Linux 容器技术
Linux 容器
已逐渐成为一种关键的开源应用程序打包和交付技术,将轻量级应用程序隔离与基于镜像的部署方法的灵活性相结合。
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
使用核心技术实现
Linux 容器
,例如:
- 控制组(
cgroups)用于资源管理 - 命名空间(
namespace)用于进程隔离 SELinux用于安全性- 安全多租户
这些技术一定程度上降低了安全漏洞的可能性,并为您提供了生成和运行企业级容器的环境。
Podman 简介
Podman
是一个开源的容器运行时项目,可在大多数
Linux
平台上使用。
Podman
提供与
Docker
非常相似的功能。
Podman
提供了一个与
Docker
兼容的
CLI
工具(命令行界面),可以这样说,会使用
docker
基本就会使用
podman
。
Podman
是一种
无守护进程
的容器引擎,可以创建、管理和运行
OCI
容器,容器可以以非
root
身份运行(也可以使用
root
身份运行)。
Podman
是由
Red Hat
开发,从
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
开始,
Podman
成为了默认的容器引擎。
Podman
遵守了
OCI(Open Container Initiative/开放容器倡议)
规范,可以轻松查找、运行、构建、共享和部署应用程序。
相应的
Podman
也提供了一个类似
GUI
的桌面端管理工具 —
Podman Desktop
;

Podman 与 Docker 对比
Podman
与其他容器工具实现不同,这里描述的工具不以单一的
Docker
容器引擎和
docker
命令为中心。

相反,红帽提供了
一组命令行工具
,
无需容器引擎
即可操作。它们是:
podman- 用于直接管理pod和容器镜像(run、stop、start、ps、attach和exec,等等);buildah- 用于构建、推送和签名容器镜像;skopeo- 用于复制、检查、删除和签名镜像;runc- 为podman和buildah提供容器运行和构建功能;crun- 可选运行时,可以配置,并为rootless容器提供更大的灵活性、控制和安全性;
由于这些工具与开放容器项目(
OCI
)兼容,因此它们可用于管理由
Docker
和其他兼容
OCI
的容器引擎生成和管理的相同的
Linux
容器。然而,它们特别适用于直接在
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
中运行在单节点用例。
Podman 的一组模块化工具
Podman、Skopeo 和 Buildah
工具被开发来取代
Docker
命令功能。这种场景中的每个工具都是非常轻量级且模块化的,并专注于功能的子集。
- Podman、Skopeo 和 Buildah 工具的主要优点包括:
- 以无根模式运行 -
rootless容器更安全,因为它们在运行时不需要添加任何特权; - 不需要守护进程 - 这些工具在空闲时对资源的要求要低得多,因为如果您没有运行容器,
Podman就不会运行。相反,Docker有一个始终运行的守护进程; - 原生
systemd集成 -Podman允许您创建systemd单元文件,并作为系统服务运行容器;
- Podman、Skopeo 和 Buildah 的特点包括:
Podman、Buildah 和 CRI-O容器引擎都使用相同的后端存储目录,/var/lib/containers,而不是默认使用Docker存储位置/var/lib/docker。- 虽然
Podman、Buildah 和 CRI-O 共享相同的存储目录,但它们不能相互交互。这些工具可以共享镜像。 - 要以编程方式与
Podman进行交互,您可以使用Podman v2.0 RESTful API,它可以在有根和无根的环境中工作。如需更多信息,请参阅 使用容器-工具 API 章节。
使用
container-tools API
Podman 与 Docker 的主要区别
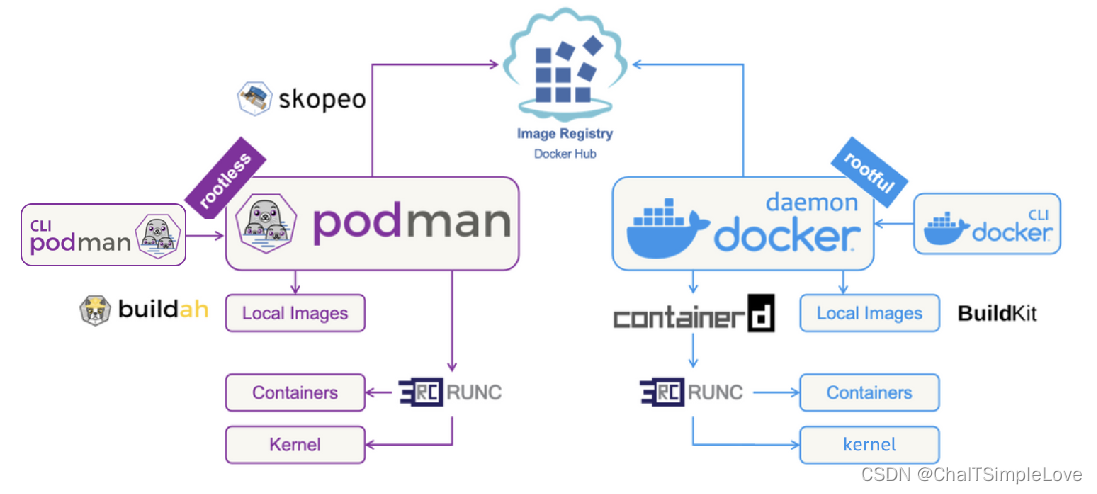
- 守护进程(
deamon):Docker使用守护进程来创建镜像和运行容器,而Podman则没有守护进程,可以在启动容器的用户下直接运行容器。这意味着Podman中的容器默认情况下不具有Root访问权限,在Root级别和Rootless级别之间添加了一个自然屏障,提高了安全性。 - 安全性:
Podman支持rootless容器,这种容器被认为比具有Root访问权限的容器更安全。在Docker中,守护进程拥有Root权限,这使得它们易成为攻击者的首选入侵点。 - 镜像构建:作为一款自给自足的工具,
Docker可以自己构建容器镜像。而Podman需要使用另一种名为Buildah的工具来构建镜像。 - 多合一和模块化:
Docker是一个独立的、强大的工具,在整个循环中处理所有的容器化任务,有优点也有缺点。而Podman采用模块化的方法,依靠一组专门的工具(podman、skopeo、buildah,runc)来完成特定的任务。 - 适用平台:
Docker在MacOS和Windows上也能够运行,而Podman主要面向Linux系统。但是podman也对Windows和MacOS做了支持(需要借助虚拟机来实现,称为podman machine,在MacOS上借助QEMU虚拟机,在Windows上借助Linux子系统WSL2)。
Podman 支持多种操作系统
