基本介绍
在rabbitmq中,生产者发信息不会直接将信息投递到队列中,而是先将信息投递到交换机中,在交换机转发在具体的队列,队列再将信息推送或者拉取消费者进行消费
路由键(Routingkey)
生产者将信息发送给交换机的时候 会指定Routingkey指定路由规则
绑定键(Bindingkey)
通过绑定键将交换机与队列关联起来,这样rabbtamq就知道如何正确的将信息路由到队列
Direct(直连)Exchange
首部交换机和扇形交换机都不需 要路由键routingKey,交换机时通过 Headers 头部来将消息映射到队列的 ,有点像 HTTP的 Headers.
Hash结构中要求携带一个键 "x-match", 这个键的Val ue可以是any或者all, 这代表消息携带的 Hash是需要全部匹配(all), 还是仅匹配一个键(any) 就可以了。
相比直连交换机 ,首部交换机的优势是匹配的规则不被限定为字符串(string)而是 Object 类型。
all: 在发布消息时携带的所有Entry必须和绑定在队列上的所有 Entry完全匹配any: 只要在发布消息时携带的有一对键值对 headers满足队列定义的多个参数 arguments的其中一 个就能 匹配上 ,注意这里是键值对的完全匹配,只匹配到键了,值却不—样是不行的
使用Headers Exchange的时候匹配规则和当前的route key无关
springboot代码演示
演示架构
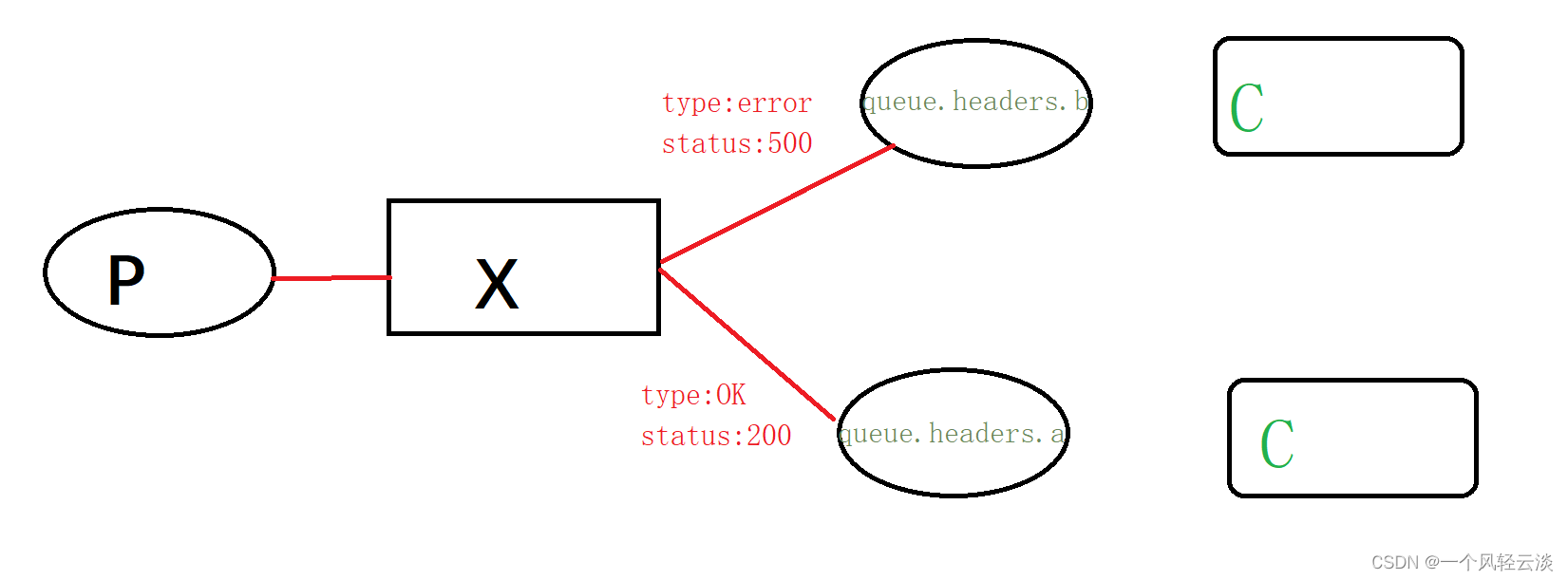
生产者发送消息道headers交换机上面,队列A和队列B绑定一个headers交换机,对于队列a来说,它对应的Headers 头部需要全部满足type为OK,status为200,对于队列b来说,它对应的Headers 头部需要全部满足type为error,status为500
工程概述
工程采用springboot架构,主要用到的依赖为:
<!-- rabbit的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml配置文件如下:
server:
port: 8080
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 123.249.70.148
port: 5673
username: admin
password: 123456
virtual-host: /
RabbitConfig配置类:创建队列及交换机并进行绑定
** 创建 RabbitConfig类,这是一个配置类**
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
}
定义交换机
@Bean
public HeadersExchange headersExchange(){
return new HeadersExchange("exchange.headers");
}
**定义队列 **
@Bean
public Queue queueA(){
return new Queue("queue.headers.a");
}
@Bean
public Queue queueB(){
return new Queue("queue.headers.b");
}
绑定交换机和队列
@Bean
public Binding bindingA(HeadersExchange headersExchange,Queue queueA){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("type","OK");
map.put("status","200");
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA).to(headersExchange).whereAll(map).match();
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingB(HeadersExchange headersExchange,Queue queueB){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("type","error");
map.put("status","500");
return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(headersExchange).whereAll(map).match();
}
MessageService业务类:发送消息及接收消息
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MessageService {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
}
** 发送消息方法**
public void sendMsg(){
//消息属性
MessageProperties messageProperties=new MessageProperties();
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("type","error");
map.put("status","500");
//设置消息头
messageProperties.setHeaders(map);
//添加消息属性
