一、列转行
1、相关函数
列转行:将某列一行中的数据拆分成多行
1)Explode炸裂函数
将hive某列一行中复杂的 array 或 map 结构拆分成多行(只能输入array或map)
语法:
select explode(字段) as 字段命名 from 表名;
举例:
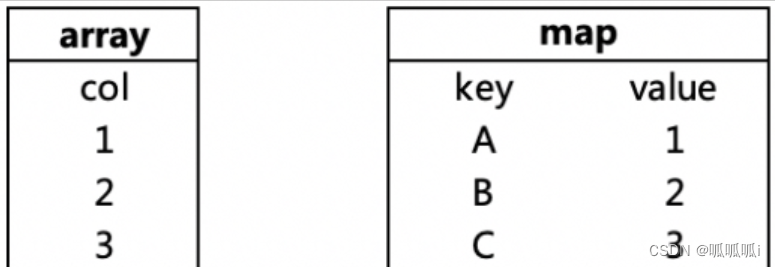
explode(array)使得结果中将array列表里的每个元素生成一行
select(array('1','2','3'))
explode(map)使得结果中将map里的每一对元素作为一行,key为一列,value为一列
select explode(map('A','1','B','2','C','3'))
局限性:
1、不能关联原有的表中的其他字段
2、不能与group by、cluster by、distribute by、sort by联用
3、不能进行UDTF嵌套
2)posexplode()函数
explode():对一列进行炸裂可以使用
posexplode():对两列都进行多行转换,可以将index和数据都取出来,使用两次posexplode并令两次取到的index相等即可
举例:
select posexplode(collect_set('AA'))
pos****val0AA
collect_set:将某字段进行去重处理,返回array类型
3)Lateral View
Lateral View配合 split, explode 等UDTF函数一起使用,它能够将一列数据拆成多行数据,并且对拆分后结果进行聚合,即将多行结果组合成一个支持别名的虚拟表。相当于拆出一张虚拟表,与原表进行关联。
语法:
select o.*, table_view.new_col
from table_origin o
lateral view UDTF(expression) table_view as new_col_1, new_col_2
lateral view:表示将UDTF分裂的字段放在虚拟表中, 然后和主表table_origin进行关联。
UDTF(expression):使用的UDTF函数,例如explode()
table_view : 对应的虚拟表的表名
new_col: 虚拟表里存放的有效字段(可多个)
注意:
- lateral view的位置是from后where条件前
- 生成的虚拟表的表名不可省略
- from后可带多个lateral view
- 如果要拆分的字段有null值,需要使用lateral view outer 替代,避免数据缺失
2、案例
例子1-explode+split
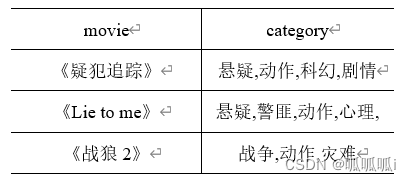
假设有如下movies表,字段名分别为
movie(string)
和
category(array<string>)
转换为
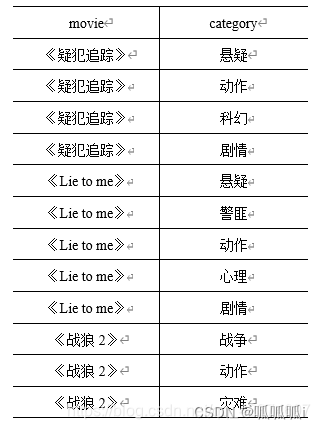
select movie,category_name
from movies
lateral view explode(category) table_tmp as category_name;
-- 结果:
--《疑犯追踪》 悬疑
--《疑犯追踪》 动作
--《疑犯追踪》 科幻
--《疑犯追踪》 剧情
--《海豹突击队》 动作
-- ...
