在深度学习中,第一步要做的往往就是处理数据集,尤其是学习百度飞桨PaddlePaddle的小伙伴,数据集经常要用Voc格式的,比如性能突出的ppyolo等模型。所以学会数据集转化的本领是十分必要的。这篇博客就带你一起进行Yolo与Voc格式的相互转化,附详细代码!
文章目录
YOLO数据集介绍
Yolo数据集主要是txt文件,一般包括train文件夹和val文件夹,每一个文件夹下有与图片同名的txt文件,基本结构如下:
|–image
- ||–train
- ||–val
|–label
- ||–train
- ||–val
txt的标签如下图所示:
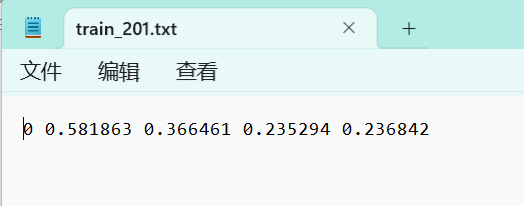
第一列为目标类别,后面四个数字为方框左上角与右下角的坐标,可以看到都是小于1的数字,是因为对应的整张图片的比例,所以就算图像被拉伸放缩,这种txt格式的标签也可以找到相应的目标。
VOC数据集介绍
VOC格式数据集一般有着如下的目录结构:
VOC_ROOT #根目录
├── JPEGImages # 存放源图片
│ ├── aaaa.jpg
│ ├── bbbb.jpg
│ └── cccc.jpg
├── Annotations # 存放xml文件,与JPEGImages中的图片一一对应,解释图片的内容等等
│ ├── aaaa.xml
│ ├── bbbb.xml
│ └── cccc.xml
└── ImageSets
└── Main
├── train.txt # txt文件中每一行包含一个图片的名称
└── val.txt
其中JPEGImages目录中存放的是源图片的数据,(当然图片并不一定要是.jpg格式的,只是规定文件夹名字叫JPEGImages);Annotations目录中存放的是标注数据,VOC的标注是xml格式的,文件名与JPEGImages中的图片一一对应。
重点看下xml格式的标注格式:
<annotation><folder>VOC_ROOT</folder><filename>aaaa.jpg</filename># 文件名<size># 图像尺寸(长宽以及通道数) <width>500</width><height>332</height><depth>3</depth></size><segmented>1</segmented># 是否用于分割(在图像物体识别中无所谓)<object># 检测到的物体<name>horse</name># 物体类别<pose>Unspecified</pose># 拍摄角度,如果是自己的数据集就Unspecified<truncated>0</truncated># 是否被截断(0表示完整)<difficult>0</difficult># 目标是否难以识别(0表示容易识别)<bndbox># bounding-box(包含左下角和右上角xy坐标)<xmin>100</xmin><ymin>96</ymin><xmax>355</xmax><ymax>324</ymax></bndbox></object><object># 检测到多个物体<name>person</name><pose>Unspecified</pose><truncated>0</truncated><difficult>0</difficult><bndbox><xmin>198</xmin><ymin>58</ymin><xmax>286</xmax><ymax>197</ymax></bndbox></object></annotation>
Yolo转VOC
文件结构如下:
Yolo转VOC #根目录
├── dataset
│ ├── Annotations
│ ├── image
└──image图像
│ └── label
└──txt文件
├── Yolo转VOC.py # 代码文件
具体代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-"""
@Project :Yolo与VOC转化
@File :Yolo转Voc.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :咋
@Date :2023/3/6 16:45
"""from xml.dom.minidom import Document
import os
import cv2
# def makexml(txtPath, xmlPath, picPath): # txt所在文件夹路径,xml文件保存路径,图片所在文件夹路径defmakexml(picPath, txtPath, xmlPath):# txt所在文件夹路径,xml文件保存路径,图片所在文件夹路径"""此函数用于将yolo格式txt标注文件转换为voc格式xml标注文件
"""
dic ={'0':"blue",# 创建字典用来对类型进行转换'1':"red",# 此处的字典要与自己的classes.txt文件中的类对应,且顺序要一致}
files = os.listdir(txtPath)for i, name inenumerate(files):
xmlBuilder = Document()
annotation = xmlBuilder.createElement("annotation")# 创建annotation标签
xmlBuilder.appendChild(annotation)
txtFile =open(txtPath + name)
txtList = txtFile.readlines()
img = cv2.imread(picPath + name[0:-4]+".jpg")
Pheight, Pwidth, Pdepth = img.shape
folder = xmlBuilder.createElement("folder")# folder标签
foldercontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("driving_annotation_dataset")
folder.appendChild(foldercontent)
annotation.appendChild(folder)# folder标签结束
filename = xmlBuilder.createElement("filename")# filename标签
filenamecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(name[0:-4]+".jpg")
filename.appendChild(filenamecontent)
annotation.appendChild(filename)# filename标签结束
size = xmlBuilder.createElement("size")# size标签
width = xmlBuilder.createElement("width")# size子标签width
widthcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pwidth))
width.appendChild(widthcontent)
size.appendChild(width)# size子标签width结束
height = xmlBuilder.createElement("height")# size子标签height
heightcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pheight))
height.appendChild(heightcontent)
size.appendChild(height)# size子标签height结束
depth = xmlBuilder.createElement("depth")# size子标签depth
depthcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(Pdepth))
depth.appendChild(depthcontent)
size.appendChild(depth)# size子标签depth结束
annotation.appendChild(size)# size标签结束for j in txtList:
