三体星人非常幸运有两颗恒星,所以他们的生活非常悲惨。
设两颗恒星的质量分别为
M
1
,
M
2
M_1,M_2
M1,M2,而行星的质量对于恒星而言可忽略不计,那么这两颗恒星的运动方程是可以近似为解析解的,而且是高中水平的解析解。
设二者的初始位置是
(
−
x
1
,
0
)
,
(
x
2
,
0
)
(-x_1,0),(x_2,0)
(−x1,0),(x2,0),令
L
=
x
1
+
x
2
L=x_1+x_2
L=x1+x2,则
x
1
x
2
=
M
2
M
1
\frac{x_1}{x_2}=\frac{M_2}{M_1}
x2x1=M1M2,记
μ
=
M
2
M
1
\mu=\frac{M_2}{M_1}
μ=M1M2,则
x
1
=
μ
x
2
x_1=\mu x_2
x1=μx2,从而
x
2
=
L
μ
+
1
,
x
1
=
μ
L
μ
+
1
x_2=\frac{L}{\mu+1},x_1=\frac{\mu L}{\mu+1}
x2=μ+1L,x1=μ+1μL。由于
x
1
,
x
2
x_1,x_2
x1,x2一会儿要用于坐标变量,所以将二者初始位置记为
(
−
μ
L
μ
+
1
,
0
)
(
L
μ
+
1
,
0
)
(-\frac{\mu L}{\mu+1},0)\quad (\frac{L}{\mu+1},0)
(−μ+1μL,0)(μ+1L,0)
从而二者的角速度为
ω
=
1
L
G
M
1
x
2
=
G
(
M
1
+
M
2
)
L
3
\omega=\frac{1}{L}\sqrt{\frac{GM_1}{x_2}}=\sqrt{\frac{G(M_1+M_2)}{L^3}}
ω=L1x2GM1=L3G(M1+M2),则二者逆时针旋转,其与
x
x
x轴夹角随时间的变化过程为
θ
1
=
π
+
ω
t
θ
2
=
ω
t
\theta_1=\pi+\omega t\\ \theta_2=\omega t
θ1=π+ωtθ2=ωt
转化为直角坐标
x
2
=
L
μ
+
1
cos
ω
t
x
1