注:explode函数输入了一个string类型的参数,搭配split()函数
例子2-explode+split

转换为

select col1, col2, col5
from test
lateral view explode(split(col3,',')) b AS col5
-- split(col3,",")相对字符串切割,得到数组
注:explode函数输入了一个string类型的参数,搭配split()函数
例子3-explode+split
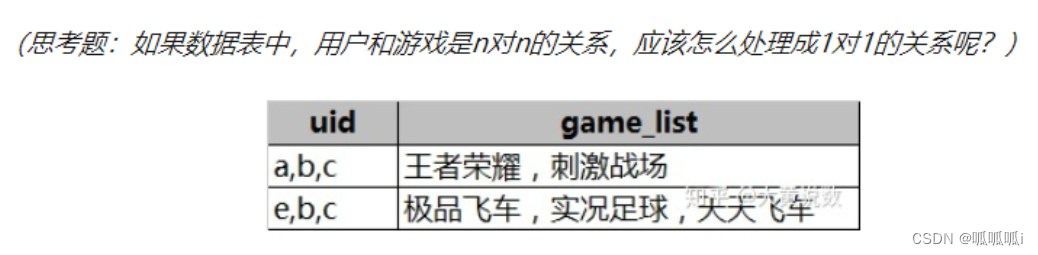
select uid_split, game
from (
select uid,game
from user_game
lateral view explode(split(game_list,",")) tmpTable as game
) a
lateral view explode(split(uid, ",")) m as uid_split
例子4-多列炸裂
1)创建测试表,插入数据
CREATE table student_score(
stu_id string comment '学号',
stu_name string comment '姓名',
courses string comment '各个科目',
scores string comment '各个分数'
) comment '学生成绩表';
insert into student_score values
("1001", "张三","语文,数学,英语,历史,地理", "88,87,94,86,84"),
("1002", "李四", "语文,数学,英语,历史,地理", "78,89,75,79,68"),
("1003", "王五", "语文,数学,英语,历史,地理", "98,97,91,93,92"),
("1004", "朱六", "语文,数学,英语,历史,地理", "66,63,64,67,68");
** 2)测试explode 行转列**
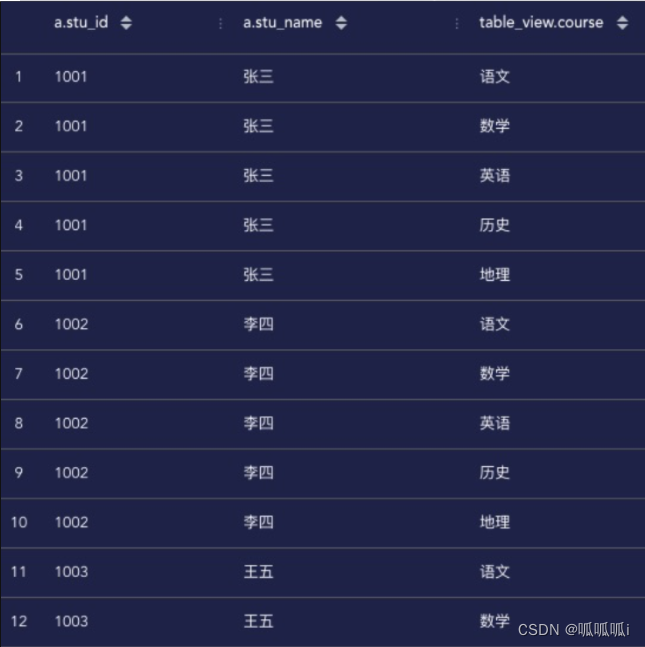
select a.stu_id, a.stu_name, table_view.course
from student_score a
lateral view explode(split(courses, ',')) table_view as `course`;
**3)查询每个学生课程对应的分数,使用posexplode函数 **
先测试使用explode, 看看效果:
select a.stu_id, a.stu_name,
table_view1.course, table_view2.score
from student_score a
lateral view explode(split(courses, ',')) table_view1 as `course`
lateral view explode(split(scores, ',')) table_view2 as `score`;
结果:
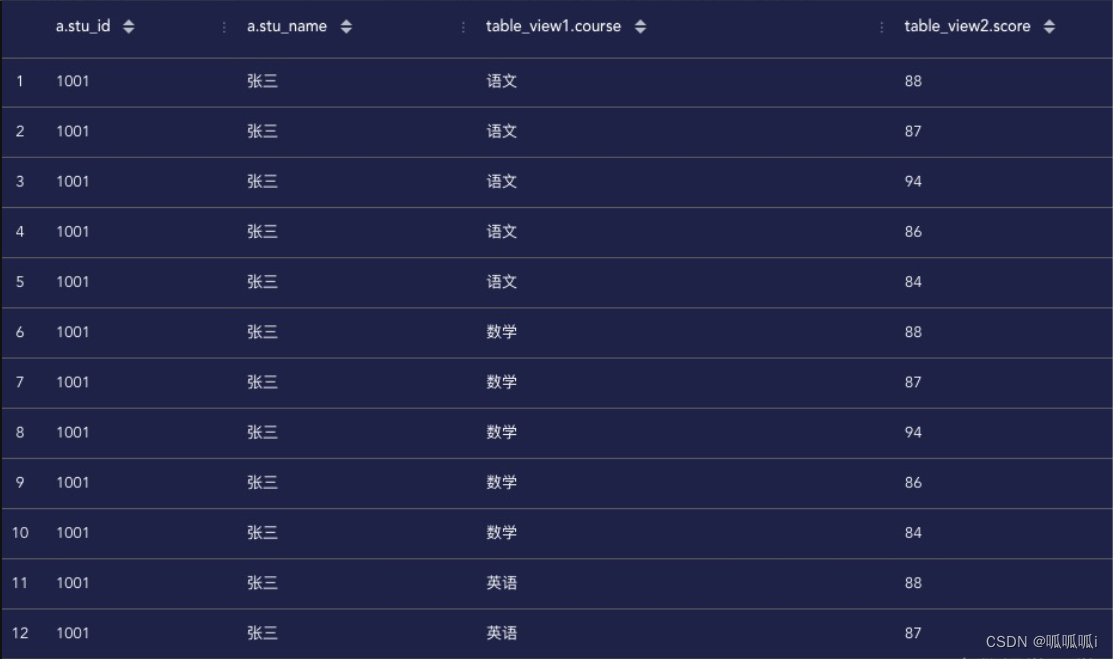
出现这种情况是因为两个并列的explode的sql没办法识别每个科目对应的成绩是多少,对于多个数组的行转列可以使用posexplode函数。
例如使用如下查询语句:
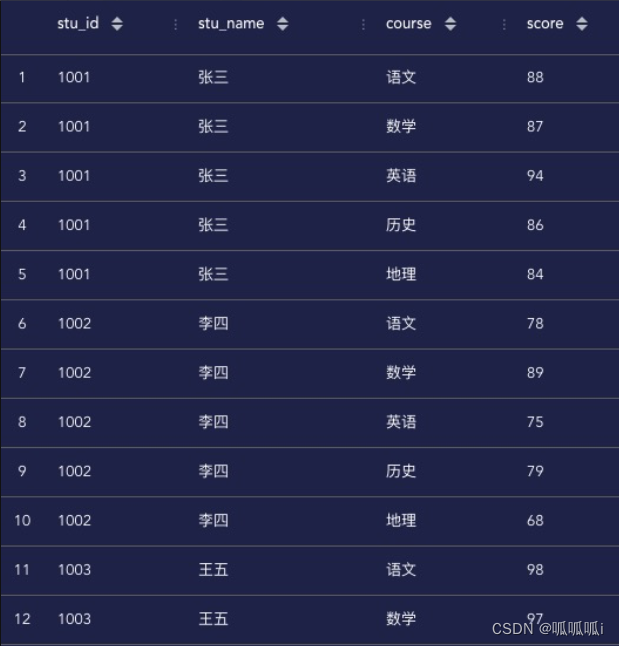
select stu_id, stu_name, course, score
from student_score
lateral view posexplode(split(courses, ',')) table_view1 as a, course
lateral view posexplode(split(scores, ',')) table_view2 as b, score
where a = b;
例子5-posexplode

转换为

一次posexplode
select id,tim,single_id_index,single_id
from test.a
lateral view posexplode(split(id,',')) t as single_id_index, single_id;d;
结果
single_id_index single_id
0 a
1 b
2 c
3 d
0 f
1 b
2 c
3 d
两次posexplode+where筛选
select
id,tim,single_id,single_tim
from
test.a
lateral view posexplode(split(id,',')) t as single_id_index, single_id
lateral view posexplode(split(tim,',')) t as single_yim_index, single_tim
where
single_id_index = single_yim_index;
例子6-explode+map

select column1, column2, column3, m_key, m_val from