Podman
支持多种操作系统,包括
Linux、macOS
和
Windows
。
OS 系统平台Podman 后端运行环境是否借助虚拟机(podman machine)Linux原生后端运行否macOS使用 Lima 后端来运行QEMUWindows使用 WSL(Windows Subsystem for Linux)作为后端来运行WSL2
QEMU 是纯软件实现的虚拟化模拟器,几乎可以模拟任何硬件设备。
因此,无论您使用的是哪种操作系统,只要安装了相应的后端和依赖项,您都可以使用
Podman
来管理和运行容器。
Podman 配置国内镜像
由于国内网络环境被墙原因,默认使用
podman
的镜像源是无法访问的,因此我们需要修改为国内可访问的镜像源替代。
配置
registries.conf
的两种方式:
podman全局配置文件:/etc/containers/registries.conf- 用户单独配置文件:
~/.config/containers/registries.conf
注意:配置文件有两种版本格式,
v1和
v2,两种格式的配置不能混用,混用会提示错误。
registries.conf v2 格式
# 例:使用 podman pull registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8-minimal 时,# 仅仅会从registry.access.redhat.com去获取镜像。# 如果直接使用 podman pull ubuntu 时,没有明确指明仓库的时候,使用以下配置的仓库顺序去获取
unqualified-search-registries =["docker.io", "registry.access.redhat.com"]# 配置仓库的地址,可以直接在location里配置国内镜像例如:docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn# 直接在location里配置的时候,可以不需要后面的 [[registry.mirror]] 内容,# 但是这样只能配置一个镜像地址,这个镜像挂了就没法尝试其它镜像。# prefix的值与unqualified-search-registries里配置的得一样,但是可以支持通配符。# prefix不写的情况下,默认与location的指一样。[[registry]]
prefix ="docker.io"
location ="docker.io"# 在这里可以配置多个镜像地址,前提是至少有一个[[registry]]配置。# 需要注意的是,无论 unqualified-search-registries 选择了哪个仓库,# 都会先从这里的上下顺序开始去拉取镜像,最后才会去匹配上[[registry]]里prefix对应的location位置拉取镜像。# 所以这里需要注意,上面配置的不同仓库类型,这里配置的镜像并不能是通用的,所以 unqualified-search-registries 配置了多个仓库的时候,就最好直接使用[[registry]] 的 location 指定镜像地址,不要配置 [[registry.mirror]] 了。# redhat 的国内镜像暂未发现。[[registry.mirror]]
location ="docker.nju.edu.cn"[[registry.mirror]]
location ="docker.mirrors.sjtug.sjtu.edu.cn"# 当使用 podman pod create 命令时候,因需要从k8s.gcr.io拉取 pause 镜像,但是该站点在国内被墙了。# 所以给该站点搞个镜像。以下镜像是阿里云第三方用户,非官方。# 或者 registry.aliyuncs.com/googlecontainersmirror ,也是第三方用户。# 目前没找到国内官方的镜像。gcr.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn 返回403不能用了[[registry]]
prefix ="k8s.gcr.io"
location ="registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers"
registries.conf v1 格式
# 使用tls[registries.search]
registries =['registry.access.redhat.com', 'registry.redhat.io', 'docker.io']# 不使用tls[registries.insecure]
registries =[]# 不允许使用的[registries.block]
registries =[]
此处我们以
registries.conf v2
格式举例,使用如下命令方式修改:
sudotee /etc/containers/registries.conf <<-'EOF'> unqualified-search-registries =["docker.io"]>>[[registry]]> prefix ="docker.io"> location ="y55otr6h.mirror.aliyuncs.com"> EOF
Linux tee命令用于读取标准输入的数据,并将其内容输出成文件。tee指令会从标准输入设备读取数据,将其内容输出到标准输出设备,同时保存成文件。
注意:和 docker 修改镜像源不同的是,【location】这不需要写【http://】。