oneline = j.strip().split(" ")object= xmlBuilder.createElement("object")# object 标签
picname = xmlBuilder.createElement("name")# name标签
namecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(dic[oneline[0]])
picname.appendChild(namecontent)object.appendChild(picname)# name标签结束
pose = xmlBuilder.createElement("pose")# pose标签
posecontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("Unspecified")
pose.appendChild(posecontent)object.appendChild(pose)# pose标签结束
truncated = xmlBuilder.createElement("truncated")# truncated标签
truncatedContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
truncated.appendChild(truncatedContent)object.appendChild(truncated)# truncated标签结束
difficult = xmlBuilder.createElement("difficult")# difficult标签
difficultcontent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode("0")
difficult.appendChild(difficultcontent)object.appendChild(difficult)# difficult标签结束
bndbox = xmlBuilder.createElement("bndbox")# bndbox标签
xmin = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmin")# xmin标签
mathData =int(((float(oneline[1]))* Pwidth +1)-(float(oneline[3]))*0.5* Pwidth)
xminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
xmin.appendChild(xminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmin)# xmin标签结束
ymin = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymin")# ymin标签
mathData =int(((float(oneline[2]))* Pheight +1)-(float(oneline[4]))*0.5* Pheight)
yminContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
ymin.appendChild(yminContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymin)# ymin标签结束
xmax = xmlBuilder.createElement("xmax")# xmax标签
mathData =int(((float(oneline[1]))* Pwidth +1)+(float(oneline[3]))*0.5* Pwidth)
xmaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
xmax.appendChild(xmaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(xmax)# xmax标签结束
ymax = xmlBuilder.createElement("ymax")# ymax标签
mathData =int(((float(oneline[2]))* Pheight +1)+(float(oneline[4]))*0.5* Pheight)
ymaxContent = xmlBuilder.createTextNode(str(mathData))
ymax.appendChild(ymaxContent)
bndbox.appendChild(ymax)# ymax标签结束object.appendChild(bndbox)# bndbox标签结束
annotation.appendChild(object)# object标签结束
f =open(xmlPath + name[0:-4]+".xml",'w')
xmlBuilder.writexml(f, indent='\t', newl='\n', addindent='\t', encoding='utf-8')
f.close()if __name__ =="__main__":
picPath ="dataset/JPEGImages/"# 图片所在文件夹路径,后面的/一定要带上
txtPath ="dataset/YOLOLables/"# txt所在文件夹路径,后面的/一定要带上
xmlPath ="dataset/annotations/"# xml文件保存路径,后面的/一定要带上
makexml(picPath, txtPath, xmlPath)
VOC转Yolo
相当于上述操作的逆运算,这里直接给出代码:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
import random
from shutil import copyfile
from lxml import etree
#自己的类别
classes = [“0”, “1”,‘2’,‘3’,‘person’]
classes=[“ball”]
TRAIN_RATIO = 80 #训练集比例
def clear_hidden_files(path):
dir_list = os.listdir(path)
for i in dir_list:
abspath = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(path), i)
if os.path.isfile(abspath):
if i.startswith(“._”):
os.remove(abspath)
else:
clear_hidden_files(abspath)
#数据转换
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
#编写格式
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open(‘./dataset/annotations/%s.xml’ % image_id)
out_file = open(‘./dataset/YOLOLabels/%s.txt’ % image_id, ‘w’)
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find(‘size’)
w = int(size.find(‘width’).text)
h = int(size.find(‘height’).text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
in_file.close()
out_file.close()
#创建上述目录结构
wd = os.getcwd()
work_sapce_dir = os.path.join(wd, “dataset/”)
if not os.path.isdir(work_sapce_dir):
os.mkdir(work_sapce_dir)
annotation_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, “annotations/”)
if not os.path.isdir(annotation_dir):