=
−
μ
L
μ
+
1
cos
ω
t
=
−
μ
x
2
y
2
=
L
μ
+
1
sin
ω
t
y
1
=
−
μ
L
μ
+
1
sin
ω
t
=
−
μ
y
2
ω
=
G
(
M
1
+
M
2
)
L
3
\begin{aligned} x_2&=\frac{L}{\mu+1}\cos\omega t &x_1&=-\frac{\mu L}{\mu+1}\cos\omega t=-\mu x_2\\ y_2&=\frac{L}{\mu+1}\sin\omega t &y_1&=-\frac{\mu L}{\mu+1}\sin\omega t=-\mu y_2\\ \omega&=\sqrt{\frac{G(M_1+M_2)}{L^3}} \end{aligned}
x2y2ω=μ+1Lcosωt=μ+1Lsinωt=L3G(M1+M2)x1y1=−μ+1μLcosωt=−μx2=−μ+1μLsinωt=−μy2
其中,距离单位为千米,当时间单位不同时,万有引力常数为
G
=
6.67
×
1
0
−
11
N
⋅
m
2
/
k
g
2
=
6.67
×
1
0
−
11
m
3
s
−
2
k
g
−
1
=
4.98
×
1
0
−
10
k
m
3
d
−
2
k
g
−
1
\begin{aligned} G&=6.67\times10^{-11}N\cdot m^2/kg^2\\ &=6.67\times10^{-11} m^3s^{-2}kg^{-1}\\ &=4.98\times10^{-10} km^3d^{-2}kg^{-1}\\ \end{aligned}
G=6.67×10−11N⋅m2/kg2=6.67×10−11m3s−2kg−1=4.98×10−10km3d−2kg−1
这部分内容不存在任何技术上的问题,如果
μ
=
1.2
\mu=1.2
μ=1.2,则可得如图所示
