LSTM的反向传播过程相对复杂,主要因为其对应的控制门较多,而对于每一个控制门我们都需要求导,所以工作量较大。
首先我们根据LSTM结构图分析一下每个控制门的求导过程。在讲解反向传播之前,先了解一些要用到的参数意义。
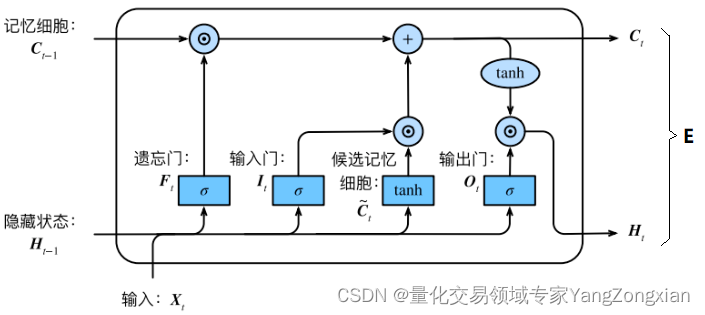
一般来说LSTM在层后会接一个全连接层FNN,全连接层后面再接一个损失函数Loss,所以这里我将全连接层反向传回给LSTM层的总误差称之为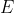。
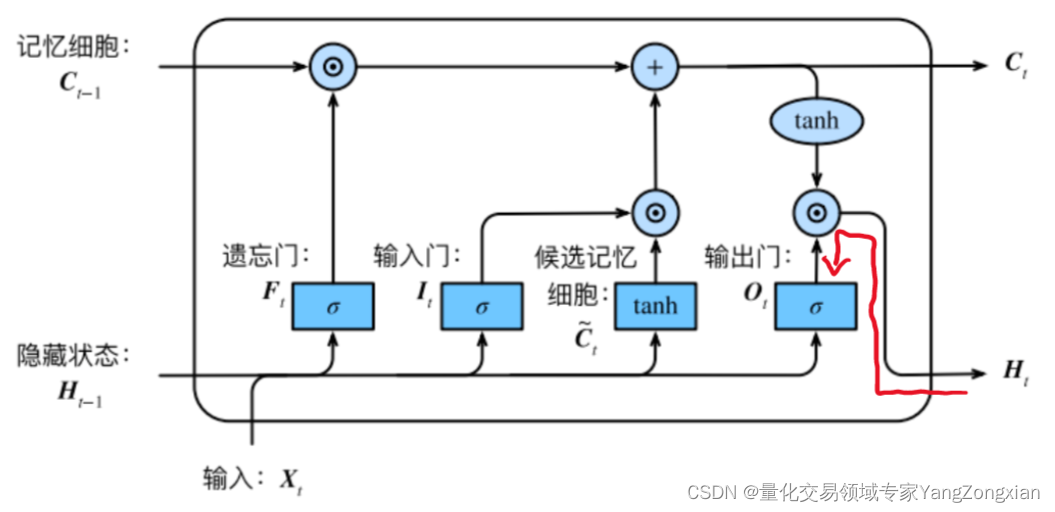
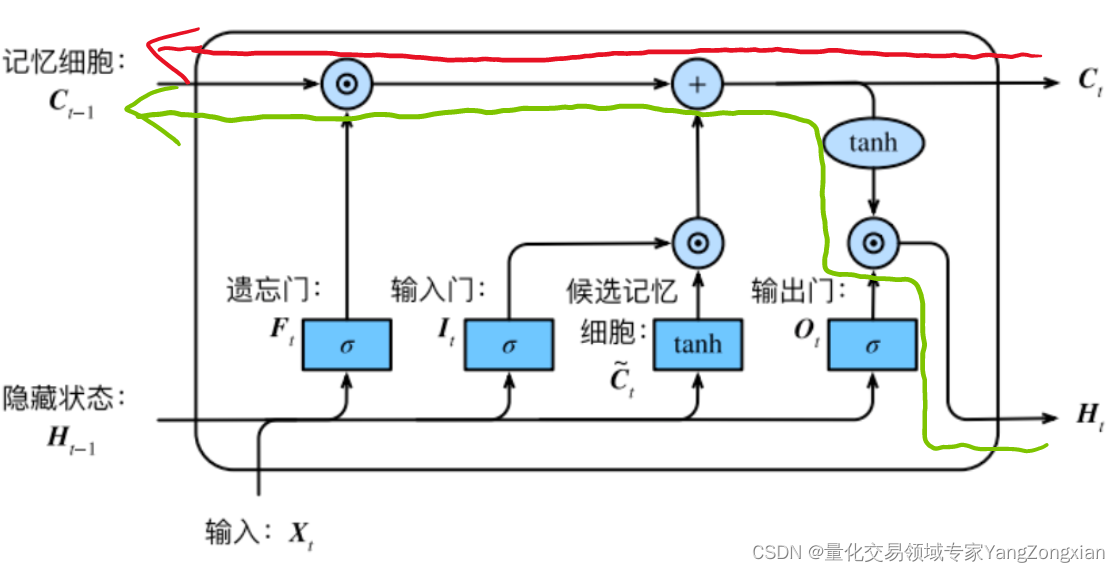
从上图LSTM的结构可以观察出,回传的总误差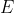其实会由两个分支进入LSTM内部,分别是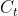和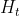。因此从宏观上看,每个LSTM单元误差传播的起始点为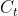和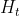,终点为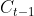和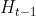,在起始点和终点之间分别夹杂着4个控制门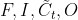,上述的这些元素,其实就是LSTM整个反向传播求导过程要涉及的全部内容。
下面我们详细介绍每个元素在求导中的处理方法。
二、反向传播过程符号定义和说明
2.1.符号意义说明
LSTM单元中误差反向传播的过程大体分为两种情况:一种是反向传播的误差来源只包含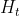一条链,比如控制门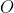;另一种是反向传播的误差来源包含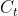和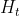两条传播链,比如控制门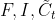以及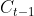。如下图所示的遗忘门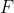,其反向传播的误差就是来自于红色和绿色两条传播链,计算时两条链都要计算。
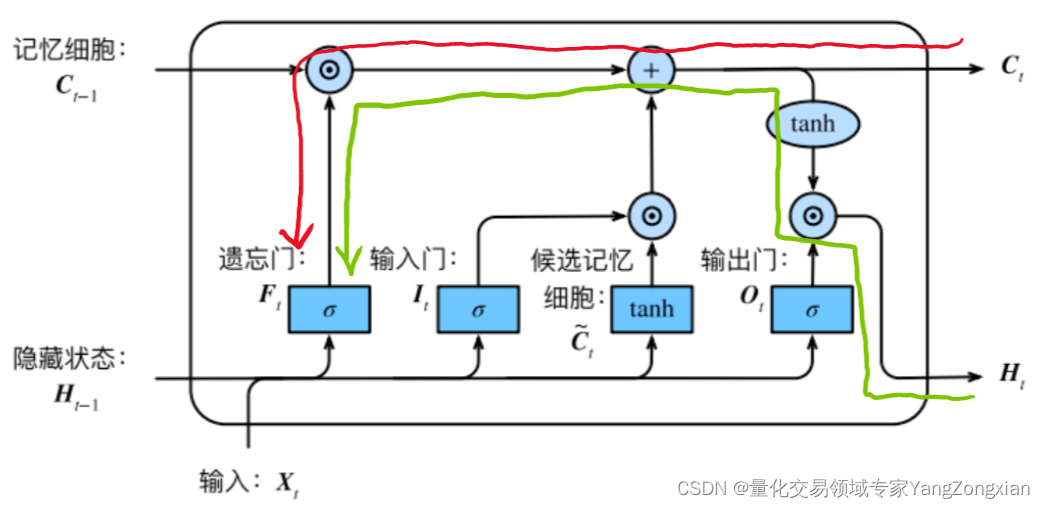
下面我们分别列举各个元素的反向传播路径:
的误差来自于
和
两条传播链,传播路径为:
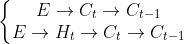
的误差来自于四条传播链,分别对应下面
四个控制门:
(1)控制门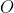的误差由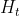传来,传播路径为:
(2)控制门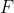的误差由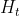和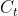传来,传播路径为:
(3)控制门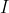的误差由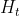和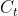传来,传播路径为:
(4)控制门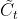的误差由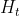和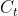传来,传播路径为:
列举一下每个元素求偏导过程中的符号定义
- LSTM单元反向传播的起点
和
的误差,是由上一层传递来的,这里表示为
和
,是已知常量。
- LSTM单元中的
是由
和
计算而来,所以求导过程中存在
到
的偏导数
,以及
到
的偏导数
。
分别由
计算而来,所以求导过程中存在
分别到
的偏导数
,
,
。
- LSTM单元中从控制门
到
存在偏导数
,
,
,
。从
和
到
的偏导数则为
和
。
- 最后在求偏导的过程中还会用到一些前向传播的数值,如
,
,
,
等,这些参数在计算前向传播过程中都可以加以保留。
- 在理清上述这些反向传播中存在的关系后,下面我们就可以完成整个LSTM单元的反向传播计算了。
LSTM计算顺序如下图所示:
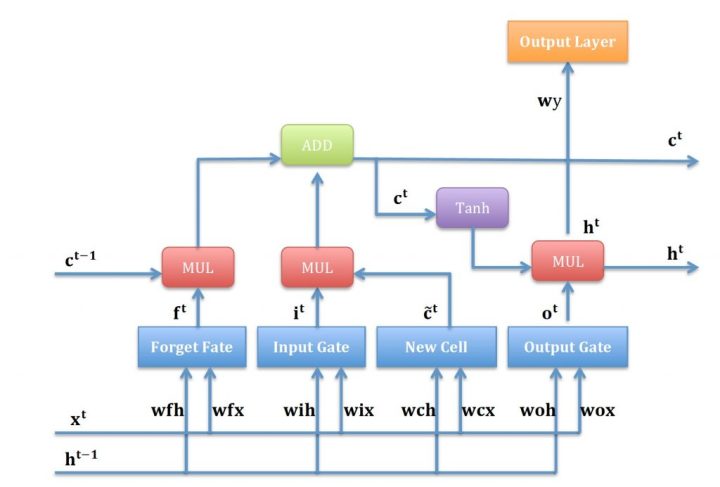
介绍完这些符号定义后,下面就可以开始LSTM的反向传播计算了。
2.2.重要细节——特殊的传播链Ct
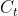是一条比较特殊的传播链,在前向传播时,每个sample都中包含n个Timestep,在第一个Timestep计算时,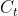的初始值是零矩阵,在后续的Timestep计算时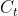会进行不断累计和向后传递。在当前LSTM层计算完成后,向下个LSTM层传递时,只向后传递输出的状态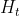,作为下个LSTM层的输入Xh,而当前层的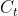值不再向下个LSTM层传递。
所以同理,在反向传播时,下一层的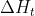会反向传播到上一层作为误差输入,但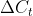不会回传,所以每一层LSTM按照时间步倒序计算反向传播过程中,计算第一个Timestep时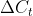的初始值也是零矩阵,并且在后续时间步中进行累计和传递。