os.mkdir(annotation_dir)
clear_hidden_files(annotation_dir)
image_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, “JPEGImages/”)
if not os.path.isdir(image_dir):
os.mkdir(image_dir)
clear_hidden_files(image_dir)
yolo_labels_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, “YOLOLabels/”)
if not os.path.isdir(yolo_labels_dir):
os.mkdir(yolo_labels_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolo_labels_dir)
yolov5_images_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, “images/”)
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_dir)
yolov5_labels_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, “labels/”)
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_dir)
yolov5_images_train_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, “train/”)
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_train_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_train_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_train_dir)
yolov5_images_test_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, “val/”)
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_test_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_test_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_test_dir)
yolov5_labels_train_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_labels_dir, “train/”)
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_train_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_train_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_train_dir)
yolov5_labels_test_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_labels_dir, “val/”)
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_test_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_test_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_test_dir)
#创建两个记录照片名字的文件
train_file = open(os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, “yolov5_train.txt”), ‘w’)
test_file = open(os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, “yolov5_val.txt”), ‘w’)
train_file.close()
test_file.close()
train_file = open(os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, “yolov5_train.txt”), ‘a’)
test_file = open(os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, “yolov5_val.txt”), ‘a’)
#随机划分
list_imgs = os.listdir(image_dir) # list image files
prob = random.randint(1, 100)
print(“Probability: %d” % prob)
for i in range(0, len(list_imgs)):
path = os.path.join(image_dir, list_imgs[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
image_path = image_dir + list_imgs[i]
voc_path = list_imgs[i]
(nameWithoutExtention, extention) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_path))
(voc_nameWithoutExtention, voc_extention) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(voc_path))
annotation_name = nameWithoutExtention + ‘.xml’
annotation_path = os.path.join(annotation_dir, annotation_name)
label_name = nameWithoutExtention + ‘.txt’
label_path = os.path.join(yolo_labels_dir, label_name)
prob = random.randint(1, 100)
print(“Probability: %d” % prob)
if (prob < TRAIN_RATIO): # train dataset
if os.path.exists(annotation_path):
train_file.write(image_path + ‘\n’)
convert_annotation(nameWithoutExtention) # convert label
copyfile(image_path, yolov5_images_train_dir + voc_path)
copyfile(label_path, yolov5_labels_train_dir + label_name)
else: # test dataset
if os.path.exists(annotation_path):
test_file.write(image_path + ‘\n’)
convert_annotation(nameWithoutExtention) # convert label
copyfile(image_path, yolov5_images_test_dir + voc_path)
copyfile(label_path, yolov5_labels_test_dir + label_name)
train_file.close()
test_file.close()
版权归原作者 爱睡觉的咋 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。