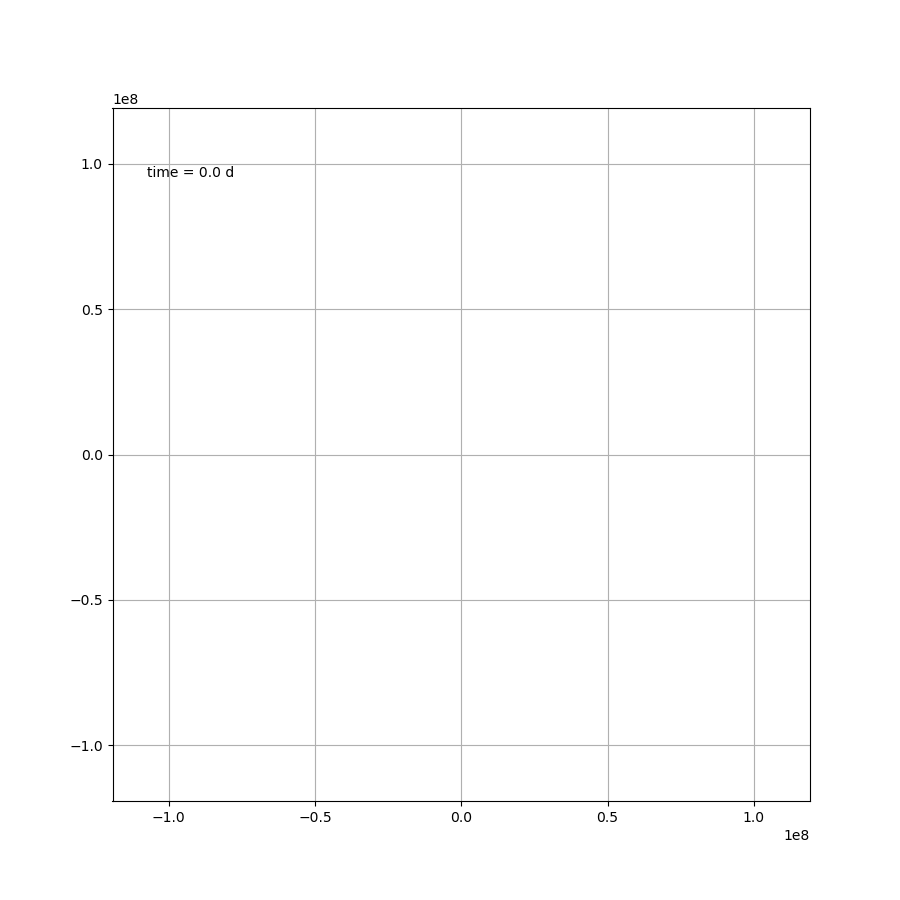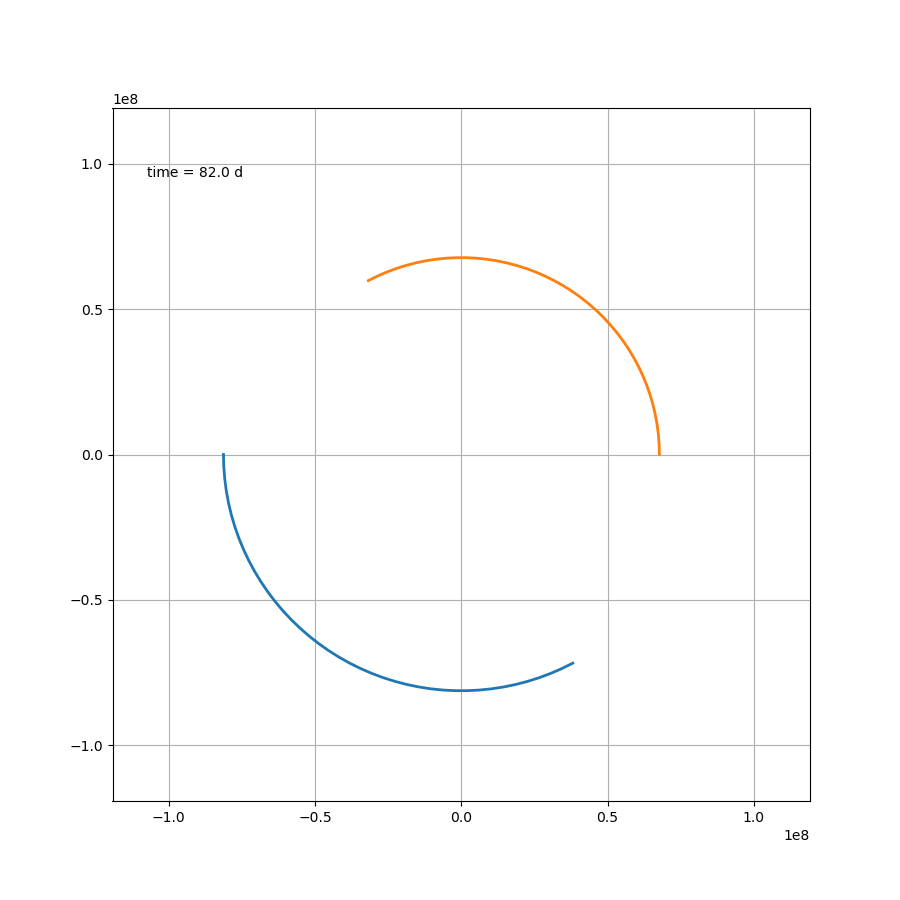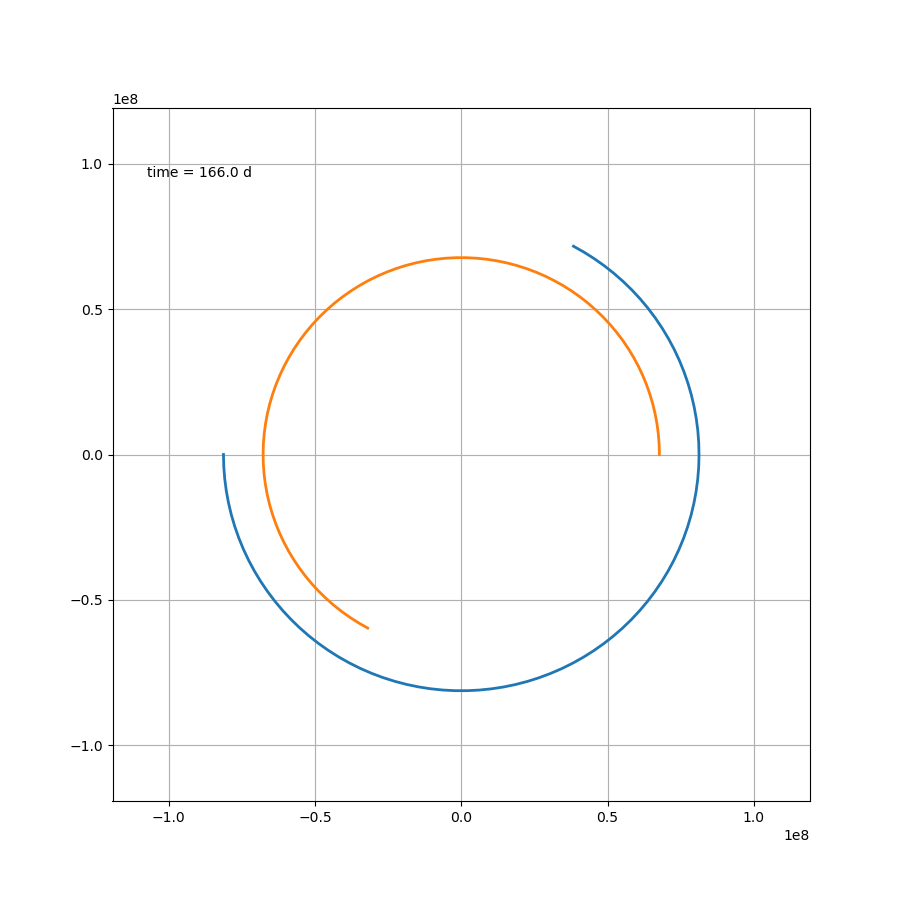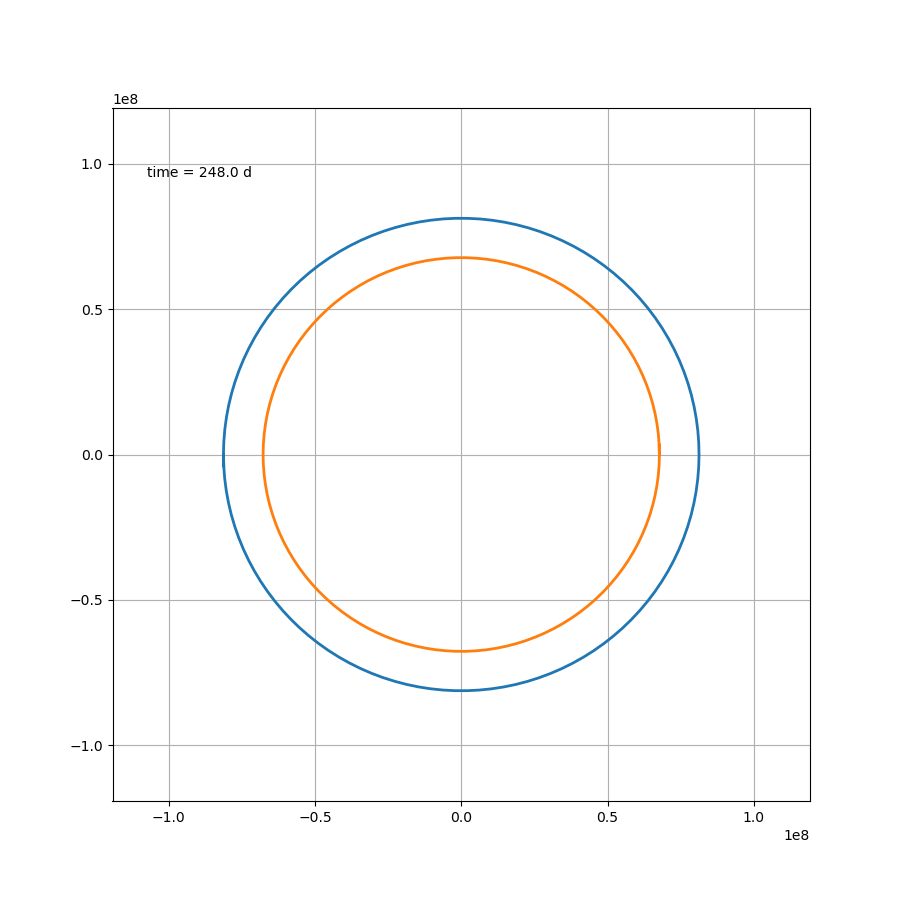
代码为:
import numpy as np
import scipy.integrate as integrate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
G =4.98e-10#时间单位为天
M1 =2e30
mu =1.2
M2 = mu*M1
L =1.49e8#km
om = np.sqrt(G*(M1+M2)/L**3)
dt =2
t = np.arange(0,250, dt)
x2 = L/(mu+1)*np.cos(om*t)
y2 = L/(mu+1)*np.sin(om*t)
x1,y1 =-mu*x2,-mu*y2
# 下面为绘图过程
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(9,9))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, autoscale_on=False,
xlim=(-0.8*L,0.8*L), ylim=(-0.8*L,0.8*L))
ax.grid()
line1,= ax.plot([],[], lw=2)
line2,= ax.plot([],[], lw=2)
time_template ='time = %.1f d'
time_text = ax.text(0.05,0.9,'', transform=ax.transAxes)defanimate(i):
line1.set_data(x1[:i],y1[:i])
line2.set_data(x2[:i],y2[:i])
time_text.set_text(time_template %(i*dt))return line1, line2, time_text
