一.简单参数
1. 参数名与形参变量名相同,定义形参可接收参数
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/getPeople?username=hz&password=123456 ',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@GetMapping("/getPeople")
public Result selectByUserNameAndPassword(String username,String password){
System.out.println("username:"+username +" password:"+password);
return Result.success("ok");
}
以下都是方便展示,就直接赋值了,一般都是动态传参。(如果想了解Axios的可以看看这个博主写的Axios各种参选携带方式🔎)
不管是GET请求还是POST 请求 只要请求参数名与后端形参名一致就可以自动接收。
可以看看打印效果:
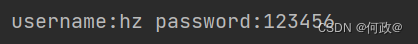
浏览器返回结果:

2.如果参数名与形参名字不同就会接收不到但是后端是不会报错的,只会赋值为null

这个时候如果需要 使用Sprngboot 提供的注解 @RequestParam 来完成映射
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/getPeople?name=hz&password=123456 ',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@GetMapping("/getPeople")
public Result selectByUserNameAndPassword(@RequestParam(required = false, name = "name") String username,String password){
System.out.println("username:"+username +" password:"+password);
return Result.success("ok");
}
运行效果:

注意: @RequestParam 里面有2个属性。required 和 name
required 属性是默认为true,代表该请求参数必须传递,如果不传递将报错。如果该参数要设置为可选的,可以把手动把required属性设置为false。
name 属性是指定请求参数名,如何把请求参数映射到形参对应的形参中
二.实体参数
请求参数名与形参对应属性名相同,定义POJO接收即可
说简单就是前端请求参数如果太多,还是用简单参数传递,后端形参太多,臃肿且不易维护,后端直接把请求参数封装到一个实体类中(也必须保证请求参数名与实体类的属性名保持一致才可以)
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/getPOJO?username=hz&password=123456 ',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserDTO {
private String username;
private String password;
}
@GetMapping("/getPOJO")
public Result selectByUserNameAndPassword(UserDTO userDTO){
System.out.println("username:"+userDTO.getUsername() +" password:"+userDTO.getPassword());
return Result.success("ok");
}
运行效果:
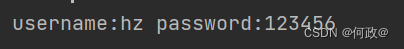
对于复杂实体类 比如实体类中又嵌套了一个实体类携带参数赋值
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/getPOJO?username=hz&password=123456&addressDTO.where=CN&addressDTO.city=CD',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
public class UserDTO {
private String username;
private String password;
private AddressDTO addressDTO;
}
public class AddressDTO {
private String where;
private String city;
}
@GetMapping("/getPOJO")
public Result selectByUserNameAndPassword(UserDTO userDTO){
System.out.println(userDTO);
return Result.success("ok");
}
可以看看打印结果:

三.数组集合参数
前端应用场景如果是复选框会设计到多个值,这个时候可以通过数组的封装来传递 后端可通过数组集和来接收
1.数组接收:只需要后端形参的数组名与前端请求参数名字一致就可以了
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/array?array=hz&array=mz&array=mn',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@GetMapping("/array")
public Result selectArray(String[] array) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
return Result.success("ok");
}
打印结果:

2.集合接收:请求参数名与形参集合名称相同,且需要@RequestParam 绑定参数关系
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/array?array=唱&array=跳&array=rap&array=篮球',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@GetMapping("/array")
public Result selectArray( @RequestParam List<String> array ) {
System.out.println(array);
return Result.success("ok");
}
打印结果:

四.日期参数
使用@DateTimeFormat 注解完成日期参数格式转换 指定前端传来的格式 后端接收
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/dataTimeParam?localDateTime=2024-05-02 12:52:00',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@GetMapping("/dataTimeParam")
public Result selectArray( @DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") LocalDateTime localDateTime) {
System.out.println(localDateTime);
return Result.success("ok");
}
看看打印结果:
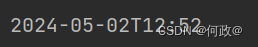
其他的根据自己需求更改只需要前后端格式相同即可!!!
注意: 月,日,时分秒,都要两位数,如果是一个就前面补个0(蛋)不然不符合格式!!!
五.Json参数
Json 在前后端异步交互使用的比较频繁 使用规则:JSON数据键名与形参对象属性名相同,定义POJO类型形参即可接收参数,需要使用**@RequestBody** 注解标识
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/jsonParam',
data: {
username:'hz',
password:'123456',
addressDTO: {
where:'CN',
city:'CD'
}
},
method:'POST'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
public class UserDTO {
private String username;
private String password;
private AddressDTO addressDTO;
}
public class AddressDTO {
private String where;
private String city;
}
@PostMapping("/jsonParam")
public Result selectArray(@RequestBody UserDTO userDTO) {
System.out.println(userDTO);
return Result.success("ok");
}
打印结果:

注意:GET请求无请求体,可以有body,但是不建议带 这里如果使用GET 请求直接携带JSON 格式传递给后端会报400的 ,所以这里演示用POST 请求
当然我这里只是随便简单列举了一下,其他我就不列举了!!!更加详细的可以去了解一下!!JSON格式数据通常需要根据我们前后端数据格式规定了,一般后端实体类中可能还包含了一个集合 ,集合的泛型又可能是一个实体类。也可能包含数组。这些都是比较灵活的,我们只需要按照给的规格是什么类型的数据 前端就给什么类型数据通过动态赋值然后通过JSON传递给后端就可以了!!!练多了也就不复杂了!!!
六.路径参数
通过请求URL 直接传递参数,后端使用{...}来标识路径参数,需要使用注解**@PathVariable**获取路径参数
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/path/1',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@GetMapping("/path/{id}")
public Result pathParam(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println(id);
return Result.success("ok");
}
打印结果:

如果有多个路径参数只需要后面斜杠加内容添加就可以
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/path/1/hz',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@GetMapping("/path/{id}/{name}")
public Result pathParam(@PathVariable Integer id,@PathVariable String name){
System.out.println(id+":"+name);
return Result.success("ok");
}
打印结果:

当然根据需求我们也可路径参数和简单参数一起使用
axios({
url:'http://localhost:8080/user/path/1?name=hz',
method:'GET'
}).then((res)=>{
alert(res.data.data)
})
@GetMapping("/path/{id}")
public Result pathParam(@PathVariable Integer id,String name){
System.out.println(id+":"+name);
return Result.success("ok");
}
打印结果:

注意:形参id 需要于路径id 保持一致且加注解@PathVariable
**@PathVariable **获取到路径参数id 本且绑定到形参 id 这样 形参id 就可以接收到路径参数了!
版权归原作者 何政@ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。