Podman 使用
运行 nginx 的简单示例
以
nginx
为例,使用
Podman
拉取
Nginx
镜像并建立容器的示例如下:
# 拉取 Nginx 镜像
podman pull nginx:latest
# 创建并启动 Nginx 容器
podman run -d --name mynginx nginx
# 停止 mynginx 容器
podman stop mynginx
# 重启 mynginx 容器
podman restart mynginx
# 进入 mynginx 容器
podman exec -it mynginx /bin/bash
# 查看 mynginx 容器日志
podman logs mynginx
# 删除 mynginx 容器
podman rm mynginx
# 删除 Nginx 镜像
podman image rm nginx:latest
通过上面简单应用的举例,你是不是有种很熟悉的感觉呢,似曾相识
Podman
归来。
podman 常见命令
您可以使用以下基本命令,使用
podman
工具管理镜像、容器和容器资源。
attach,附加到正在运行的容器。commit,从更改的容器创建新镜像。compose,通过外部提供程序(如docker compose或podman-compose)运行compose工作负载。container,管理容器。build,使用Containerfile指令构建镜像。create,创建但不启动容器。diff,检查容器的文件系统上的变化。exec,在正在运行的容器中运行一个进程。export,将容器的文件系统内容导出为tar存档。help, h,显示某个命令的命令列表或帮助。healthcheck,运行容器健康检查。history,显示指定镜像的历史记录。images,列出本地存储中的镜像。import,导入一个tar包以创建一个文件系统镜像。info,显示系统信息。inspect,显示容器或镜像的配置。kill,向一个或多个正在运行的容器发送一个特定的信号。kube generate,根据容器、Pod或卷生成Kubernetes YAML。kube play,根据Kubernetes YAML创建容器、pod和卷。load,从存档加载一个镜像。login,登录到容器注册中心。logout,退出容器注册中心。logs,获取容器的日志。mount,挂载一个工作容器的根文件系统。pause,暂停一个或多个容器中的所有进程。ps,列出容器。port,列出容器的端口映射或特定映射。pull,从注册中心拉取一个镜像。push,将镜像推送到指定的目的地。restart,重启一个或多个容器。rm,从主机中删除一个或多个容器。如果要运行,添加 -f。rmi,从本地存储删除一个或多个镜像。run,在新容器中运行一个命令。save,将镜像保存到存档。search,在注册中心搜索镜像。start,启动一个或多个容器。stats,显示一个或多个容器的CPU、内存、网络I/O、块I/O和PID的百分比。stop,停止一个或多个容器。tag,为本地镜像添加一个额外名称。top,显示容器的运行进程。umount, unmount,卸载工作容器的根文件系统。unpause,取消一个或多个容器中暂停的进程。version,显示podman版本信息。wait,阻止一个或多个容器。
要显示所有
Podman
命令的完整列表,请使用
podman -h
。
PS C:\Users\Jeffrey.Chai> podman -h
Manage pods, containers and images
Usage:
podman.exe [options][command]
Available Commands:
attach Attach to a running container
build Build an image using instructions from Containerfiles
commit Create new image based on the changed container
compose Run compose workloads via an external provider such as docker-compose or podman-compose
container Manage containers
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create but do not start a container
diff Display the changes to the object's file system
events Show podman system events
exec Run a process in a running container
export Export container's filesystem contents as a tar archive
generate Generate structured data based on containers, pods or volumes
healthcheck Manage health checks on containers
help Help about any commandhistory Show history of a specified image
image Manage images
images List images inlocal storage