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate,range(len(t)),
interval=10, blit=True)
ani.save("tri_1.gif",writer='imagemagick')
plt.show()
现在,假设有一颗不知死活的行星闯入了二星世界,若其所在位置是
(
x
,
y
)
(x,y)
(x,y),质量为
m
m
m,则其动能为
T
=
1
2
m
(
x
˙
2
+
y
˙
2
)
T=\frac{1}{2}m(\dot x^2+\dot y^2)
T=21m(x˙2+y˙2)
引力势能为
V
=
−
G
M
1
m
(
x
−
x
1
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
1
)
2
−
G
M
2
m
(
x
−
x
2
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
2
)
2
V=-\frac{GM_1m}{\sqrt{(x-x_1)^2+(y-y_1)^2}}-\frac{GM_2m}{\sqrt{(x-x_2)^2+(y-y_2)^2}}
V=−(x−x1)2+(y−y1)2GM1m−(x−x2)2+(y−y2)2GM2m
拉格朗日量为
L
=
T
−
V
L=T-V
L=T−V,根据拉格朗日方程
d
d
t
∂
L
∂
r
˙
−
∂
L
∂
r
=
0
,
r
=
x
,
y
\frac{\text d}{\text dt}\frac{\partial L}{\partial\dot r}-\frac{\partial L}{\partial r}=0,r=x,y
dtd∂r˙∂L−∂r∂L=0,r=x,y
有
x
¨
=
G
M
1
(
x
−
x
1
)
(
x
−
x
1
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
1
)
2
3
+
G
M
2
(
