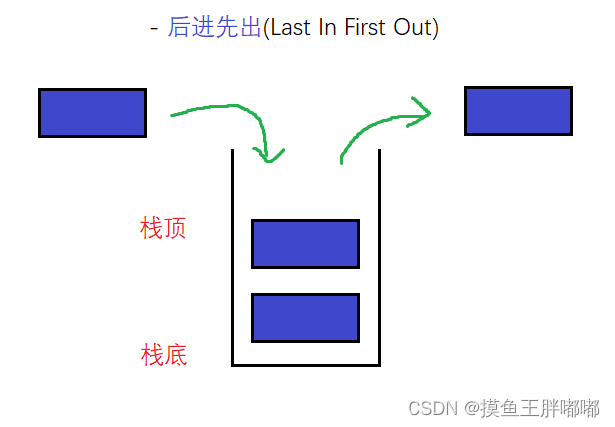
一、什么是栈?
栈(stack)又名堆栈,它是一种运算受限的线性表。限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底。向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶。
二、怎么使用栈?
栈的基本操作主要有:判空、判满、取栈顶元素、在栈顶进行插入和删除。在栈顶插入元素称为入栈,在栈顶删除元素称为出栈。
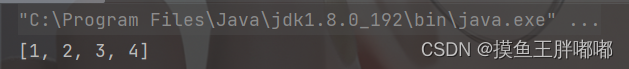
2.1 入栈 - push()
Stack<Integer> s1 =newStack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);System.out.println(s1);
2.2 判空 - empty()
Stack<Integer> s1 =newStack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);System.out.println(s1.empty());

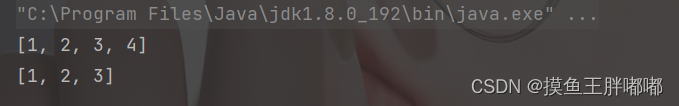
2.3 出栈 - pop()
Stack<Integer> s1 =newStack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);System.out.println(s1);
s1.pop();System.out.println(s1);
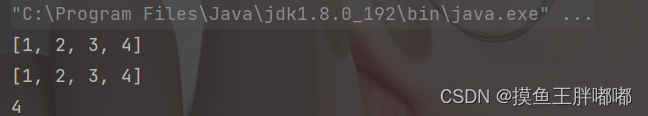
2.4 获取栈顶元素 - peek()
Stack<Integer> s1 =newStack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);System.out.println(s1);
s1.peek();System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s1.peek());
2.5 获取栈中有效元素个数 - size()
Stack<Integer> s1 =newStack<>();
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);System.out.println(s1.size());

三、栈的模拟实现
3.1 push
publicbooleanisFull(){returnthis.usedSize ==this.elem.length;}publicvoidpush(int val){if(isFull()){//扩容this.elem =Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.usedSize);}this.elem[this.usedSize]= val;this.usedSize++;}
3.2 isEmpty
publicbooleanisEmpty(){returnthis.usedSize ==0;}
3.3 pop
publicintpop(){if(isEmpty()){thrownewRuntimeException("栈为空");}int oldVal =this.elem[usedSize-1];this.usedSize--;return oldVal;}
3.4 peek
publicintpeek(){if(isEmpty()){thrownewRuntimeException("栈为空");}returnthis.elem[usedSize-1];}
3.5 MyStack.java
importjava.lang.reflect.Array;importjava.util.Arrays;@SuppressWarnings({"all"})publicclassMyStack{publicint[] elem;publicint usedSize;publicMyStack(){this.elem =newint[5];}publicvoidpush(int val){if(isFull()){//扩容this.elem =Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.usedSize);}this.elem[this.usedSize]= val;this.usedSize++;}publicbooleanisFull(){returnthis.usedSize ==this.elem.length;}publicintpop(){if(isEmpty()){thrownewRuntimeException("栈为空");}int oldVal =this.elem[usedSize-1];this.usedSize--;return oldVal;}publicintpeek(){if(isEmpty()){thrownewRuntimeException("栈为空");}returnthis.elem[usedSize-1];}publicbooleanisEmpty(){returnthis.usedSize ==0;}}
四、经典题
4.1 有效的括号

classSolution{publicbooleanisValid(String s){Stack<Character> stack =newStack<>();for(int i =0; i < s.length(); i++){char ch = s.charAt(i);if(ch =='('|| ch =='['|| ch =='{'){//如果是左括号 直接入栈
stack.push(ch);}else{//遇到了右括号if(stack.empty()){System.out.println("右括号多");returnfalse;}char top = stack.peek();//哪个左括号if(top =='('&& ch ==')'|| top =='['&& ch ==']'|| top =='{'&& ch =='}'){
stack.pop();}else{System.out.println("左右括号不匹配");returnfalse;}}}if(!stack.empty()){System.out.println("左括号多");returnfalse;}returntrue;}}
4.2 逆波兰表达式求值

classSolution{publicintevalRPN(String[] tokens){Stack<Integer> stack =newStack<>();for(int i =0; i < tokens.length; i++){String val = tokens[i];if(!isOperation(val)){
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(val));}else{int num2 = stack.pop();int num1 = stack.pop();switch(val){case"+":
stack.push(num1+num2);break;case"-":
stack.push(num1-num2);break;case"*":
stack.push(num1*num2);break;case"/":
stack.push(num1/num2);break;}}}return stack.pop();}privatebooleanisOperation(String x){if(x.equals("+")|| x.equals("-")|| x.equals("*")|| x.equals("/")){returntrue;}returnfalse;}}
版权归原作者 摸鱼王胖嘟嘟 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。