这一规则十分重要,在这里单独强调,后续内容不再重复说明。
三、LSTM反向传播流程解析
上一节我们说过,从反向传播链终点的角度出发,有两种类型的传播链,即 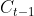链和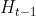链 。而细分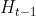的传播链其实又有两种类型,即包含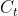的和不包含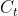的。所以反向传播链大体上可分为三类,下面来讲解这三种流程。
3.1.第一类偏导: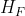 ,
,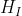 ,
,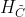

3.1.1.遗忘门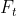 求导过程
求导过程
两条完整求导路径表达式如下
**3.1.1.1.**绿色路径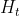到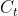的偏导
**3.1.1.2.**红色路径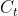到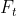的偏导
**3.1.1.3.**遗忘门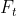到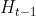的偏导
**3.1.1.4.**两条路径表达式合并
3.1.2.输入门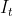 求导过程
求导过程
原理同上,这里直接写
** 3.1.2.1.**到
的偏导
**3.1.2.2.**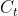到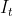的偏导
**3.1.2.3.**输入门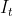到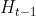的偏导
**3.1.2.4.**两条路径表达式合并
3.1.3.候选记忆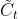 求导过程
求导过程
原理同上,这里直接写
** 3.1.3.1.**到
的偏导
**3.1.3.2.**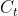到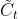的偏导
**3.1.3.3.**候选记忆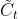到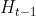的偏导
**3.1.3.4.**两条路径表达式合并
3.2.第二类偏导: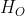