x
−
x
2
)
(
x
−
x
2
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
2
)
2
3
y
¨
=
G
M
1
(
y
−
y
1
)
(
x
−
x
1
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
1
)
2
3
+
G
M
2
(
y
−
y
2
)
(
x
−
x
2
)
2
+
(
y
−
y
2
)
2
3
\ddot x=\frac{GM_1(x-x_1)}{\sqrt{(x-x_1)^2+(y-y_1)^2}^3}+\frac{GM_2(x-x_2)}{\sqrt{(x-x_2)^2+(y-y_2)^2}^3}\\ \ddot y=\frac{GM_1(y-y_1)}{\sqrt{(x-x_1)^2+(y-y_1)^2}^3}+\frac{GM_2(y-y_2)}{\sqrt{(x-x_2)^2+(y-y_2)^2}^3}
x¨=(x−x1)2+(y−y1)23GM1(x−x1)+(x−x2)2+(y−y2)23GM2(x−x2)y¨=(x−x1)2+(y−y1)23GM1(y−y1)+(x−x2)2+(y−y2)23GM2(y−y2)
其微分方程写为
# 其中,mu,G,M1,M2为全局变量defderivs(state, t):
dydx = np.zeros_like(state)
x, vx, y, vy = state
x2 = L/(mu+1)*np.cos(om*t)
y2 = L/(mu+1)*np.sin(om*t)
x1 =-mu*x2
y1 =-mu*y2
L1 = np.sqrt((x-x1)**2+(y-y1)**2)**3
L2 = np.sqrt((x-x2)**2+(y-y2)**2)**3
dydx[0]= state[1]
dydx[1]=-G*(M1*(x-x1)/L1+M2*(x-x2)/L2)
dydx[2]= state[3]