import Import a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display podman system information
init Initialize one or more containers
inspect Display the configuration of object denoted by ID
kill Kill one or more running containers with a specific signal
kube Play containers, pods or volumes from a structured file
load Load image(s) from a tar archive
login Log in to a container registry
logout Log out of a container registry
logs Fetch the logs of one or more containers
machine Manage a virtual machine
manifest Manipulate manifest lists and image indexes
network Manage networks
pause Pause all the processes in one or more containers
pod Manage pods
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image from a registry
push Push an image to a specified destination
rename Rename an existing container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images from local storage
run Run a commandin a new container
save Save image(s) to an archive
search Search registry for image
secret Manage secrets
start Start one or more containers
stats Display a live stream of container resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more containers
system Manage podman
tag Add an additional name to a local image
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause the processes in one or more containers
untag Remove a name from a local image
update Update an existing container
version Display the Podman version information
volume Manage volumes
wait Block on one or more containers
Options:
-c, --connection string Connection to use for remote Podman service
--help Help for podman
--identity string path to SSH identity file, (CONTAINER_SSHKEY)
--log-level string Log messages above specified level (trace, debug, info, warn, warning, error, fatal, panic)(default "warn")
--out string Send output (stdout) from podman to a file
--ssh string define the ssh mode (default "golang")
--storage-opt stringArray Used to pass an option to the storage driver
--url string URL to access Podman service(CONTAINER_HOST)(default "unix:///run/podman/podman.sock")
-v, --version version for podman.exe
总结
Podman
是一个强大、安全且易于使用的容器管理解决方案。通过无守护进程设计、开源免费、兼容性以及可扩展性等特点,
Podman
为开发者、运维人员和组织提供了一个可靠的容器管理工具。一句话简单概括,
Podman
是一个轻量级,模块化且功能专注的容器化管理平台。可以这么说,在一定程度上
Podman
是
Docker
的
"改良优化版"
。如果您一直在寻找一个替代
Docker
的方案,那么
Podman
绝对值得考虑。
版权归原作者 ChaITSimpleLove 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。