完成表达式如下
** 3.2.1.**红色路径到
偏导
**3.2.2.**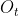到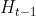偏导
**3.2.3.**表达式合并
3.3.第三类偏导: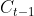
两条完整求导路径表达式如下
** 3.3.1.**红色路径到
的偏导
** 3.3.2.**绿色路径到
的偏导
** 3.3.3.**两条路径表达式合并
3.4.合并
四个控制门计算完成后,最终合并起来,表达式如下:
四、权重的反向传播
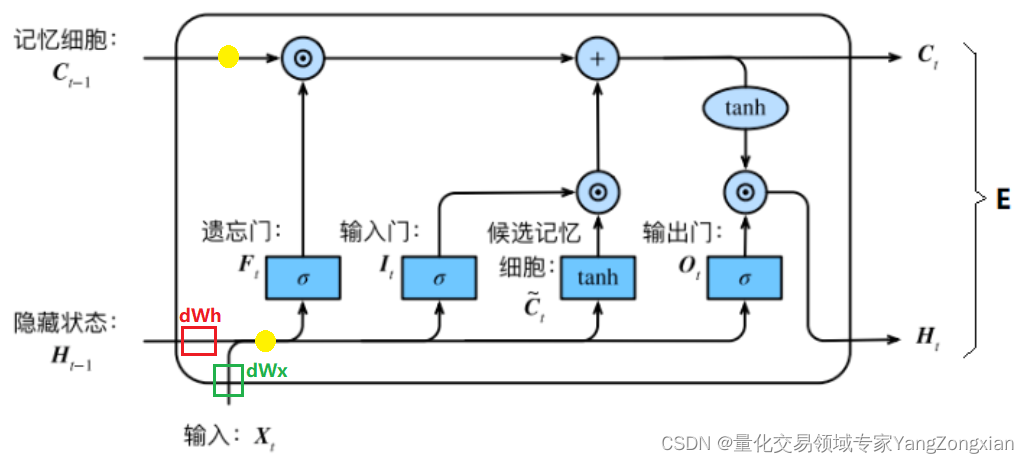
在上述第三节的求导过程结束后,此时误差就传递到了上图中的两个黄色圆圈部分,显然还差一步反向传播就完成了。最后一步就是将误差从黄色的圆圈部分分别传递到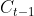,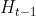,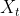。对于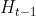和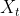来说,要计算两个权重矩阵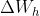和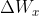,而对于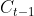来说,不必求矩阵,直接向后传递即可。
在前向传播时计算流程如下:
由上式可得,反向传播的表达式可以表达如下:
最后还剩一个偏置项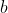,我们将上一节得出的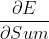直接降维即可得到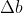,具体的程序实现方法会在下一篇文章中更直观的介绍。
五、总结
上面就是一个完整的LSTM单元反向传播流程,至此本文已经对LSTM的反向传播理论基础进行了比较清楚的讲解。结合上一篇LSTM网络前向传播原理讲解,相信大家对LSTM的基本原理有了一个比较清晰的认识了。
但这仅仅是单一的LSTM模型前向传播和反向传播原理,不足以构成一个完整的模型。但是有了上述基础,下篇文章中我们就可以1:1实现一个包含输入,隐藏层,输出,损失函数的完整的神经网络模型了。
文章正在写作中……
参考文献:
循环神经网络RNN&LSTM推导及实现 - 知乎
LSTM的推导与实现 - liujshi - 博客园
RNN、LSTM反向传播推导详解 - 灰信网(软件开发博客聚合)
手推公式:LSTM单元梯度的详细的数学推导
LSTM –随时间反向传播的推导 - 芒果文档
版权归原作者 日拱一两卒 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。