dydx[3]=-G*(M1*(y-y1)/L1+M2*(y-y2)/L2)return dydx
接下来根据微分方程的解,便可进行绘图,假设上帝把这颗行星轻轻地放在
(
L
/
4
,
L
/
4
)
(L/4,L/4)
(L/4,L/4)的位置上,那么接下来它的运行轨迹如下
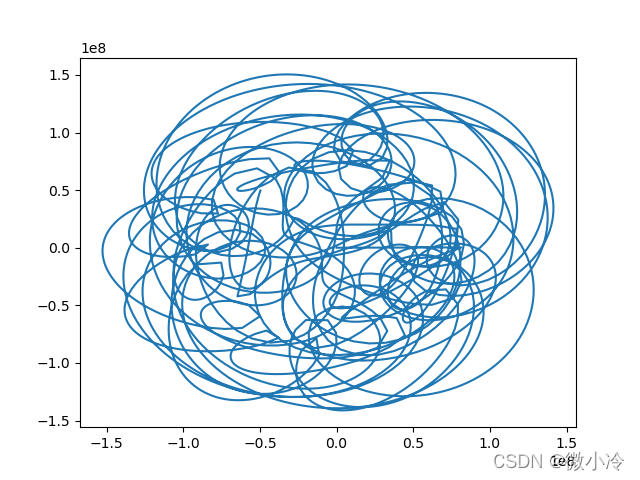
# 星体等数据可按照上面的代码来写# 生成时间
dt =1
t = np.arange(0,250, dt)
x, y =-L/3, L/3
vx0 =0
vy0 =0
state = np.array([x,vx0,y,vy0])# 微分方程组数值解
x,vx,y,vy = integrate.odeint(derivs, state, t).T
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.show()
当然也可以画下动图,可以说非常吊诡了,而这只是一种三体运动形式
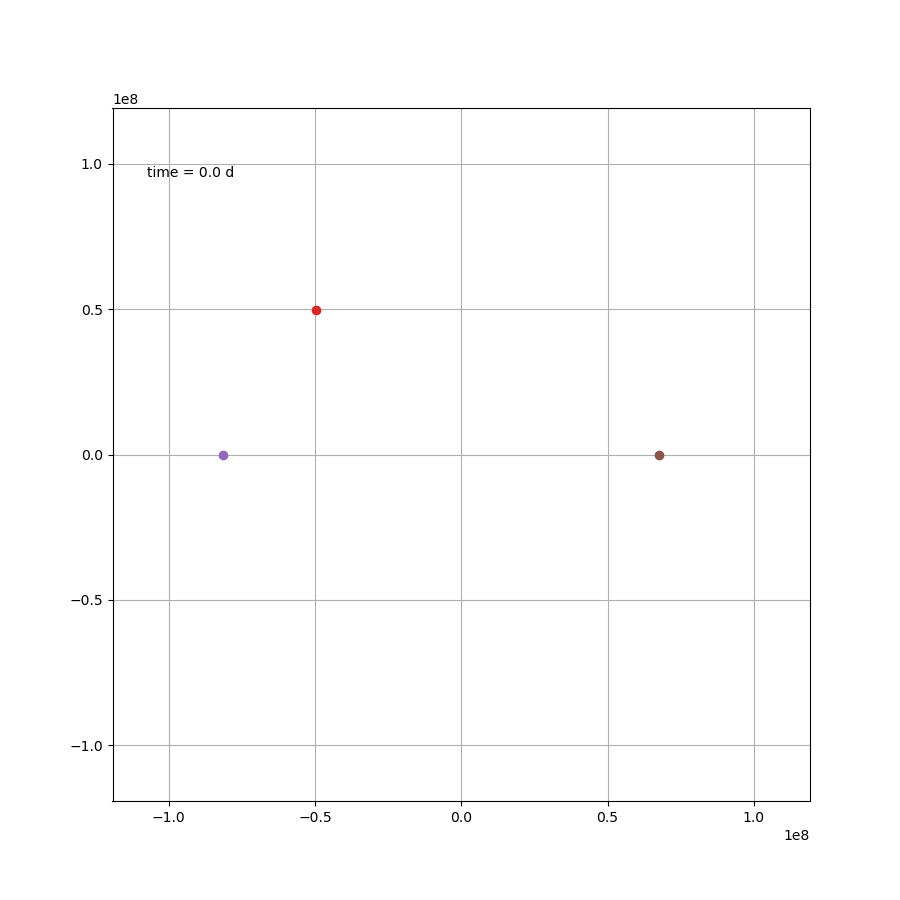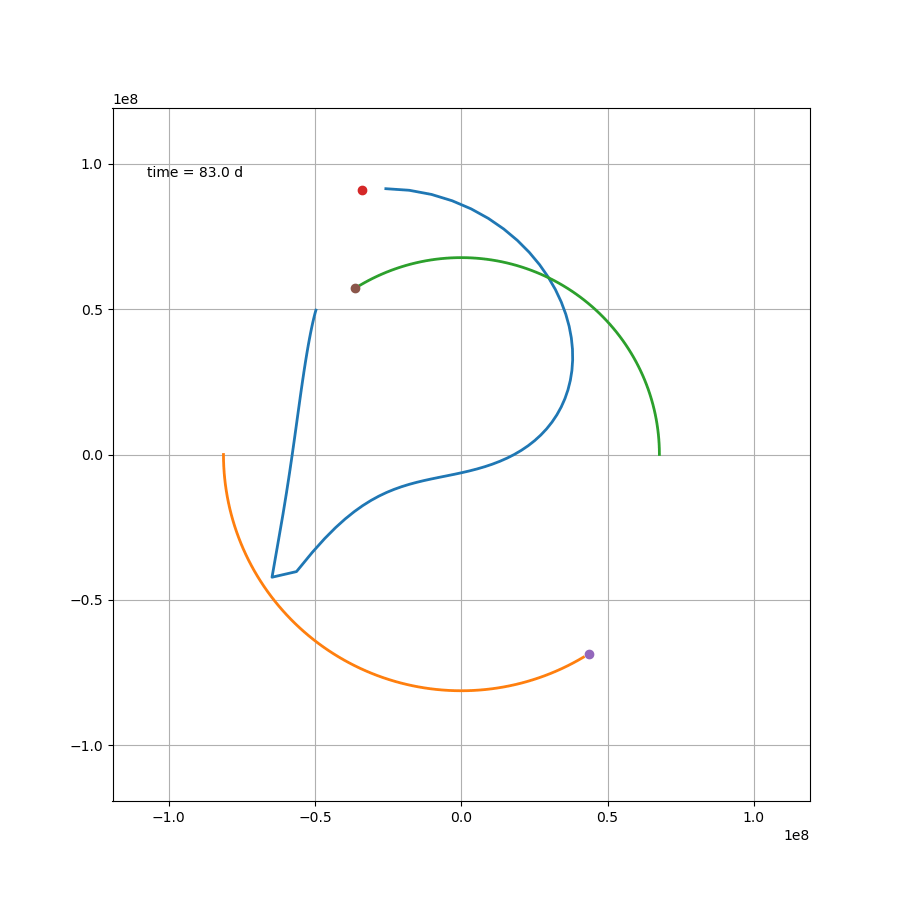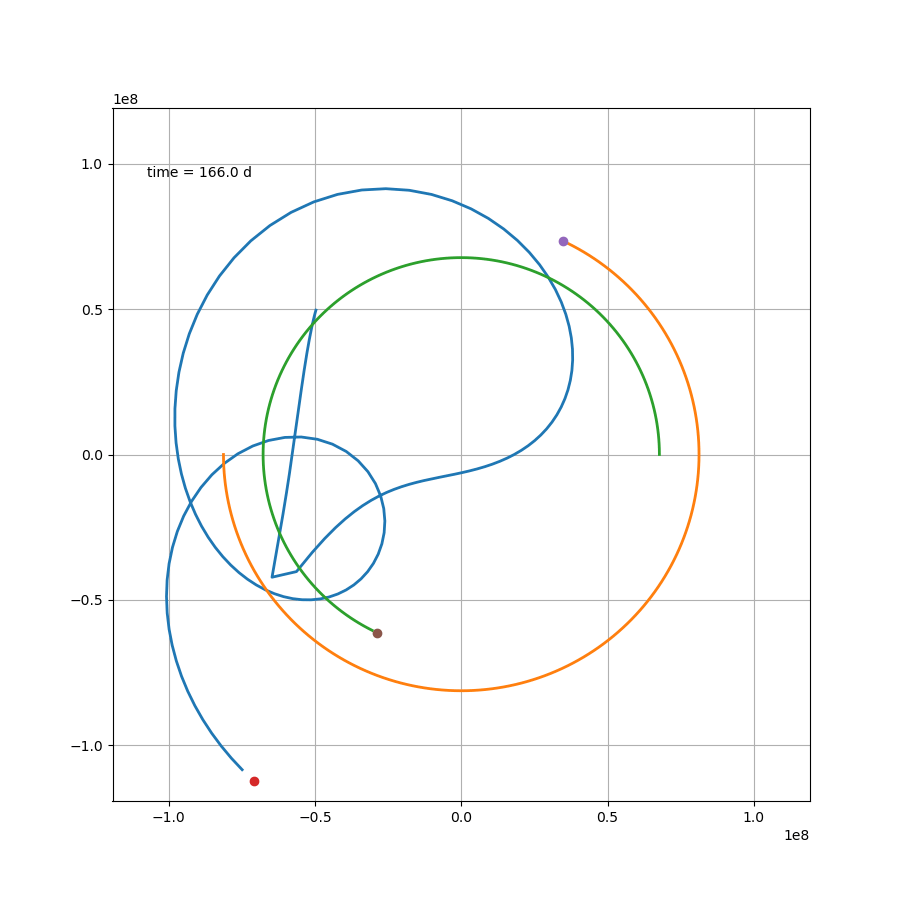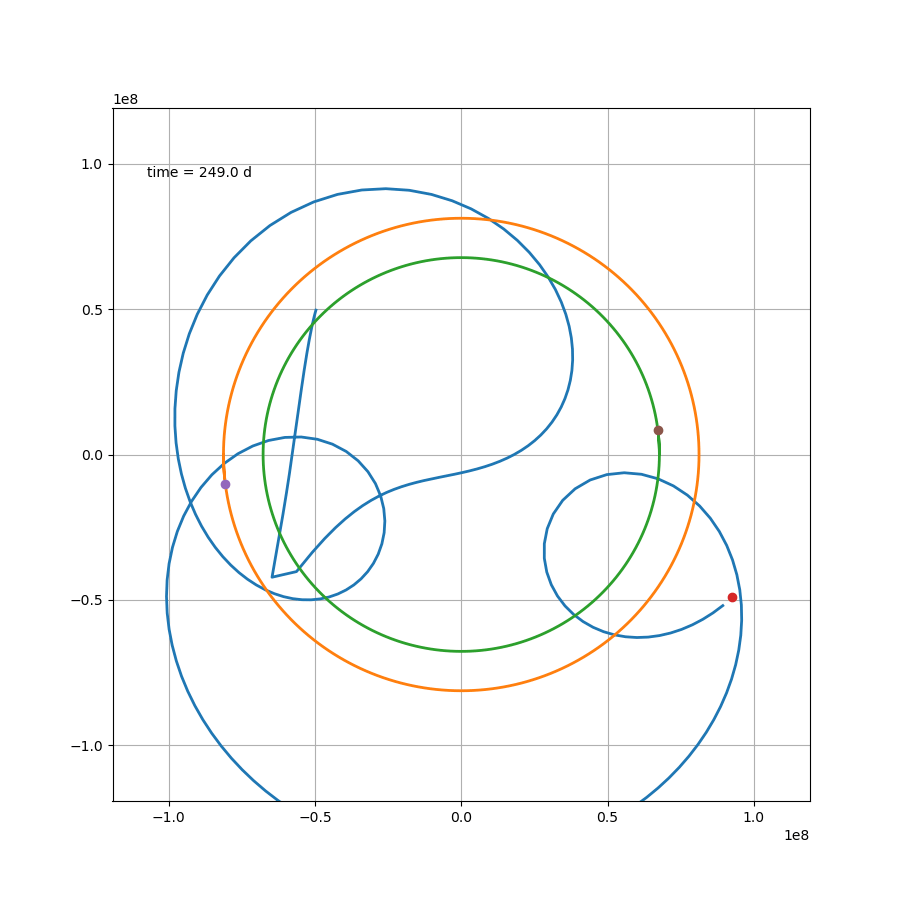
x2 = L/(mu+1)*np.cos(om*t)
y2 = L/(mu+1)*np.sin(om*t)
x1 =-mu*x2
y1 =-mu*y2
defanimate(i):
pt0.set_data(x[i],y[i])
pt1.set_data(x1[i],y1[i])
pt2.set_data(x2[i],y2[i])
line0.set_data(x[:i],y[:i])
line1.set_data(x1[:i],y1[:i])
line2.set_data(x2[:i],y2[:i])