(select column1, column2, column3, map("X1", X1, "X2", X2, "X3", X3, "X4", X4) as map1
from table1) as t1
lateral view explode(map1) xyz as m_key, m_val
例子7-explode+str_to_map
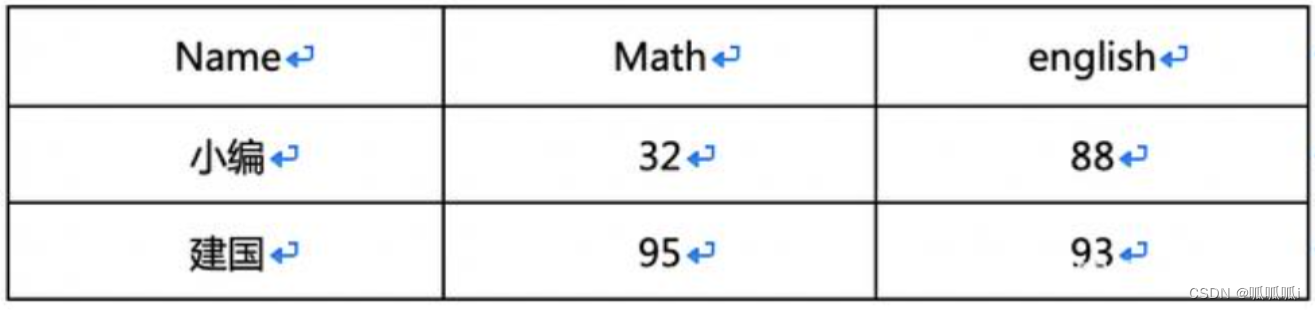
转换为
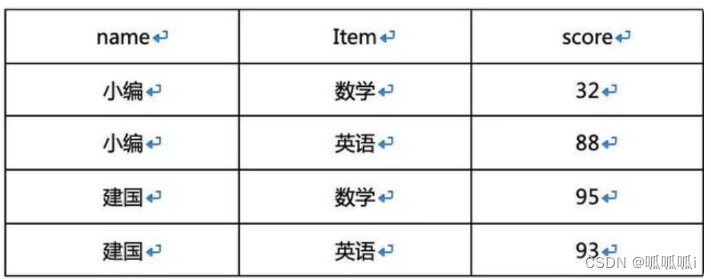
select table_4.name,
a.item,
a.score
from table_4
lateral view explode(
str_to_map(concat('math=',math,'&english=',english),'&','=')
) a as item,score;
解析:首先使用str_to_map函数将math字段与english字段拼接后的结果转换为map类型,然后通过侧视图和explode函数将其爆炸开,给生成的临时侧视图一个名字,取名a并给列名取名为item,score,因为explode(map)爆炸的结果是每一个item为行,key为1列,value为1列,这样就恰好形成我们想要的结果。
二、行专列
1、相关函数
行转列:将多个列中的数据在一列中输出
1)Concat
concat(string1/col, string2/col, …)
输入任意个字符串(或字段,可以为int类型等),返回拼接后的结果
select concat(id,'-',name,'-',age)
from student;
2)Concat_ws
concat_ws(separator, str1, str2, …)
特殊形式的 concat(),参数只能为字符串,第一个参数为后面参数的分隔符。分隔符可以是与后面参数一样的字符串。如果分隔符是 NULL,返回值也将为 NULL。这个函数会跳过分隔符参数后的任何 NULL 和空字符串。分隔符将被加到被连接的字符串之间;
select concat_ws('-', name, gender)
from student;
3)Collect_set(聚合,返回数组类型)
collect_set(col)
将某字段进行去重处理,返回array类型;该函数只接受基本数据类型
select collect_set(age)
from student;
collect_set 与 collect_list 的区别就是set去重,list不去重
4)case when