Message message = MessageBuilder.withBody("hello word!".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
.andProperties(messageProperties).build();
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange.headers","",message);
}
对应消息的Headers 头部全部满足type为OK,status为200,按照架构设计应该会到队列A
MessageConvert
- 涉及网络传输的应用序列化不可避免,发送端以某种规则将消息转成 byte 数组进行发送,接收端则以约定的规则进行 byte[] 数组的解析
- RabbitMQ 的序列化是指
Message的body属性,即我们真正需要传输的内容,RabbitMQ 抽象出一个 MessageConvert 接口处理消息的序列化,其实现有SimpleMessageConverter(默认)、Jackson2JsonMessageConverter等
** 接受消息**
@RabbitListener(queues = {"queue.headers.a","queue.headers.b"})
public void receiveMsg(Message message){
byte[] body = message.getBody();
String queue = message.getMessageProperties().getConsumerQueue();
String msg=new String(body);
log.info(queue+"接收到消息:"+msg);
}
** Message**
在消息传递的过程中,实际上传递的对象为
org.springframework.amqp.core.Message,它主要由两部分组成:
- MessageProperties // 消息属性
- byte[] body // 消息内容
@RabbitListener
使用 @RabbitListener 注解标记方法,当监听到队列 debug 中有消息时则会进行接收并处理
- 消息处理方法参数是由 MessageConverter 转化,若使用自定义 MessageConverter 则需要在 RabbitListenerContainerFactory 实例中去设置(默认 Spring 使用的实现是 SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory)
- 消息的 content_type 属性表示消息 body 数据以什么数据格式存储,接收消息除了使用 Message 对象接收消息(包含消息属性等信息)之外,还可直接使用对应类型接收消息 body 内容,但若方法参数类型不正确会抛异常:- application/octet-stream:二进制字节数组存储,使用 byte[]- application/x-java-serialized-object:java 对象序列化格式存储,使用 Object、相应类型(反序列化时类型应该同包同名,否者会抛出找不到类异常)- text/plain:文本数据类型存储,使用 String- application/json:JSON 格式,使用 Object、相应类型
主启动类RabbitMq01Application:实现ApplicationRunner接口
/**
* @author 风轻云淡
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class RabbitMq01Application implements ApplicationRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RabbitMq01Application.class, args);
}
@Resource
private MessageService messageService;
/**
* 程序一启动就会调用该方法
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
messageService.sendMsg();
}
}
在SpringBoot中,提供了一个接口:ApplicationRunner。 该接口中,只有一个run方法,他执行的时机是:spring容器启动完成之后,就会紧接着执行这个接口实现类的run方法。
由于该方法是在容器启动完成之后,才执行的,所以,这里可以从spring容器中拿到其他已经注入的bean。
启动主启动类后查看控制台:
2023-09-26 23:00:57.773 INFO 2448 --- [ main]
c.e.rabbitmq01.RabbitMq01Application :
Started RabbitMq01Application in 2.873 seconds (JVM running for 4.572)
2023-09-26 23:00:57.868 INFO 2448 --- [ntContainer#0-1]
c.e.rabbitmq01.service.MessageService :
queue.headers.b接收到消息:hello word!
版权归原作者 一个风轻云淡 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。