time_text.set_text(time_template %(i*dt))return line0, line1, line2, pt0, pt1, pt2, time_text
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(9,9))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, autoscale_on=False,
xlim=(-0.8*L,0.8*L), ylim=(-0.8*L,0.8*L))
ax.grid()
line0,= ax.plot([],[], lw=2)
line1,= ax.plot([],[], lw=2)
line2,= ax.plot([],[], lw=2)
pt0,= ax.plot([x[0]],[y[0]],marker='o')
pt1,= ax.plot([x1[0]],[y1[0]],marker='o')
pt2,= ax.plot([x2[0]],[y2[0]],marker='o')
time_template ='time = %.1f d'
time_text = ax.text(0.05,0.9,'',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, t,
interval=0.1, blit=True)
plt.show()
ani.save("tri_3.gif")
如果站在这颗行星上,去观察另外两颗恒星,那么可能会更加感受到这种压迫感。然而就这个案例来说,除了最开始那一下好像贴上恒星了,后面的状态要比预想中要好一些。然而这只是几百天的运行轨迹,不知道几百万年还会跑出什么花样。总之,三体星能产生个生命也是绝了。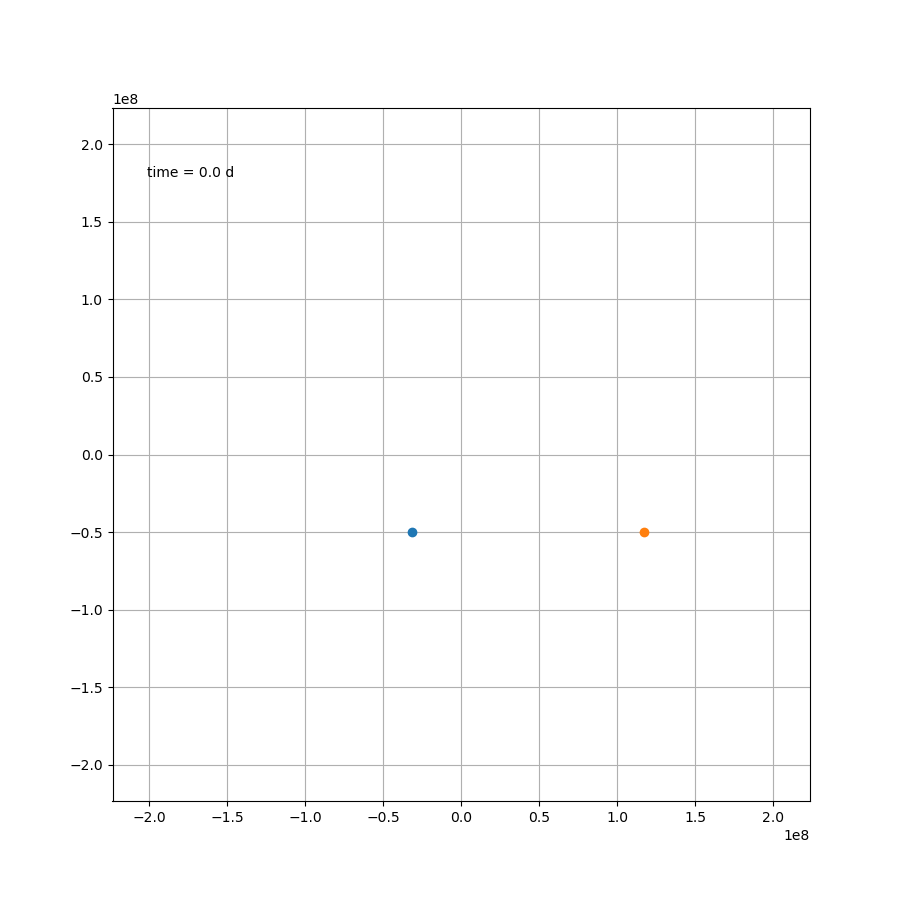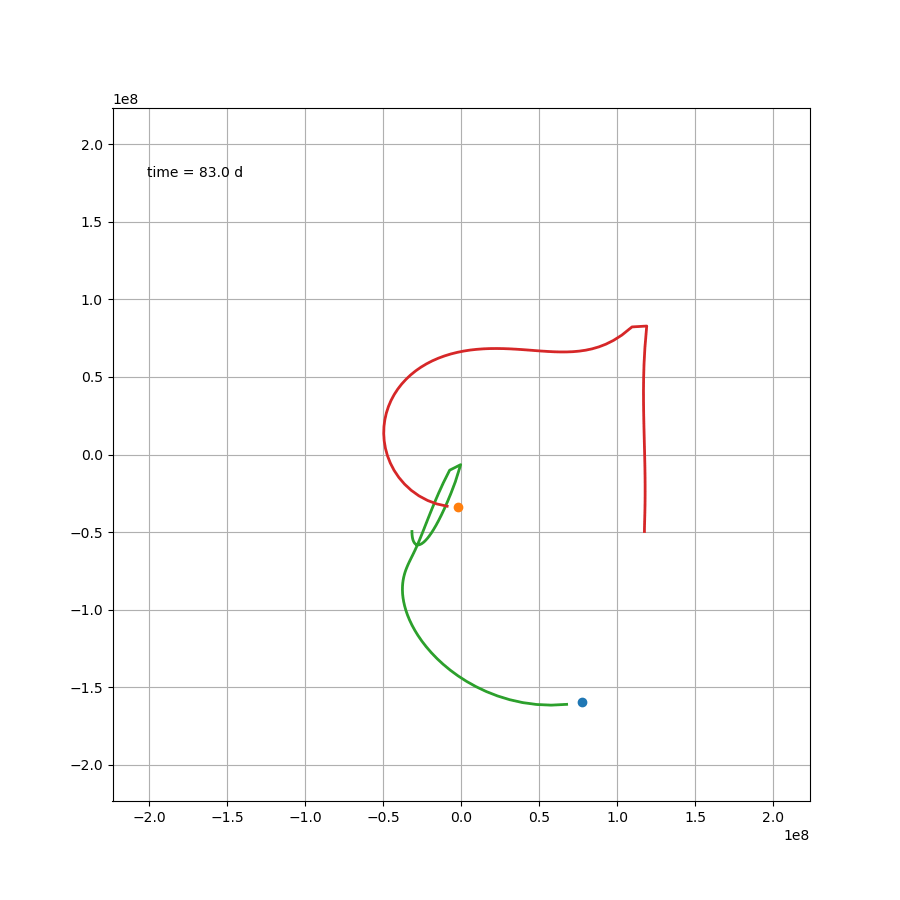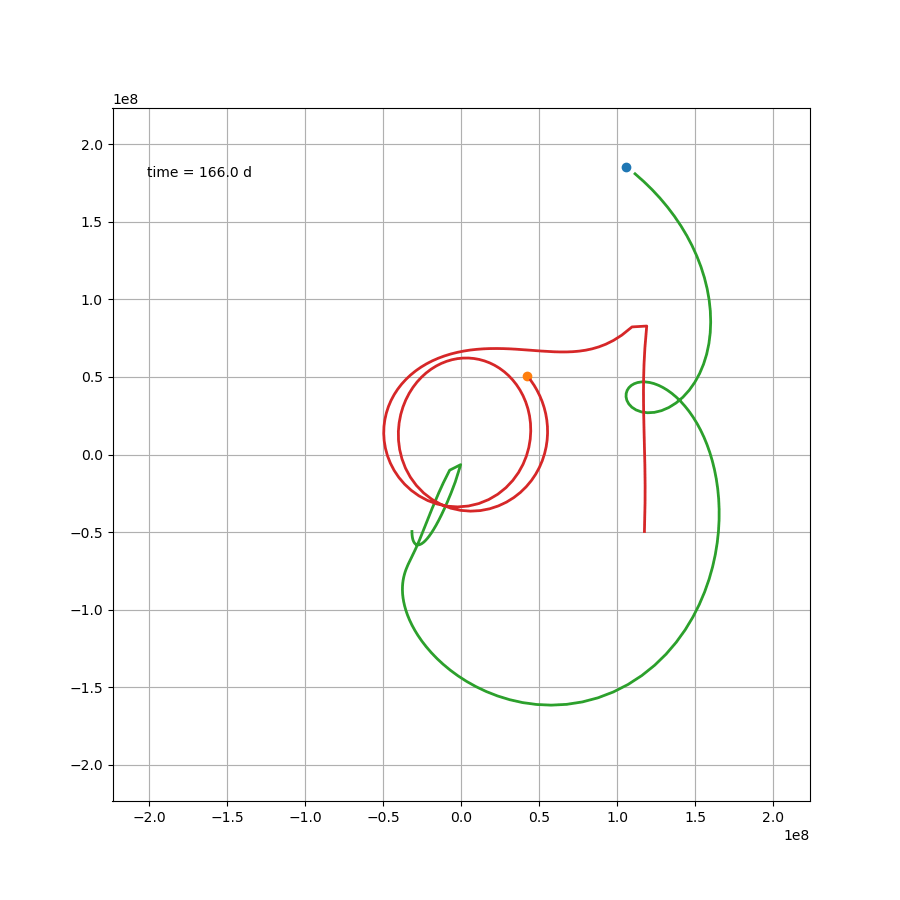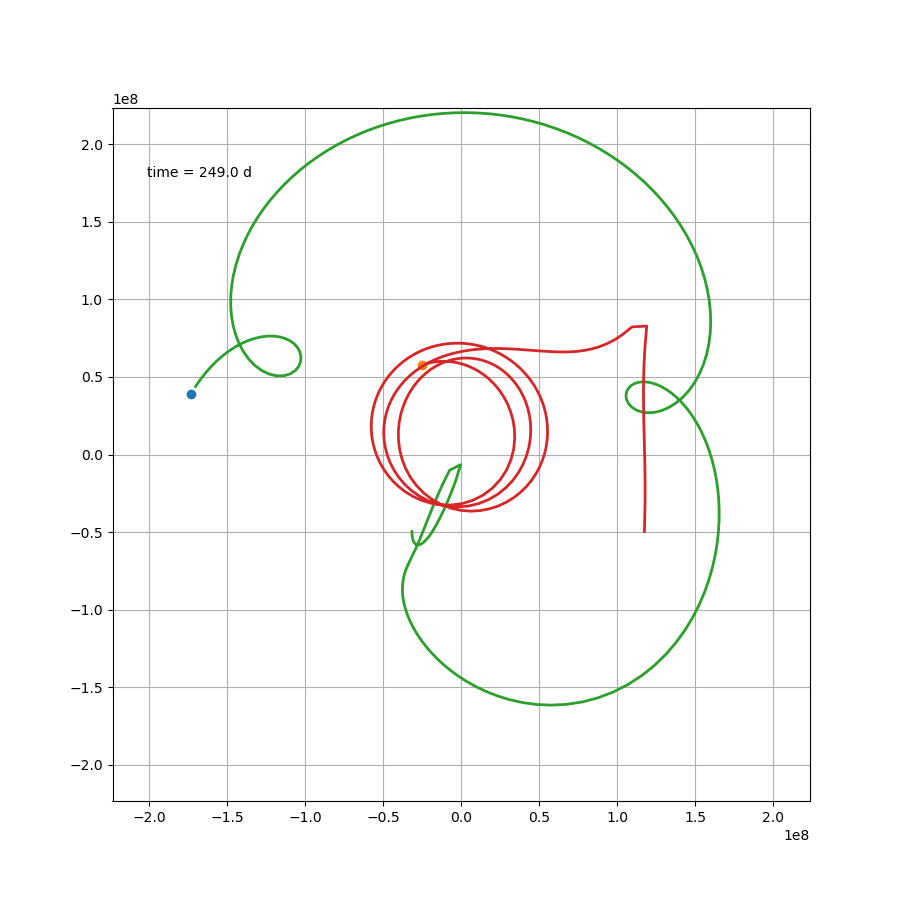
X1,X2 = x1-x,x2-x
Y1,Y2 = y1-y,y2-y
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(9,9))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, autoscale_on=False,
xlim=(-1.5*L,1.5*L), ylim=(-1.5*L,1.5*L))
ax.grid()
pt1,= ax.plot([X1[0]],[Y1[0]],marker='o')
pt2,= ax.plot([X2[0]],[Y2[0]],marker='o')
line1,= ax.plot([],[], lw=2)
line2,= ax.plot([],[], lw=2)
time_template ='time = %.1f d'
time_text = ax.text(0.05,0.9,'', transform=ax.transAxes)defanimate(i):
pt1.set_data(X1[i],Y1[i])
pt2.set_data(X2[i],Y2[i])
line1.set_data(X1[:i],Y1[:i])
line2.set_data(X2[:i],Y2[:i])
time_text.set_text(time_template %(i*dt))return line1, line2, pt1, pt2, time_text
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate,range(len(t)),
interval=10, blit=True)
ani.save("tri_4.gif",writer='imagemagick')
plt.show()
版权归原作者 微小冷 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。