case when <expr> then <result>…else <default> end
if(expr, true_result, false_result)
case when 语句是SQL中的一个非常重要的功能,可以完成很多复杂的计算,相当于一个表达式,可以放在任何可放表达式的地方。
2、案例
例子1
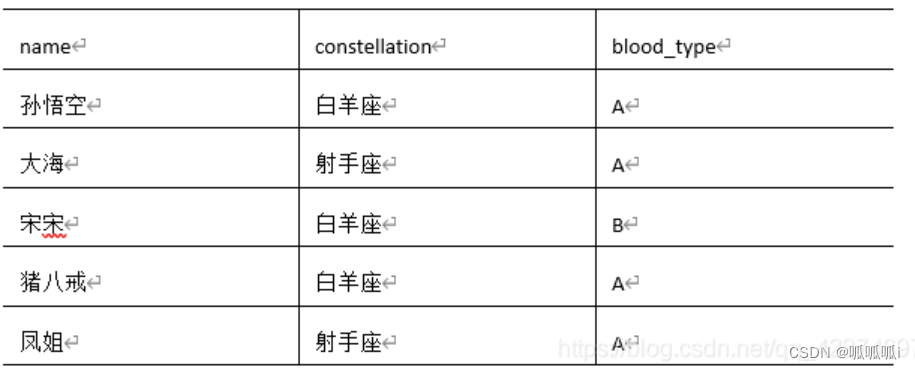
转换为

select
t1.base,
concat_ws('|', collect_set(t1.name)) as name
from
(select name,concat(constellation, ",", blood_type) as base
from person_info) as t1
group by
t1.base;
例子2
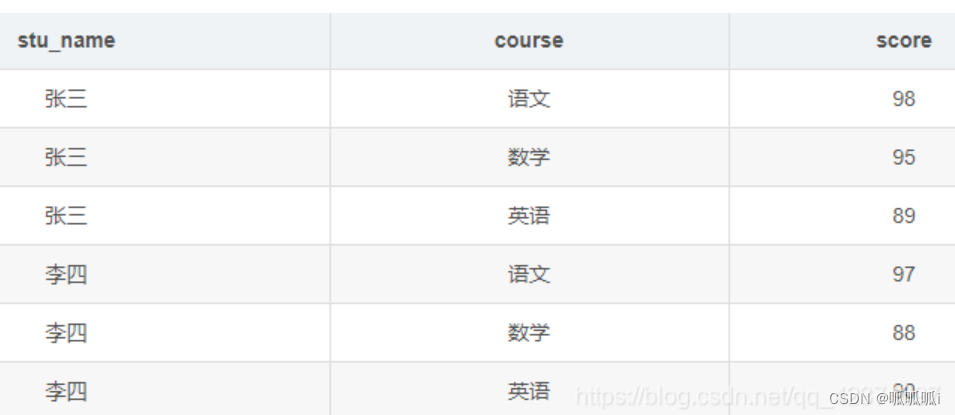
转换为

select
stu_name,
concat_ws(',',collect_set(course)) as course,
concat_ws(',',collect_set(score)) as score
from student
group by stu_name
例子3
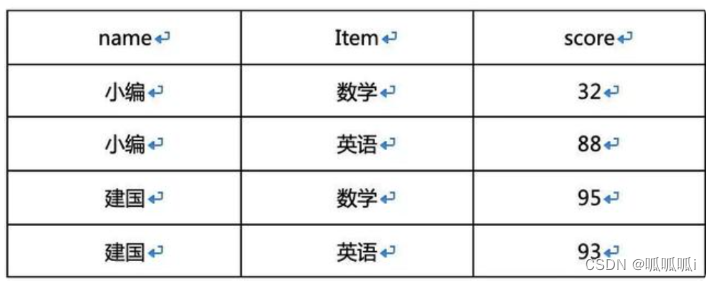
转换为
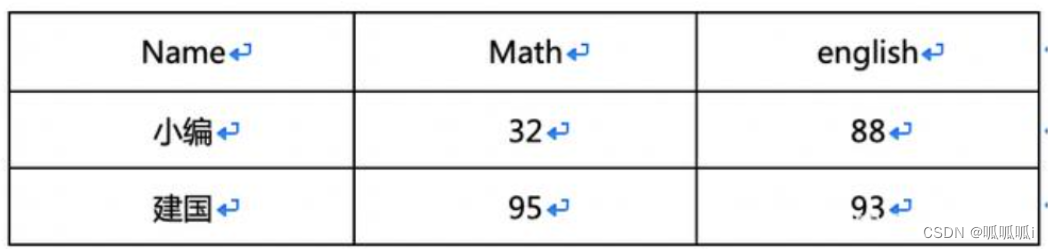
Select
name,
sum(case when item=数学 then score end) as math,
sum(case when item=英语 then score end) as english,
From table
Group by name
解析:首先写出select name from table group by name, 因为select后有几个字段,最终输出就是几个字段,所以我们需要把目标数据的”math”和“english”两个字段想办法得出来。
之后可以对item字段所有枚举的结果进行case when判断,将score填值进入,因为最后我们需要对name做一下聚合,需要明确的是一般选取字段一定要出现在groupby里面。
聚合函数可以不用,所以我们在外面套一层sum做聚合,这样得到sum的结果和单人得分结果是一致的,因为我们以name做了一遍聚合,而每个用户对一门课程只有一个成绩,所以这样就可以得到最终结果。
版权归原作者 呱呱呱i 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。